學(xué)會 CompletableFuture:讓你的代碼免受阻塞之苦!
 來源:juejin.cn/post/6844904024332828685
來源:juejin.cn/post/6844904024332828685
?? 歡迎加入小哈的星球 ,你將獲得: 專屬的項目實戰(zhàn)/ Java 學(xué)習(xí)路線 / 一對一提問 / 學(xué)習(xí)打卡/贈書福利
目前, 正在星球內(nèi)部帶小伙伴做第一個項目:全棧前后端分離博客,手摸手,后端 + 前端全棧開發(fā),從 0 到 1 講解每個功能點開發(fā)步驟,1v1 答疑,直到項目上線。目前已更新了135小節(jié),累計20w+字,講解圖:886張,還在持續(xù)爆肝中.. 后續(xù)還會上新更多項目,目標(biāo)是將Java領(lǐng)域典型的項目都整一波,如秒殺系統(tǒng), 在線商城, IM即時通訊,Spring Cloud Alibaba 等等,戳我加入學(xué)習(xí),已有420+小伙伴加入(早鳥價超低)
-
寫在前面 -
場景說明 -
CompletableFuture使用 -
同步方法Pick異步方法查詢所有店鋪某個商品價格 -
為什么仍需要CompletableFuture -
其他API介紹 -
CompletableFuture的應(yīng)用場景 -
優(yōu)化空間
寫在前面
通過閱讀本篇文章你將了解到:
-
CompletableFuture的使用 -
CompletableFure異步和同步的性能測試 -
已經(jīng)有了Future為什么仍需要在JDK1.8中引入CompletableFuture -
CompletableFuture的應(yīng)用場景 -
對CompletableFuture的使用優(yōu)化
場景說明
查詢所有商店某個商品的價格并返回,并且查詢商店某個商品的價格的API為同步 一個Shop類,提供一個名為getPrice的同步方法
-
店鋪類:Shop.java
public class Shop {
private Random random = new Random();
/**
* 根據(jù)產(chǎn)品名查找價格
* */
public double getPrice(String product) {
return calculatePrice(product);
}
/**
* 計算價格
*
* @param product
* @return
* */
private double calculatePrice(String product) {
delay();
//random.nextDouble()隨機返回折扣
return random.nextDouble() * product.charAt(0) + product.charAt(1);
}
/**
* 通過睡眠模擬其他耗時操作
* */
private void delay() {
try {
Thread.sleep(1000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
查詢商品的價格為同步方法,并通過sleep方法模擬其他操作。這個場景模擬了當(dāng)需要調(diào)用第三方API,但第三方提供的是同步API,在無法修改第三方API時如何設(shè)計代碼調(diào)用提高應(yīng)用的性能和吞吐量,這時候可以使用CompletableFuture類
CompletableFuture使用
Completable是Future接口的實現(xiàn)類,在JDK1.8中引入
-
CompletableFuture的創(chuàng)建:
說明:
CompletableFuture<Double> futurePrice = new CompletableFuture<>();public static <U> CompletableFuture<U> completedFuture(U value) {
return new CompletableFuture<U>((value == null) ? NIL : value);
}參數(shù)的值為任務(wù)執(zhí)行完的結(jié)果,一般該方法在實際應(yīng)用中較少應(yīng)用
//方法一
public static <U> CompletableFuture<U> supplyAsync(Supplier<U> supplier) {
return asyncSupplyStage(asyncPool, supplier);
}
//方法二
public static <U> CompletableFuture<U> supplyAsync(Supplier<U> supplier,
Executor executor) {
return asyncSupplyStage(screenExecutor(executor), supplier);
}//方法一
public static CompletableFuture<Void> runAsync(Runnable runnable) {
return asyncRunStage(asyncPool, runnable);
}
//方法二
public static CompletableFuture<Void> runAsync(Runnable runnable, Executor executor) {
return asyncRunStage(screenExecutor(executor), runnable);
} -
-
使用CompletableFuture#runAsync靜態(tài)方法創(chuàng)建 runAsync有兩個重載方法 -
使用 CompletableFuture#supplyAsync靜態(tài)方法創(chuàng)建 supplyAsync有兩個重載方法: -
使用CompletableFuture#completedFuture靜態(tài)方法創(chuàng)建 -
兩個重載方法之間的區(qū)別 => 后者可以傳入自定義Executor,前者是默認的,使用的ForkJoinPool -
supplyAsync和runAsync方法之間的區(qū)別 => 前者有返回值,后者無返回值 -
Supplier是函數(shù)式接口,因此該方法需要傳入該接口的實現(xiàn)類,追蹤源碼會發(fā)現(xiàn)在run方法中會調(diào)用該接口的方法。因此使用該方法創(chuàng)建CompletableFuture對象只需重寫Supplier中的get方法,在get方法中定義任務(wù)即可。又因為函數(shù)式接口可以使用Lambda表達式,和new創(chuàng)建CompletableFuture對象相比代碼會簡潔 不少 -
使用new方法 -
結(jié)果的獲取: 對于結(jié)果的獲取CompltableFuture類提供了四種方式
//方式一
public T get()
//方式二
public T get(long timeout, TimeUnit unit)
//方式三
public T getNow(T valueIfAbsent)
//方式四
public T join()說明:
示例:
-
-
get()和get(long timeout, TimeUnit unit) => 在Future中就已經(jīng)提供了,后者提供超時處理,如果在指定時間內(nèi)未獲取結(jié)果將拋出超時異常 -
getNow => 立即獲取結(jié)果不阻塞,結(jié)果計算已完成將返回結(jié)果或計算過程中的異常,如果未計算完成將返回設(shè)定的valueIfAbsent值 -
join => 方法里不會拋出異常
public class AcquireResultTest {
public static void main(String[] args) throws ExecutionException, InterruptedException {
//getNow方法測試
CompletableFuture<String> cp1 = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {
try {
Thread.sleep(60 * 1000 * 60 );
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
return "hello world";
});
System.out.println(cp1.getNow("hello h2t"));
//join方法測試
CompletableFuture<Integer> cp2 = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync((()-> 1 / 0));
System.out.println(cp2.join());
//get方法測試
CompletableFuture<Integer> cp3 = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync((()-> 1 / 0));
System.out.println(cp3.get());
}
}
說明:
-
第一個執(zhí)行結(jié)果為hello h2t,因為要先睡上1分鐘結(jié)果不能立即獲取 -
join方法獲取結(jié)果方法里不會拋異常,但是執(zhí)行結(jié)果會拋異常,拋出的異常為CompletionException -
get方法獲取結(jié)果方法里將拋出異常,執(zhí)行結(jié)果拋出的異常為ExecutionException -
異常處理: 使用靜態(tài)方法創(chuàng)建的CompletableFuture對象無需顯示處理異常,使用new創(chuàng)建的對象需要調(diào)用completeExceptionally方法設(shè)置捕獲到的異常,舉例說明:
CompletableFuture completableFuture = new CompletableFuture();
new Thread(() -> {
try {
//doSomething,調(diào)用complete方法將其他方法的執(zhí)行結(jié)果記錄在completableFuture對象中
completableFuture.complete(null);
} catch (Exception e) {
//異常處理
completableFuture.completeExceptionally(e);
}
}).start();
同步方法Pick異步方法查詢所有店鋪某個商品價格
店鋪為一個列表:
private static List<Shop> shopList = Arrays.asList(
new Shop("BestPrice"),
new Shop("LetsSaveBig"),
new Shop("MyFavoriteShop"),
new Shop("BuyItAll")
);
同步方法:
private static List<String> findPriceSync(String product) {
return shopList.stream()
.map(shop -> String.format("%s price is %.2f",
shop.getName(), shop.getPrice(product))) //格式轉(zhuǎn)換
.collect(Collectors.toList());
}
異步方法:
private static List<String> findPriceAsync(String product) {
List<CompletableFuture<String>> completableFutureList = shopList.stream()
//轉(zhuǎn)異步執(zhí)行
.map(shop -> CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(
() -> String.format("%s price is %.2f",
shop.getName(), shop.getPrice(product)))) //格式轉(zhuǎn)換
.collect(Collectors.toList());
return completableFutureList.stream()
.map(CompletableFuture::join) //獲取結(jié)果不會拋出異常
.collect(Collectors.toList());
}
性能測試結(jié)果:
Find Price Sync Done in 4141
Find Price Async Done in 1033
異步 執(zhí)行效率提高四倍
為什么仍需要CompletableFuture
在JDK1.8以前,通過調(diào)用線程池的submit方法可以讓任務(wù)以異步的方式運行,該方法會返回一個Future對象,通過調(diào)用get方法獲取異步執(zhí)行的結(jié)果:
private static List<String> findPriceFutureAsync(String product) {
ExecutorService es = Executors.newCachedThreadPool();
List<Future<String>> futureList = shopList.stream().map(shop -> es.submit(() -> String.format("%s price is %.2f",
shop.getName(), shop.getPrice(product)))).collect(Collectors.toList());
return futureList.stream()
.map(f -> {
String result = null;
try {
result = f.get();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (ExecutionException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
return result;
}).collect(Collectors.toList());
}
既生瑜何生亮,為什么仍需要引入CompletableFuture?對于簡單的業(yè)務(wù)場景使用Future完全沒有,但是想將多個異步任務(wù)的計算結(jié)果組合起來,后一個異步任務(wù)的計算結(jié)果需要前一個異步任務(wù)的值等等,使用Future提供的那點API就囊中羞澀,處理起來不夠優(yōu)雅,這時候還是讓CompletableFuture以聲明式 的方式優(yōu)雅的處理這些需求。而且在Future編程中想要拿到Future的值然后拿這個值去做后續(xù)的計算任務(wù),只能通過輪詢的方式去判斷任務(wù)是否完成這樣非常占CPU并且代碼也不優(yōu)雅,用偽代碼表示如下:
while(future.isDone()) {
result = future.get();
doSomrthingWithResult(result);
}
但CompletableFuture提供了API幫助我們實現(xiàn)這樣的需求
其他API介紹
whenComplete計算結(jié)果的處理:
對前面計算結(jié)果進行處理,無法返回新值 提供了三個方法:
//方法一
public CompletableFuture<T> whenComplete(BiConsumer<? super T,? super Throwable> action)
//方法二
public CompletableFuture<T> whenCompleteAsync(BiConsumer<? super T,? super Throwable> action)
//方法三
public CompletableFuture<T> whenCompleteAsync(BiConsumer<? super T,? super Throwable> action, Executor executor)
說明:
-
BiFunction<? super T,? super U,? extends V> fn參數(shù) => 定義對結(jié)果的處理 -
Executor executor參數(shù) => 自定義線程池 -
以async結(jié)尾的方法將會在一個新的線程中執(zhí)行組合操作
示例:
public class WhenCompleteTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
CompletableFuture<String> cf1 = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> "hello");
CompletableFuture<String> cf2 = cf1.whenComplete((v, e) ->
System.out.println(String.format("value:%s, exception:%s", v, e)));
System.out.println(cf2.join());
}
}
thenApply轉(zhuǎn)換:
將前面計算結(jié)果的的CompletableFuture傳遞給thenApply,返回thenApply處理后的結(jié)果。可以認為通過thenApply方法實現(xiàn)CompletableFuture<T>至CompletableFuture<U>的轉(zhuǎn)換。白話一點就是將CompletableFuture的計算結(jié)果作為thenApply方法的參數(shù),返回thenApply方法處理后的結(jié)果 提供了三個方法:
//方法一
public <U> CompletableFuture<U> thenApply(
Function<? super T,? extends U> fn) {
return uniApplyStage(null, fn);
}
//方法二
public <U> CompletableFuture<U> thenApplyAsync(
Function<? super T,? extends U> fn) {
return uniApplyStage(asyncPool, fn);
}
//方法三
public <U> CompletableFuture<U> thenApplyAsync(
Function<? super T,? extends U> fn, Executor executor) {
return uniApplyStage(screenExecutor(executor), fn);
}
說明:
-
Function<? super T,? extends U> fn參數(shù) => 對前一個CompletableFuture 計算結(jié)果的轉(zhuǎn)化操作 -
Executor executor參數(shù) => 自定義線程池 -
以async結(jié)尾的方法將會在一個新的線程中執(zhí)行組合操作 示例:
public class ThenApplyTest {
public static void main(String[] args) throws ExecutionException, InterruptedException {
CompletableFuture<Integer> result = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(ThenApplyTest::randomInteger).thenApply((i) -> i * 8);
System.out.println(result.get());
}
public static Integer randomInteger() {
return 10;
}
}
這里將前一個CompletableFuture計算出來的結(jié)果擴大八倍
thenAccept結(jié)果處理:
thenApply也可以歸類為對結(jié)果的處理,thenAccept和thenApply的區(qū)別就是沒有返回值 提供了三個方法:
//方法一
public CompletableFuture<Void> thenAccept(Consumer<? super T> action) {
return uniAcceptStage(null, action);
}
//方法二
public CompletableFuture<Void> thenAcceptAsync(Consumer<? super T> action) {
return uniAcceptStage(asyncPool, action);
}
//方法三
public CompletableFuture<Void> thenAcceptAsync(Consumer<? super T> action,
Executor executor) {
return uniAcceptStage(screenExecutor(executor), action);
}
說明:
-
Consumer<? super T> action參數(shù) => 對前一個CompletableFuture計算結(jié)果的操作 -
Executor executor參數(shù) => 自定義線程池 -
同理以async結(jié)尾的方法將會在一個新的線程中執(zhí)行組合操作 示例:
public class ThenAcceptTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(ThenAcceptTest::getList).thenAccept(strList -> strList.stream()
.forEach(m -> System.out.println(m)));
}
public static List<String> getList() {
return Arrays.asList("a", "b", "c");
}
}
將前一個CompletableFuture計算出來的結(jié)果打印出來
thenCompose異步結(jié)果流水化:
thenCompose方法可以將兩個異步操作進行流水操作 提供了三個方法:
//方法一
public <U> CompletableFuture<U> thenCompose(
Function<? super T, ? extends CompletionStage<U>> fn) {
return uniComposeStage(null, fn);
}
//方法二
public <U> CompletableFuture<U> thenComposeAsync(
Function<? super T, ? extends CompletionStage<U>> fn) {
return uniComposeStage(asyncPool, fn);
}
//方法三
public <U> CompletableFuture<U> thenComposeAsync(
Function<? super T, ? extends CompletionStage<U>> fn,
Executor executor) {
return uniComposeStage(screenExecutor(executor), fn);
}
說明:
-
Function<? super T, ? extends CompletionStage<U>> fn參數(shù) => 當(dāng)前CompletableFuture計算結(jié)果的執(zhí)行 -
Executor executor參數(shù) => 自定義線程池 -
同理以async結(jié)尾的方法將會在一個新的線程中執(zhí)行組合操作 示例:
public class ThenComposeTest {
public static void main(String[] args) throws ExecutionException, InterruptedException {
CompletableFuture<Integer> result = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(ThenComposeTest::getInteger)
.thenCompose(i -> CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> i * 10));
System.out.println(result.get());
}
private static int getInteger() {
return 666;
}
private static int expandValue(int num) {
return num * 10;
}
}
執(zhí)行流程圖:
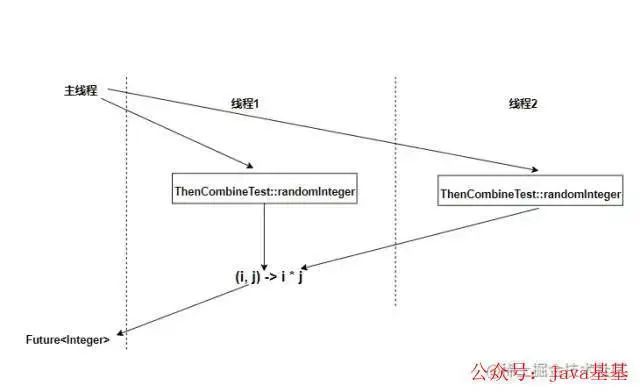
thenCombine組合結(jié)果:
thenCombine方法將兩個無關(guān)的CompletableFuture組合起來,第二個Completable并不依賴第一個Completable的結(jié)果 提供了三個方法:
//方法一
public <U,V> CompletableFuture<V> thenCombine(
CompletionStage<? extends U> other,
BiFunction<? super T,? super U,? extends V> fn) {
return biApplyStage(null, other, fn);
}
//方法二
public <U,V> CompletableFuture<V> thenCombineAsync(
CompletionStage<? extends U> other,
BiFunction<? super T,? super U,? extends V> fn) {
return biApplyStage(asyncPool, other, fn);
}
//方法三
public <U,V> CompletableFuture<V> thenCombineAsync(
CompletionStage<? extends U> other,
BiFunction<? super T,? super U,? extends V> fn, Executor executor) {
return biApplyStage(screenExecutor(executor), other, fn);
}
說明:
-
CompletionStage<? extends U> other參數(shù) => 新的CompletableFuture的計算結(jié)果 -
BiFunction<? super T,? super U,? extends V> fn參數(shù) => 定義了兩個CompletableFuture對象完成計算后 如何合并結(jié)果,該參數(shù)是一個函數(shù)式接口,因此可以使用Lambda表達式 -
Executor executor參數(shù) => 自定義線程池 -
同理以async結(jié)尾的方法將會在一個新的線程中執(zhí)行組合操作
示例:
public class ThenCombineTest {
private static Random random = new Random();
public static void main(String[] args) throws ExecutionException, InterruptedException {
CompletableFuture<Integer> result = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(ThenCombineTest::randomInteger).thenCombine(
CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(ThenCombineTest::randomInteger), (i, j) -> i * j
);
System.out.println(result.get());
}
public static Integer randomInteger() {
return random.nextInt(100);
}
}
將兩個線程計算出來的值做一個乘法在返回 執(zhí)行流程圖:

allOf&anyOf組合多個CompletableFuture:
方法介紹:
//allOf
public static CompletableFuture<Void> allOf(CompletableFuture<?>... cfs) {
return andTree(cfs, 0, cfs.length - 1);
}
//anyOf
public static CompletableFuture<Object> anyOf(CompletableFuture<?>... cfs) {
return orTree(cfs, 0, cfs.length - 1);
}
說明:
-
allOf => 所有的CompletableFuture都執(zhí)行完后執(zhí)行計算。 -
anyOf => 任意一個CompletableFuture執(zhí)行完后就會執(zhí)行計算
示例:
-
allOf方法測試
public class AllOfTest {
public static void main(String[] args) throws ExecutionException, InterruptedException {
CompletableFuture<Void> future1 = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {
System.out.println("hello");
return null;
});
CompletableFuture<Void> future2 = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {
System.out.println("world"); return null;
});
CompletableFuture<Void> result = CompletableFuture.allOf(future1, future2);
System.out.println(result.get());
}
}
allOf方法沒有返回值,適合沒有返回值并且需要前面所有任務(wù)執(zhí)行完畢才能執(zhí)行后續(xù)任務(wù)的應(yīng)用場景
-
anyOf方法測試
public class AnyOfTest {
private static Random random = new Random();
public static void main(String[] args) throws ExecutionException, InterruptedException {
CompletableFuture<String> future1 = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {
randomSleep();
System.out.println("hello");
return "hello";});
CompletableFuture<String> future2 = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {
randomSleep();
System.out.println("world");
return "world";
});
CompletableFuture<Object> result = CompletableFuture.anyOf(future1, future2);
System.out.println(result.get());
}
private static void randomSleep() {
try {
Thread.sleep(random.nextInt(10));
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
兩個線程都會將結(jié)果打印出來,但是get方法只會返回最先完成任務(wù)的結(jié)果。該方法比較適合只要有一個返回值就可以繼續(xù)執(zhí)行其他任務(wù)的應(yīng)用場景
注意點
很多方法都提供了異步實現(xiàn)【帶async后綴】,但是需小心謹(jǐn)慎使用這些異步方法,因為異步意味著存在上下文切換,可能性能不一定比同步好。如果需要使用異步的方法,先做測試 ,用測試數(shù)據(jù)說話!!!
CompletableFuture的應(yīng)用場景
存在IO密集型的任務(wù)可以選擇CompletableFuture,IO部分交由另外一個線程去執(zhí)行。Logback、Log4j2異步日志記錄的實現(xiàn)原理就是新起了一個線程去執(zhí)行IO操作,這部分可以以CompletableFuture.runAsync(()->{ioOperation();})的方式去調(diào)用。如果是CPU密集型就不推薦使用了推薦使用并行流
優(yōu)化空間
supplyAsync執(zhí)行任務(wù)底層實現(xiàn):
public static <U> CompletableFuture<U> supplyAsync(Supplier<U> supplier) {
return asyncSupplyStage(asyncPool, supplier);
}
static <U> CompletableFuture<U> asyncSupplyStage(Executor e, Supplier<U> f) {
if (f == null) throw new NullPointerException();
CompletableFuture<U> d = new CompletableFuture<U>();
e.execute(new AsyncSupply<U>(d, f));
return d;
}
底層調(diào)用的是線程池去執(zhí)行任務(wù),而CompletableFuture中默認線程池為ForkJoinPool
private static final Executor asyncPool = useCommonPool ?
ForkJoinPool.commonPool() : new ThreadPerTaskExecutor();
ForkJoinPool線程池的大小取決于CPU的核數(shù)。CPU密集型任務(wù)線程池大小配置為CPU核心數(shù)就可以了,但是IO密集型,線程池的大小由CPU數(shù)量 * CPU利用率 * (1 + 線程等待時間/線程CPU時間) 確定。而CompletableFuture的應(yīng)用場景就是IO密集型任務(wù),因此默認的ForkJoinPool一般無法達到最佳性能,我們需自己根據(jù)業(yè)務(wù)創(chuàng)建線程池。
?? 歡迎加入小哈的星球 ,你將獲得: 專屬的項目實戰(zhàn)/ Java 學(xué)習(xí)路線 / 一對一提問 / 學(xué)習(xí)打卡/贈書福利
目前, 正在星球內(nèi)部帶小伙伴做第一個項目:全棧前后端分離博客,手摸手,后端 + 前端全棧開發(fā),從 0 到 1 講解每個功能點開發(fā)步驟,1v1 答疑,直到項目上線。目前已更新了135小節(jié),累計20w+字,講解圖:886張,還在持續(xù)爆肝中.. 后續(xù)還會上新更多項目,目標(biāo)是將Java領(lǐng)域典型的項目都整一波,如秒殺系統(tǒng), 在線商城, IM即時通訊,Spring Cloud Alibaba 等等,戳我加入學(xué)習(xí),已有420+小伙伴加入(早鳥價超低)

最近面試BAT,整理一份面試資料《Java面試BATJ通關(guān)手冊》,覆蓋了Java核心技術(shù)、JVM、Java并發(fā)、SSM、微服務(wù)、數(shù)據(jù)庫、數(shù)據(jù)結(jié)構(gòu)等等。
獲取方式:點“在看”,關(guān)注公眾號并回復(fù) Java 領(lǐng)取,更多內(nèi)容陸續(xù)奉上。
PS:因公眾號平臺更改了推送規(guī)則,如果不想錯過內(nèi)容,記得讀完點一下“在看”,加個“星標(biāo)”,這樣每次新文章推送才會第一時間出現(xiàn)在你的訂閱列表里。
點“在看”支持小哈呀,謝謝啦
