深度學(xué)習(xí)中的數(shù)據(jù)增強(qiáng)方法
點(diǎn)擊下方卡片,關(guān)注“新機(jī)器視覺(jué)”公眾號(hào)
視覺(jué)/圖像重磅干貨,第一時(shí)間送達(dá)
一、為什么數(shù)據(jù)增強(qiáng)
我們看上面這幅漫畫(huà),故事里是一個(gè)顧客去拍風(fēng)景照,因?yàn)椴皇菍?shí)地取景,又想拍出多種不同的效果。
當(dāng)前現(xiàn)狀是,影樓只有一個(gè)實(shí)地的照片背景,那么如何滿足顧客要求呢?沒(méi)錯(cuò),有請(qǐng)我們的P圖大神,從各個(gè)不同的角度給顧客P圖。
那么P出來(lái)的效果是什么呢?
效果就是照片看起來(lái)更加豐富,顧客很滿意,可以乖乖掏錢了。。。
那么這個(gè)漫畫(huà)和數(shù)據(jù)增強(qiáng)有啥關(guān)系呢?我們接著往下看:
(他們的共同點(diǎn)都是數(shù)據(jù)(圖像)不足,同時(shí)又想得到多樣化的數(shù)據(jù)效果)
那么我們?cè)跈C(jī)器學(xué)習(xí)中,為何要進(jìn)行數(shù)據(jù)增強(qiáng)呢?
在深度學(xué)習(xí)中,一般要求樣本的數(shù)量要充足,樣本數(shù)量越多,訓(xùn)練出來(lái)的模型效果越好,模型的泛化能力越強(qiáng)。但是實(shí)際中,樣本數(shù)量不足或者樣本質(zhì)量不夠好,這就要對(duì)樣本做數(shù)據(jù)增強(qiáng),來(lái)提高樣本質(zhì)量。
關(guān)于數(shù)據(jù)增強(qiáng)的作用總結(jié)如下:
1,增加訓(xùn)練的數(shù)據(jù)量,提高模型的泛化能力
2,增加噪聲數(shù)據(jù),提升模型的魯棒性
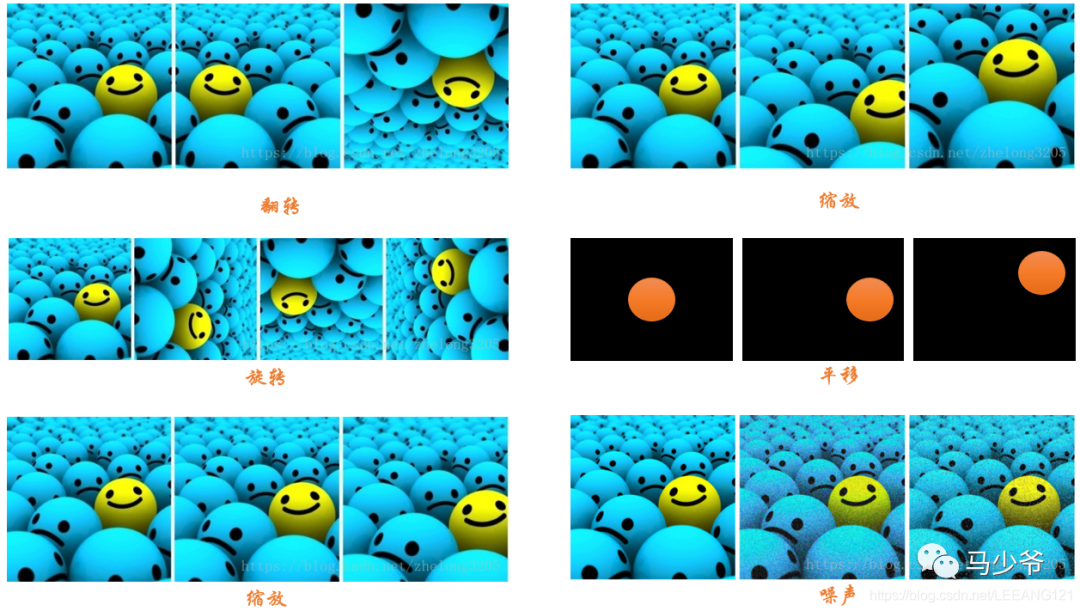
數(shù)據(jù)增強(qiáng)的方法(我們以圖像數(shù)據(jù)為例):
1,數(shù)據(jù)翻轉(zhuǎn):數(shù)據(jù)翻轉(zhuǎn)是一種常用的數(shù)據(jù)增強(qiáng)方法,這種方法不同于旋轉(zhuǎn) 180 °。這種方法是做一種類似于鏡面的翻折。
2,數(shù)據(jù)旋轉(zhuǎn):旋轉(zhuǎn)就是順時(shí)針或者逆時(shí)針的旋轉(zhuǎn),注意在旋轉(zhuǎn)的時(shí)候, 最好旋轉(zhuǎn) 90 - 180 度否則會(huì)出現(xiàn)尺度的問(wèn)題
3,圖像縮放:圖像可以被放大或縮小。放大時(shí),放大后的圖像尺寸會(huì)大于原始尺寸。大多數(shù)圖像處理架構(gòu)會(huì)按照原始尺寸對(duì)放大后的圖像進(jìn)行裁切而圖像縮小會(huì)減小圖像尺寸,這使我們不得不對(duì)圖像邊界之外的東西做出假設(shè)。
4,圖像剪裁:這種方法更流行的叫法是隨機(jī)裁剪,我們隨機(jī)從圖像中選擇一部分,然后降這部分圖像裁剪出來(lái),然后調(diào)整為原圖像的大小
5,圖像平移:平移是將圖像沿著 x 或者 y 方向 (或者兩個(gè)方向) 移動(dòng)。我們?cè)谄揭频臅r(shí)候需對(duì)背景進(jìn)行假設(shè),比如說(shuō)假設(shè)為黑色等等,因?yàn)槠揭频臅r(shí)候有一部分圖像是空的,由于圖片中的物體可能出現(xiàn)在任意的位置,所以說(shuō)平移增強(qiáng)方法十分有用。
6,添加噪聲:過(guò)擬合通常發(fā)生在神經(jīng)網(wǎng)絡(luò)學(xué)習(xí)高頻特征的時(shí)候 (因?yàn)榈皖l特征神經(jīng)網(wǎng)絡(luò)很容易就可以學(xué)到,而高頻特征只有在最后的時(shí)候才可以學(xué)到) 而這些特征對(duì)于神經(jīng)網(wǎng)絡(luò)所做的任務(wù)可能沒(méi)有幫助,而且會(huì)對(duì)低頻特征產(chǎn)生影響,為了消除高頻特征我們隨機(jī)加入噪聲數(shù)據(jù)來(lái)消除這些特征。
以下是上述方式的圖像示例:
二、Mosaic數(shù)據(jù)增強(qiáng)
Yolov4的mosaic數(shù)據(jù)增強(qiáng)參考了CutMix數(shù)據(jù)增強(qiáng)方式,理論上具有一定的相似性!
CutMix數(shù)據(jù)增強(qiáng)方式利用兩張圖片進(jìn)行拼接。
但是mosaic利用了四張圖片,根據(jù)論文所說(shuō)其擁有一個(gè)巨大的優(yōu)點(diǎn)是豐富檢測(cè)物體的背景!且在BN計(jì)算的時(shí)候一下子會(huì)計(jì)算四張圖片的數(shù)據(jù)!
就像下圖這樣:
1、每次讀取四張圖片。
2、分別對(duì)四張圖片進(jìn)行翻轉(zhuǎn)、縮放、色域變化等,并且按照四個(gè)方向位置擺好。
3、進(jìn)行圖片的組合和框的組合
全部代碼構(gòu)成如下:
from PIL import Image, ImageDrawimport numpy as npfrom matplotlib.colors import rgb_to_hsv, hsv_to_rgbimport mathdef rand(a=0, b=1):return np.random.rand()*(b-a) + adef merge_bboxes(bboxes, cutx, cuty):merge_bbox = []for i in range(len(bboxes)):for box in bboxes[i]:tmp_box = []x1,y1,x2,y2 = box[0], box[1], box[2], box[3]if i == 0:if y1 > cuty or x1 > cutx:continueif y2 >= cuty and y1 <= cuty:y2 = cutyif y2-y1 < 5:continueif x2 >= cutx and x1 <= cutx:x2 = cutxif x2-x1 < 5:continueif i == 1:if y2 < cuty or x1 > cutx:continueif y2 >= cuty and y1 <= cuty:y1 = cutyif y2-y1 < 5:continueif x2 >= cutx and x1 <= cutx:x2 = cutxif x2-x1 < 5:continueif i == 2:if y2 < cuty or x2 < cutx:continueif y2 >= cuty and y1 <= cuty:y1 = cutyif y2-y1 < 5:continueif x2 >= cutx and x1 <= cutx:x1 = cutxif x2-x1 < 5:continueif i == 3:if y1 > cuty or x2 < cutx:continueif y2 >= cuty and y1 <= cuty:y2 = cutyif y2-y1 < 5:continueif x2 >= cutx and x1 <= cutx:x1 = cutxif x2-x1 < 5:continuetmp_box.append(x1)tmp_box.append(y1)tmp_box.append(x2)tmp_box.append(y2)tmp_box.append(box[-1])merge_bbox.append(tmp_box)return merge_bboxdef get_random_data(annotation_line, input_shape, random=True, hue=.1, sat=1.5, val=1.5, proc_img=True):'''random preprocessing for real-time data augmentation'''h, w = input_shapemin_offset_x = 0.4min_offset_y = 0.4scale_low = 1-min(min_offset_x,min_offset_y)scale_high = scale_low+0.2image_datas = []box_datas = []index = 0place_x = [0,0,int(w*min_offset_x),int(w*min_offset_x)]place_y = [0,int(h*min_offset_y),int(w*min_offset_y),0]for line in annotation_line:# 每一行進(jìn)行分割line_content = line.split()# 打開(kāi)圖片image = Image.open(line_content[0])image = image.convert("RGB")# 圖片的大小iw, ih = image.size# 保存框的位置box = np.array([np.array(list(map(int,box.split(',')))) for box in line_content[1:]])# image.save(str(index)+".jpg")# 是否翻轉(zhuǎn)圖片flip = rand()<.5if flip and len(box)>0:image = image.transpose(Image.FLIP_LEFT_RIGHT)box[:, [0,2]] = iw - box[:, [2,0]]# 對(duì)輸入進(jìn)來(lái)的圖片進(jìn)行縮放new_ar = w/hscale = rand(scale_low, scale_high)if new_ar < 1:nh = int(scale*h)nw = int(nh*new_ar)else:nw = int(scale*w)nh = int(nw/new_ar)image = image.resize((nw,nh), Image.BICUBIC)# 進(jìn)行色域變換hue = rand(-hue, hue)sat = rand(1, sat) if rand()<.5 else 1/rand(1, sat)val = rand(1, val) if rand()<.5 else 1/rand(1, val)x = rgb_to_hsv(np.array(image)/255.)x[..., 0] += huex[..., 0][x[..., 0]>1] -= 1x[..., 0][x[..., 0]<0] += 1x[..., 1] *= satx[..., 2] *= valx[x>1] = 1x[x<0] = 0image = hsv_to_rgb(x)image = Image.fromarray((image*255).astype(np.uint8))# 將圖片進(jìn)行放置,分別對(duì)應(yīng)四張分割圖片的位置dx = place_x[index]dy = place_y[index]new_image = Image.new('RGB', (w,h), (128,128,128))new_image.paste(image, (dx, dy))image_data = np.array(new_image)/255# Image.fromarray((image_data*255).astype(np.uint8)).save(str(index)+"distort.jpg")index = index + 1box_data = []# 對(duì)box進(jìn)行重新處理if len(box)>0:np.random.shuffle(box)box[:, [0,2]] = box[:, [0,2]]*nw/iw + dxbox[:, [1,3]] = box[:, [1,3]]*nh/ih + dybox[:, 0:2][box[:, 0:2]<0] = 0box[:, 2][box[:, 2]>w] = wbox[:, 3][box[:, 3]>h] = hbox_w = box[:, 2] - box[:, 0]box_h = box[:, 3] - box[:, 1]box = box[np.logical_and(box_w>1, box_h>1)]box_data = np.zeros((len(box),5))box_data[:len(box)] = boximage_datas.append(image_data)box_datas.append(box_data)img = Image.fromarray((image_data*255).astype(np.uint8))for j in range(len(box_data)):thickness = 3left, top, right, bottom = box_data[j][0:4]draw = ImageDraw.Draw(img)for i in range(thickness):draw.rectangle([left + i, top + i, right - i, bottom - i],outline=(255,255,255))img.show()# 將圖片分割,放在一起cutx = np.random.randint(int(w*min_offset_x), int(w*(1 - min_offset_x)))cuty = np.random.randint(int(h*min_offset_y), int(h*(1 - min_offset_y)))new_image = np.zeros([h,w,3])new_image[:cuty, :cutx, :] = image_datas[0][:cuty, :cutx, :]new_image[cuty:, :cutx, :] = image_datas[1][cuty:, :cutx, :]new_image[cuty:, cutx:, :] = image_datas[2][cuty:, cutx:, :]new_image[:cuty, cutx:, :] = image_datas[3][:cuty, cutx:, :]# 對(duì)框進(jìn)行進(jìn)一步的處理new_boxes = merge_bboxes(box_datas, cutx, cuty)return new_image, new_boxesdef normal_(annotation_line, input_shape):'''random preprocessing for real-time data augmentation'''line = annotation_line.split()image = Image.open(line[0])box = np.array([np.array(list(map(int,box.split(',')))) for box in line[1:]])iw, ih = image.sizeimage = image.transpose(Image.FLIP_LEFT_RIGHT)box[:, [0,2]] = iw - box[:, [2,0]]return image, boxif __name__ == "__main__":with open("2007_train.txt") as f:lines = f.readlines()a = np.random.randint(0,len(lines))# index = 0# line_all = lines[a:a+4]# for line in line_all:# image_data, box_data = normal_(line,[416,416])# img = image_data# for j in range(len(box_data)):# thickness = 3# left, top, right, bottom = box_data[j][0:4]# draw = ImageDraw.Draw(img)# for i in range(thickness):# draw.rectangle([left + i, top + i, right - i, bottom - i],outline=(255,255,255))# img.show()# # img.save(str(index)+"box.jpg")# index = index+1line = lines[a:a+4]image_data, box_data = get_random_data(line,[416,416])img = Image.fromarray((image_data*255).astype(np.uint8))for j in range(len(box_data)):thickness = 3left, top, right, bottom = box_data[j][0:4]draw = ImageDraw.Draw(img)for i in range(thickness):draw.rectangle([left + i, top + i, right - i, bottom - i],outline=(255,255,255))img.show()# img.save("box_all.jpg")
三、CutMix數(shù)據(jù)增強(qiáng)
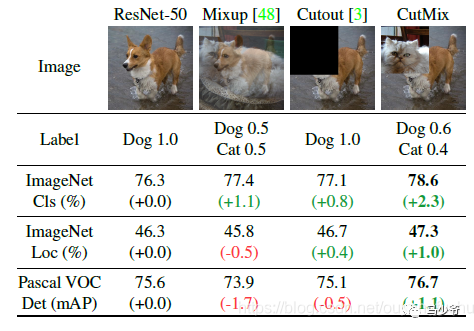
之前有一篇博客學(xué)習(xí)了mixup數(shù)據(jù)增強(qiáng),對(duì)于提升模型的性能非常顯著。長(zhǎng)江后浪推前浪,這一篇CutMix數(shù)據(jù)增強(qiáng)居然將其推在沙灘上。簡(jiǎn)單回顧下mixup數(shù)據(jù)增強(qiáng):從訓(xùn)練樣本中隨機(jī)抽取兩個(gè)樣本進(jìn)行簡(jiǎn)單的隨機(jī)加權(quán)求和,同時(shí)樣本的標(biāo)簽也對(duì)應(yīng)加權(quán)求和,然后預(yù)測(cè)結(jié)果與加權(quán)求和之后的標(biāo)簽求損失,在反向求導(dǎo)更新參數(shù)。
CutMix的處理方式也比較簡(jiǎn)單,同樣也是對(duì)一對(duì)圖片做操作,簡(jiǎn)單講就是隨機(jī)生成一個(gè)裁剪框Box,裁剪掉A圖的相應(yīng)位置,然后用B圖片相應(yīng)位置的ROI放到A圖中被裁剪的區(qū)域形成新的樣本,計(jì)算損失時(shí)同樣采用加權(quán)求和的方式進(jìn)行求解,最后作者對(duì)比了mixup、cutout和baseline,數(shù)據(jù)上看似乎也是小小地吊打的節(jié)奏。
為什么會(huì)這樣呢,論文的意思我姑且這樣描述,mixup是直接求和兩張圖,如同附身,鬼影一樣,模型很難學(xué)到準(zhǔn)確的特征圖響應(yīng)分布。而cutmix相當(dāng)于換某個(gè)零件,模型更容易區(qū)分異類。
算法的核心過(guò)程在論文中這樣描述:
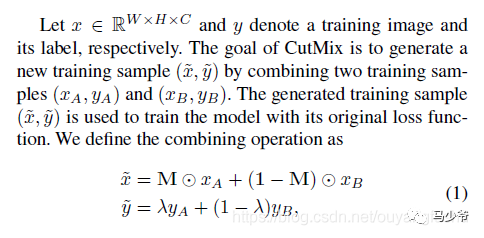
M是一個(gè)與圖像尺寸一致的由0和1標(biāo)記的掩碼矩陣,實(shí)際就是標(biāo)記需要裁剪的區(qū)域和保留的區(qū)域,裁剪的區(qū)域值均為0,其余位置為1,圖像A和B組合得到新樣本,最后兩個(gè)圖的標(biāo)簽也對(duì)應(yīng)求加權(quán)和(其實(shí)這個(gè)公式想要表達(dá)的是再求接損失時(shí),二者的loss求加權(quán)和,這樣說(shuō)更準(zhǔn)確)。那么問(wèn)題來(lái)了這個(gè)裁剪區(qū)域的box是如何得到,加權(quán)的系數(shù)如何確定?
權(quán)值同mixup一樣是采用bata分布隨機(jī)得到,alpha的值為論文中取值為1,這樣加權(quán)系數(shù)[0-1]就服從beta分布,實(shí)際上從論文的代碼實(shí)現(xiàn)上看,beta分布真正的用途是為了生成裁剪區(qū)域。論文這樣描述:
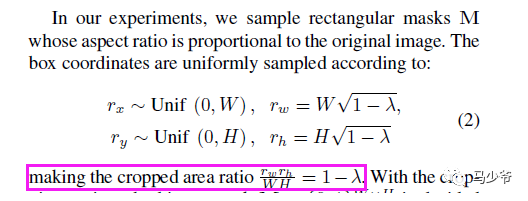
裁剪框box的左上角坐標(biāo)采集服從寬高(W和H)的均勻分布,及隨其采點(diǎn),box的寬高計(jì)算則需要用到beta分布產(chǎn)生的加權(quán)系數(shù)納悶噠(懶得打公式了),這樣裁剪區(qū)box的面積與圖像面積之比為1-納悶噠。這樣損失的加權(quán)和(公式(1))說(shuō)采用的納悶噠就與面積比相對(duì)應(yīng)。這里我對(duì)代碼進(jìn)行了簡(jiǎn)答整理,以便更好地嵌入自己的框架:
def rand_bbox(size, lam):W = size[2]H = size[3]cut_rat = np.sqrt(1. - lam)cut_w = np.int(W * cut_rat)cut_h = np.int(H * cut_rat) # uniformcx = np.random.randint(W)cy = np.random.randint(H)bbx1 = np.clip(cx - cut_w // 2, 0, W)bby1 = np.clip(cy - cut_h // 2, 0, H)bbx2 = np.clip(cx + cut_w // 2, 0, W)bby2 = np.clip(cy + cut_h // 2, 0, H)return bbx1, bby1, bbx2, bby2def cutmix_data(x, y, alpha=1., use_cuda=True):if alpha > 0.:lam = np.random.beta(alpha, alpha)else:lam = 1.batch_size = x.size()[0]if use_cuda:index = torch.randperm(batch_size).cuda()else:index = torch.randperm(batch_size)size=x.size()bbx1, bby1, bbx2, bby2=rand_bbox(size,lam)x[:, :, bbx1:bbx2, bby1:bby2] = x[index, :, bbx1:bbx2, bby1:bby2] # adjust lambda to exactly match pixel ratiolam = 1 - ((bbx2 - bbx1) * (bby2 - bby1) / (x.size()[-1] *x.size()[-2]))y_a, y_b = y, y[index]return x, y_a, y_b, lam嚴(yán)格的講,生成的box可能超出圖像邊界而被裁減,所以再代碼中最終的加權(quán)系數(shù)重新計(jì)算了一下:
lam = 1 - ((bbx2 - bbx1) * (bby2 - bby1) / (x.size()[-1] *x.size()[-2]))訓(xùn)練過(guò)程完整的使用代碼如下:
if mixType=='mixup': inputs, targets_a, targets_b, lam = mixup_data(inputs, targets, args.alpha, use_cuda)elif mixType=='cutmix': inputs, targets_a, targets_b, lam = cutmix_data(inputs, targets, args.alpha, use_cuda) optimizer.zero_grad()inputs, targets_a, targets_b = Variable(inputs), Variable(targets_a), Variable(targets_b)outputs = net(inputs)loss = criterion(outputs, target_a) * lam + criterion(outputs, target_b) * (1. -lam)
我在最近工作中的私有數(shù)據(jù)集中進(jìn)行了試驗(yàn),同樣的數(shù)據(jù),其他參數(shù)一致,僅僅更換mixup為cutmix,模型性能確有提升。對(duì)于困難樣本的效果有很好的提升。同時(shí)心中有一個(gè)疑問(wèn),如果在mini-batch中隨機(jī)采樣中,樣本對(duì)組合新數(shù)據(jù)時(shí),圖像A和B在裁剪區(qū)域均為背景區(qū)域,且背景區(qū)域幾乎相似,而非目標(biāo)所在區(qū)域,這樣訓(xùn)練強(qiáng)制模型擬合,是否合理,還是會(huì)引入噪聲樣?
參考鏈接:
https://blog.csdn.net/weixin_44791964/article/details/105996954
https://blog.csdn.net/ouyangfushu/article/details/105575258
—版權(quán)聲明—
僅用于學(xué)術(shù)分享,版權(quán)屬于原作者。
若有侵權(quán),請(qǐng)聯(lián)系微信號(hào):yiyang-sy 刪除或修改!