Redis(五):hash/hset/hget 命令源碼解析
Redis作為nosql數(shù)據(jù)庫(kù),kv string型數(shù)據(jù)的支持是最基礎(chǔ)的,但是如果僅有kv的操作,也不至于有redis的成功。(memcache就是個(gè)例子)
Redis除了string, 還有hash,list,set,zset。
所以,我們就來(lái)看看hash的相關(guān)操作實(shí)現(xiàn)吧。
首先,我們從作用上理解hash存在的意義:Redis hash 是一個(gè) string 類型的 field 和 value 的映射表,hash 特別適合用于存儲(chǔ)對(duì)象。從另一個(gè)方面來(lái)說(shuō)是,hash可以聚合很多類似的屬性,這是string中難以實(shí)現(xiàn)的。
所以,總體來(lái)說(shuō),hash的命令與string的命令差不太多。其操作手冊(cè)如下:
1> hdel 命令:刪除一個(gè)或多個(gè)哈希表字段
格式:HDEL key field2 [field2]
返回值:被成功刪除字段的數(shù)量,不包括被忽略的字段。2> hexists 命令:查看哈希表 key 中,指定的字段是否存在
格式:HEXISTS key field
返回值:如果哈希表含有給定字段,返回 1 。如果哈希表不含有給定字段,或 key 不存在,返回 0 。3> hget 命令:獲取存儲(chǔ)在哈希表中指定字段的值
格式:HGET key field
返回值:返回給定字段的值。如果給定的字段或 key 不存在時(shí),返回 nil 。4> hgetall 命令:獲取在哈希表中指定 key 的所有字段和值
格式:HGETALL key
返回值:以列表形式返回哈希表的字段及字段值。若 key 不存在,返回空列表。5> hincrby 命令:為哈希表 key 中的指定字段的整數(shù)值加上增量 increment
格式:HINCRBY key field increment
返回值:執(zhí)行 HINCRBY 命令之后,哈希表中字段的值。6> hincrbyfloat 命令:為哈希表 key 中的指定字段的浮點(diǎn)數(shù)值加上增量 increment
格式:HINCRBYFLOAT key field increment
返回值:執(zhí)行 Hincrbyfloat 命令之后,哈希表中字段的值。7> hkeys 命令:獲取所有哈希表中的字段
格式:HKEYS key
返回值:包含哈希表中所有字段的列表。當(dāng) key 不存在時(shí),返回一個(gè)空列表。8> hlen 命令:獲取哈希表中字段的數(shù)量
格式:HLEN key
返回值:哈希表中字段的數(shù)量。當(dāng) key 不存在時(shí),返回 0 。9> hmget 命令:獲取所有給定字段的值
格式:HMGET key field1 [field2]
返回值:一個(gè)包含多個(gè)給定字段關(guān)聯(lián)值的表,表值的排列順序和指定字段的請(qǐng)求順序一樣。10> hmset 命令:同時(shí)將多個(gè) field-value (域-值)對(duì)設(shè)置到哈希表 key 中
格式:HMSET key field1 value1 [field2 value2 ]
返回值:如果命令執(zhí)行成功,返回 OK 。11> hset 命令:將哈希表 key 中的字段 field 的值設(shè)為 value
格式:HSET key field value
返回值:如果字段是哈希表中的一個(gè)新建字段,并且值設(shè)置成功,返回 1 。如果哈希表中域字段已經(jīng)存在且舊值已被新值覆蓋,返回 0 。12> hsetnx 命令:只有在字段 field 不存在時(shí),設(shè)置哈希表字段的值
格式:HSETNX key field value
返回值:設(shè)置成功,返回 1 。如果給定字段已經(jīng)存在且沒(méi)有操作被執(zhí)行,返回 0 。13> hvals 命令:獲取哈希表中所有值
格式:HVALS key
返回值:一個(gè)包含哈希表中所有值的表。當(dāng) key 不存在時(shí),返回一個(gè)空表。14> hscan 命令:迭代哈希表中的鍵值對(duì)
格式:HSCAN key cursor [MATCH pattern] [COUNT count]
其中,有的是單kv操作有的是指量操作,有的是寫(xiě)操作有的是讀操作。從實(shí)現(xiàn)上看,大體上很多命令是類似的:
比如:hset/hmset/hincrbyXXX 可以是一類的
比如:hget/hgetall/hexists/hkeys/hmget 可以是一類
注意:以上分法僅是為了讓我們看清本質(zhì),對(duì)實(shí)際使用并無(wú)實(shí)際參考意義。
所以,我們就挑幾個(gè)方法來(lái)解析下 hash 的操作實(shí)現(xiàn)吧。
零、hash數(shù)據(jù)結(jié)構(gòu)
hash相關(guān)的命令定義如下:
{"hset",hsetCommand,4,"wmF",0,NULL,1,1,1,0,0},{"hsetnx",hsetnxCommand,4,"wmF",0,NULL,1,1,1,0,0},{"hget",hgetCommand,3,"rF",0,NULL,1,1,1,0,0},{"hmset",hmsetCommand,-4,"wm",0,NULL,1,1,1,0,0},{"hmget",hmgetCommand,-3,"r",0,NULL,1,1,1,0,0},{"hincrby",hincrbyCommand,4,"wmF",0,NULL,1,1,1,0,0},{"hincrbyfloat",hincrbyfloatCommand,4,"wmF",0,NULL,1,1,1,0,0},{"hdel",hdelCommand,-3,"wF",0,NULL,1,1,1,0,0},{"hlen",hlenCommand,2,"rF",0,NULL,1,1,1,0,0},{"hstrlen",hstrlenCommand,3,"rF",0,NULL,1,1,1,0,0},{"hkeys",hkeysCommand,2,"rS",0,NULL,1,1,1,0,0},{"hvals",hvalsCommand,2,"rS",0,NULL,1,1,1,0,0},{"hgetall",hgetallCommand,2,"r",0,NULL,1,1,1,0,0},{"hexists",hexistsCommand,3,"rF",0,NULL,1,1,1,0,0},{"hscan",hscanCommand,-3,"rR",0,NULL,1,1,1,0,0},
ziplist 數(shù)據(jù)結(jié)構(gòu)
typedef struct zlentry {unsigned int prevrawlensize, prevrawlen;unsigned int lensize, len;unsigned int headersize;unsigned char encoding;unsigned char *p;} zlentry;#define ZIPLIST_BYTES(zl) (*((uint32_t*)(zl)))#define ZIPLIST_TAIL_OFFSET(zl) (*((uint32_t*)((zl)+sizeof(uint32_t))))#define ZIPLIST_LENGTH(zl) (*((uint16_t*)((zl)+sizeof(uint32_t)*2)))#define ZIPLIST_HEADER_SIZE (sizeof(uint32_t)*2+sizeof(uint16_t))#define ZIPLIST_END_SIZE (sizeof(uint8_t))#define ZIPLIST_ENTRY_HEAD(zl) ((zl)+ZIPLIST_HEADER_SIZE)#define ZIPLIST_ENTRY_TAIL(zl) ((zl)+intrev32ifbe(ZIPLIST_TAIL_OFFSET(zl)))#define ZIPLIST_ENTRY_END(zl) ((zl)+intrev32ifbe(ZIPLIST_BYTES(zl))-1)
hashtable 數(shù)據(jù)結(jié)構(gòu):
typedef struct dict {dictType *type;void *privdata;dictht ht[2];long rehashidx; /* rehashing not in progress if rehashidx == -1 */unsigned long iterators; /* number of iterators currently running */} dict;typedef struct dictht {dictEntry **table;unsigned long size;unsigned long sizemask;unsigned long used;} dictht;typedef struct dictEntry {void *key;void *val;struct dictEntry *next;} dictEntry;
一、hset 設(shè)置單個(gè) field -> value
“增刪改查”中的“增改” 就是它了。
// t_hash.c, set key field valuevoid hsetCommand(client *c) {int update;robj *o;// 1. 查找hash的key是否存在,不存在則新建一個(gè),然后在其上進(jìn)行數(shù)據(jù)操作if ((o = hashTypeLookupWriteOrCreate(c,c->argv[1])) == NULL) return;// 2. 檢查2-3個(gè)參數(shù)是否需要將簡(jiǎn)單版(ziplist)hash表轉(zhuǎn)換為復(fù)雜的hash表,轉(zhuǎn)換后的表通過(guò) o->ptr 體現(xiàn)hashTypeTryConversion(o,c->argv,2,3);// 3. 添加kv到 o 的hash表中update = hashTypeSet(o,c->argv[2]->ptr,c->argv[3]->ptr,HASH_SET_COPY);addReply(c, update ? shared.czero : shared.cone);// 變更命令傳播signalModifiedKey(c->db,c->argv[1]);notifyKeyspaceEvent(NOTIFY_HASH,"hset",c->argv[1],c->db->id);server.dirty++;}// 1. 獲取db外部的key, 即整體hash數(shù)據(jù)實(shí)例// t_hash.crobj *hashTypeLookupWriteOrCreate(client *c, robj *key) {robj *o = lookupKeyWrite(c->db,key);if (o == NULL) {// 此處創(chuàng)建的hashObject是以 ziplist 形式的o = createHashObject();dbAdd(c->db,key,o);} else {// 不是hash類型的鍵已存在,不可覆蓋,返回錯(cuò)誤if (o->type != OBJ_HASH) {addReply(c,shared.wrongtypeerr);return NULL;}}return o;}// object.c, 創(chuàng)建hashObject, 以 ziplist 形式創(chuàng)建robj *createHashObject(void) {unsigned char *zl = ziplistNew();robj *o = createObject(OBJ_HASH, zl);o->encoding = OBJ_ENCODING_ZIPLIST;return o;}// ziplist.cstatic unsigned char *createList() {unsigned char *zl = ziplistNew();zl = ziplistPush(zl, (unsigned char*)"foo", 3, ZIPLIST_TAIL);zl = ziplistPush(zl, (unsigned char*)"quux", 4, ZIPLIST_TAIL);zl = ziplistPush(zl, (unsigned char*)"hello", 5, ZIPLIST_HEAD);zl = ziplistPush(zl, (unsigned char*)"1024", 4, ZIPLIST_TAIL);return zl;}// 2. 檢查參數(shù),是否需要將 ziplist 形式的hash表轉(zhuǎn)換為真正的hash表/* Check the length of a number of objects to see if we need to convert a* ziplist to a real hash. Note that we only check string encoded objects* as their string length can be queried in constant time. */void hashTypeTryConversion(robj *o, robj **argv, int start, int end) {int i;if (o->encoding != OBJ_ENCODING_ZIPLIST) return;for (i = start; i <= end; i++) {// 參數(shù)大于設(shè)置的 hash_max_ziplist_value (默認(rèn): 64)時(shí),會(huì)直接將 ziplist 轉(zhuǎn)換為 ht// OBJ_ENCODING_RAW, OBJ_ENCODING_EMBSTR// 循環(huán)檢查參數(shù),只要發(fā)生了一次轉(zhuǎn)換就結(jié)束檢查(沒(méi)必要繼續(xù)了)if (sdsEncodedObject(argv[i]) &&sdslen(argv[i]->ptr) > server.hash_max_ziplist_value){// 這個(gè)轉(zhuǎn)換過(guò)程很有意思,我們深入看看hashTypeConvert(o, OBJ_ENCODING_HT);break;}}}// t_hash.c, 轉(zhuǎn)換編碼方式 (如上, ziplist -> ht)void hashTypeConvert(robj *o, int enc) {if (o->encoding == OBJ_ENCODING_ZIPLIST) {// 此處我們只處理這種情況hashTypeConvertZiplist(o, enc);} else if (o->encoding == OBJ_ENCODING_HT) {serverPanic("Not implemented");} else {serverPanic("Unknown hash encoding");}}// t_hash.c, 轉(zhuǎn)換編碼 ziplist 為目標(biāo) enc (實(shí)際只能是 OBJ_ENCODING_HT)void hashTypeConvertZiplist(robj *o, int enc) {serverAssert(o->encoding == OBJ_ENCODING_ZIPLIST);if (enc == OBJ_ENCODING_ZIPLIST) {/* Nothing to do... */} else if (enc == OBJ_ENCODING_HT) {hashTypeIterator *hi;dict *dict;int ret;// 迭代器創(chuàng)建hi = hashTypeInitIterator(o);// 一個(gè)hash的數(shù)據(jù)結(jié)構(gòu)就是一個(gè) dict, 從這個(gè)級(jí)別來(lái)說(shuō), hash 與 db 是一個(gè)級(jí)別的dict = dictCreate(&hashDictType, NULL);// 依次迭代 o, 賦值到 hi->fptr, hi->vptr// 依次添加到 dict 中while (hashTypeNext(hi) != C_ERR) {sds key, value;// 從 hi->fptr 中獲取key// 從 hi->vptr 中獲取valuekey = hashTypeCurrentObjectNewSds(hi,OBJ_HASH_KEY);value = hashTypeCurrentObjectNewSds(hi,OBJ_HASH_VALUE);// 添加到 dict 中ret = dictAdd(dict, key, value);if (ret != DICT_OK) {serverLogHexDump(LL_WARNING,"ziplist with dup elements dump",o->ptr,ziplistBlobLen(o->ptr));serverPanic("Ziplist corruption detected");}}// 釋放迭代器hashTypeReleaseIterator(hi);zfree(o->ptr);// 將變更反映到o對(duì)象上返回o->encoding = OBJ_ENCODING_HT;o->ptr = dict;} else {serverPanic("Unknown hash encoding");}}// 2.1. 迭代ziplist元素// t_hash.c, 迭代器/* Move to the next entry in the hash. Return C_OK when the next entry* could be found and C_ERR when the iterator reaches the end. */int hashTypeNext(hashTypeIterator *hi) {if (hi->encoding == OBJ_ENCODING_ZIPLIST) {unsigned char *zl;unsigned char *fptr, *vptr;// 每次都是基于原始字符器進(jìn)行計(jì)算偏移// 迭代的是 fptr,vptrzl = hi->subject->ptr;fptr = hi->fptr;vptr = hi->vptr;// 第一次查找時(shí)使用index查找,后續(xù)則使用 fptr,vptr 進(jìn)行迭代if (fptr == NULL) {/* Initialize cursor */serverAssert(vptr == NULL);fptr = ziplistIndex(zl, 0);} else {/* Advance cursor */serverAssert(vptr != NULL);fptr = ziplistNext(zl, vptr);}if (fptr == NULL) return C_ERR;/* Grab pointer to the value (fptr points to the field) */vptr = ziplistNext(zl, fptr);serverAssert(vptr != NULL);/* fptr, vptr now point to the first or next pair */hi->fptr = fptr;hi->vptr = vptr;} else if (hi->encoding == OBJ_ENCODING_HT) {if ((hi->de = dictNext(hi->di)) == NULL) return C_ERR;} else {serverPanic("Unknown hash encoding");}return C_OK;}// ziplist.c, 查找 index 的元素/* Returns an offset to use for iterating with ziplistNext. When the given* index is negative, the list is traversed back to front. When the list* doesn't contain an element at the provided index, NULL is returned. */unsigned char *ziplistIndex(unsigned char *zl, int index) {unsigned char *p;unsigned int prevlensize, prevlen = 0;if (index < 0) {// 小于0時(shí),反向查找index = (-index)-1;p = ZIPLIST_ENTRY_TAIL(zl);if (p[0] != ZIP_END) {ZIP_DECODE_PREVLEN(p, prevlensize, prevlen);while (prevlen > 0 && index--) {p -= prevlen;ZIP_DECODE_PREVLEN(p, prevlensize, prevlen);}}} else {p = ZIPLIST_ENTRY_HEAD(zl);while (p[0] != ZIP_END && index--) {p += zipRawEntryLength(p);}}// 迭代完成還沒(méi)找到元素 p[0]=ZIP_END// index 超出整體ziplist大小則遍歷完成后 index>0return (p[0] == ZIP_END || index > 0) ? NULL : p;}// ziplist.c, 由 fptr,vptr 進(jìn)行迭代元素/* Return pointer to next entry in ziplist.** zl is the pointer to the ziplist* p is the pointer to the current element** The element after 'p' is returned, otherwise NULL if we are at the end. */unsigned char *ziplistNext(unsigned char *zl, unsigned char *p) {((void) zl);/* "p" could be equal to ZIP_END, caused by ziplistDelete,* and we should return NULL. Otherwise, we should return NULL* when the *next* element is ZIP_END (there is no next entry). */if (p[0] == ZIP_END) {return NULL;}// 當(dāng)前指針偏移當(dāng)前元素長(zhǎng)度(根據(jù)ziplist協(xié)議),即到下一元素指針位置p += zipRawEntryLength(p);if (p[0] == ZIP_END) {return NULL;}return p;}/* Return the total number of bytes used by the entry pointed to by 'p'. */static unsigned int zipRawEntryLength(unsigned char *p) {unsigned int prevlensize, encoding, lensize, len;ZIP_DECODE_PREVLENSIZE(p, prevlensize);ZIP_DECODE_LENGTH(p + prevlensize, encoding, lensize, len);return prevlensize + lensize + len;}// 2.2. t_hash.c, 獲取 hashTypeIterator 的具體值,寫(xiě)入 vstr, vlen 中/* Return the key or value at the current iterator position as a new* SDS string. */sds hashTypeCurrentObjectNewSds(hashTypeIterator *hi, int what) {unsigned char *vstr;unsigned int vlen;long long vll;hashTypeCurrentObject(hi,what,&vstr,&vlen,&vll);if (vstr) return sdsnewlen(vstr,vlen);return sdsfromlonglong(vll);}/* Higher level function of hashTypeCurrent*() that returns the hash value* at current iterator position.** The returned element is returned by reference in either *vstr and *vlen if* it's returned in string form, or stored in *vll if it's returned as* a number.** If *vll is populated *vstr is set to NULL, so the caller* can always check the function return by checking the return value* type checking if vstr == NULL. */void hashTypeCurrentObject(hashTypeIterator *hi, int what, unsigned char **vstr, unsigned int *vlen, long long *vll) {if (hi->encoding == OBJ_ENCODING_ZIPLIST) {*vstr = NULL;hashTypeCurrentFromZiplist(hi, what, vstr, vlen, vll);} else if (hi->encoding == OBJ_ENCODING_HT) {sds ele = hashTypeCurrentFromHashTable(hi, what);*vstr = (unsigned char*) ele;*vlen = sdslen(ele);} else {serverPanic("Unknown hash encoding");}}// t_hash.c, 從ziplist中獲取某個(gè) hashTypeIterator 的具體值,結(jié)果定稿 vstr, vlen/* Get the field or value at iterator cursor, for an iterator on a hash value* encoded as a ziplist. Prototype is similar to `hashTypeGetFromZiplist`. */void hashTypeCurrentFromZiplist(hashTypeIterator *hi, int what,unsigned char **vstr,unsigned int *vlen,long long *vll){int ret;serverAssert(hi->encoding == OBJ_ENCODING_ZIPLIST);// OBJ_HASH_KEY 從 fptr 中獲取, 否則從 vptr 中獲取if (what & OBJ_HASH_KEY) {ret = ziplistGet(hi->fptr, vstr, vlen, vll);serverAssert(ret);} else {ret = ziplistGet(hi->vptr, vstr, vlen, vll);serverAssert(ret);}}// ziplist.c,/* Get entry pointed to by 'p' and store in either '*sstr' or 'sval' depending* on the encoding of the entry. '*sstr' is always set to NULL to be able* to find out whether the string pointer or the integer value was set.* Return 0 if 'p' points to the end of the ziplist, 1 otherwise. */unsigned int ziplistGet(unsigned char *p, unsigned char **sstr, unsigned int *slen, long long *sval) {zlentry entry;if (p == NULL || p[0] == ZIP_END) return 0;if (sstr) *sstr = NULL;// 按照ziplist的編碼協(xié)議, 獲取頭部信息zipEntry(p, &entry);if (ZIP_IS_STR(entry.encoding)) {if (sstr) {*slen = entry.len;*sstr = p+entry.headersize;}} else {if (sval) {*sval = zipLoadInteger(p+entry.headersize,entry.encoding);}}return 1;}// ziplist.c, 解析原始字符串為 zlentry/* Return a struct with all information about an entry. */static void zipEntry(unsigned char *p, zlentry *e) {// 按照ziplist的編碼協(xié)議,依次讀取 prevrawlensize, prevrawlenZIP_DECODE_PREVLEN(p, e->prevrawlensize, e->prevrawlen);// 指向下一位置偏移,按照ziplist的編碼協(xié)議,依次讀取 encoding, lensize, lenZIP_DECODE_LENGTH(p + e->prevrawlensize, e->encoding, e->lensize, e->len);// 除去header得到 body偏移e->headersize = e->prevrawlensize + e->lensize;e->p = p;}
具體header解析如下, 有興趣的點(diǎn)開(kāi)瞅瞅:
// ziplist.c/* Decode the length of the previous element, from the perspective of the entry* pointed to by 'ptr'. */#define ZIP_DECODE_PREVLEN(ptr, prevlensize, prevlen) do { \// 解析第1個(gè)字符為 prevlensizeZIP_DECODE_PREVLENSIZE(ptr, prevlensize); \if ((prevlensize) == 1) { \(prevlen) = (ptr)[0]; \} else if ((prevlensize) == 5) { \assert(sizeof((prevlensize)) == 4); \// 當(dāng)ptr[0]>254時(shí),代表內(nèi)容有點(diǎn)大,需要使用 5個(gè)字符保存上一字符長(zhǎng)度memcpy(&(prevlen), ((char*)(ptr)) + 1, 4); \memrev32ifbe(&prevlen); \} \} while(0);/* Decode the number of bytes required to store the length of the previous* element, from the perspective of the entry pointed to by 'ptr'. */#define ZIP_DECODE_PREVLENSIZE(ptr, prevlensize) do { \if ((ptr)[0] < ZIP_BIGLEN) { \(prevlensize) = 1; \} else { \(prevlensize) = 5; \} \} while(0);/* Decode the length encoded in 'ptr'. The 'encoding' variable will hold the* entries encoding, the 'lensize' variable will hold the number of bytes* required to encode the entries length, and the 'len' variable will hold the* entries length. */#define ZIP_DECODE_LENGTH(ptr, encoding, lensize, len) do { \// 解析第1個(gè)字符為 編碼格式 &ZIP_STR_MASK=0xc0ZIP_ENTRY_ENCODING((ptr), (encoding)); \if ((encoding) < ZIP_STR_MASK) { \// 0 << 6 =0// 具體解析如下代碼,if ((encoding) == ZIP_STR_06B) { \(lensize) = 1; \(len) = (ptr)[0] & 0x3f; \}// 1 << 6 =64else if ((encoding) == ZIP_STR_14B) { \(lensize) = 2; \(len) = (((ptr)[0] & 0x3f) << 8) | (ptr)[1]; \}// 2 << 6 =128else if (encoding == ZIP_STR_32B) { \(lensize) = 5; \(len) = ((ptr)[1] << 24) | \((ptr)[2] << 16) | \((ptr)[3] << 8) | \((ptr)[4]); \} else { \assert(NULL); \} \} else { \// 超過(guò) 0xc0 的長(zhǎng)度了,直接使用 1,2,3,4 表示len(lensize) = 1; \(len) = zipIntSize(encoding); \} \} while(0);/* Extract the encoding from the byte pointed by 'ptr' and set it into* 'encoding'. */#define ZIP_ENTRY_ENCODING(ptr, encoding) do { \(encoding) = (ptr[0]); \if ((encoding) < ZIP_STR_MASK) (encoding) &= ZIP_STR_MASK; \} while(0)/* Different encoding/length possibilities */#define ZIP_STR_MASK 0xc0#define ZIP_INT_MASK 0x30#define ZIP_STR_06B (0 << 6) // 0x00#define ZIP_STR_14B (1 << 6) // 0x40#define ZIP_STR_32B (2 << 6) // 0x80#define ZIP_INT_16B (0xc0 | 0<<4) // 0xc0#define ZIP_INT_32B (0xc0 | 1<<4) // 0xd0#define ZIP_INT_64B (0xc0 | 2<<4) // 0xe0#define ZIP_INT_24B (0xc0 | 3<<4) // 0xf0#define ZIP_INT_8B 0xfe // 0xfe
添加kv到對(duì)應(yīng)的key實(shí)例中:
// 3. 添加kv到 hash表中, 稍微復(fù)雜// t_hash.c, 做變更到hash表中int hashTypeSet(robj *o, sds field, sds value, int flags) {int update = 0;// 針對(duì)ziplist 的添加, 與 ht 編碼的添加, 自然是分別處理if (o->encoding == OBJ_ENCODING_ZIPLIST) {unsigned char *zl, *fptr, *vptr;zl = o->ptr;// 找到ziplist 的頭節(jié)點(diǎn)指針fptr = ziplistIndex(zl, ZIPLIST_HEAD);if (fptr != NULL) {// 嘗試查找該 field 對(duì)應(yīng)的元素(從1開(kāi)始),如果找到則先刪除原值,然后統(tǒng)一添加fptr = ziplistFind(fptr, (unsigned char*)field, sdslen(field), 1);if (fptr != NULL) {/* Grab pointer to the value (fptr points to the field) */// value 不可以為null, 否則 ziplist 將無(wú)法工作vptr = ziplistNext(zl, fptr);serverAssert(vptr != NULL);update = 1;/* Delete value */// 先刪除舊的 value, 再以插入的形式更新, 后續(xù)講刪除時(shí)再詳解zl = ziplistDelete(zl, &vptr);/* Insert new value */// 重點(diǎn),將value添加到 ziplist 中zl = ziplistInsert(zl, vptr, (unsigned char*)value,sdslen(value));}}// 沒(méi)有找到對(duì)應(yīng)元素,則直接將元素添加到尾部即可if (!update) {/* Push new field/value pair onto the tail of the ziplist */zl = ziplistPush(zl, (unsigned char*)field, sdslen(field),ZIPLIST_TAIL);zl = ziplistPush(zl, (unsigned char*)value, sdslen(value),ZIPLIST_TAIL);}o->ptr = zl;/* Check if the ziplist needs to be converted to a hash table */// 大于設(shè)置的閥值后,轉(zhuǎn)換ziplist為ht(默認(rèn): 512)if (hashTypeLength(o) > server.hash_max_ziplist_entries)hashTypeConvert(o, OBJ_ENCODING_HT);} else if (o->encoding == OBJ_ENCODING_HT) {dictEntry *de = dictFind(o->ptr,field);if (de) {sdsfree(dictGetVal(de));if (flags & HASH_SET_TAKE_VALUE) {dictGetVal(de) = value;value = NULL;} else {dictGetVal(de) = sdsdup(value);}update = 1;} else {sds f,v;if (flags & HASH_SET_TAKE_FIELD) {f = field;field = NULL;} else {f = sdsdup(field);}if (flags & HASH_SET_TAKE_VALUE) {v = value;value = NULL;} else {v = sdsdup(value);}dictAdd(o->ptr,f,v);}} else {serverPanic("Unknown hash encoding");}/* Free SDS strings we did not referenced elsewhere if the flags* want this function to be responsible. */if (flags & HASH_SET_TAKE_FIELD && field) sdsfree(field);if (flags & HASH_SET_TAKE_VALUE && value) sdsfree(value);return update;}// 3.1. 使用ziplist進(jìn)行保存 field -> value// ziplist.c, 查找某個(gè) field 是否存在于ziplist中/* Find pointer to the entry equal to the specified entry. Skip 'skip' entries* between every comparison. Returns NULL when the field could not be found. */unsigned char *ziplistFind(unsigned char *p, unsigned char *vstr, unsigned int vlen, unsigned int skip) {int skipcnt = 0;unsigned char vencoding = 0;long long vll = 0;while (p[0] != ZIP_END) {unsigned int prevlensize, encoding, lensize, len;unsigned char *q;// 解析整個(gè)字符串p的 prevlensize,encoding,lensize,lenZIP_DECODE_PREVLENSIZE(p, prevlensize);ZIP_DECODE_LENGTH(p + prevlensize, encoding, lensize, len);q = p + prevlensize + lensize;// 傳入1, 代表要跳過(guò)一個(gè)元素, 比如: 查找key時(shí),跳過(guò)1個(gè)v,然后繼續(xù)迭代// 跳過(guò)了n個(gè)元素后,再?gòu)拇碎_(kāi)始key的比對(duì)過(guò)程if (skipcnt == 0) {/* Compare current entry with specified entry */// 針對(duì)不同的編碼使用不同的比較方式if (ZIP_IS_STR(encoding)) {// 找到相應(yīng)的元素,直接返回 p 指針if (len == vlen && memcmp(q, vstr, vlen) == 0) {return p;}} else {/* Find out if the searched field can be encoded. Note that* we do it only the first time, once done vencoding is set* to non-zero and vll is set to the integer value. */if (vencoding == 0) {if (!zipTryEncoding(vstr, vlen, &vll, &vencoding)) {/* If the entry can't be encoded we set it to* UCHAR_MAX so that we don't retry again the next* time. */vencoding = UCHAR_MAX;}/* Must be non-zero by now */assert(vencoding);}/* Compare current entry with specified entry, do it only* if vencoding != UCHAR_MAX because if there is no encoding* possible for the field it can't be a valid integer. */if (vencoding != UCHAR_MAX) {long long ll = zipLoadInteger(q, encoding);if (ll == vll) {return p;}}}/* Reset skip count */// 查找一次,跳過(guò)skip次skipcnt = skip;} else {/* Skip entry */skipcnt--;}/* Move to next entry */p = q + len;}return NULL;}// ziplist.c, 添加value到ziplist中// zl:ziplist實(shí)例, p:要插入的key字串, s:要插入的value字串, len:要插入的value的長(zhǎng)度/* Insert an entry at "p". */unsigned char *ziplistInsert(unsigned char *zl, unsigned char *p, unsigned char *s, unsigned int slen) {return __ziplistInsert(zl,p,s,slen);}/* Insert item at "p". */static unsigned char *__ziplistInsert(unsigned char *zl, unsigned char *p, unsigned char *s, unsigned int slen) {size_t curlen = intrev32ifbe(ZIPLIST_BYTES(zl)), reqlen;unsigned int prevlensize, prevlen = 0;size_t offset;int nextdiff = 0;unsigned char encoding = 0;long long value = 123456789; /* initialized to avoid warning. Using a valuethat is easy to see if for some reasonwe use it uninitialized. */zlentry tail;/* Find out prevlen for the entry that is inserted. */if (p[0] != ZIP_END) {ZIP_DECODE_PREVLEN(p, prevlensize, prevlen);} else {unsigned char *ptail = ZIPLIST_ENTRY_TAIL(zl);if (ptail[0] != ZIP_END) {prevlen = zipRawEntryLength(ptail);}}/* See if the entry can be encoded */if (zipTryEncoding(s,slen,&value,&encoding)) {/* 'encoding' is set to the appropriate integer encoding */reqlen = zipIntSize(encoding);} else {/* 'encoding' is untouched, however zipEncodeLength will use the* string length to figure out how to encode it. */reqlen = slen;}/* We need space for both the length of the previous entry and* the length of the payload. */// 加上prevlen,encoding,slen 的長(zhǎng)度,以計(jì)算value的存放位置reqlen += zipPrevEncodeLength(NULL,prevlen);reqlen += zipEncodeLength(NULL,encoding,slen);/* When the insert position is not equal to the tail, we need to* make sure that the next entry can hold this entry's length in* its prevlen field. */nextdiff = (p[0] != ZIP_END) ? zipPrevLenByteDiff(p,reqlen) : 0;/* Store offset because a realloc may change the address of zl. */// 存儲(chǔ)當(dāng)前偏移位置,以便在擴(kuò)容之后,還能找到相應(yīng)位置// p = p -zl + zloffset = p-zl;zl = ziplistResize(zl,curlen+reqlen+nextdiff);p = zl+offset;/* Apply memory move when necessary and update tail offset. */if (p[0] != ZIP_END) {/* Subtract one because of the ZIP_END bytes */// 字符拷貝memmove(p+reqlen,p-nextdiff,curlen-offset-1+nextdiff);/* Encode this entry's raw length in the next entry. */zipPrevEncodeLength(p+reqlen,reqlen);/* Update offset for tail */ZIPLIST_TAIL_OFFSET(zl) =intrev32ifbe(intrev32ifbe(ZIPLIST_TAIL_OFFSET(zl))+reqlen);/* When the tail contains more than one entry, we need to take* "nextdiff" in account as well. Otherwise, a change in the* size of prevlen doesn't have an effect on the *tail* offset. */zipEntry(p+reqlen, &tail);if (p[reqlen+tail.headersize+tail.len] != ZIP_END) {ZIPLIST_TAIL_OFFSET(zl) =intrev32ifbe(intrev32ifbe(ZIPLIST_TAIL_OFFSET(zl))+nextdiff);}} else {/* This element will be the new tail. */ZIPLIST_TAIL_OFFSET(zl) = intrev32ifbe(p-zl);}/* When nextdiff != 0, the raw length of the next entry has changed, so* we need to cascade the update throughout the ziplist */if (nextdiff != 0) {// 如果本次更新后數(shù)據(jù)位置變化,則需要更新后續(xù)的元素位置offset = p-zl;zl = __ziplistCascadeUpdate(zl,p+reqlen);p = zl+offset;}/* Write the entry */// 將 value 寫(xiě)入 p 中, 即寫(xiě)入了 ziplist 中p += zipPrevEncodeLength(p,prevlen);p += zipEncodeLength(p,encoding,slen);if (ZIP_IS_STR(encoding)) {memcpy(p,s,slen);} else {zipSaveInteger(p,value,encoding);}ZIPLIST_INCR_LENGTH(zl,1);return zl;}// 另外,如果沒(méi)有舊的元素值時(shí),直接在hash表的末尾添加對(duì)應(yīng)的field->value 即可// ziplist.c, 在尾部進(jìn)行添加元素,沒(méi)有許多的情況要考慮,但是代碼完全復(fù)用 __ziplistInsert()unsigned char *ziplistPush(unsigned char *zl, unsigned char *s, unsigned int slen, int where) {unsigned char *p;p = (where == ZIPLIST_HEAD) ? ZIPLIST_ENTRY_HEAD(zl) : ZIPLIST_ENTRY_END(zl);return __ziplistInsert(zl,p,s,slen);}
鑒于插入過(guò)程稍微復(fù)雜,咱們畫(huà)個(gè)圖重新理一下思路:
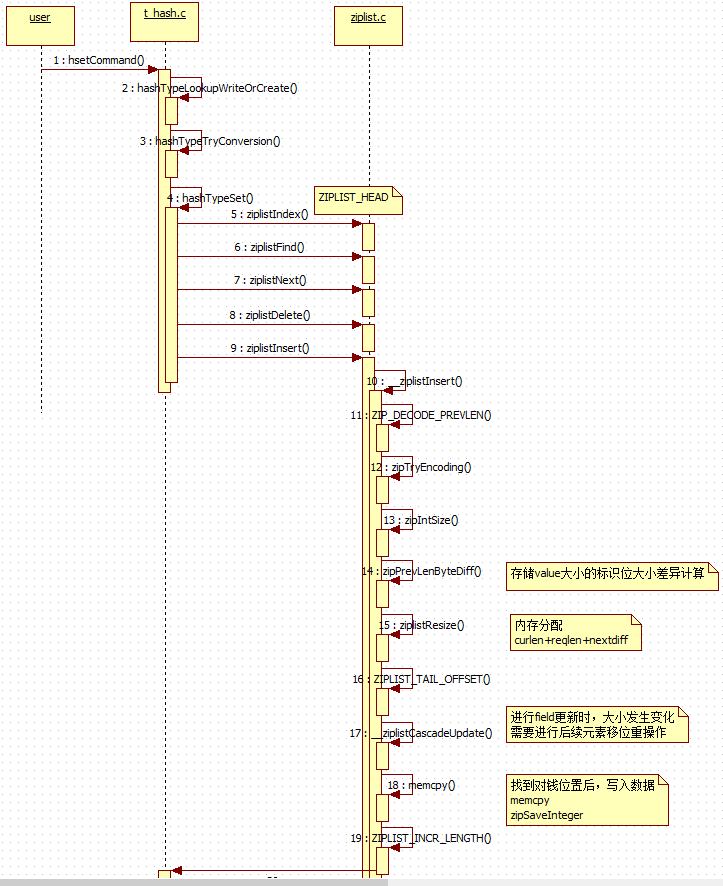
看起來(lái)沒(méi)ziplist好像沒(méi)那么簡(jiǎn)單呢,為啥還要搞這么復(fù)雜呢?其實(shí)以上代碼,僅是在人看來(lái)復(fù)雜,對(duì)機(jī)器來(lái)說(shuō)就是更多的移位計(jì)算操作,多消耗點(diǎn)cpu就換來(lái)了空間上的節(jié)省,是可以的。軟件本身的復(fù)雜性帶來(lái)了效益,是軟件的價(jià)值體現(xiàn),所以,并非所有的東西都是簡(jiǎn)單即美。
接下來(lái),我們來(lái)看一下使用 HT 的編碼又如何存儲(chǔ)field->value呢?
// 3.2. OBJ_ENCODING_HT 的 field -> value 的添加if (o->encoding == OBJ_ENCODING_HT) {// hash 表中查找對(duì)應(yīng)的 fielddictEntry *de = dictFind(o->ptr,field);if (de) {sdsfree(dictGetVal(de));// hset 時(shí)使用 HASH_SET_COPY, 所以直接使用 sdsdup() 即可if (flags & HASH_SET_TAKE_VALUE) {dictGetVal(de) = value;value = NULL;} else {dictGetVal(de) = sdsdup(value);}update = 1;} else {// 新增 field -> valuesds f,v;if (flags & HASH_SET_TAKE_FIELD) {f = field;field = NULL;} else {f = sdsdup(field);}if (flags & HASH_SET_TAKE_VALUE) {v = value;value = NULL;} else {v = sdsdup(value);}// 添加到 hash 表中,前些篇章講解過(guò),大概就是計(jì)算hash,放入v的過(guò)程dictAdd(o->ptr,f,v);}}
如此看來(lái),OBJ_ENCODING_HT 的實(shí)現(xiàn)反而簡(jiǎn)單了哦。
總結(jié)下 hash的插入過(guò)程,hash 初始創(chuàng)建時(shí)都是使用ziplist 進(jìn)行容納元素的,在特定情況下會(huì)觸發(fā) ziplist 為 ht 的編碼方式, 比如:
1. hset時(shí)自身的參數(shù)大于設(shè)置值(默認(rèn): 64)時(shí)直接轉(zhuǎn)換 ziplist -> ht;
2. hash表的元素?cái)?shù)量大于設(shè)置值(默認(rèn): 512)時(shí)轉(zhuǎn)換 ziplist -> ht;
這么設(shè)計(jì)的原因是,元素較少且占用空間較小時(shí),使用ziplist會(huì)節(jié)省空間,且時(shí)間消耗與hash表相關(guān)并不大,所以 ziplist 是優(yōu)先的選擇了。但是大量數(shù)據(jù)還是必須要使用hash表存儲(chǔ)的。
二、hmset 批量添加元素
hset 和 hmset 在實(shí)現(xiàn)上基本如出一轍,所以簡(jiǎn)單瞅瞅就得了。
// t_hash.c, hmset key f1 v1 f2 v2void hmsetCommand(client *c) {int i;robj *o;// 參數(shù)個(gè)數(shù)檢查,必定是2nif ((c->argc % 2) == 1) {addReplyError(c,"wrong number of arguments for HMSET");return;}// 插入方式與 hset 一毛一樣,差別在于批量插入時(shí),會(huì)循環(huán)向 key-hash表中添加field->valueif ((o = hashTypeLookupWriteOrCreate(c,c->argv[1])) == NULL) return;hashTypeTryConversion(o,c->argv,2,c->argc-1);// 循環(huán)insertfor (i = 2; i < c->argc; i += 2) {hashTypeSet(o,c->argv[i]->ptr,c->argv[i+1]->ptr,HASH_SET_COPY);}addReply(c, shared.ok);signalModifiedKey(c->db,c->argv[1]);notifyKeyspaceEvent(NOTIFY_HASH,"hset",c->argv[1],c->db->id);server.dirty++;}
三、hget 獲取某字段值
這種命令的時(shí)間復(fù)雜度都是 O(1), 所以一般是簡(jiǎn)單至上。
// t_hash.cvoid hgetCommand(client *c) {robj *o;// 查找key, 不存在或者類型不一致則直接返回if ((o = lookupKeyReadOrReply(c,c->argv[1],shared.nullbulk)) == NULL ||checkType(c,o,OBJ_HASH)) return;// 基于o, 返回 field 對(duì)應(yīng)的元素值即可addHashFieldToReply(c, o, c->argv[2]->ptr);}// t_hash.cstatic void addHashFieldToReply(client *c, robj *o, sds field) {int ret;if (o == NULL) {addReply(c, shared.nullbulk);return;}if (o->encoding == OBJ_ENCODING_ZIPLIST) {unsigned char *vstr = NULL;unsigned int vlen = UINT_MAX;long long vll = LLONG_MAX;// 基于 ziplist,ret = hashTypeGetFromZiplist(o, field, &vstr, &vlen, &vll);if (ret < 0) {// 響應(yīng)為空addReply(c, shared.nullbulk);} else {// 添加到輸出緩沖if (vstr) {addReplyBulkCBuffer(c, vstr, vlen);} else {addReplyBulkLongLong(c, vll);}}} else if (o->encoding == OBJ_ENCODING_HT) {// hash 表類型則查找 hash 表即可sds value = hashTypeGetFromHashTable(o, field);// 添加到輸出緩沖if (value == NULL)// 響應(yīng)為空addReply(c, shared.nullbulk);elseaddReplyBulkCBuffer(c, value, sdslen(value));} else {serverPanic("Unknown hash encoding");}}// t_hash.c, 從 ziplist 中查找 field 值/* Get the value from a ziplist encoded hash, identified by field.* Returns -1 when the field cannot be found. */int hashTypeGetFromZiplist(robj *o, sds field,unsigned char **vstr,unsigned int *vlen,long long *vll){unsigned char *zl, *fptr = NULL, *vptr = NULL;int ret;serverAssert(o->encoding == OBJ_ENCODING_ZIPLIST);zl = o->ptr;fptr = ziplistIndex(zl, ZIPLIST_HEAD);if (fptr != NULL) {fptr = ziplistFind(fptr, (unsigned char*)field, sdslen(field), 1);if (fptr != NULL) {/* Grab pointer to the value (fptr points to the field) */vptr = ziplistNext(zl, fptr);serverAssert(vptr != NULL);}}if (vptr != NULL) {ret = ziplistGet(vptr, vstr, vlen, vll);serverAssert(ret);return 0;}return -1;}// t_hash.c, 從hash表中查找 field 字段的值/* Get the value from a hash table encoded hash, identified by field.* Returns NULL when the field cannot be found, otherwise the SDS value* is returned. */sds hashTypeGetFromHashTable(robj *o, sds field) {dictEntry *de;serverAssert(o->encoding == OBJ_ENCODING_HT);de = dictFind(o->ptr, field);if (de == NULL) return NULL;return dictGetVal(de);}
四、hmget 批量獲取值
與hget如出一轍。
// t_hash.cvoid hmgetCommand(client *c) {robj *o;int i;/* Don't abort when the key cannot be found. Non-existing keys are empty* hashes, where HMGET should respond with a series of null bulks. */o = lookupKeyRead(c->db, c->argv[1]);if (o != NULL && o->type != OBJ_HASH) {addReply(c, shared.wrongtypeerr);return;}// 循環(huán)輸出值addReplyMultiBulkLen(c, c->argc-2);for (i = 2; i < c->argc; i++) {addHashFieldToReply(c, o, c->argv[i]->ptr);}}
五、hgetall 獲取所有hash的kv
hgetall 和 hmget 方式稍微有點(diǎn)不一樣,原因是為了讓 hkeysCommand/hvalsCommand 進(jìn)行復(fù)用。
// t_hash.cvoid hgetallCommand(client *c) {genericHgetallCommand(c,OBJ_HASH_KEY|OBJ_HASH_VALUE);}void genericHgetallCommand(client *c, int flags) {robj *o;hashTypeIterator *hi;int multiplier = 0;int length, count = 0;if ((o = lookupKeyReadOrReply(c,c->argv[1],shared.emptymultibulk)) == NULL|| checkType(c,o,OBJ_HASH)) return;if (flags & OBJ_HASH_KEY) multiplier++;if (flags & OBJ_HASH_VALUE) multiplier++;length = hashTypeLength(o) * multiplier;addReplyMultiBulkLen(c, length);hi = hashTypeInitIterator(o);while (hashTypeNext(hi) != C_ERR) {if (flags & OBJ_HASH_KEY) {addHashIteratorCursorToReply(c, hi, OBJ_HASH_KEY);count++;}if (flags & OBJ_HASH_VALUE) {addHashIteratorCursorToReply(c, hi, OBJ_HASH_VALUE);count++;}}hashTypeReleaseIterator(hi);serverAssert(count == length);}static void addHashIteratorCursorToReply(client *c, hashTypeIterator *hi, int what) {if (hi->encoding == OBJ_ENCODING_ZIPLIST) {unsigned char *vstr = NULL;unsigned int vlen = UINT_MAX;long long vll = LLONG_MAX;hashTypeCurrentFromZiplist(hi, what, &vstr, &vlen, &vll);if (vstr)addReplyBulkCBuffer(c, vstr, vlen);elseaddReplyBulkLongLong(c, vll);} else if (hi->encoding == OBJ_ENCODING_HT) {sds value = hashTypeCurrentFromHashTable(hi, what);addReplyBulkCBuffer(c, value, sdslen(value));} else {serverPanic("Unknown hash encoding");}}
六、hincrby 增加x某字段
hincrby key field 1
// t_hash.c,void hincrbyCommand(client *c) {long long value, incr, oldvalue;robj *o;sds new;unsigned char *vstr;unsigned int vlen;// 解析增加字段值到 incr 中if (getLongLongFromObjectOrReply(c,c->argv[3],&incr,NULL) != C_OK) return;// 獲取原值或者設(shè)置為0if ((o = hashTypeLookupWriteOrCreate(c,c->argv[1])) == NULL) return;if (hashTypeGetValue(o,c->argv[2]->ptr,&vstr,&vlen,&value) == C_OK) {if (vstr) {if (string2ll((char*)vstr,vlen,&value) == 0) {addReplyError(c,"hash value is not an integer");return;}} /* Else hashTypeGetValue() already stored it into &value */} else {value = 0;}oldvalue = value;if ((incr < 0 && oldvalue < 0 && incr < (LLONG_MIN-oldvalue)) ||(incr > 0 && oldvalue > 0 && incr > (LLONG_MAX-oldvalue))) {addReplyError(c,"increment or decrement would overflow");return;}// 將相加后的值重置設(shè)置回hash表中value += incr;new = sdsfromlonglong(value);hashTypeSet(o,c->argv[2]->ptr,new,HASH_SET_TAKE_VALUE);addReplyLongLong(c,value);signalModifiedKey(c->db,c->argv[1]);notifyKeyspaceEvent(NOTIFY_HASH,"hincrby",c->argv[1],c->db->id);server.dirty++;}
七、hdel 刪除某字段
hdel key field
// t_hash.c,void hdelCommand(client *c) {robj *o;int j, deleted = 0, keyremoved = 0;if ((o = lookupKeyWriteOrReply(c,c->argv[1],shared.czero)) == NULL ||checkType(c,o,OBJ_HASH)) return;// 循環(huán)刪除給定字段列表for (j = 2; j < c->argc; j++) {if (hashTypeDelete(o,c->argv[j]->ptr)) {deleted++;// 當(dāng)沒(méi)有任何元素后,直接將key刪除if (hashTypeLength(o) == 0) {dbDelete(c->db,c->argv[1]);keyremoved = 1;break;}}}if (deleted) {signalModifiedKey(c->db,c->argv[1]);notifyKeyspaceEvent(NOTIFY_HASH,"hdel",c->argv[1],c->db->id);if (keyremoved)notifyKeyspaceEvent(NOTIFY_GENERIC,"del",c->argv[1],c->db->id);server.dirty += deleted;}addReplyLongLong(c,deleted);}// 具體刪除 field, 同樣區(qū)分編碼類型,不同處理邏輯/* Delete an element from a hash.* Return 1 on deleted and 0 on not found. */int hashTypeDelete(robj *o, sds field) {int deleted = 0;if (o->encoding == OBJ_ENCODING_ZIPLIST) {unsigned char *zl, *fptr;zl = o->ptr;fptr = ziplistIndex(zl, ZIPLIST_HEAD);if (fptr != NULL) {// ziplist 刪除,依次刪除 field, valuefptr = ziplistFind(fptr, (unsigned char*)field, sdslen(field), 1);if (fptr != NULL) {// ziplistDelete 為原地刪除,所以只要調(diào)用2次,即把kv刪除zl = ziplistDelete(zl,&fptr);zl = ziplistDelete(zl,&fptr);o->ptr = zl;deleted = 1;}}} else if (o->encoding == OBJ_ENCODING_HT) {if (dictDelete((dict*)o->ptr, field) == C_OK) {deleted = 1;/* Always check if the dictionary needs a resize after a delete. */// hash 刪除的,可能需要進(jìn)行縮容操作,這種處理方法相對(duì)特殊些if (htNeedsResize(o->ptr)) dictResize(o->ptr);}} else {serverPanic("Unknown hash encoding");}return deleted;}// server.c, 是否需要進(jìn)行 resizeint htNeedsResize(dict *dict) {long long size, used;size = dictSlots(dict);used = dictSize(dict);// HASHTABLE_MIN_FILL=10, 即使用率小于 1/10 時(shí),可以進(jìn)行縮容操作了return (size && used && size > DICT_HT_INITIAL_SIZE &&(used*100/size < HASHTABLE_MIN_FILL));}
至此,整個(gè)hash數(shù)據(jù)結(jié)構(gòu)的解析算是完整了。總體來(lái)說(shuō),hash由兩種數(shù)據(jù)結(jié)構(gòu)承載,ziplist在小數(shù)據(jù)量時(shí)使用,稍微復(fù)雜,但對(duì)于昂貴的內(nèi)存來(lái)說(shuō)是值得的。hash表在數(shù)據(jù)量大時(shí)使用,容易理解。通過(guò)本文的講解,相信可以驗(yàn)證了你對(duì)redis hash 的實(shí)現(xiàn)的猜想了。

騰訊、阿里、滴滴后臺(tái)面試題匯總總結(jié) — (含答案)
面試:史上最全多線程面試題 !
最新阿里內(nèi)推Java后端面試題
JVM難學(xué)?那是因?yàn)槟銢](méi)認(rèn)真看完這篇文章

關(guān)注作者微信公眾號(hào) —《JAVA爛豬皮》
了解更多java后端架構(gòu)知識(shí)以及最新面試寶典

看完本文記得給作者點(diǎn)贊+在看哦~~~大家的支持,是作者源源不斷出文的動(dòng)力
作者:等你歸去來(lái)
出處:https://www.cnblogs.com/yougewe/p/12234983.html
