Android自定義控件坐標(biāo)系解析
自定義控件要想徹底的把握,掌握Android各種坐標(biāo)系及一些API的坐標(biāo)含義毫無(wú)疑問(wèn)是不可忽視的技能,對(duì)于控件的擺放位置、觸摸點(diǎn)、控件繪制等都離不開坐標(biāo)系,所以學(xué)習(xí)自定義控件之前我們就先來(lái)談一下Android坐標(biāo)系。
一、Android屏幕坐標(biāo)系和數(shù)學(xué)坐標(biāo)系的區(qū)別
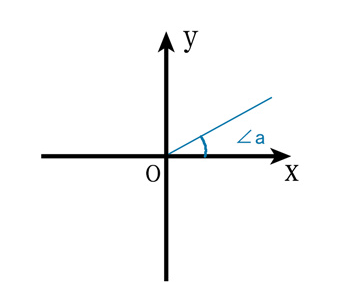
(1)、在數(shù)學(xué)坐標(biāo)系中以xy軸的交點(diǎn)為坐標(biāo)原點(diǎn),x軸向右為正方向,y軸向上為正方向,這對(duì)于童鞋們來(lái)說(shuō)已經(jīng)再熟悉不過(guò)了,如圖:
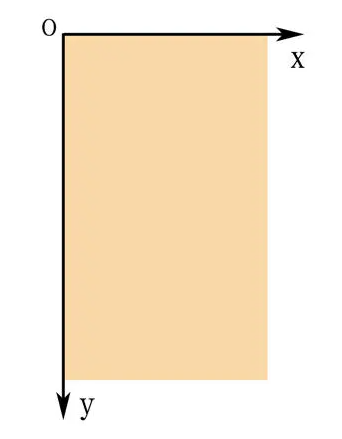
(2)、而在手機(jī)屏幕上的坐標(biāo)系與數(shù)學(xué)坐標(biāo)系還是有差別的,移動(dòng)設(shè)備一般定義屏幕左上角為坐標(biāo)原點(diǎn),x軸向右為正方向,y軸向下為正方向,如圖:
二、Android屏幕區(qū)域的劃分
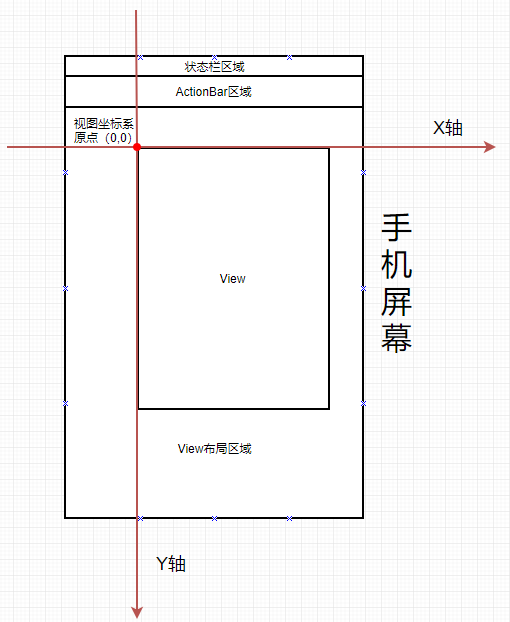
Android屏幕區(qū)域主要?jiǎng)澐譃槲鍌€(gè)區(qū)域分別為:狀態(tài)欄區(qū)域、ActionBar區(qū)域、View布局區(qū)域、應(yīng)用程序App區(qū)域、屏幕區(qū)域,相互之間又存在嵌套關(guān)系。如圖所示:

下面我們來(lái)看看各個(gè)區(qū)域高度的獲取:
(1)、狀態(tài)欄區(qū)域高度獲取:
//第一種方式,使用此方法一定要等界面渲染結(jié)束Rect rect = new Rect();getWindow().getDecorView().getWindowVisibleDisplayFrame(rect);int statusBarHeight = rect.top;//第二種方式,獲取狀態(tài)欄高度Resources resources = this.getResources();int resourceId = resources.getIdentifier("status_bar_height", "dimen", "android");int height = resources.getDimensionPixelSize(resourceId);//此次獲取狀態(tài)欄高度//第三種方式,通過(guò)反射方式獲取狀態(tài)欄高度int statusHeight = -1;try {Class clazz = Class.forName("com.android.internal.R$dimen");Object object = clazz.newInstance();int intheight = Integer.parseInt(clazz.getField("status_bar_height").get(object).toString());//獲取狀態(tài)欄高度statusHeight = this.getResources().getDimensionPixelSize(intheight);} catch (Exception e) {e.printStackTrace();}
(2)、ActionBar區(qū)域高度獲取:
//第一種方式,此方法要等界面渲染結(jié)束int actionBarHeight = getSupportActionBar().getHeight();//第二種方式TypedValue tv = new TypedValue();if (this.getTheme().resolveAttribute(android.R.attr.actionBarSize, tv, true)) {int actionBarHeightOther = TypedValue.complexToDimensionPixelSize(tv.data, this.getResources().getDisplayMetrics());}
(3)、View布局區(qū)域高度獲取:
//第一種方式Rect rect = new Rect();getWindow().findViewById(Window.ID_ANDROID_CONTENT).getDrawingRect(rect);//第二種方式//可見(jiàn)當(dāng)執(zhí)行onResume和onPause時(shí),onWindowFocusChanged都會(huì)被調(diào)用。此時(shí)界面已渲染結(jié)束public void onWindowFocusChanged(boolean hasFocus) {super.onWindowFocusChanged(hasFocus);if (hasFocus) {int width = view.getMeasuredWidth();//獲得寬度int height = view.getMeasuredHeight();//獲得高度}}//第三種方式view.post(new Runnable() {public void run() {int width=view.getMeasuredWidth();int height=view.getMeasuredHeight();}})//第四種方式view.getViewTreeObserver().addOnGlobalLayoutListener(new ViewTreeObserver.OnGlobalLayoutListener() {public void onGlobalLayout() {view.getViewTreeObserver().removeOnGlobalLayoutListener(this);int width=view.getMeasuredWidth();int height=view.getMeasuredHeight();}});
(4)、應(yīng)用程序App區(qū)域高度獲取:
Rect rect = new Rect();getWindow().getDecorView().getWindowVisibleDisplayFrame(rect);
(5)、屏幕區(qū)域高度獲取:
//第一種方式,該方式在4.1版本后已過(guò)時(shí)。Display display = getWindowManager().getDefaultDisplay();int width = display.getWidth();int height = display.getHeight();//第二種方式Display defaultDisplay = getWindowManager().getDefaultDisplay();Point point = new Point();defaultDisplay.getSize(point);int x = point.x;int y = point.y;//第三種方式Rect outSize = new Rect();getWindowManager().getDefaultDisplay().getRectSize(outSize);int left = outSize.left;int top = outSize.top;int right = outSize.right;int bottom = outSize.bottom;//第四種方式DisplayMetrics outMetrics = new DisplayMetrics();getWindowManager().getDefaultDisplay().getMetrics(outMetrics);int widthPixels = outMetrics.widthPixels;int heightPixels = outMetrics.heightPixels;//第五種方式Point outSizeOther = new Point();getWindowManager().getDefaultDisplay().getRealSize(outSizeOther);int x1 = outSizeOther.x;int y1 = outSizeOther.y;//第六種方式DisplayMetrics outMetrics1 = new DisplayMetrics();getWindowManager().getDefaultDisplay().getRealMetrics(outMetrics1);int widthPixel = outMetrics1.widthPixels;int heightPixel = outMetrics1.heightPixels;
特別注意:上面這些方法最好在Activity的onWindowFocusChanged()方法或者之后調(diào)用,因?yàn)橹挥羞@時(shí)候才是真正的顯示完全。
三、Android坐標(biāo)系的分類
上面我們分析了Android屏幕區(qū)域的劃分,接著我們分析一下與區(qū)域相關(guān)的Android坐標(biāo)系,在Android坐標(biāo)系中可以分為:屏幕坐標(biāo)系,視圖坐標(biāo)系。
(1)、屏幕坐標(biāo)系
屏幕坐標(biāo)系我們前面在和數(shù)學(xué)坐標(biāo)系的區(qū)別已經(jīng)介紹過(guò)了,以屏幕左上角為坐標(biāo)原點(diǎn),x軸向右為正方向,y軸向下為正方向,如圖所示:

(2)、視圖坐標(biāo)系
視圖坐標(biāo)系在View繪制過(guò)程中,繪制的內(nèi)容將以坐標(biāo)系作為參考,最后確定繪制內(nèi)容在View里面的位置。
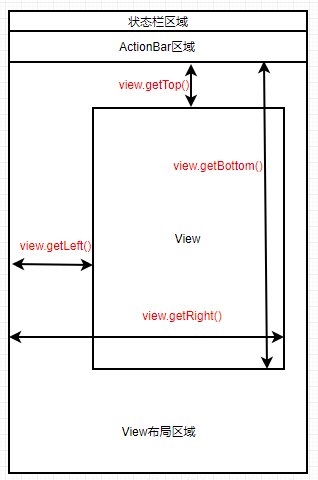
下面我們來(lái)看看常用的坐標(biāo)方法,注意這些方法是相對(duì)父容器而言的:
| View相關(guān)方法 | 方法說(shuō)明 |
| view.getLeft() | 當(dāng)前View的左邊緣與它父View的左邊緣的距離(視圖坐標(biāo)); |
| view.getRight() | 當(dāng)前View的右邊緣與它父View的左邊緣的距離(視圖坐標(biāo)); |
| view.getTop() | 當(dāng)前View的上邊緣與它父View的上邊緣(頂部)的距離(視圖坐標(biāo)); |
| view.getBottom() | 當(dāng)前View的下邊緣與它父View的上邊緣(頂部)的距離(視圖坐標(biāo)); |
| View.getTranslationX() | 當(dāng)前View在X軸的偏移量。初始值為0,向左偏移值為負(fù),向右偏移值為正;(常見(jiàn)于屬性動(dòng)畫中) |
| View.getTranslationY() | 當(dāng)前View在Y軸的偏移量。初始值為0,向上偏移為負(fù),向下偏移為正;(常見(jiàn)于屬性動(dòng)畫中) |
| View.getX | 當(dāng)前View在X軸的偏移量。初始值為0,向左偏移值為負(fù),向右偏移值為正;返回值為getLeft()+getTranslationX(),當(dāng)setTranslationX()變getLeft()不變時(shí),getX()變。 |
| View.getY | 當(dāng)前View在Y軸的偏移量。初始值為0,向上偏移為負(fù),向下偏移為正;返回值為getTop()+getTranslationY(),當(dāng)setTranslationY()變getTop()不變時(shí),getY()變。 |
為了解釋清楚這些方法,準(zhǔn)備了張圖,如圖所示:
此時(shí)我們可以獲取視圖(View)寬高的方法:
| View寬高方法 | 方法說(shuō)明 |
| getWidth() | 當(dāng)前View的寬度,即getRight()-getLeft() |
| getHeight() | 當(dāng)前View寬度,即getBottom()-getTop() |
需要注意的是使用以上方法的過(guò)程中要在View測(cè)量結(jié)束即渲染完成后,不然獲取到的值為0。
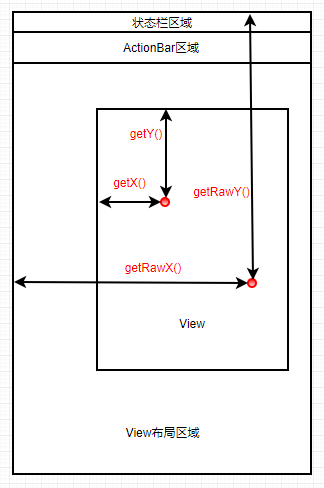
我們?cè)賮?lái)看看手指觸摸屏幕時(shí)MotionEvent提供的一些方法解釋:
| MotionEvent坐標(biāo)方法 | 方法說(shuō)明 |
| getX() | 觸摸中心點(diǎn)與該View左邊緣的距離(相對(duì)坐標(biāo)) |
| getY() | 觸摸中心點(diǎn)與該View上邊緣的距離(相對(duì)坐標(biāo)) |
| getRawX() | 觸摸中心點(diǎn)與屏幕左邊緣的距離(絕對(duì)坐標(biāo)) |
| getRawY() | 觸摸中心點(diǎn)與屏幕上邊緣的距離(絕對(duì)坐標(biāo)) |
為了解釋清楚這些方法,準(zhǔn)備了張圖,如圖所示:
今天的內(nèi)容就到這啦,本文主要就是闡述View里常用方法及坐標(biāo)相關(guān)的概念,也是為后期的內(nèi)容做鋪墊。
