吹爆了這個(gè)可視化神器,上手后直接開大~
回復(fù)“書籍”即可獲贈(zèng)Python從入門到進(jìn)階共10本電子書
大家好,我是明哥。
今天給大家推薦一個(gè)可視化神器 - Plotly_express ,上手非常的簡單,基本所有的圖都只要一行代碼就能繪出一張非常酷炫的可視化圖。
以下是這個(gè)神器的詳細(xì)使用方法,文中附含大量的 GIF 動(dòng)圖示例圖。
注:源代碼( .ipypnb 文件)的獲取方式,我放在文末了。記得下載
1. 環(huán)境準(zhǔn)備
本文的是在如下環(huán)境下測試完成的。
Python3.7 Jupyter notebook Pandas1.1.3 Plotly_express0.4.1
其中 Plotly_express0.4.1 是本文的主角,安裝它非常簡單,只需要使用 pip install 就可以
$ python3 -m pip install plotly_express
2. 工具概述
在說 plotly_express之前,我們先了解下plotly。Plotly是新一代的可視化神器,由TopQ量化團(tuán)隊(duì)開源。雖然Ploltly功能非常之強(qiáng)大,但是一直沒有得到重視,主要原因還是其設(shè)置過于繁瑣。因此,Plotly推出了其簡化接口:Plotly_express,下文中統(tǒng)一簡稱為px。
px是對(duì)Plotly.py的一種高級(jí)封裝,其內(nèi)置了很多實(shí)用且現(xiàn)代的繪圖模板,用戶只需要調(diào)用簡單的API函數(shù)即可實(shí)用,從而快速繪制出漂亮且動(dòng)態(tài)的可視化圖表。
px是完全免費(fèi)的,用戶可以任意使用它。最重要的是,px和plotly生態(tài)系統(tǒng)的其他部分是完全兼容的。用戶不僅可以在Dash中使用,還能通過Orca將數(shù)據(jù)導(dǎo)出為幾乎任意文件格式。
官網(wǎng)的學(xué)習(xí)資料:https://plotly.com/
px的安裝是非常簡單的,只需要通過pip install plotly_express來安裝即可。安裝之后的使用:
import plotly_express as px
3. 開始繪圖
接下來我們通過px中自帶的數(shù)據(jù)集來繪制各種精美的圖形。
gapminder tips wind
3.1 數(shù)據(jù)集
首先我們看下px中自帶的數(shù)據(jù)集:
import pandas as pd
import numpy as np
import plotly_express as px # 現(xiàn)在這種方式也可行:import plotly.express as px
# 數(shù)據(jù)集
gapminder = px.data.gapminder()
gapminder.head() # 取出前5條數(shù)據(jù)
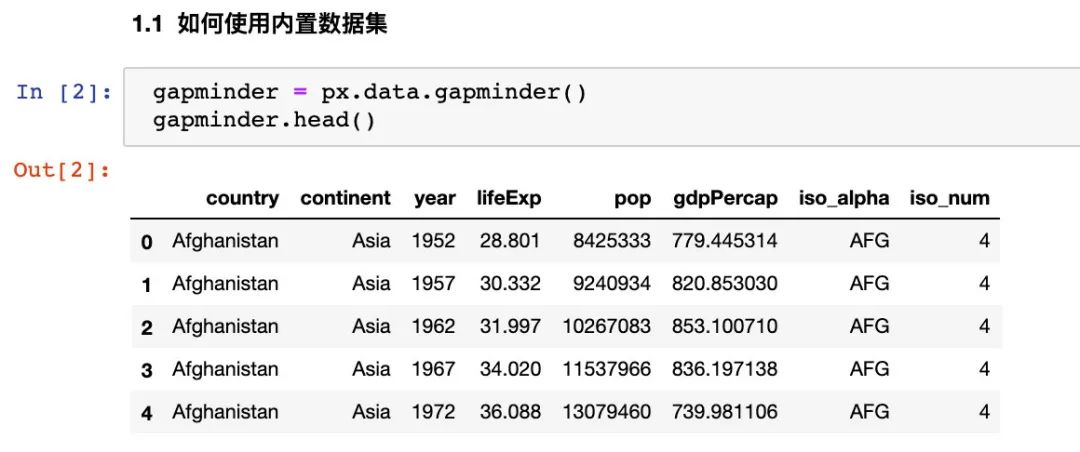
我們看看全部屬性值:

3.2 線型圖
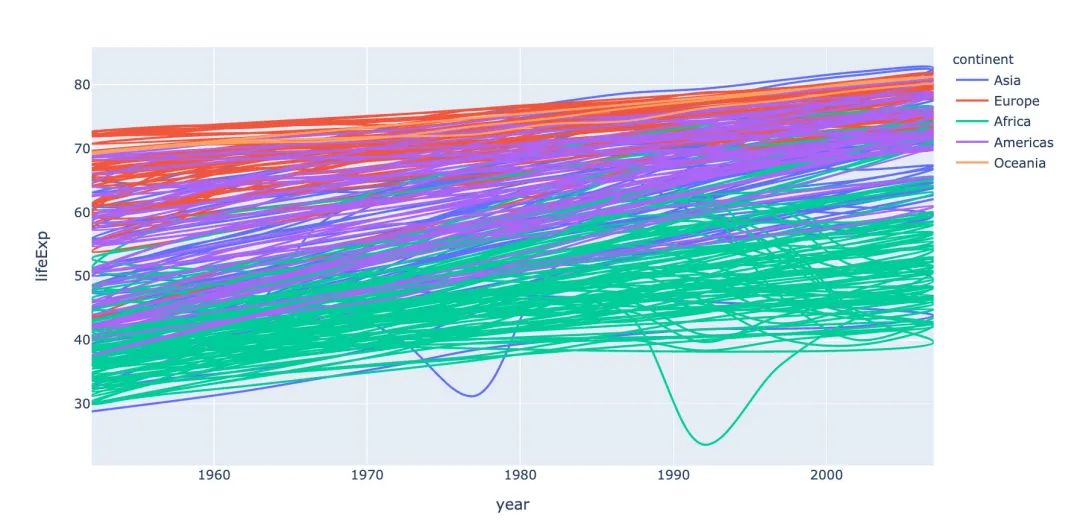
線型圖line在可視化制圖中是很常見的。利用px能夠快速地制作線型圖:
# line 圖
fig = px.line(
gapminder, # 數(shù)據(jù)集
x="year", # 橫坐標(biāo)
y="lifeExp", # 縱坐標(biāo)
color="continent", # 顏色的數(shù)據(jù)
line_group="continent", # 線性分組
hover_name="country", # 懸停hover的數(shù)據(jù)
line_shape="spline", # 線的形狀
render_mode="svg" # 生成的圖片模式
)
fig.show()
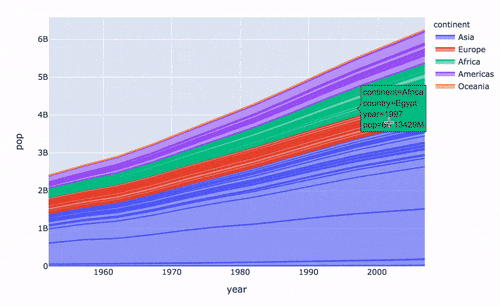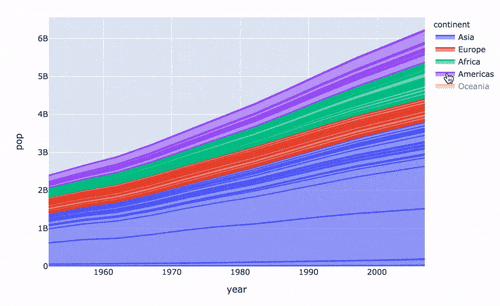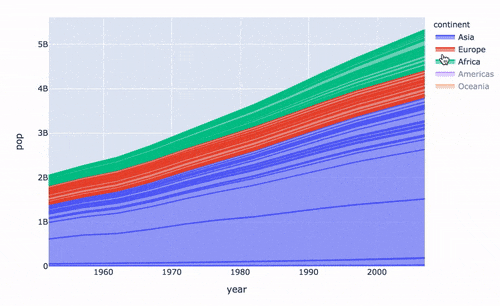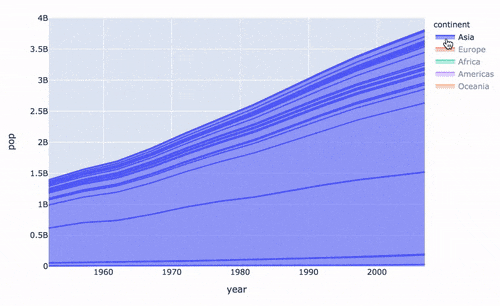
再來制作面積圖:
# area 圖
fig = px.area(
gapminder, # 數(shù)據(jù)集
x="year", # 橫坐標(biāo)
y="pop", # 縱坐標(biāo)
color="continent", # 顏色
line_group="country" # 線性組別
)
fig.show()
3.3 散點(diǎn)圖
散點(diǎn)圖的制作調(diào)用scatter方法:
指定size參數(shù)還能改變每個(gè)點(diǎn)的大小:
px.scatter(
gapminder2007 # 繪圖DataFrame數(shù)據(jù)集
,x="gdpPercap" # 橫坐標(biāo)
,y="lifeExp" # 縱坐標(biāo)
,color="continent" # 區(qū)分顏色
,size="pop" # 區(qū)分圓的大小
,size_max=60 # 散點(diǎn)大小
)
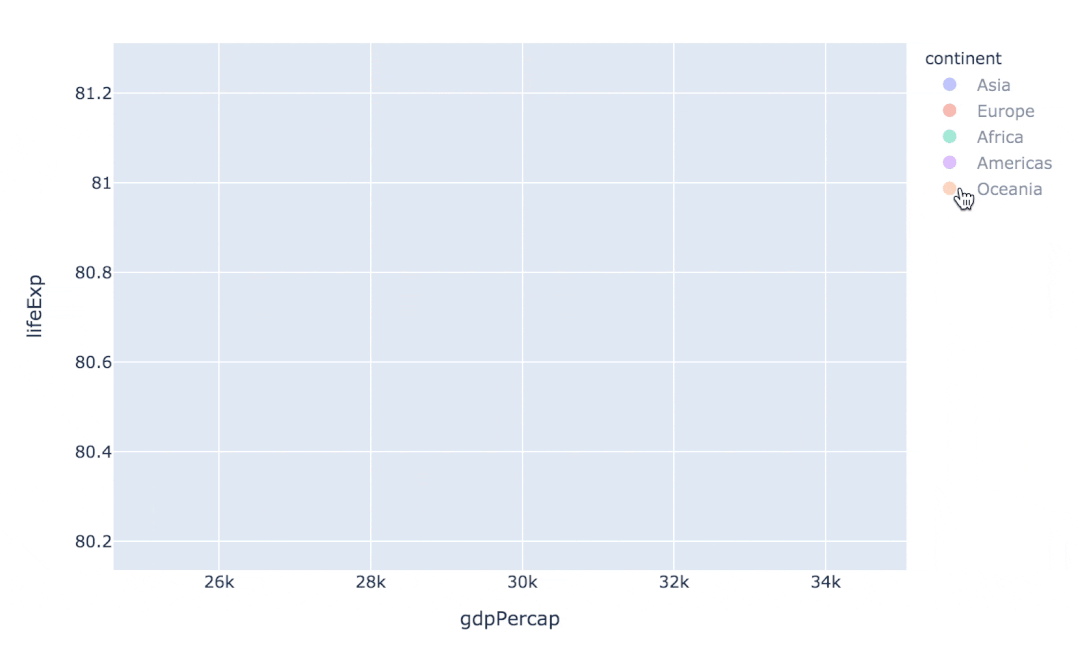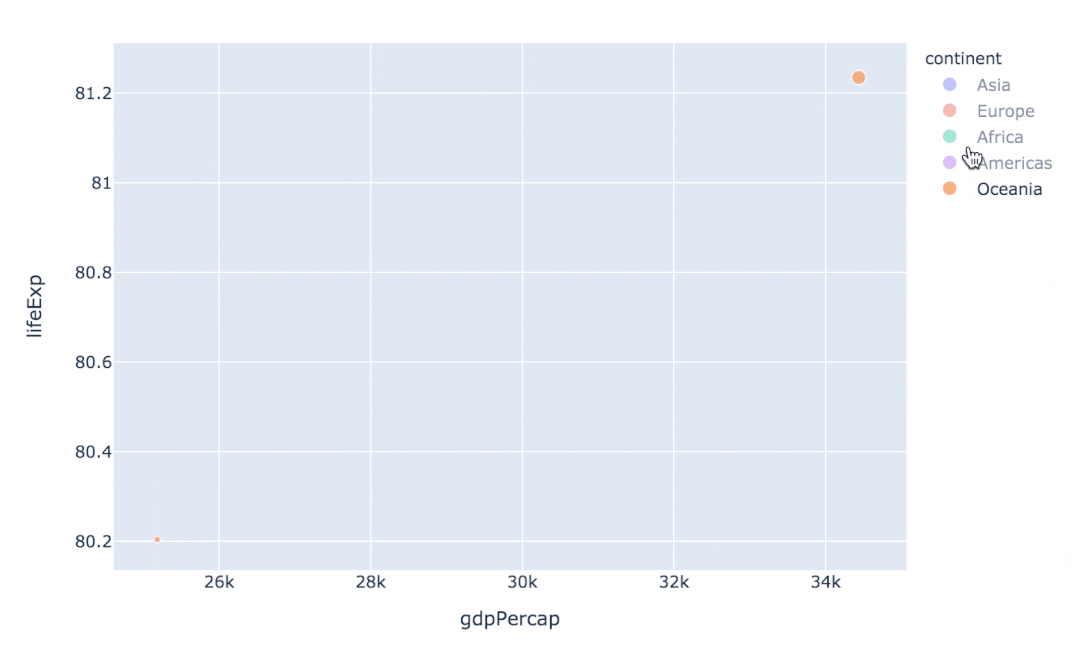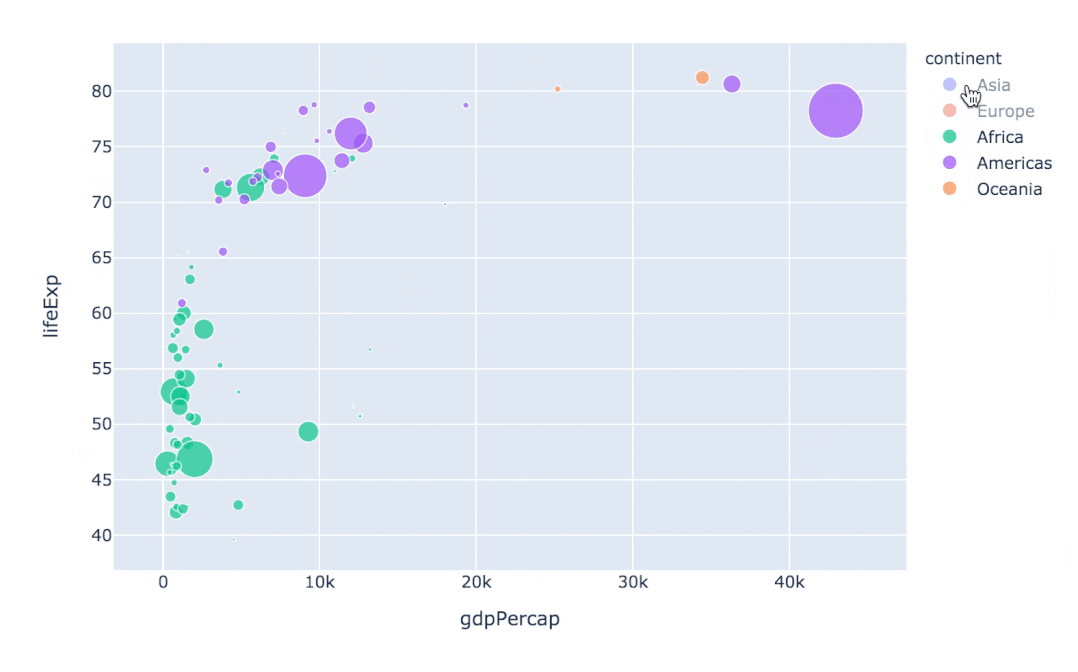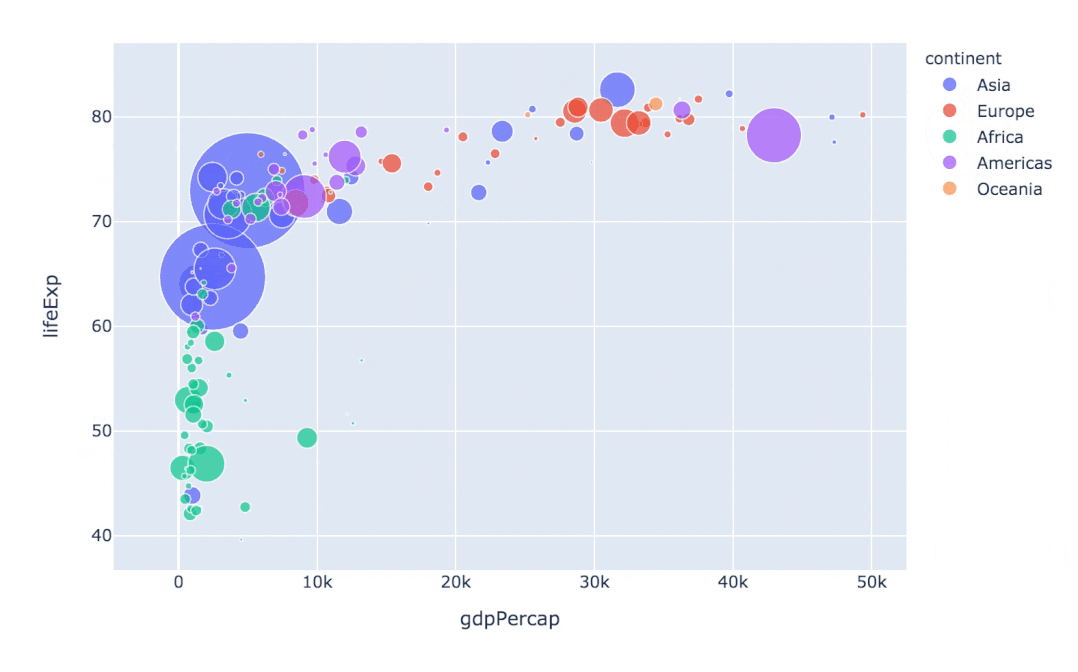
通過指定facet_col、animation_frame參數(shù)還能將散點(diǎn)進(jìn)行分塊顯示:
px.scatter(
gapminder # 繪圖使用的數(shù)據(jù)
,x="gdpPercap" # 橫縱坐標(biāo)使用的數(shù)據(jù)
,y="lifeExp" # 縱坐標(biāo)數(shù)據(jù)
,color="continent" # 區(qū)分顏色的屬性
,size="pop" # 區(qū)分圓的大小
,size_max=60 # 圓的最大值
,hover_name="country" # 圖中可視化最上面的名字
,animation_frame="year" # 橫軸滾動(dòng)欄的屬性year
,animation_group="country" # 標(biāo)注的分組
,facet_col="continent" # 按照國家country屬性進(jìn)行分格顯示
,log_x=True # 橫坐標(biāo)表取對(duì)數(shù)
,range_x=[100,100000] # 橫軸取值范圍
,range_y=[25,90] # 縱軸范圍
,labels=dict(pop="Populations", # 屬性名字的變化,更直觀
gdpPercap="GDP per Capital",
lifeExp="Life Expectancy")
)

3.4 地理數(shù)據(jù)繪圖
在實(shí)際的工作中,我們可能會(huì)接觸到中國地圖甚至是全球地圖,使用px也能制作:
px.choropleth(
gapminder, # 數(shù)據(jù)集
locations="iso_alpha", # 配合顏色color顯示
color="lifeExp", # 顏色的字段選擇
hover_name="country", # 懸停字段名字
animation_frame="year", # 注釋
color_continuous_scale=px.colors.sequential.Plasma, # 顏色變化
projection="natural earth" # 全球地圖
)
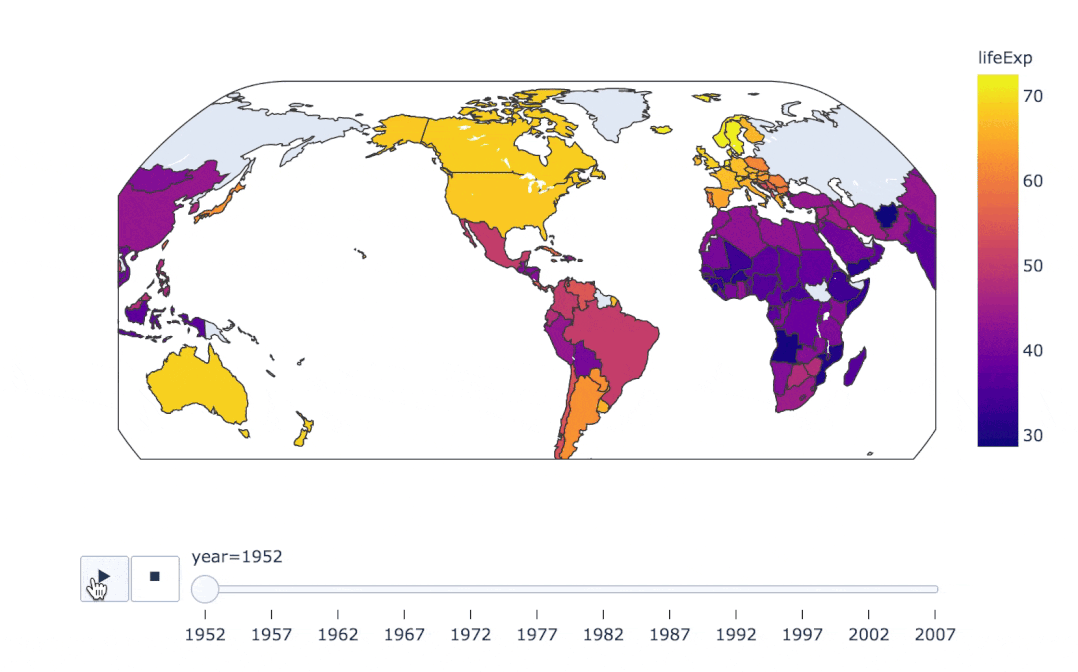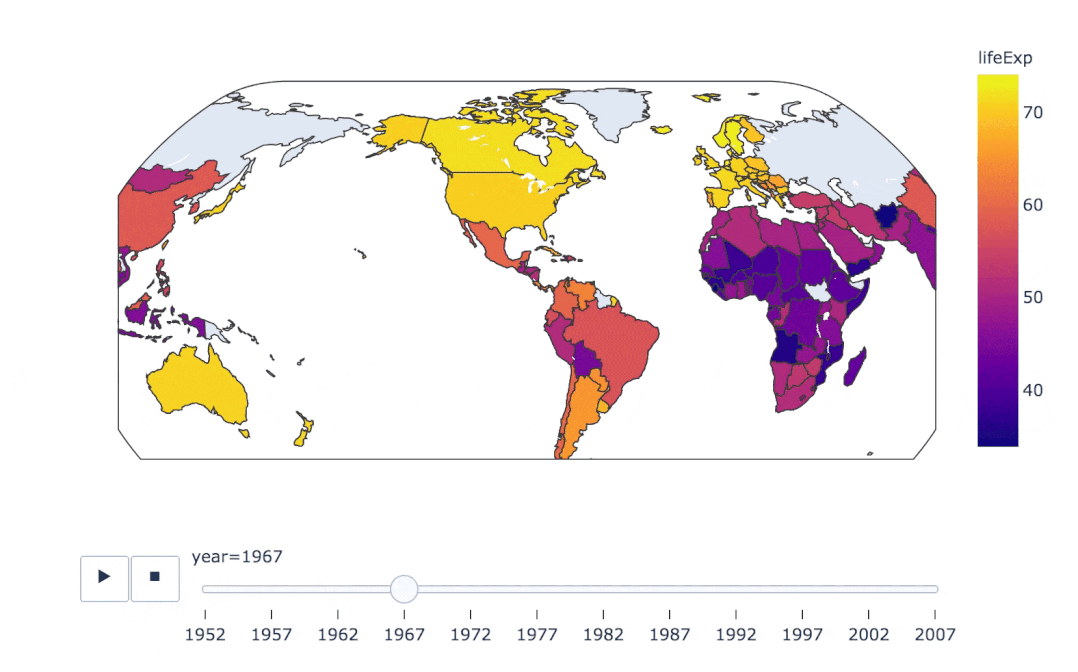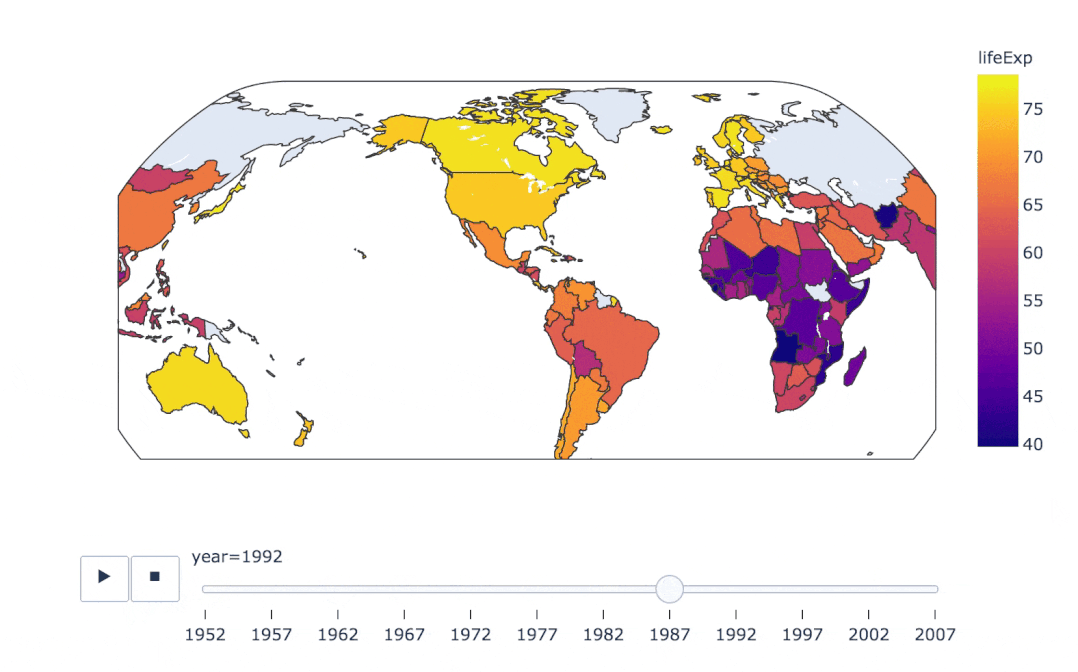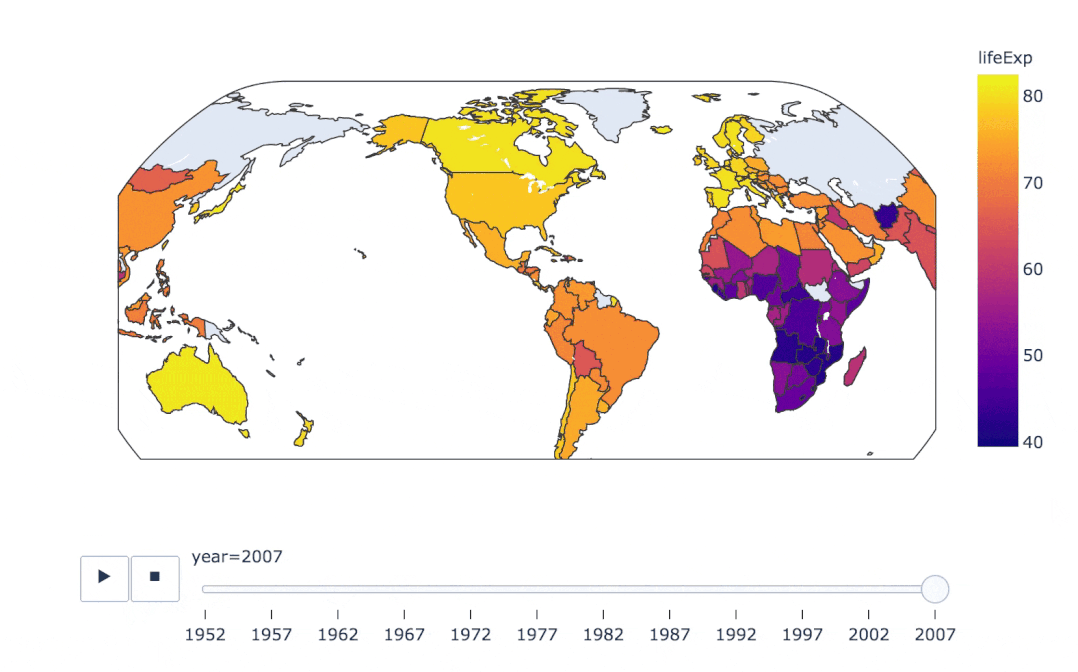
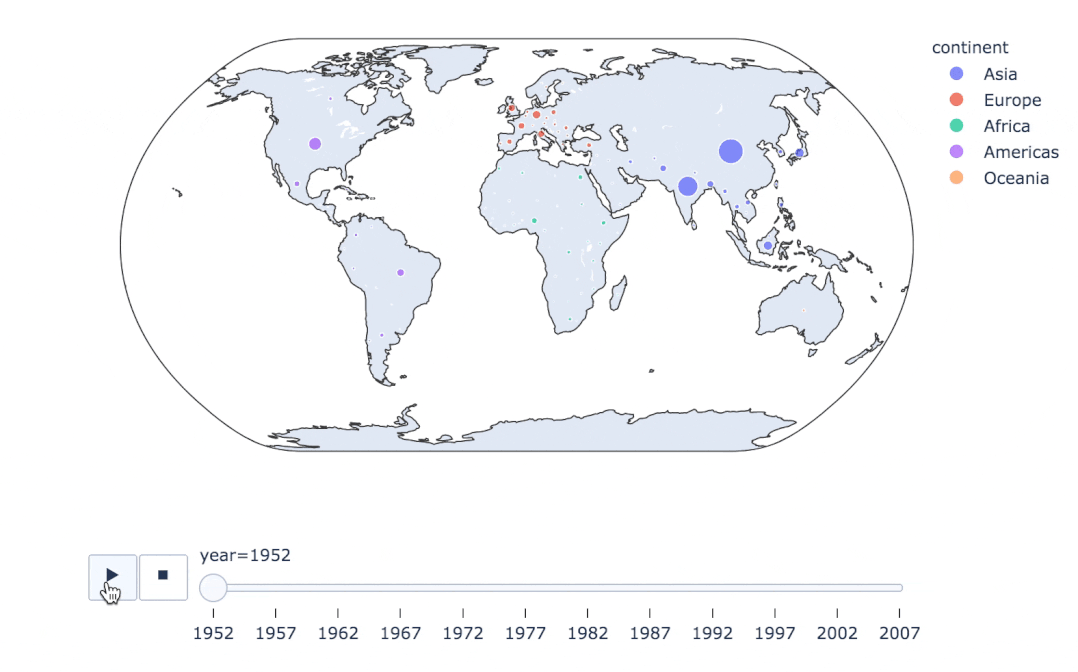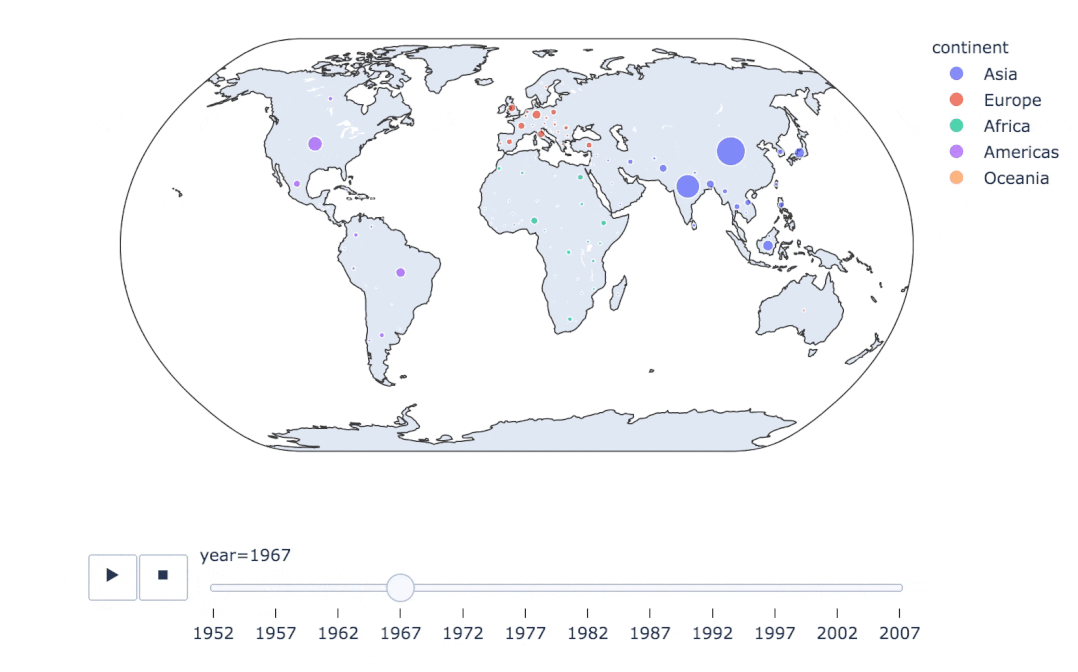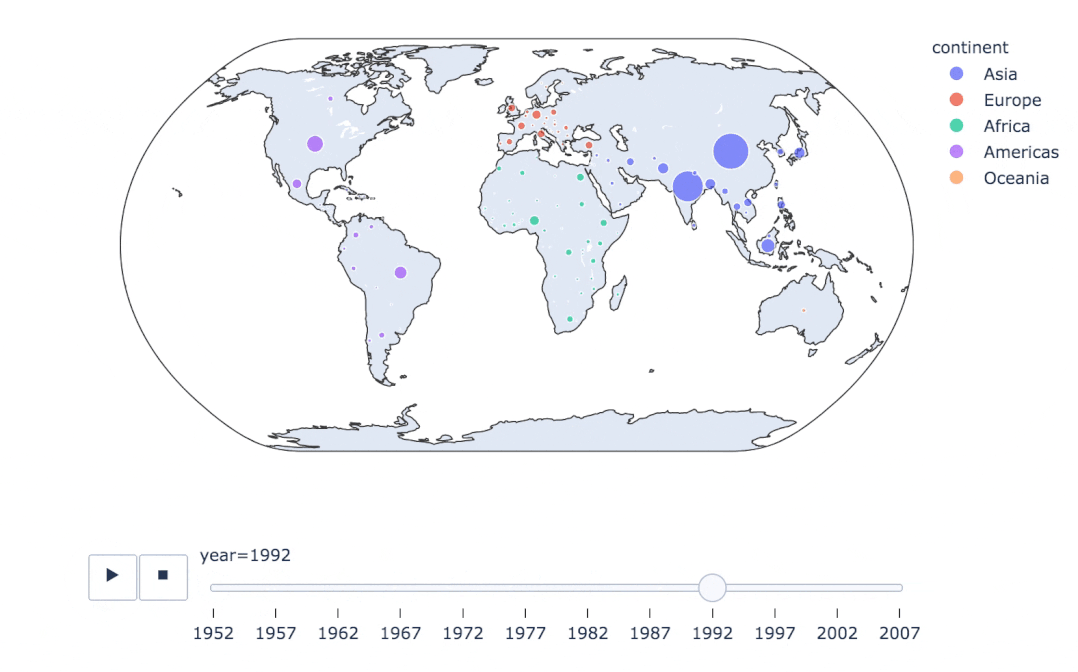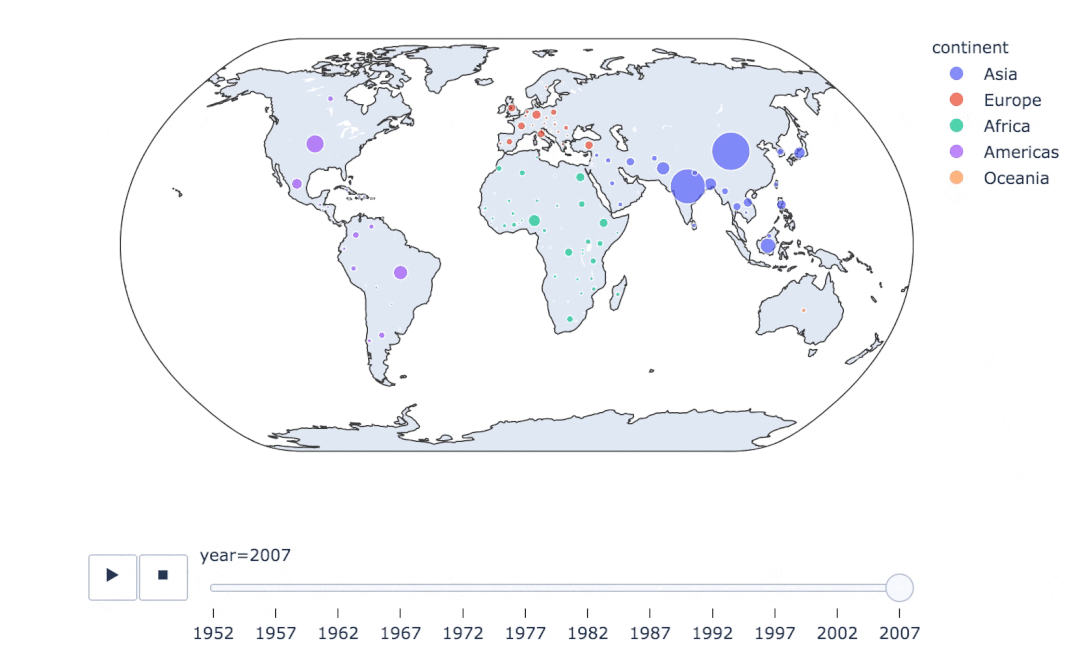
fig = px.scatter_geo(
gapminder, # 數(shù)據(jù)
locations="iso_alpha", # 配合顏色color顯示
color="continent", # 顏色
hover_name="country", # 懸停數(shù)據(jù)
size="pop", # 大小
animation_frame="year", # 數(shù)據(jù)幀的選擇
projection="natural earth" # 全球地圖
)
fig.show()
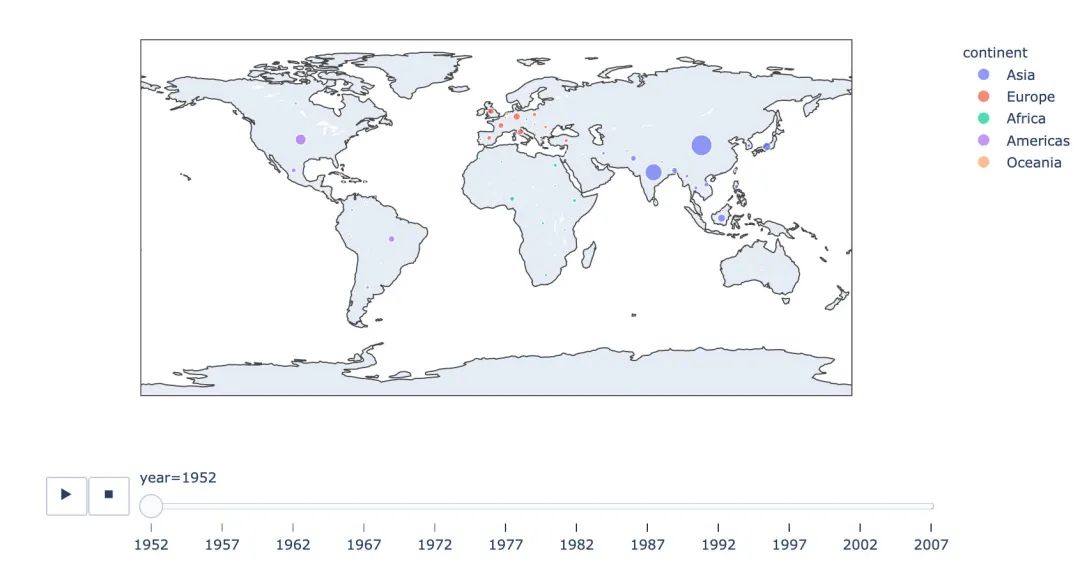
px.scatter_geo(gapminder, # 數(shù)據(jù)集
locations="iso_alpha", # 配和color顯示顏色
color="continent", # 顏色的字段顯示
hover_name="country", # 懸停數(shù)據(jù)
size="pop", # 大小
animation_frame="year" # 數(shù)據(jù)聯(lián)動(dòng)變化的選擇
#,projection="natural earth" # 去掉projection參數(shù)
)
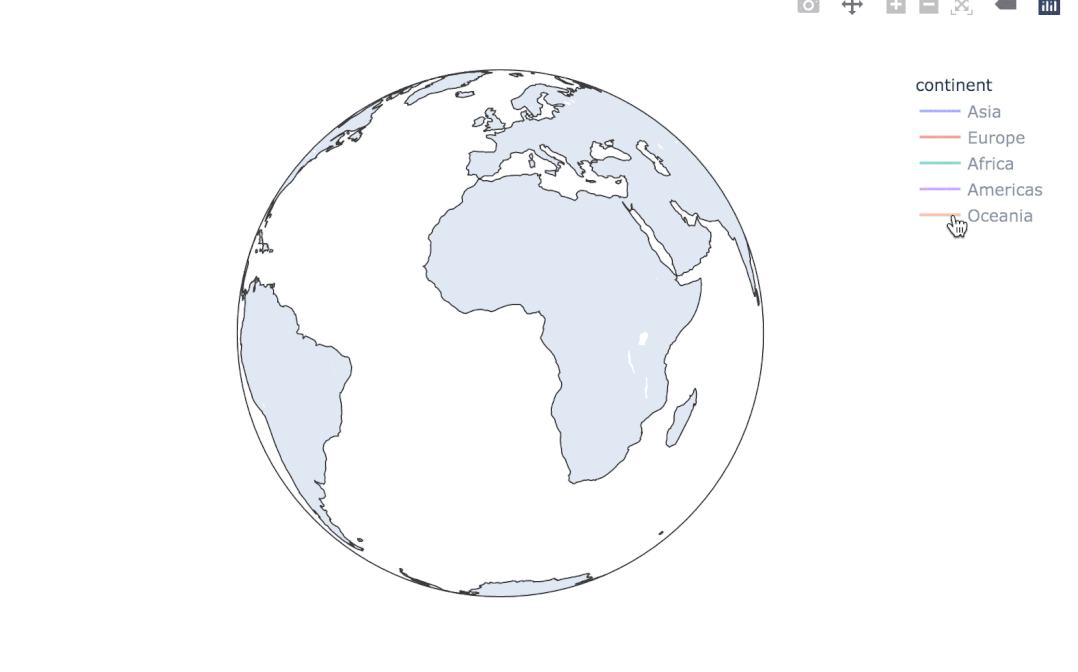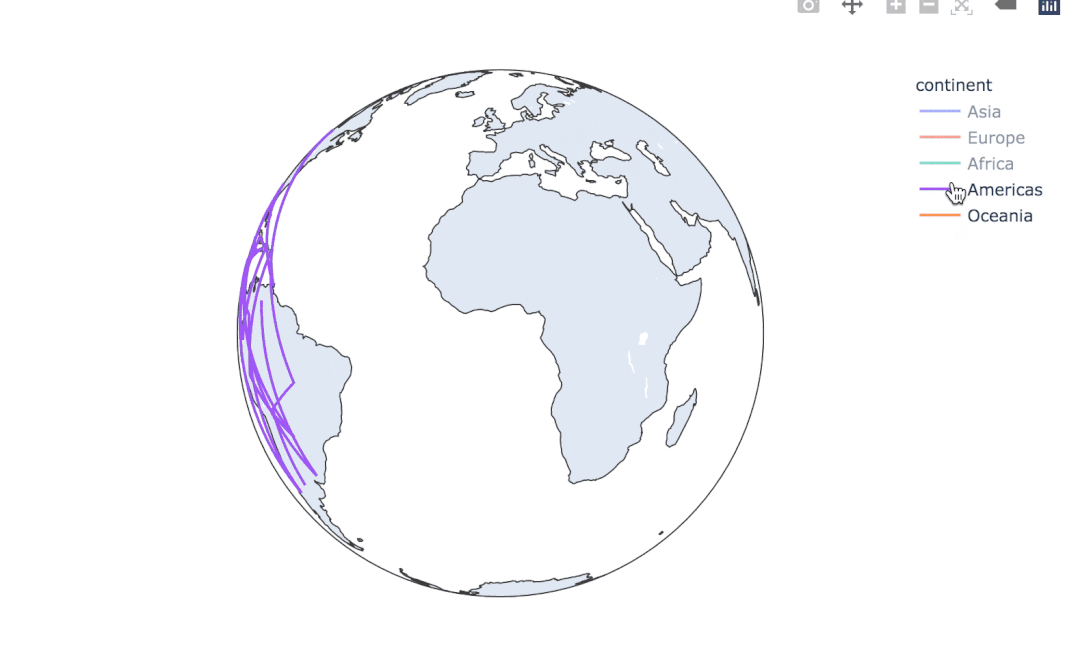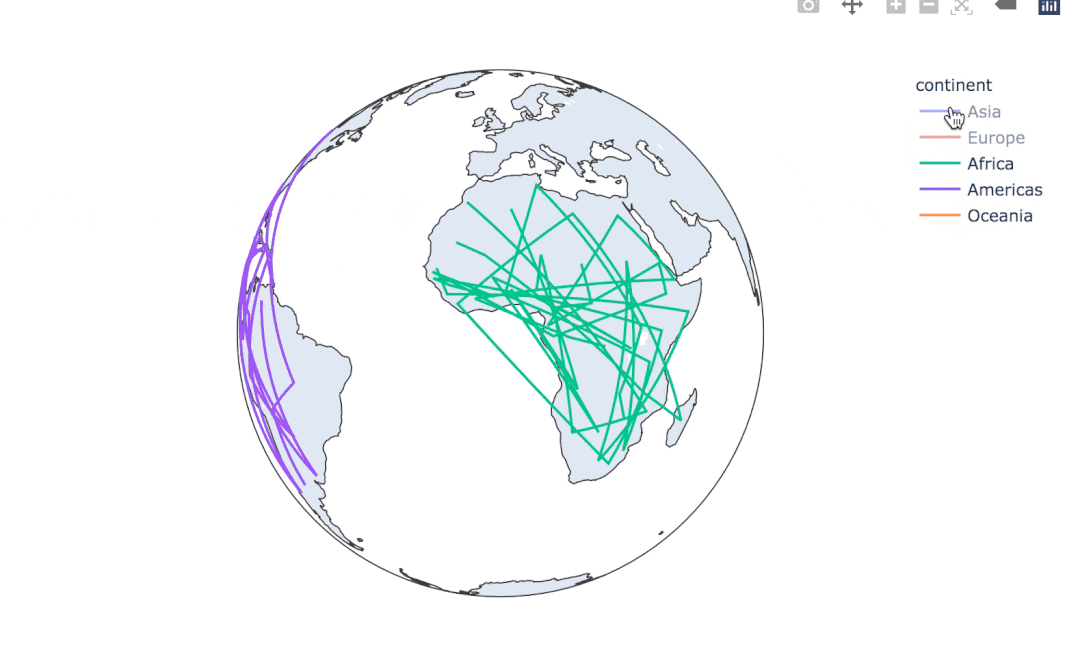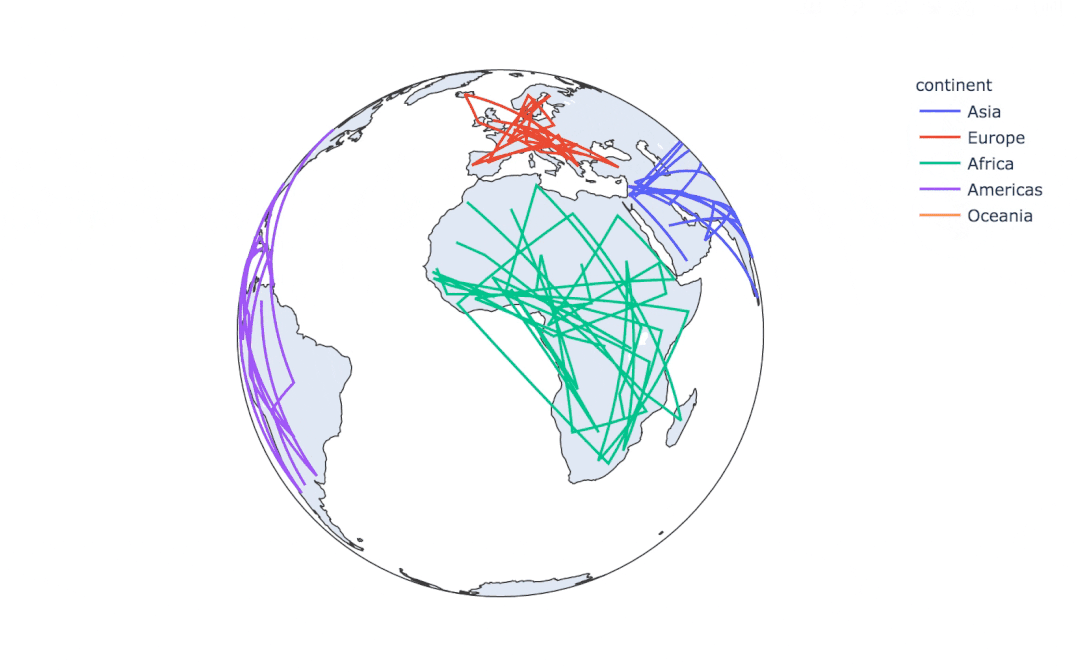
使用line_geo來制圖:
fig = px.line_geo(
gapminder2007, # 數(shù)據(jù)集
locations="iso_alpha", # 配合和color顯示數(shù)據(jù)
color="continent", # 顏色
projection="orthographic") # 球形的地圖
fig.show()
3.5 使用內(nèi)置iris數(shù)據(jù)
我們先看看怎么使用px來查看內(nèi)置數(shù)據(jù)的文檔:
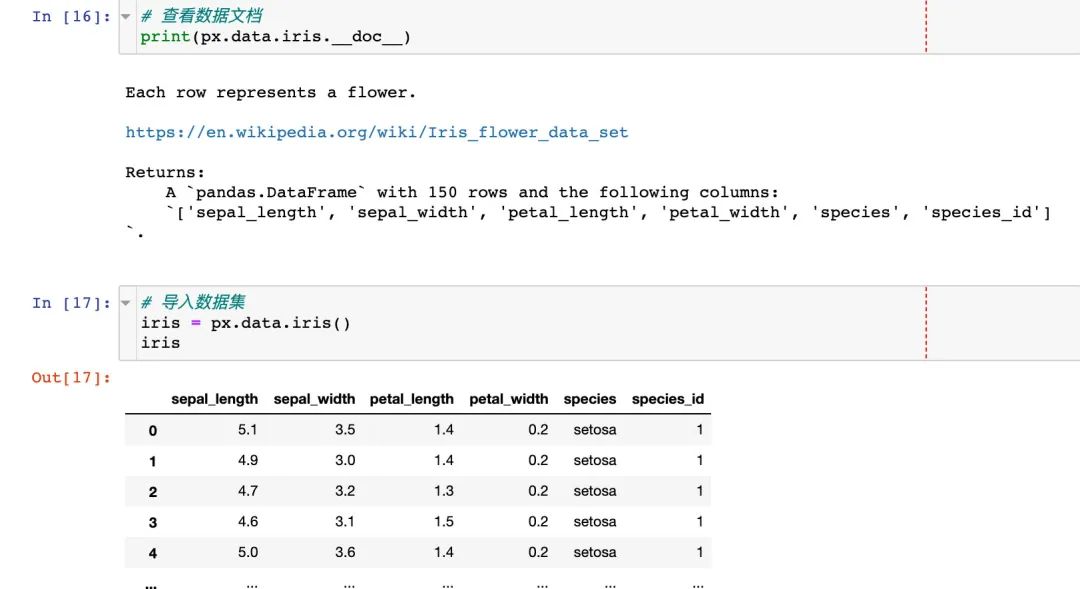
選擇兩個(gè)屬性制圖
選擇兩個(gè)屬性作為橫縱坐標(biāo)來繪制散點(diǎn)圖
fig = px.scatter(
iris, # 數(shù)據(jù)集
x="sepal_width", # 橫坐標(biāo)
y="sepal_length" # 縱坐標(biāo)
)
fig.show()
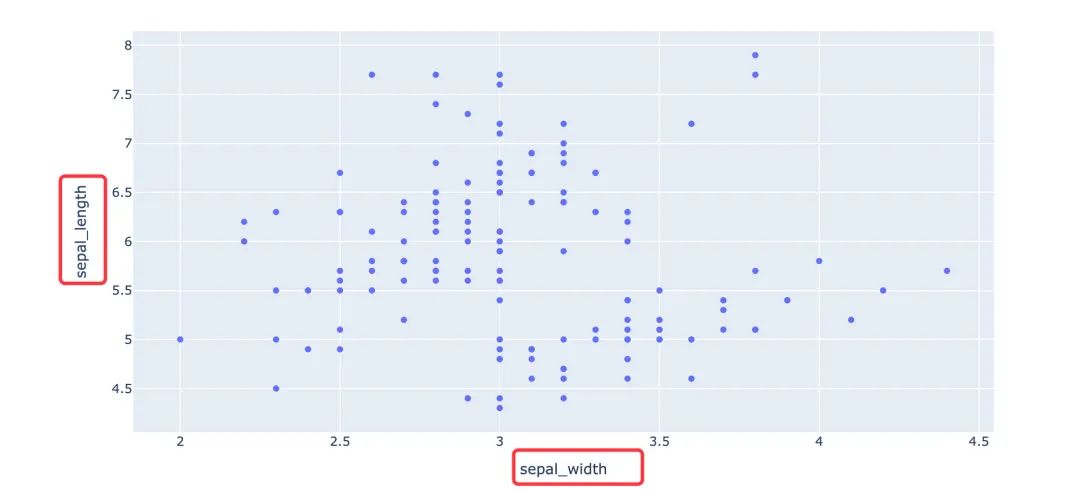
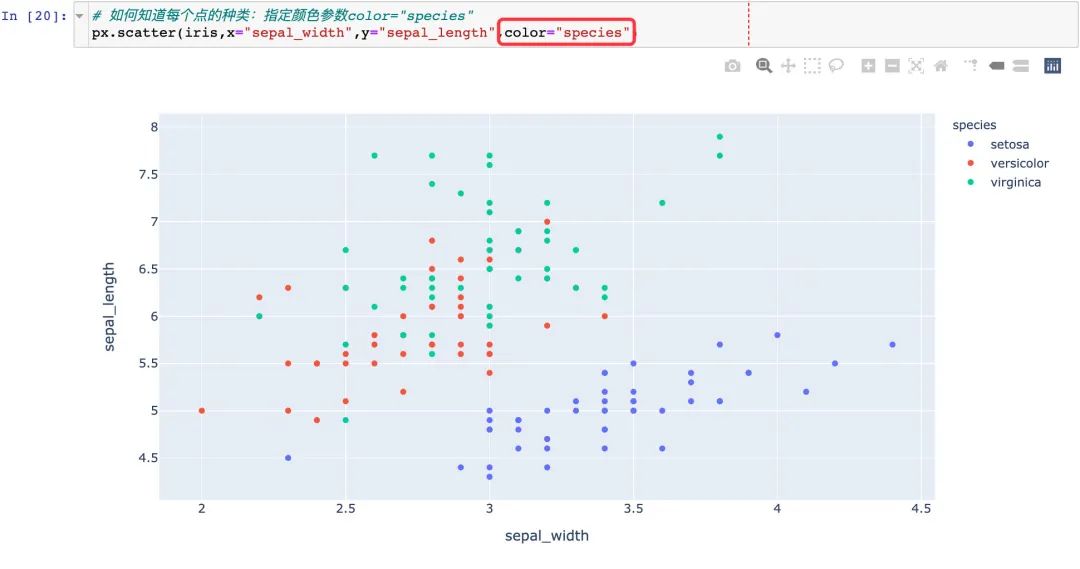
通過color參數(shù)來顯示不同的顏色:
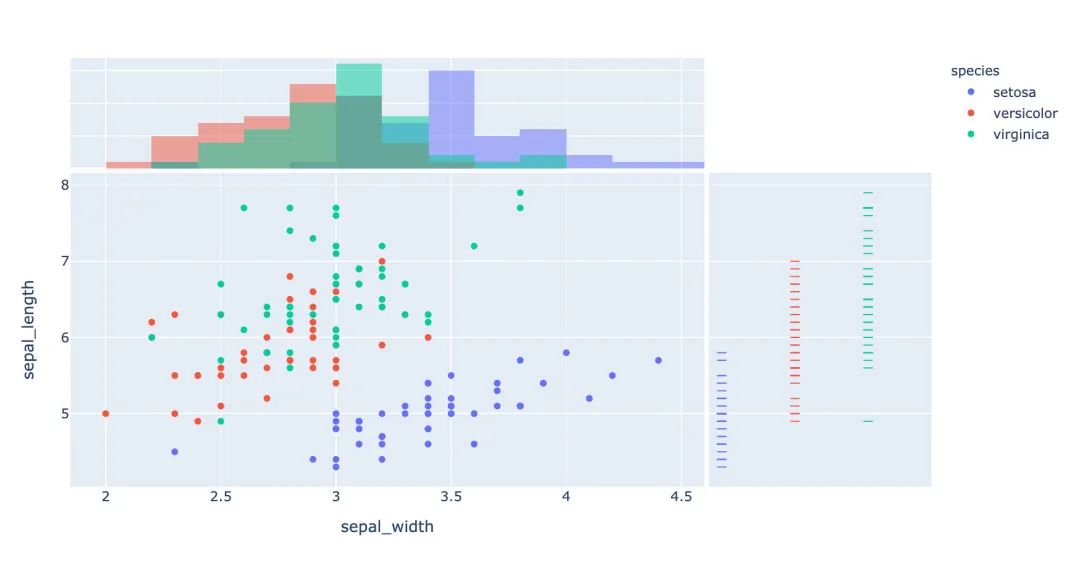
3.6 聯(lián)合分布圖
我們一個(gè)圖形中能夠?qū)⑸Ⅻc(diǎn)圖和直方圖組合在一起顯示:
px.scatter(
iris, # 數(shù)據(jù)集
x="sepal_width", # 橫坐標(biāo)
y="sepal_length", # 縱坐標(biāo)
color="species", # 顏色
marginal_x="histogram", # 橫坐標(biāo)直方圖
marginal_y="rug" # 細(xì)條圖
)
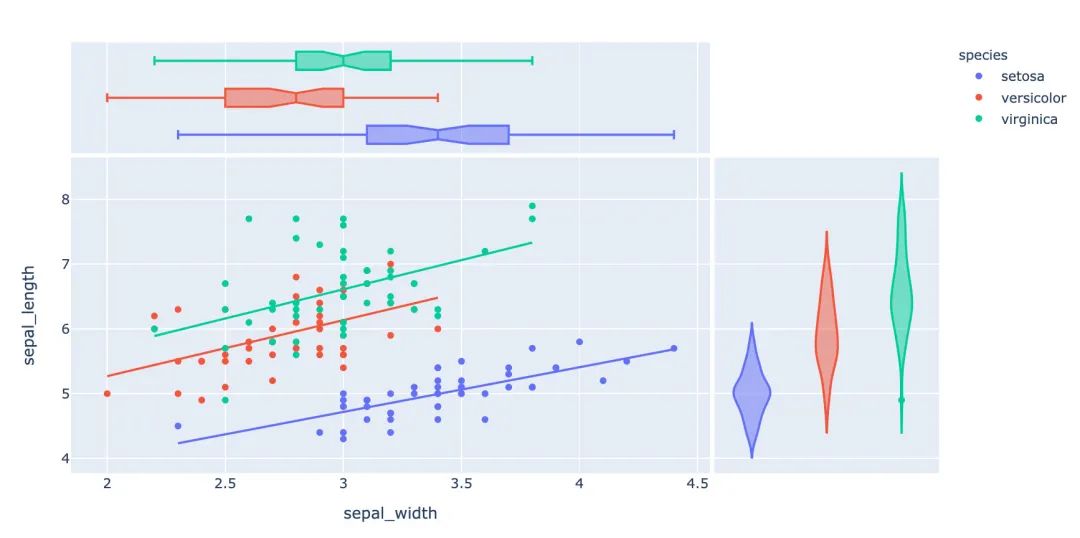
3.7 小提琴圖
小提琴圖能夠很好的顯示數(shù)據(jù)的分布和誤差情況,一行代碼利用也能顯示小提琴圖:
px.scatter(
iris, # 數(shù)據(jù)集
x="sepal_width", # 橫坐標(biāo)
y="sepal_length", # 縱坐標(biāo)
color="species", # 顏色
marginal_y="violin", # 縱坐標(biāo)小提琴圖
marginal_x="box", # 橫坐標(biāo)箱型圖
trendline="ols" # 趨勢線
)
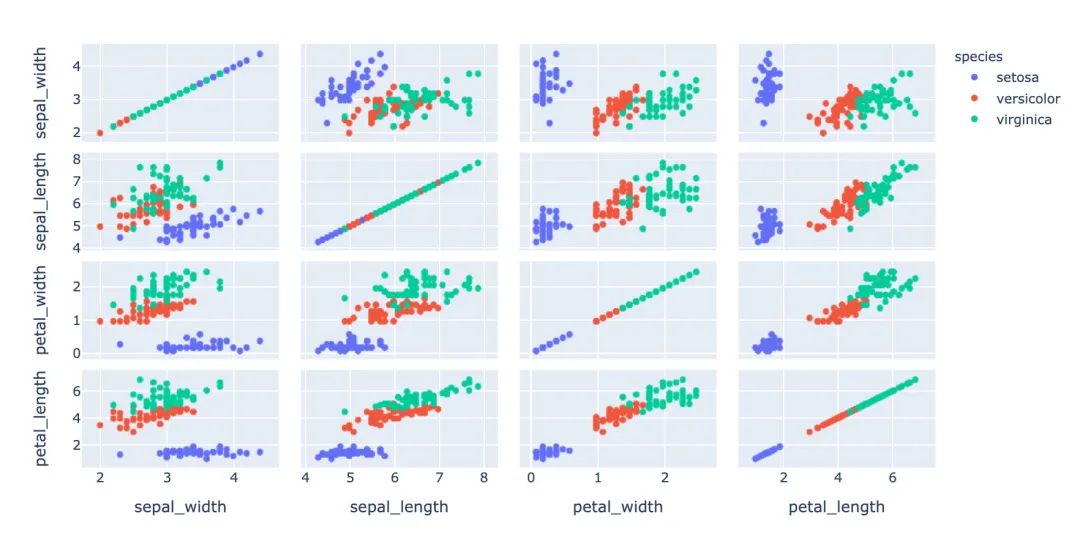
3.8 散點(diǎn)矩陣圖
px.scatter_matrix(
iris, # 數(shù)據(jù)
dimensions=["sepal_width","sepal_length","petal_width","petal_length"], # 維度選擇
color="species") # 顏色
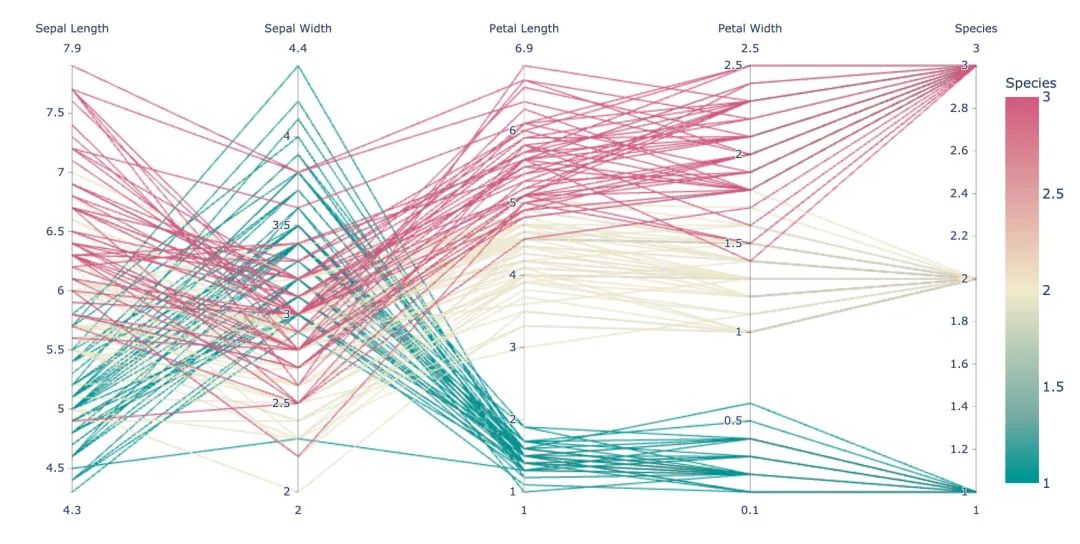
3.9 平行坐標(biāo)圖
px.parallel_coordinates(
iris, # 數(shù)據(jù)集
color="species_id", # 顏色
labels={"species_id":"Species", # 各種標(biāo)簽值
"sepal_width":"Sepal Width",
"sepal_length":"Sepal Length",
"petal_length":"Petal Length",
"petal_width":"Petal Width"},
color_continuous_scale=px.colors.diverging.Tealrose,
color_continuous_midpoint=2)
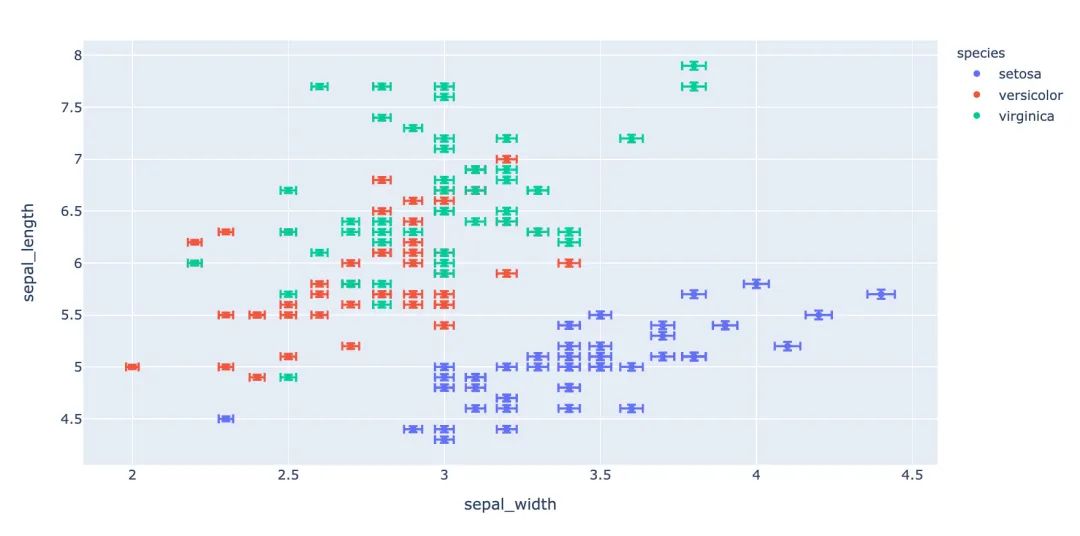
3.10 箱體誤差圖
# 對(duì)當(dāng)前值加上下兩個(gè)誤差值
iris["e"] = iris["sepal_width"] / 100
px.scatter(
iris, # 繪圖數(shù)據(jù)集
x="sepal_width", # 橫坐標(biāo)
y="sepal_length", # 縱坐標(biāo)
color="species", # 顏色值
error_x="e", # 橫軸誤差
error_y="e" # 縱軸誤差
)
3.11 等高線圖
等高線圖反映數(shù)據(jù)的密度情況:
px.density_contour(
iris, # 繪圖數(shù)據(jù)集
x="sepal_width", # 橫坐標(biāo)
y="sepal_length", # 縱坐標(biāo)值
color="species" # 顏色
)
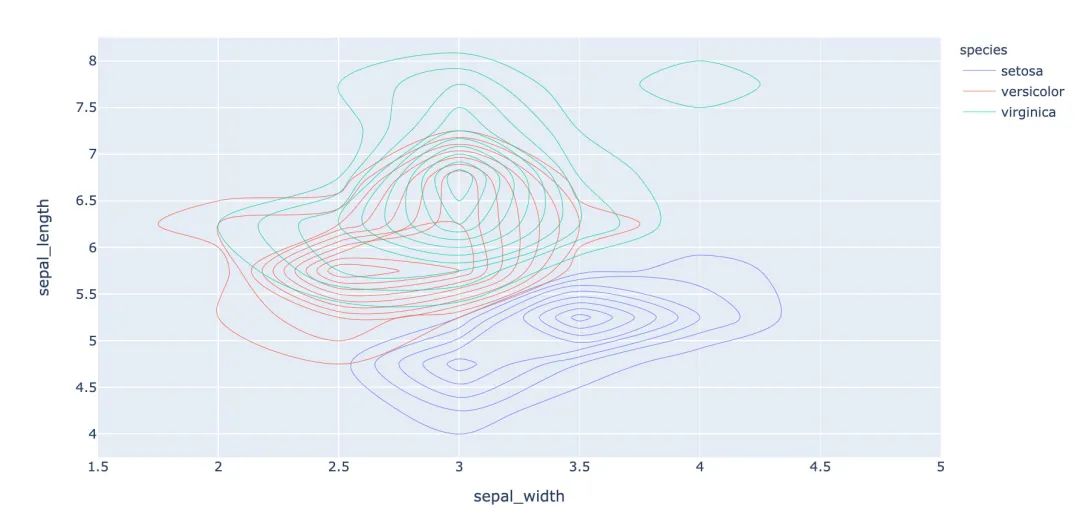
等高線圖和直方圖的倆和使用:
px.density_contour(
iris, # 數(shù)據(jù)集
x="sepal_width", # 橫坐標(biāo)值
y="sepal_length", # 縱坐標(biāo)值
color="species", # 顏色
marginal_x="rug", # 橫軸為線條圖
marginal_y="histogram" # 縱軸為直方圖
)
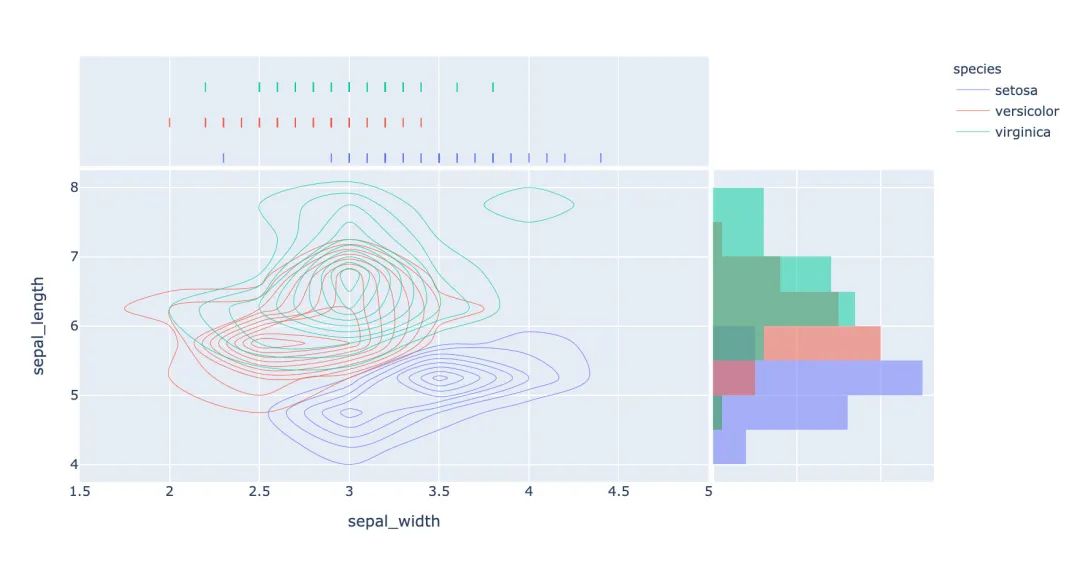
3.12 密度熱力圖
px.density_heatmap(
iris, # 數(shù)據(jù)集
x="sepal_width", # 橫坐標(biāo)值
y="sepal_length", # 縱坐標(biāo)值
marginal_y="rug", # 縱坐標(biāo)值為線型圖
marginal_x="histogram" # 直方圖
)
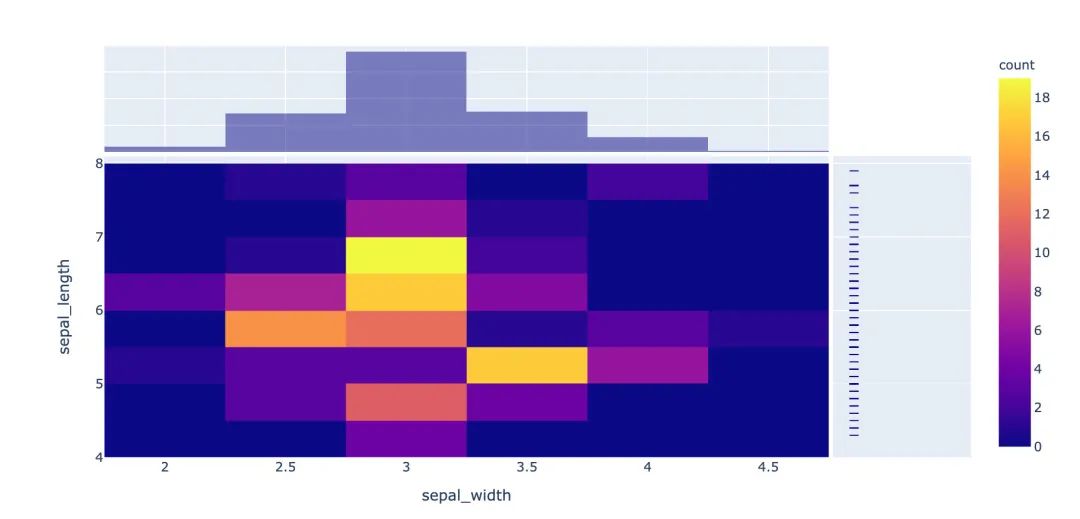
3.13 并行類別圖
在接下來的圖形中我們使用的小費(fèi)tips實(shí)例,首先是導(dǎo)入數(shù)據(jù):
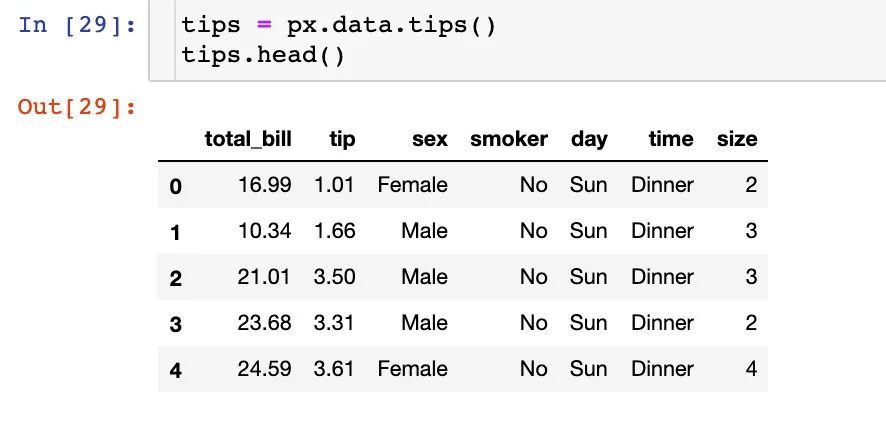
fig = px.parallel_categories(
tips, # 數(shù)據(jù)集
color="size", # 顏色
color_continuous_scale=px.colors.sequential.Inferno) # 顏色變化取值
fig.show()
3.14 柱狀圖
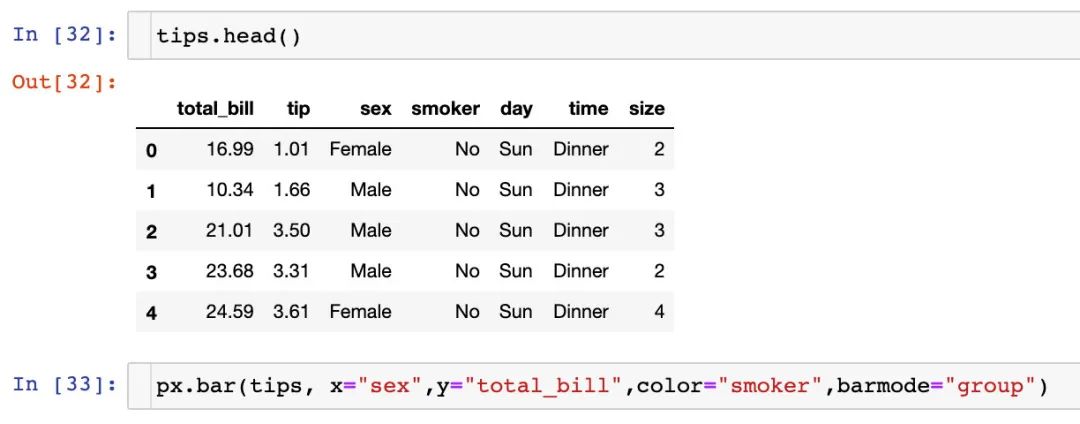
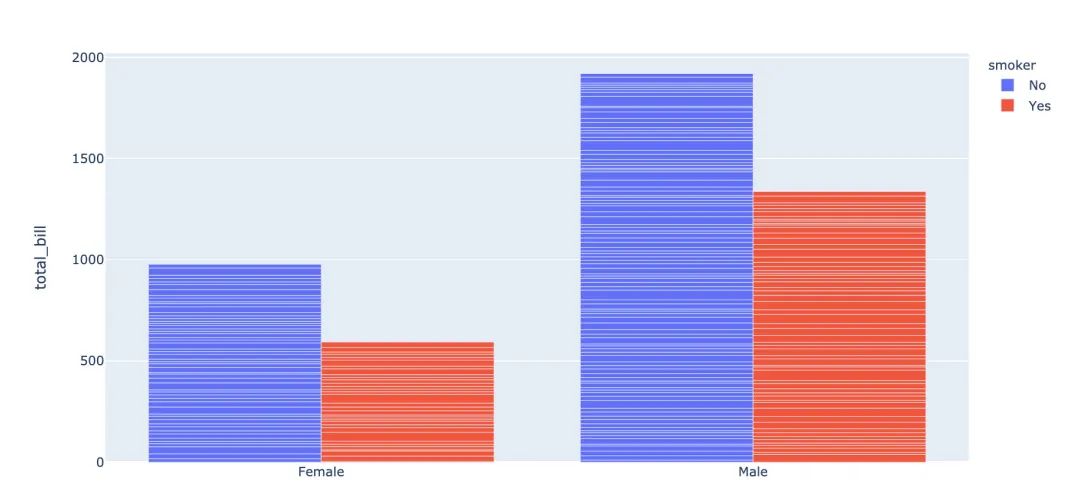
fig = px.bar(
tips, # 數(shù)據(jù)集
x="sex", # 橫軸
y="total_bill", # 縱軸
color="smoker", # 顏色參數(shù)取值
barmode="group", # 柱狀圖模式取值
facet_row="time", # 行取值
facet_col="day", # 列元素取值
category_orders={
"day": ["Thur","Fri","Sat","Sun"], # 分類順序
"time":["Lunch", "Dinner"]})
fig.show()
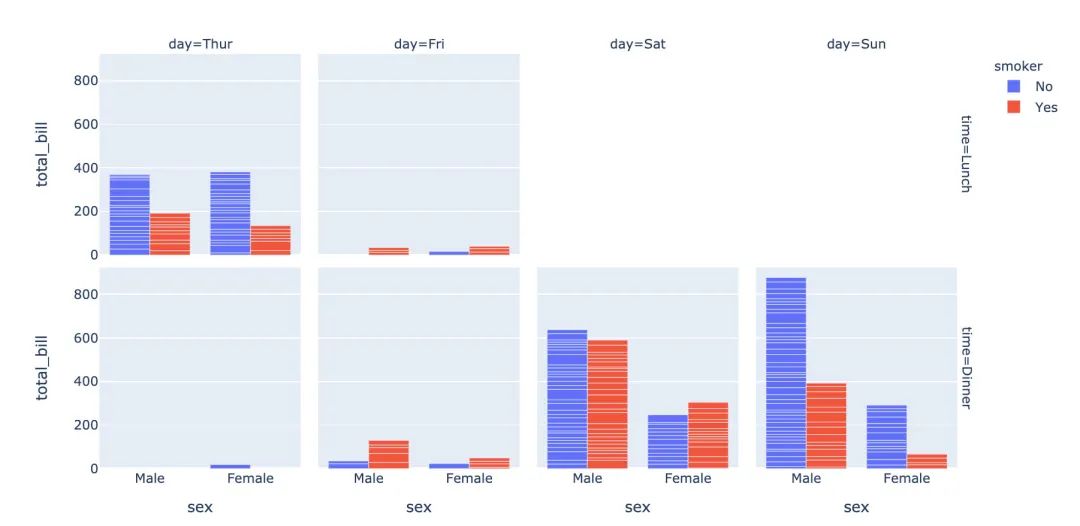
3.15 直方圖
fig = px.histogram(
tips, # 繪圖數(shù)據(jù)集
x="sex", # 橫軸為性別
y="tip", # 縱軸為費(fèi)用
histfunc="avg", # 直方圖顯示的函數(shù)
color="smoker", # 顏色
barmode="group", # 柱狀圖模式
facet_row="time", # 行取值
facet_col="day", # 列取值
category_orders={ # 分類順序
"day":["Thur","Fri","Sat","Sun"],
"time":["Lunch","Dinner"]}
)
fig.show()
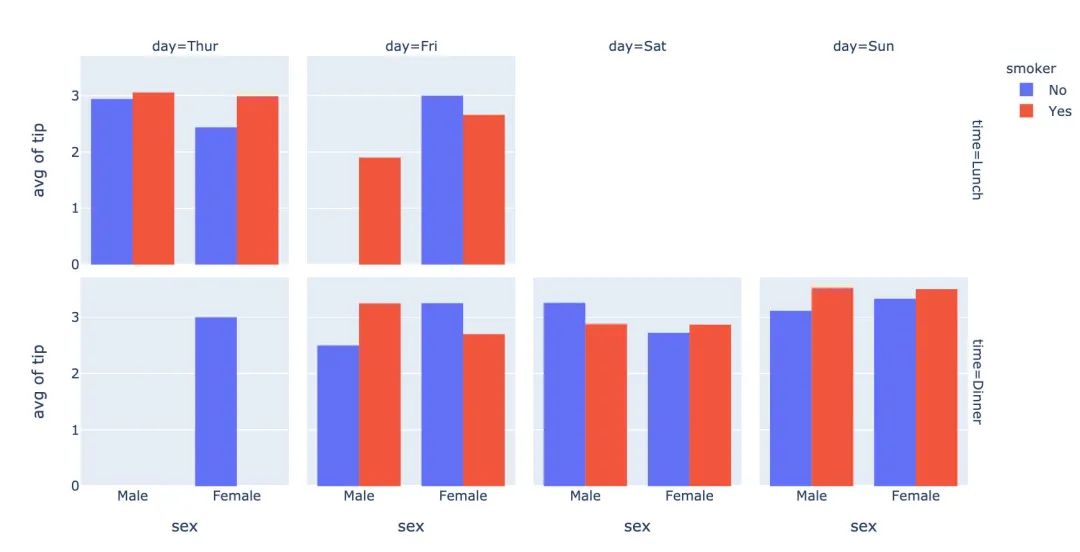
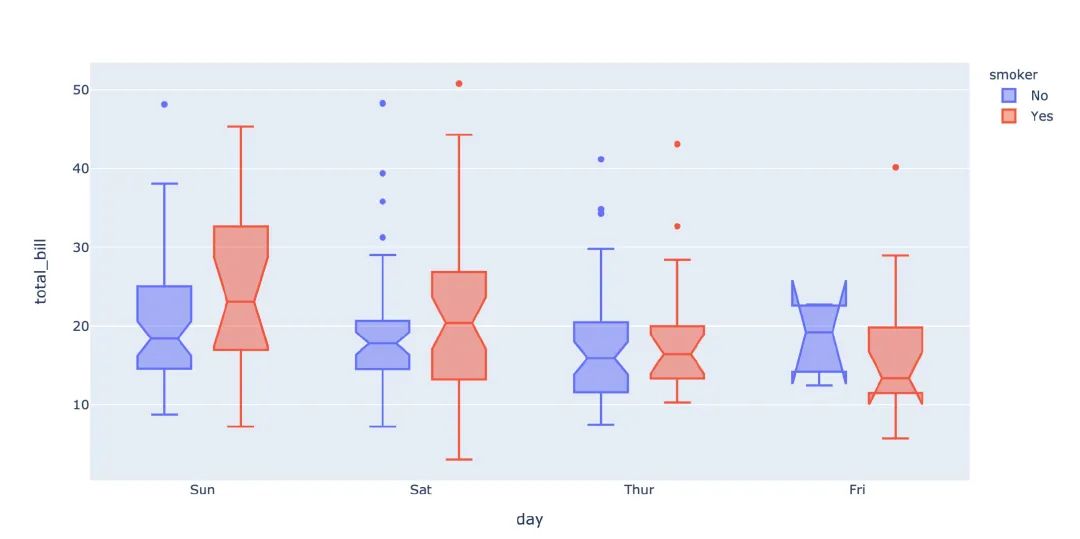
3.16 箱型圖
箱型圖也是現(xiàn)實(shí)數(shù)據(jù)的誤差和分布情況:
# notched=True顯示連接處的錐形部分
px.box(tips, # 數(shù)據(jù)集
x="day", # 橫軸數(shù)據(jù)
y="total_bill", # 縱軸數(shù)據(jù)
color="smoker", # 顏色
notched=True) # 連接處的錐形部分顯示出來
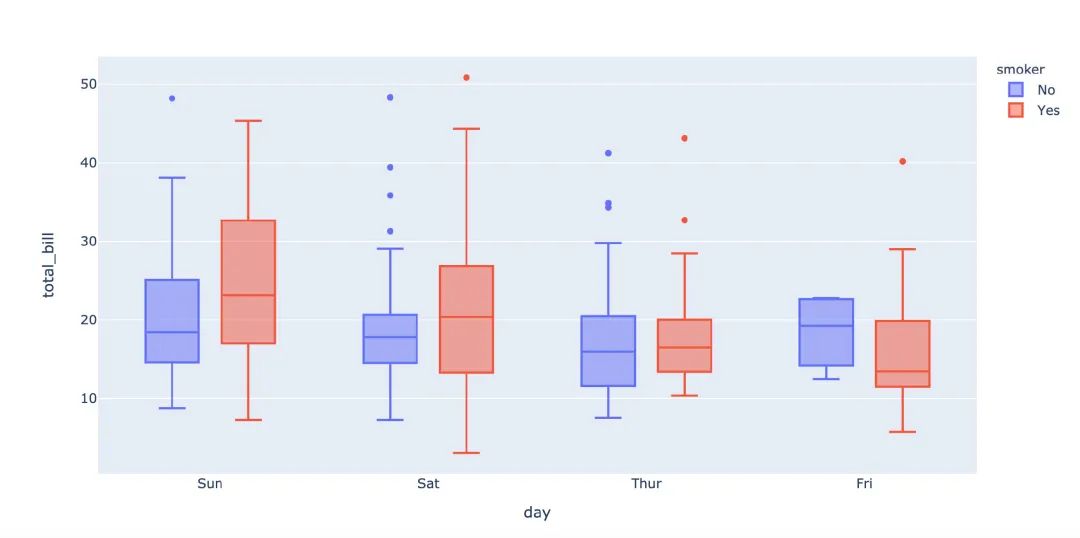
px.box(
tips, # 數(shù)據(jù)集
x="day", # 橫軸
y="total_bill", # 縱軸
color="smoker", # 顏色
# notched=True # 隱藏參數(shù)
)
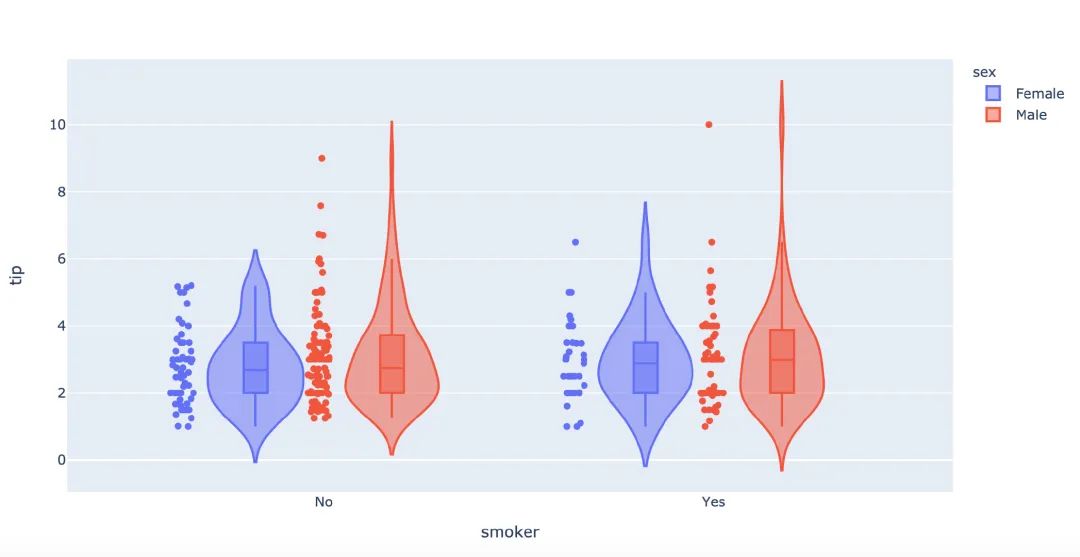
再來畫一次小提琴圖:
px.violin(
tips, # 數(shù)據(jù)集
x="smoker", # 橫軸坐標(biāo)
y="tip", # 縱軸坐標(biāo)
color="sex", # 顏色參數(shù)取值
box=True, # box是顯示內(nèi)部的箱體
points="all", # 同時(shí)顯示數(shù)值點(diǎn)
hover_data=tips.columns) # 結(jié)果中顯示全部數(shù)據(jù)
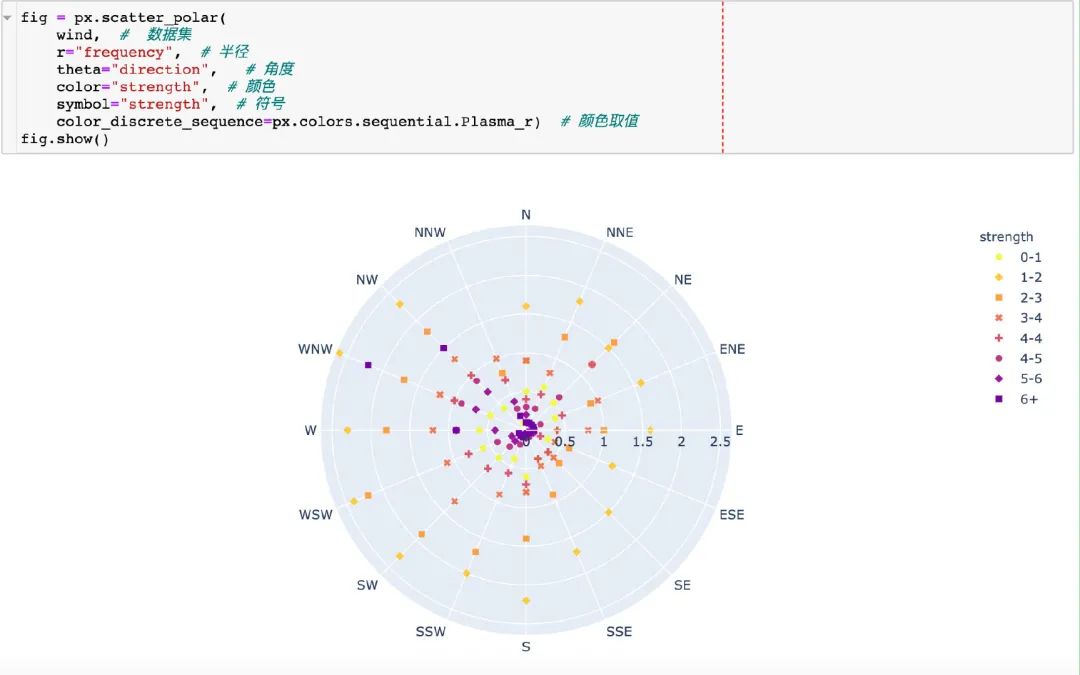
3.17 極坐標(biāo)圖
在這里我們使用的是內(nèi)置的wind數(shù)據(jù):
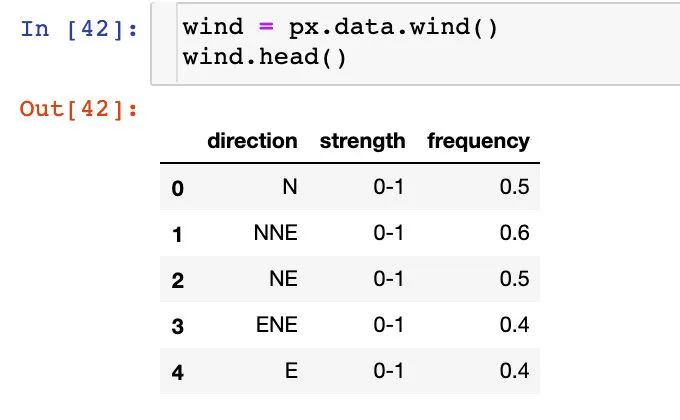
散點(diǎn)極坐標(biāo)圖
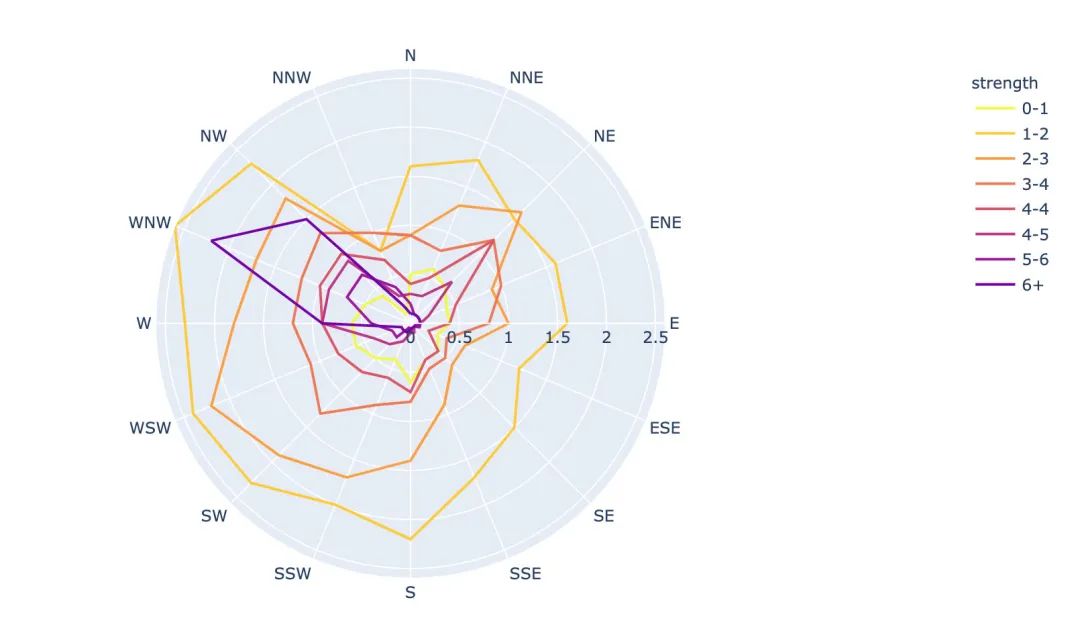
線性極坐標(biāo)圖
fig = px.line_polar(
wind, # 數(shù)據(jù)集
r="frequency", # 半徑
theta="direction", # 角度
color="strength", # 顏色
line_close=True, # 線性閉合
color_discrete_sequence=px.colors.sequential.Plasma_r) # 顏色變化
fig.show()
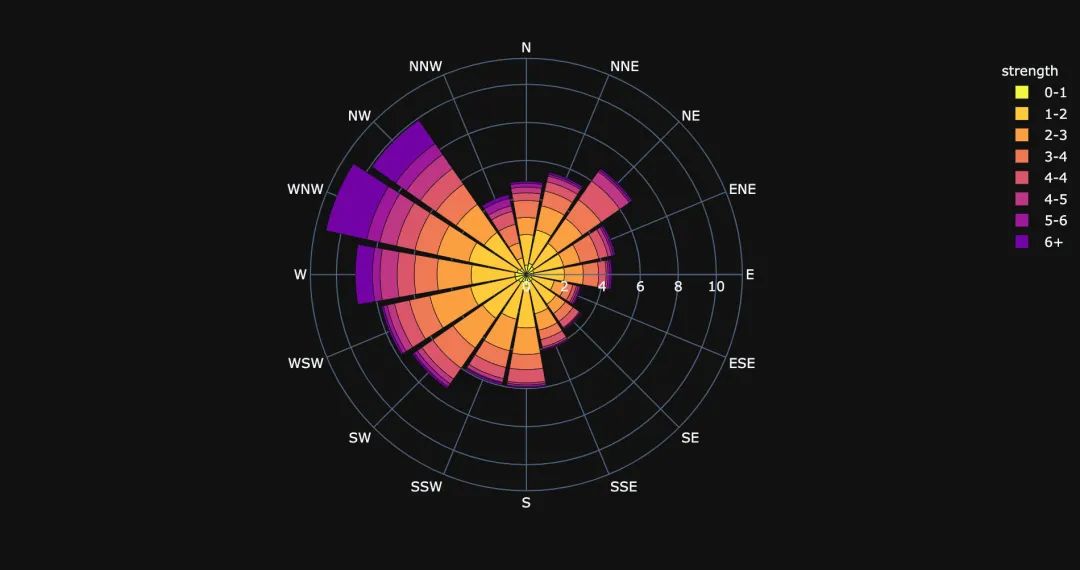
柱狀極坐標(biāo)圖
fig = px.bar_polar(
wind, # 數(shù)據(jù)集
r="frequency", # 半徑
theta="direction", # 角度
color="strength", # 顏色
template="plotly_dark", # 主題
color_discrete_sequence=px.colors.sequential.Plasma_r) # 顏色變化
fig.show()
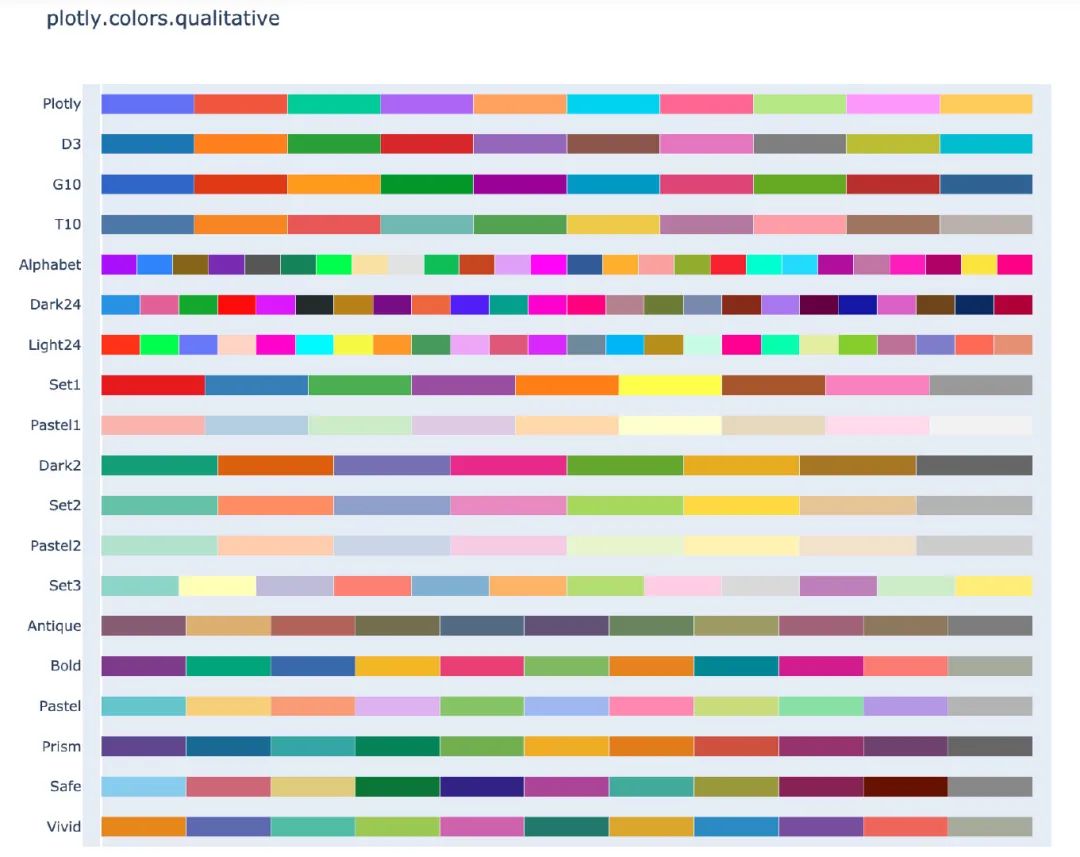
4. 顏色面板
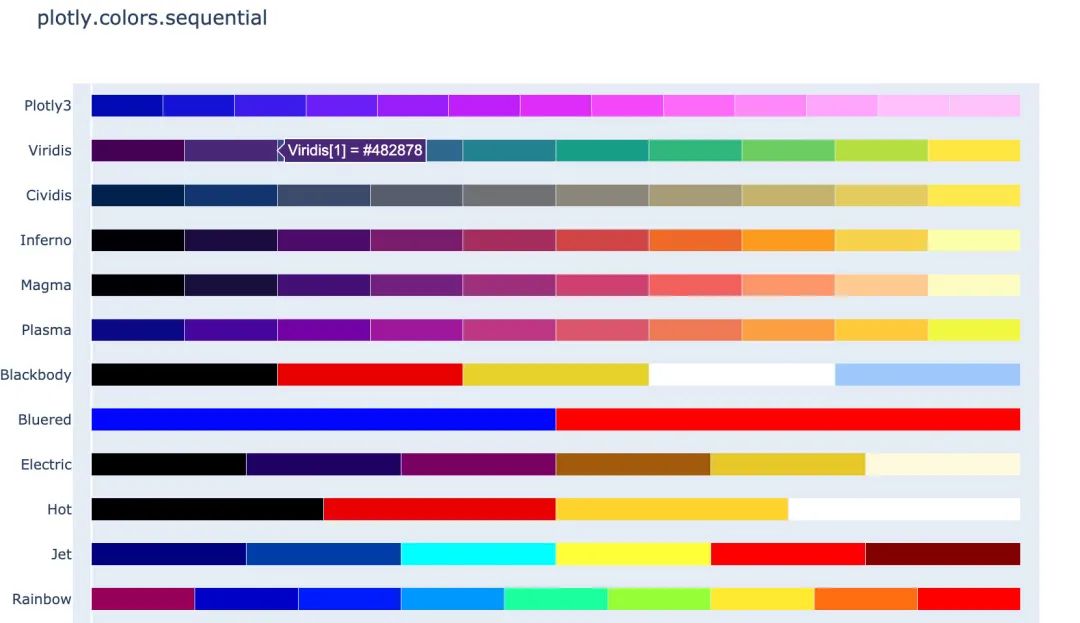
在px中有很多的顏色可以供選擇,提供了一個(gè)顏色面板:
px.colors.qualitative.swatches()
px.colors.sequential.swatches()
5. 主題
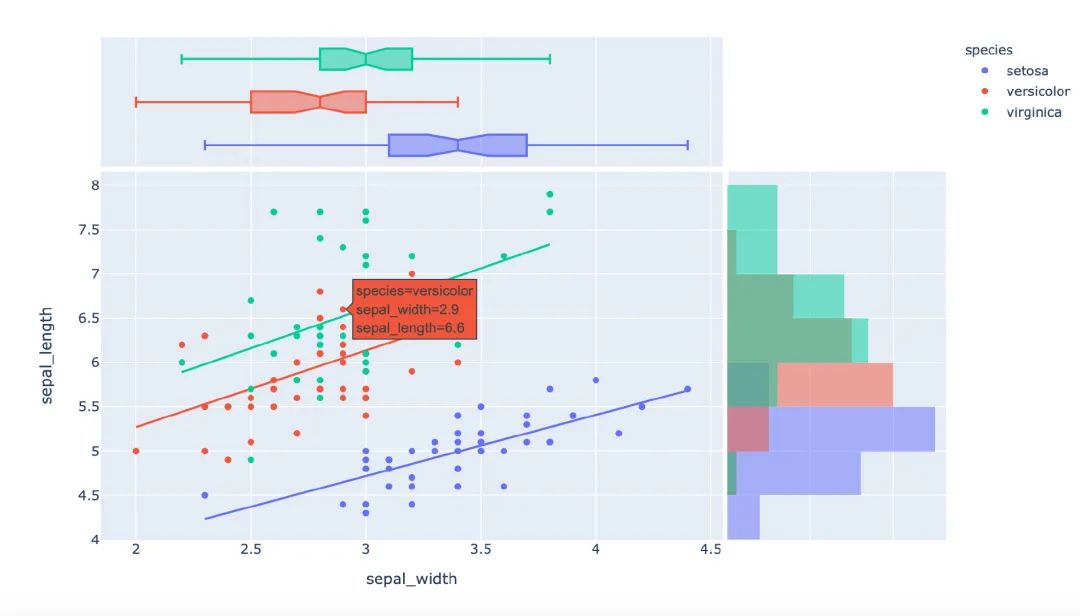
px中存在3種主題:
plotly plotly_white plotly_dark
px.scatter(
iris, # 數(shù)據(jù)集
x="sepal_width", # 橫坐標(biāo)值
y="sepal_length", # 縱坐標(biāo)取值
color="species", # 顏色
marginal_x="box", # 橫坐標(biāo)為箱型圖
marginal_y="histogram", # 縱坐標(biāo)為直方圖
height=600, # 高度
trendline="ols", # 顯示趨勢線
template="plotly") # 主題
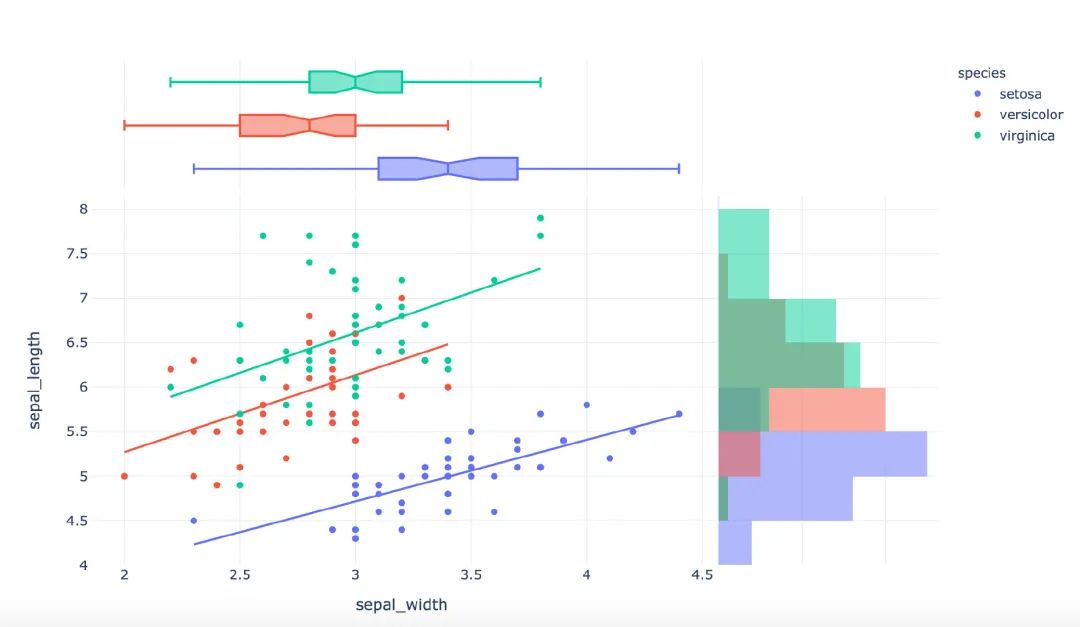
px.scatter(
iris, # 數(shù)據(jù)集
x="sepal_width", # 橫坐標(biāo)值
y="sepal_length", # 縱坐標(biāo)取值
color="species", # 顏色
marginal_x="box", # 橫坐標(biāo)為箱型圖
marginal_y="histogram", # 縱坐標(biāo)為直方圖
height=600, # 高度
trendline="ols", # 顯示趨勢線
template="plotly_white") # 主題
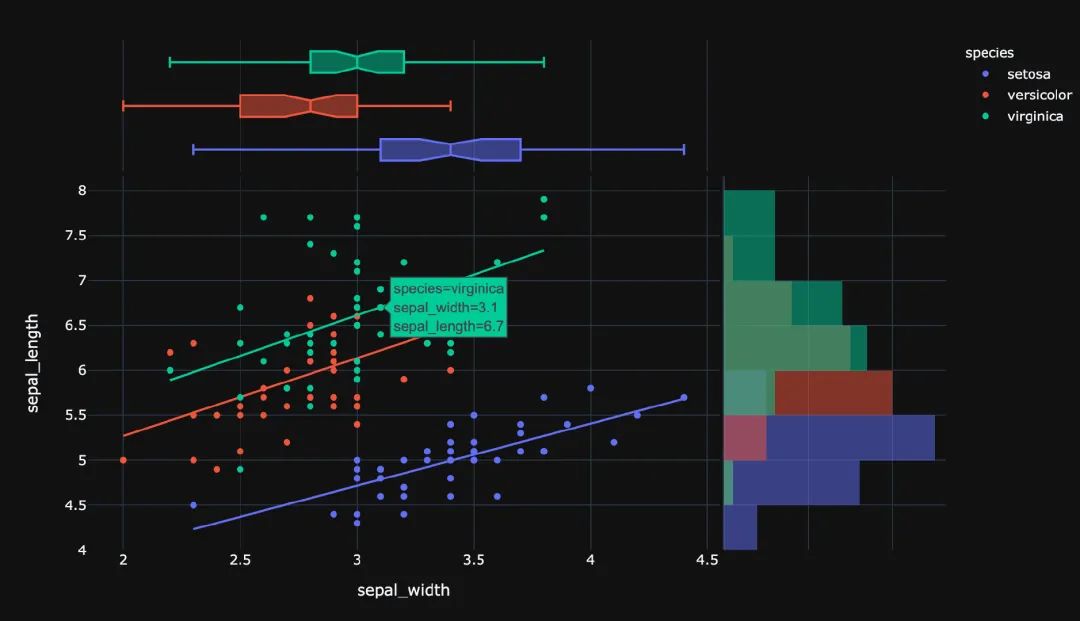
px.scatter(
iris, # 數(shù)據(jù)集
x="sepal_width", # 橫坐標(biāo)值
y="sepal_length", # 縱坐標(biāo)取值
color="species", # 顏色
marginal_x="box", # 橫坐標(biāo)為箱型圖
marginal_y="histogram", # 縱坐標(biāo)為直方圖
height=600, # 高度
trendline="ols", # 顯示趨勢線
template="plotly_dark") # 主題
6. 總結(jié)一下
本文中利用大量的篇幅講解了如何通過plotly_express來繪制:柱狀圖、線型圖、散點(diǎn)圖、小提琴圖、極坐標(biāo)圖等各種常見的圖形。通過觀察上面Plotly_express繪制圖形過程,我們不難發(fā)現(xiàn)它有三個(gè)主要的優(yōu)點(diǎn):
快速出圖,少量的代碼就能滿足多數(shù)的制圖要求。基本上都是幾個(gè)參數(shù)的設(shè)置我們就能快速出圖 圖形漂亮,繪制出來的可視化圖形顏色亮麗,也有很多的顏色供選擇。 圖形是動(dòng)態(tài)可視化的。文章中圖形都是截圖,如果是在 Jupyter notebook中都是動(dòng)態(tài)圖形
希望通過本文的講解能夠幫助堵住快速入門plotly_express可視化神器。
------------------- End -------------------
往期精彩文章推薦:
Python自帶爬蟲庫urllib使用大全
一篇文章教會(huì)你使用Python定時(shí)抓取微博評(píng)論
一篇文章教會(huì)你使用Python圖片格式轉(zhuǎn)換器并識(shí)別圖片中的文字
歡迎大家點(diǎn)贊,留言,轉(zhuǎn)發(fā),轉(zhuǎn)載,感謝大家的相伴與支持
想加入Python學(xué)習(xí)群請(qǐng)?jiān)诤笈_(tái)回復(fù)【入群】
萬水千山總是情,點(diǎn)個(gè)【在看】行不行
/今日留言主題/
隨便說一兩句吧~~
