終于有人把HashTable這種數(shù)據(jù)結(jié)構(gòu)講清楚了!
概論
HashTable是遺留類,很多映射的常用功能與HashMap類似,不同的是它承自Dictionary類,并且是線程安全的,并發(fā)性不如ConcurrentHashMap,因為ConcurrentHashMap引入了分段鎖。
Hashtable不建議在新代碼中使用,不需要線程安全的場合可以用HashMap替換,需要線程安全的場合可以用ConcurrentHashMap替換。
對比HashMap 的初始容量
默認11 的初始容量
需要注意的是Hashtable的默認初始容量大小是11,而HashMap 是16,但是他們的加載因子都是0.75f
????/**
?????*?Constructs?a?new,?empty?hashtable?with?a?default?initial?capacity?(11)
?????*?and?load?factor?(0.75).
?????*/
????public?Hashtable()?{
????????this(11,?0.75f);
????}
/**
?*?Constructs?an?empty?HashMap?with?the?default?initial?capacity
?*?(16)?and?the?default?load?factor?(0.75).
?*/
public?HashMap()?{
????this.loadFactor?=?DEFAULT_LOAD_FACTOR;?//?all?other?fields?defaulted
}
任意指定非負的容量
還有一點就是Hashtable的initialCapacity 也就是初始容量是是可以是你指定的任何非負整數(shù),也就是你給它設置個0 也可以的
public?Hashtable(int?initialCapacity)?{
????this(initialCapacity,?0.75f);
}
public?Hashtable(int?initialCapacity,?float?loadFactor)?{
????if?(initialCapacity?0)
????????throw?new?IllegalArgumentException("Illegal?Capacity:?"+
???????????????????????????????????????????initialCapacity);
????if?(loadFactor?<=?0?||?Float.isNaN(loadFactor))
????????throw?new?IllegalArgumentException("Illegal?Load:?"+loadFactor);
????if?(initialCapacity==0)
????????initialCapacity?=?1;
????this.loadFactor?=?loadFactor;
????table?=?new?Entry[initialCapacity];
????threshold?=?(int)Math.min(initialCapacity?*?loadFactor,?MAX_ARRAY_SIZE?+?1);
}
但是你看一下HashMap 的初始容量就不那么聽話了,默認情況下,當我們設置HashMap的初始化容量時,實際上HashMap會采用第一個大于該數(shù)值的2的冪作為初始化容量(0 1 除外)
public?HashMap(int?initialCapacity,?float?loadFactor)?{
????if?(initialCapacity?0)
????????throw?new?IllegalArgumentException("Illegal?initial?capacity:?"?+?initialCapacity);
????if?(initialCapacity?>?MAXIMUM_CAPACITY)
????????initialCapacity?=?MAXIMUM_CAPACITY;
????if?(loadFactor?<=?0?||?Float.isNaN(loadFactor))
????????throw?new?IllegalArgumentException("Illegal?load?factor:?"?+?loadFactor);
????this.loadFactor?=?loadFactor;
????this.threshold?=?tableSizeFor(initialCapacity);
}
對比HashMap 的 對null 值的支持
HashTable key value 都不支持null
首先HashMap 是支持null 值做key和value 的,但是HashTable 是不支持的,key 也不支持 value 也不支持
public?synchronized?V?put(K?key,?V?value)?{
????//?Make?sure?the?value?is?not?null
????if?(value?==?null)?{
????????throw?new?NullPointerException();
????}
????//?Makes?sure?the?key?is?not?already?in?the?hashtable.
????Entry?tab[]?=?table;
????int?hash?=?key.hashCode();
????int?index?=?(hash?&?0x7FFFFFFF)?%?tab.length;
????@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
????Entry?entry?=?(Entry)tab[index];
????for(;?entry?!=?null?;?entry?=?entry.next)?{
????????if?((entry.hash?==?hash)?&&?entry.key.equals(key))?{
????????????V?old?=?entry.value;
????????????entry.value?=?value;
????????????return?old;
????????}
????}
????addEntry(hash,?key,?value,?index);
????return?null;
}
聰明的你們發(fā)現(xiàn)了嗎,上面值檢測了value ==null 則拋出NPE 但是沒有說key 啊,因為如果key 是null 的話,key.hashCode()則會拋出異常,根本不需要判斷,但是value 就不會拋出來
但是需要注意的實HashMap 對null 值雖然支持,但是可以從hash值的計算方法中看出,
static?final?int?hash(Object?key)?{
????int?h;
????return?(key?==?null)???0?:?(h?=?key.hashCode())?^?(h?>>>?16);
}
升級HashTable 使其支持null 做value
大部分代碼都是直接copy 的HashTable,只去掉了value 的空值檢測
public?class?BuerHashTable<K,?V>?extends?Hashtable<K,?V>?{
????????//?.....?省略了部分代碼,直接copy?HashTable?的即可,主要是BuerHashTable.Entry?的定義和構(gòu)造方法
????public?synchronized?V?put(K?key,?V?value)?{
????????//?Makes?sure?the?key?is?not?already?in?the?hashtable.
????????Entry?tab[]?=?table;
????????int?hash?=?key.hashCode();
????????int?index?=?(hash?&?0x7FFFFFFF)?%?tab.length;
????????@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
????????Entry?entry?=?(Entry)tab[index];
????????for(;?entry?!=?null?;?entry?=?entry.next)?{
????????????if?((entry.hash?==?hash)?&&?entry.key.equals(key))?{
????????????????V?old?=?entry.value;
????????????????entry.value?=?value;
????????????????return?old;
????????????}
????????}
????????addEntry(hash,?key,?value,?index);
????????return?null;
????}
????private?void?addEntry(int?hash,?K?key,?V?value,?int?index)?{
????????modCount++;
????????BuerHashTable.Entry?tab[]?=?table;
????????if?(count?>=?threshold)?{
????????????//?Rehash?the?table?if?the?threshold?is?exceeded
????????????rehash();
????????????tab?=?table;
????????????hash?=?key.hashCode();
????????????index?=?(hash?&?0x7FFFFFFF)?%?tab.length;
????????}
????????//?Creates?the?new?entry.
????????@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
????????BuerHashTable.Entry?e?=?(BuerHashTable.Entry)?tab[index];
????????tab[index]?=?new?BuerHashTable.Entry<>(hash,?key,?value,?e);
????????count++;
????}
}
接下來,就可以將null 值作為value 存入BuerHashTable 了
BuerHashTable?buerHashTable?=?new?BuerHashTable<>();
buerHashTable.put("a",?null);
對比 HashTable 的繼承關(guān)系
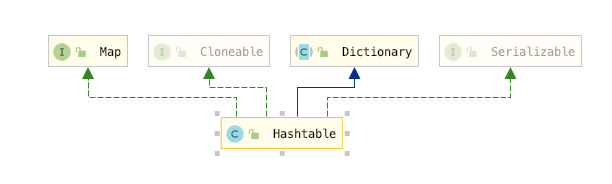
Dictionary
這個類是HashTable特有繼承的,HashMap 是沒有繼承的,但是這個抽象類其實是沒有多大意義的,因為它的方法都在Map接口中有,其實這個就是個歷史問題了,因為Map接口是在Java1.2 中才加進去的,而Dictionary抽象類在Java1.0中就存在了
public?abstract
class?Dictionary<K,V>?{
????public?Dictionary()?{
????}
????abstract?public?int?size();
????abstract?public?boolean?isEmpty();
????abstract?public?Enumeration?keys() ;
????abstract?public?Enumeration?elements() ;
????abstract?public?V?get(Object?key);
????/**
?????*?@exception??NullPointerException??if?the?key?or
?????*/
????abstract?public?V?put(K?key,?V?value);
????abstract?public?V?remove(Object?key);
}
這個地方的NullPointerException 對應的就是HashTable 中put 方法中的null 值檢測
最后一點就是Dictionary 抽象類上的注釋,新的實現(xiàn)應該實現(xiàn)Map 接口而不是該抽象類
NOTE:?This?class?is?obsolete.??New?implementations?should?implement?the?Map?interface,?rather?than?extending?this?class
其實HashMap更準確地說是繼承自AbstractMap類,而不是直接實現(xiàn)了Map 接口,所以要是Dictionary這個抽象類要是實現(xiàn)的實Map 接口,那HashMap和Hashtable 就在繼承關(guān)系上保持一致了
Hashtable
線程安全
其實HashTable 沒有那么多要說的,比較重要的一點就是線程安全,但是這個線程安全的實現(xiàn)方式就是所有的操作都加了synchronized關(guān)鍵字,哈哈!關(guān)于synchronized 我們后面會說
public?synchronized?int?size()?{}
public?synchronized?boolean?isEmpty()?{}
public?synchronized?boolean?contains(Object?value)?{}
public?synchronized?boolean?containsKey(Object?key)?{}
public?synchronized?V?get(Object?key)?{}
public?synchronized?V?put(K?key,?V?value)?{}
public?synchronized?V?remove(Object?key)?{}
而HashMap 是線程不安全的
contains方法
HashMap中沒有Hashtable中的contains方法,只有containsValue和containsKey,因為contains方法容易讓人引起誤解。
Hashtable則保留了contains,containsValue和containsKey三個方法,其中contains和containsValue功能相同。
debug 源碼 put 方法
public?synchronized?V?put(K?key,?V?value)?{
????//?Make?sure?the?value?is?not?null?確保value?不是null
????if?(value?==?null)?{
????????throw?new?NullPointerException();
????}
????//?Makes?sure?the?key?is?not?already?in?the?hashtable.
????//?這里的英文注釋很有意思啊,就是告訴你確保key?不存在,存在咋地,覆蓋又咋地
????Entry?tab[]?=?table;
????//?哈希值的計算不同,HashTable直接使用對象的hashCode。而HashMap重新計算hash值(高16位異或低16位)
????int?hash?=?key.hashCode();
????//?計算下標 HashMap 是計算key的hash再與tab.length-1進行與運算;
????//?HashTable則是key的hash值與0x7FFFFFFF進行與運算,然后再對tab.length取模
????//?先hash&0x7FFFFFFF后,再對length取模,與0x7FFFFFFF的目的是為了將負的hash值轉(zhuǎn)化為正值,因為hash值有可能為負數(shù),而&0x7FFFFFFF后,只有符號外改變,而后面的位都不變
????int?index?=?(hash?&?0x7FFFFFFF)?%?tab.length;
????@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
????//?確定?index?位置上的鏈表頭,這里主要是遍歷鏈表找到key?值相等的節(jié)點,然后返回old?value,這樣的話就不用添加新值
????//?也就是不用調(diào)用addEntry?方法
????Entry?entry?=?(Entry)tab[index];
????//?存在key?
????for(;?entry?!=?null?;?entry?=?entry.next)?{
????????if?((entry.hash?==?hash)?&&?entry.key.equals(key))?{
????????????V?old?=?entry.value;
????????????entry.value?=?value;
????????????return?old;
????????}
????}
????//?鏈表中不存在,則添加新值
????addEntry(hash,?key,?value,?index);
????//?返回null?
????return?null;
}
private?void?addEntry(int?hash,?K?key,?V?value,?int?index)?{
????modCount++;
????Entry?tab[]?=?table;
????//?判斷是否要擴容
????if?(count?>=?threshold)?{
????????//?Rehash?the?table?if?the?threshold?is?exceeded
????????rehash();
????????tab?=?table;
????????hash?=?key.hashCode();
????????index?=?(hash?&?0x7FFFFFFF)?%?tab.length;
????}
????//?Creates?the?new?entry.
????@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
????Entry?e?=?(Entry)?tab[index];
????//?e?也就是??tab[index]?是這個鏈表的頭結(jié)點,?tab[index]?=?new?Entry<>(hash,?key,?value,?e);?也就是將元素添加到鏈表的頭部,e?做為new?Entry<>(hash,?key,?value,?e)的next?節(jié)點
????tab[index]?=?new?Entry<>(hash,?key,?value,?e);
????count++;
}
這里我們對比一下HashMap 的添加方法,很明顯別人都是添加的鏈表尾部的,因為HashTable 是線程安全的,在這個前提下,使用頭查法性能更好,否則還有遍歷到鏈表的尾部插入
for?(int?binCount?=?0;?;?++binCount)?{
????if?((e?=?p.next)?==?null)?{
????????p.next?=?newNode(hash,?key,?value,?null);
????????if?(binCount?>=?TREEIFY_THRESHOLD?-?1)?//?-1?for?1st
????????????treeifyBin(tab,?hash);
????????break;
????}
????if?(e.hash?==?hash?&&
????????((k?=?e.key)?==?key?||?(key?!=?null?&&?key.equals(k))))
????????break;
????p?=?e;
}
最后我們再看一下擴容的方法
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
protected?void?rehash()?{
????int?oldCapacity?=?table.length;
????Entry[]?oldMap?=?table;
????//?overflow-conscious?code?
????//?擴容成2倍+1
????int?newCapacity?=?(oldCapacity?<1)?+?1;
????//?這里判斷是否超出了容量限制
????if?(newCapacity?-?MAX_ARRAY_SIZE?>?0)?{
????????if?(oldCapacity?==?MAX_ARRAY_SIZE)
????????????//?Keep?running?with?MAX_ARRAY_SIZE?buckets
????????????return;
????????//?最大容量?MAX_ARRAY_SIZE????
????????newCapacity?=?MAX_ARRAY_SIZE;
????}
????//?創(chuàng)建新的數(shù)組
????Entry[]?newMap?=?new?Entry[newCapacity];
????modCount++;
????//?更新?threshold
????threshold?=?(int)Math.min(newCapacity?*?loadFactor,?MAX_ARRAY_SIZE?+?1);
????table?=?newMap;
????//?數(shù)據(jù)遷移,遍歷數(shù)組
????for?(int?i?=?oldCapacity?;?i--?>?0?;)?{
????????????//?for?循環(huán)的方式遍歷鏈表
????????for?(Entry?old?=?(Entry)oldMap[i]?;?old?!=?null?;?)?{
????????????Entry?e?=?old;
????????????old?=?old.next;
????????????int?index?=?(e.hash?&?0x7FFFFFFF)?%?newCapacity;
????????????e.next?=?(Entry)newMap[index];
????????????newMap[index]?=?e;
????????}
????}
}
總結(jié)
需要注意的是Hashtable的默認初始容量大小是11,而HashMap 是16,但是他們的加載因子都是0.75f
HashTable的初始容量可以使任何非負整數(shù),但是HashMap會采用第一個大于該數(shù)值的2的冪作為初始化容量(0 1 除外,都是 1)
HashTable的線程安全是完全借助synchronized 的加持
HashTable 的元素是頭插法,也就是插入到鏈表的頭部,因為HashTable 是線程安全的,在這個前提下,使用頭查法性能更好,否則還有遍歷到鏈表的尾部插入
HashTable 是沒有紅黑樹支持的,就是不論鏈表的長度有多長,都不會轉(zhuǎn)化成紅黑樹
哈希值的計算不同,HashTable直接使用對象的hashCode。而HashMap重新計算hash值(高16位異或低16位),并且HashMap 支持key 為null 就是在這里的
Hashtable擴容時,將容量變?yōu)樵瓉淼?倍加1,而HashMap擴容時,將容量變?yōu)樵瓉淼?倍。
你覺得HashTable 還有什么可以改進的地方嗎,歡迎討論
和上一節(jié)一樣這里我依然給出這個思考題,雖然我們的說法可能不對,可能我們永遠也站不到源代碼作者當年的高度,但是我們依然積極思考,大膽討論
雖然java 源代碼的山很高,如果你想跨越,至少你得有登山的勇氣,這里我給出自己的一點點愚見,希望各位不吝指教
int?hash?=?key.hashCode();
addEntry(hash,?key,?value,?index);
private?void?addEntry(int?hash,?K?key,?V?value,?int?index)?{
????????//?記錄修改,快速失敗
????modCount++;
????Entry?tab[]?=?table;
????//?count?實際存儲的key-value?數(shù)目,在HashMap?中用size?表示
????if?(count?>=?threshold)?{
????????//?Rehash?the?table?if?the?threshold?is?exceeded
????????rehash();
????????tab?=?table;
????????//?咋地,數(shù)組擴容之后key?的hash值會變嗎,你還有重新計算一下
????????hash?=?key.hashCode();
????????index?=?(hash?&?0x7FFFFFFF)?%?tab.length;
????}
????//?Creates?the?new?entry.
????@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
????Entry?e?=?(Entry)?tab[index];
????tab[index]?=?new?Entry<>(hash,?key,?value,?e);
????count++;
}
當然這只是小問題,但是也有很多其他小問題,例如求index 時候的計算方式是直接取模,而不是用與運算,它最大的問題在設計上,例如hash值的計算方式就沒有HashMap 設計的好,還有就是沒有紅黑樹的支持,還有就是線程安全的實現(xiàn)方式也不高效,所以我們說它好像是遺留類,HashTable 在Java1.0 時代就存在了,而HashMap才是Java1.2才有的
