MyBatis 動態(tài) SQL(認真看看, 以后寫 SQL 就爽多了)
MyBatis 令人喜歡的一大特性就是動態(tài) SQL。在使用 JDBC 的過程中, 根據(jù)條件進行 SQL 的拼接是很麻煩且很容易出錯的。MyBatis 動態(tài) SQL 的出現(xiàn), 解決了這個麻煩。
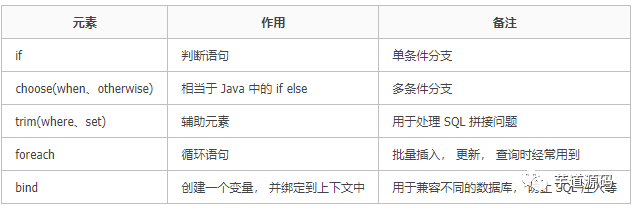
MyBatis通過 OGNL 來進行動態(tài) SQL 的使用的。目前, 動態(tài) SQL 支持以下幾種標簽:
1 數(shù)據(jù)準備
為了后面的演示, 創(chuàng)建了一個 Maven 項目 mybatis-dynamic, 創(chuàng)建了對應的數(shù)據(jù)庫和表
DROP TABLE IF EXISTS `student`;
CREATE TABLE `student` (
`student_id` int(10) unsigned NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT COMMENT '編號',
`name` varchar(20) DEFAULT NULL COMMENT '姓名',
`phone` varchar(20) DEFAULT NULL COMMENT '電話',
`email` varchar(50) DEFAULT NULL COMMENT '郵箱',
`sex` tinyint(4) DEFAULT NULL COMMENT '性別',
`locked` tinyint(4) DEFAULT NULL COMMENT '狀態(tài)(0:正常,1:鎖定)',
`gmt_created` datetime DEFAULT CURRENT_TIMESTAMP COMMENT '存入數(shù)據(jù)庫的時間',
`gmt_modified` datetime DEFAULT CURRENT_TIMESTAMP ON UPDATE CURRENT_TIMESTAMP COMMENT '修改的時間',
`delete` int(11) DEFAULT NULL,
PRIMARY KEY (`student_id`)
) ENGINE=InnoDB AUTO_INCREMENT=7 DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8mb4 COLLATE=utf8mb4_0900_ai_ci COMMENT='學生表';
對應的項目結(jié)構(gòu)
2 if 標簽
if 標簽是我們最常使用的。在查詢、刪除、更新的時候很可能會使用到。必須結(jié)合 test 屬性聯(lián)合使用。
2.1 在 WHERE 條件中使用 if 標簽
這是常見的一種現(xiàn)象, 我們在進行按條件查詢的時候, 可能會有多種情況。
2.1.1 查詢條件
根據(jù)輸入的學生信息進行條件檢索
當只輸入用戶名時, 使用用戶名進行模糊檢索; 當只輸入性別時, 使用性別進行完全匹配 當用戶名和性別都存在時, 用這兩個條件進行查詢匹配查詢
2.1.2 動態(tài) SQL
接口函數(shù)
/**
* 根據(jù)輸入的學生信息進行條件檢索
* 1. 當只輸入用戶名時, 使用用戶名進行模糊檢索;
* 2. 當只輸入郵箱時, 使用性別進行完全匹配
* 3. 當用戶名和性別都存在時, 用這兩個條件進行查詢匹配的用
* @param student
* @return
*/
List<Student> selectByStudentSelective(Student student);
對應的動態(tài) SQL
<select id="selectByStudentSelective" resultMap="BaseResultMap" parameterType="com.homejim.mybatis.entity.Student">
select
<include refid="Base_Column_List" />
from student
where 1=1
<if test="name != null and name !=''">
and name like concat('%', #{name}, '%')
</if>
<if test="sex != null">
and sex=#{sex}
</if>
</select>
在此 SQL 語句中, where 1=1 是多條件拼接時的小技巧, 后面的條件查詢就可以都用 and 了。
同時, 我們添加了 if 標簽來處理動態(tài) SQL
<if test="name != null and name !=''">
and name like concat('%', #{name}, '%')
</if>
<if test="sex != null">
and sex=#{sex}
</if>
此 if 標簽的 test 屬性值是一個符合 OGNL 的表達式, 表達式可以是 true 或 false。如果表達式返回的是數(shù)值, 則0為 false, 非 0 為 true;
2.1.3 測試
@Test
public void selectByStudent() {
SqlSession sqlSession = null;
sqlSession = sqlSessionFactory.openSession();
StudentMapper studentMapper = sqlSession.getMapper(StudentMapper.class);
Student search = new Student();
search.setName("明");
System.out.println("只有名字時的查詢");
List<Student> studentsByName = studentMapper.selectByStudentSelective(search);
for (int i = 0; i < studentsByName.size(); i++) {
System.out.println(ToStringBuilder.reflectionToString(studentsByName.get(i), ToStringStyle.MULTI_LINE_STYLE));
}
search.setName(null);
search.setSex((byte) 1);
System.out.println("只有性別時的查詢");
List<Student> studentsBySex = studentMapper.selectByStudentSelective(search);
for (int i = 0; i < studentsBySex.size(); i++) {
System.out.println(ToStringBuilder.reflectionToString(studentsBySex.get(i), ToStringStyle.MULTI_LINE_STYLE));
}
System.out.println("姓名和性別同時存在的查詢");
search.setName("明");
List<Student> studentsByNameAndSex = studentMapper.selectByStudentSelective(search);
for (int i = 0; i < studentsByNameAndSex.size(); i++) {
System.out.println(ToStringBuilder.reflectionToString(studentsByNameAndSex.get(i), ToStringStyle.MULTI_LINE_STYLE));
}
sqlSession.commit();
sqlSession.close();
}
只有名字時的查詢, 發(fā)送的語句和結(jié)果
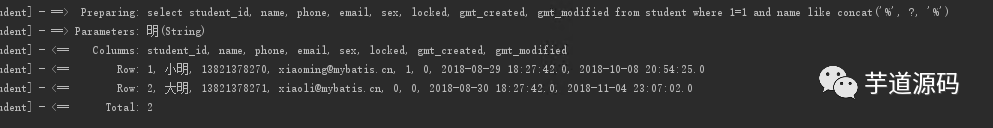
查詢的條件只發(fā)送了
where 1=1 and name like concat('%', ?, '%')
只有性別時的查詢, 發(fā)送的語句和結(jié)果
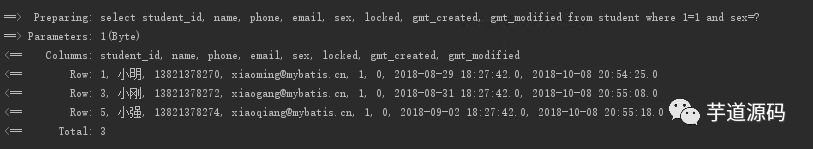
查詢的條件只發(fā)送了
where 1=1 and sex=?
姓名和性別同時存在的查詢, 發(fā)送的語句和結(jié)果
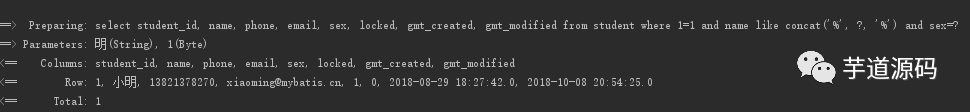
查詢條件
where 1=1 and name like concat('%', ?, '%') and sex=?
2.2 在 UPDATE 更新列中使用 if 標簽
有時候我們不希望更新所有的字段, 只更新有變化的字段。
2.2.1 更新條件
只更新有變化的字段, 空值不更新。
2.2.1 動態(tài) SQL
接口方法
/**
* 更新非空屬性
*/
int updateByPrimaryKeySelective(Student record);
對應的 SQL
<update id="updateByPrimaryKeySelective" parameterType="com.homejim.mybatis.entity.Student">
update student
<set>
<if test="name != null">
`name` = #{name,jdbcType=VARCHAR},
</if>
<if test="phone != null">
phone = #{phone,jdbcType=VARCHAR},
</if>
<if test="email != null">
email = #{email,jdbcType=VARCHAR},
</if>
<if test="sex != null">
sex = #{sex,jdbcType=TINYINT},
</if>
<if test="locked != null">
locked = #{locked,jdbcType=TINYINT},
</if>
<if test="gmtCreated != null">
gmt_created = #{gmtCreated,jdbcType=TIMESTAMP},
</if>
<if test="gmtModified != null">
gmt_modified = #{gmtModified,jdbcType=TIMESTAMP},
</if>
</set>
where student_id = #{studentId,jdbcType=INTEGER}
2.2.3 測試
@Test
public void updateByStudentSelective() {
SqlSession sqlSession = null;
sqlSession = sqlSessionFactory.openSession();
StudentMapper studentMapper = sqlSession.getMapper(StudentMapper.class);
Student student = new Student();
student.setStudentId(1);
student.setName("明明");
student.setPhone("13838438888");
System.out.println(studentMapper.updateByPrimaryKeySelective(student));
sqlSession.commit();
sqlSession.close();
}
結(jié)果如下
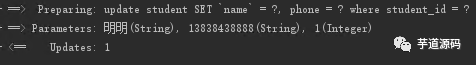
2.3 在 INSERT 動態(tài)插入中使用 if 標簽
我們插入數(shù)據(jù)庫中的一條記錄, 不是每一個字段都有值的, 而是動態(tài)變化的。在這時候使用 if 標簽, 可幫我們解決這個問題。
2.3.1 插入條件
只有非空屬性才插入。
2.3.2 動態(tài)SQL
接口方法
/**
* 非空字段才進行插入
*/
int insertSelective(Student record);
對應的SQL
<insert id="insertSelective" parameterType="com.homejim.mybatis.entity.Student">
insert into student
<trim prefix="(" suffix=")" suffixOverrides=",">
<if test="studentId != null">
student_id,
</if>
<if test="name != null">
`name`,
</if>
<if test="phone != null">
phone,
</if>
<if test="email != null">
email,
</if>
<if test="sex != null">
sex,
</if>
<if test="locked != null">
locked,
</if>
<if test="gmtCreated != null">
gmt_created,
</if>
<if test="gmtModified != null">
gmt_modified,
</if>
</trim>
<trim prefix="values (" suffix=")" suffixOverrides=",">
<if test="studentId != null">
#{studentId,jdbcType=INTEGER},
</if>
<if test="name != null">
#{name,jdbcType=VARCHAR},
</if>
<if test="phone != null">
#{phone,jdbcType=VARCHAR},
</if>
<if test="email != null">
#{email,jdbcType=VARCHAR},
</if>
<if test="sex != null">
#{sex,jdbcType=TINYINT},
</if>
<if test="locked != null">
#{locked,jdbcType=TINYINT},
</if>
<if test="gmtCreated != null">
#{gmtCreated,jdbcType=TIMESTAMP},
</if>
<if test="gmtModified != null">
#{gmtModified,jdbcType=TIMESTAMP},
</if>
</trim>
</insert>
這個 SQL 大家應該很熟悉, 畢竟是自動生成的。
2.3.3 測試
@Test
public void insertByStudentSelective() {
SqlSession sqlSession = null;
sqlSession = sqlSessionFactory.openSession();
StudentMapper studentMapper = sqlSession.getMapper(StudentMapper.class);
Student student = new Student();
student.setName("小飛機");
student.setPhone("13838438899");
student.setEmail("[email protected]");
student.setLocked((byte) 0);
System.out.println(studentMapper.insertSelective(student));
sqlSession.commit();
sqlSession.close();
}
對應的結(jié)果
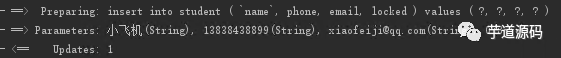
SQL 中, 只有非空的字段才進行了插入。
3 choose 標簽
choose when otherwise 標簽可以幫我們實現(xiàn) if else 的邏輯。一個 choose 標簽至少有一個 when, 最多一個otherwise。
下面是一個查詢的例子。
3.1 查詢條件
假設 name 具有唯一性, 查詢一個學生
當 studen_id 有值時, 使用 studen_id 進行查詢; 當 studen_id 沒有值時, 使用 name 進行查詢; 否則返回空
3.2 動態(tài)SQL
接口方法
/**
* - 當 studen_id 有值時, 使用 studen_id 進行查詢;
* - 當 studen_id 沒有值時, 使用 name 進行查詢;
* - 否則返回空
*/
Student selectByIdOrName(Student record);
對應的SQL
<select id="selectByIdOrName" resultMap="BaseResultMap" parameterType="com.homejim.mybatis.entity.Student">
select
<include refid="Base_Column_List" />
from student
where 1=1
<choose>
<when test="studentId != null">
and student_id=#{studentId}
</when>
<when test="name != null and name != ''">
and name=#{name}
</when>
<otherwise>
and 1=2
</otherwise>
</choose>
</select>
3.3 測試
@Test
public void selectByIdOrName() {
SqlSession sqlSession = null;
sqlSession = sqlSessionFactory.openSession();
StudentMapper studentMapper = sqlSession.getMapper(StudentMapper.class);
Student student = new Student();
student.setName("小飛機");
student.setStudentId(1);
Student studentById = studentMapper.selectByIdOrName(student);
System.out.println("有 ID 則根據(jù) ID 獲取");
System.out.println(ToStringBuilder.reflectionToString(studentById, ToStringStyle.MULTI_LINE_STYLE));
student.setStudentId(null);
Student studentByName = studentMapper.selectByIdOrName(student);
System.out.println("沒有 ID 則根據(jù) name 獲取");
System.out.println(ToStringBuilder.reflectionToString(studentByName, ToStringStyle.MULTI_LINE_STYLE));
student.setName(null);
Student studentNull = studentMapper.selectByIdOrName(student);
System.out.println("沒有 ID 和 name, 返回 null");
Assert.assertNull(studentNull);
sqlSession.commit();
sqlSession.close();
}
有 ID 則根據(jù) ID 獲取, 結(jié)果
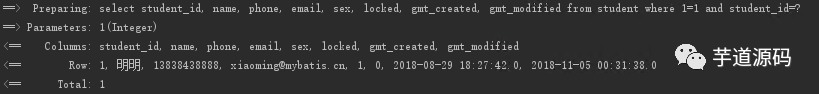
沒有 ID 則根據(jù) name 獲取
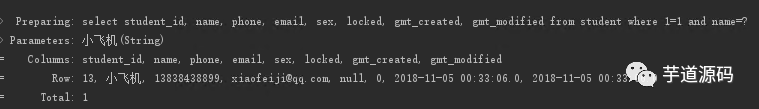
沒有 ID 和 name, 返回 null

4 trim(set、where)
這三個其實解決的是類似的問題。如我們在寫前面的[在 WHERE 條件中使用 if 標簽] SQL 的時候, where 1=1 這個條件我們是不希望存在的。
4.1 where
4.1.1 查詢條件
根據(jù)輸入的學生信息進行條件檢索。
當只輸入用戶名時, 使用用戶名進行模糊檢索; 當只輸入性別時, 使用性別進行完全匹配 當用戶名和性別都存在時, 用這兩個條件進行查詢匹配查詢
不使用 where 1=1。
4.1.2 動態(tài) SQL
很顯然, 我們要解決這幾個問題
當條件都不滿足時:此時 SQL 中應該要不能有 where , 否則導致出錯 當 if 有條件滿足時:SQL 中需要有 where, 且第一個成立的 if 標簽下的 and | or 等要去掉 這時候, 我們可以使用 where 標簽。
接口方法
/**
* 根據(jù)輸入的學生信息進行條件檢索
* 1. 當只輸入用戶名時, 使用用戶名進行模糊檢索;
* 2. 當只輸入郵箱時, 使用性別進行完全匹配
* 3. 當用戶名和性別都存在時, 用這兩個條件進行查詢匹配的用
*/
List<Student> selectByStudentSelectiveWhereTag(Student student);
對應的 SQL
<select id="selectByStudentSelectiveWhereTag" resultMap="BaseResultMap" parameterType="com.homejim.mybatis.entity.Student">
select
<include refid="Base_Column_List" />
from student
<where>
<if test="name != null and name !=''">
and name like concat('%', #{name}, '%')
</if>
<if test="sex != null">
and sex=#{sex}
</if>
</where>
</select>
4.1.3 測試
@Test
public void selectByStudentWhereTag() {
SqlSession sqlSession = null;
sqlSession = sqlSessionFactory.openSession();
StudentMapper studentMapper = sqlSession.getMapper(StudentMapper.class);
Student search = new Student();
search.setName("明");
System.out.println("只有名字時的查詢");
List<Student> studentsByName = studentMapper.selectByStudentSelectiveWhereTag(search);
for (int i = 0; i < studentsByName.size(); i++) {
System.out.println(ToStringBuilder.reflectionToString(studentsByName.get(i), ToStringStyle.MULTI_LINE_STYLE));
}
search.setSex((byte) 1);
System.out.println("姓名和性別同時存在的查詢");
List<Student> studentsBySex = studentMapper.selectByStudentSelectiveWhereTag(search);
for (int i = 0; i < studentsBySex.size(); i++) {
System.out.println(ToStringBuilder.reflectionToString(studentsBySex.get(i), ToStringStyle.MULTI_LINE_STYLE));
}
System.out.println("姓名和性別都不存在時查詢");
search.setName(null);
search.setSex(null);
List<Student> studentsByNameAndSex = studentMapper.selectByStudentSelectiveWhereTag(search);
for (int i = 0; i < studentsByNameAndSex.size(); i++) {
System.out.println(ToStringBuilder.reflectionToString(studentsByNameAndSex.get(i), ToStringStyle.MULTI_LINE_STYLE));
}
sqlSession.commit();
sqlSession.close();
}
只有名字時的查詢, 有 where
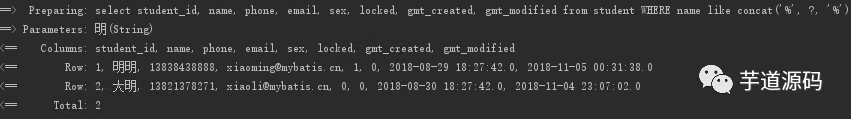
姓名和性別同時存在的查詢, 有 where
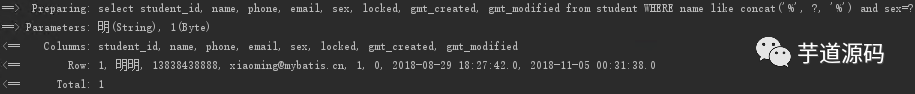
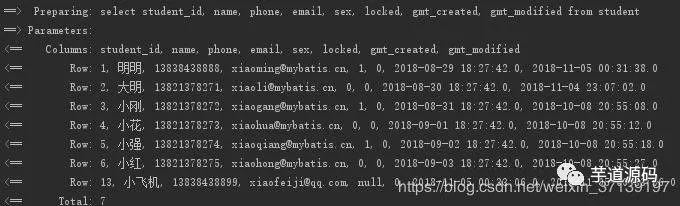
姓名和性別都不存在時查詢, 此時, where 不會再出現(xiàn)了。
4.2 set
set 標簽也類似, 在 [2.2 在 UPDATE 更新列中使用 if 標簽] 中, 如果我們的方法 updateByPrimaryKeySelective 沒有使用
4.3 trim
set 和 where 其實都是 trim 標簽的一種類型, 該兩種功能都可以使用 trim 標簽進行實現(xiàn)。
4.3.1 trim 來表示 where
如以上的 where 標簽, 我們也可以寫成
<trim prefix="where" prefixOverrides="AND |OR">
</trim>
表示當 trim 中含有內(nèi)容時, 添加 where, 且第一個為 and 或 or 時, 會將其去掉。而如果沒有內(nèi)容, 則不添加 where。
4.3.2 trim 來表示 set
相應的, set 標簽可以如下表示
<trim prefix="SET" suffixOverrides=",">
</trim>
表示當 trim 中含有內(nèi)容時, 添加 set, 且最后的內(nèi)容為 , 時, 會將其去掉。而沒有內(nèi)容, 不添加 set
4.3.3 trim 的幾個屬性
prefix: 當 trim 元素包含有內(nèi)容時, 增加 prefix 所指定的前綴 prefixOverrides: 當 trim 元素包含有內(nèi)容時, 去除 prefixOverrides 指定的 前綴 suffix: 當 trim 元素包含有內(nèi)容時, 增加 suffix 所指定的后綴 suffixOverrides:當 trim 元素包含有內(nèi)容時, 去除 suffixOverrides 指定的后綴
5 foreach 標簽
foreach 標簽可以對數(shù)組, Map 或?qū)崿F(xiàn) Iterable 接口。
foreach 中有以下幾個屬性:
collection: 必填, 集合/數(shù)組/Map的名稱. item: 變量名。即從迭代的對象中取出的每一個值 index: 索引的屬性名。當?shù)膶ο鬄?Map 時, 該值為 Map 中的 Key. open: 循環(huán)開頭的字符串 close: 循環(huán)結(jié)束的字符串 separator: 每次循環(huán)的分隔符
其他的比較好理解, collection 中的值應該怎么設定呢?
跟接口方法中的參數(shù)相關。
1. 只有一個數(shù)組參數(shù)或集合參數(shù)
默認情況:集合collection=list, 數(shù)組是collection=array
推薦:使用 @Param 來指定參數(shù)的名稱, 如我們在參數(shù)前@Param("ids"), 則就填寫 collection=ids
2. 多參數(shù)
多參數(shù)請使用 @Param 來指定, 否則SQL中會很不方便
3. 參數(shù)是Map
指定為 Map 中的對應的 Key 即可。其實上面的 @Param 最后也是轉(zhuǎn)化為 Map 的。
4. 參數(shù)是對象
使用屬性.屬性即可。
5.1 在 where 中使用 foreach
在 where條件中使用, 如按id集合查詢, 按id集合刪除等。
5.1.1 查詢條件
我們希望查詢用戶 id 集合中的所有用戶信息。
5.1.2 動態(tài) SQL
函數(shù)接口
/**
* 獲取 id 集合中的用戶信息
* @param ids
* @return
*/
List<Student> selectByStudentIdList(List<Integer> ids);
對應 SQL
<select id="selectByStudentIdList" resultMap="BaseResultMap">
select
<include refid="Base_Column_List" />
from student
where student_id in
<foreach collection="list" item="id" open="(" close=")" separator="," index="i">
#{id}
</foreach>
</select>
5.1.3 測試
@Test
public void selectByStudentIdList() {
SqlSession sqlSession = null;
sqlSession = sqlSessionFactory.openSession();
StudentMapper studentMapper = sqlSession.getMapper(StudentMapper.class);
List<Integer> ids = new LinkedList<>();
ids.add(1);
ids.add(3);
List<Student> students = studentMapper.selectByStudentIdList(ids);
for (int i = 0; i < students.size(); i++) {
System.out.println(ToStringBuilder.reflectionToString(students.get(i), ToStringStyle.MULTI_LINE_STYLE));
}
sqlSession.commit();
sqlSession.close();
}
結(jié)果
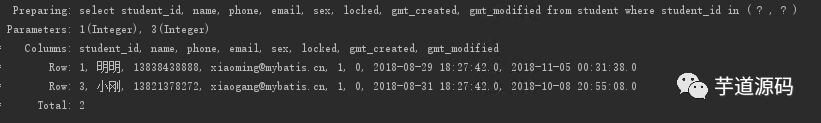
5.2 foreach 實現(xiàn)批量插入
可以通過foreach來實現(xiàn)批量插入。
5.2.1 動態(tài)SQL
接口方法
/**
* 批量插入學生
*/
int insertList(List<Student> students);
對應的SQL
<insert id="insertList">
insert into student(name, phone, email, sex, locked)
values
<foreach collection="list" item="student" separator=",">
(
#{student.name}, #{student.phone},#{student.email},
#{student.sex},#{student.locked}
)
</foreach>
</insert>
5.2.2 測試
@Test
public void insertList() {
SqlSession sqlSession = null;
sqlSession = sqlSessionFactory.openSession();
StudentMapper studentMapper = sqlSession.getMapper(StudentMapper.class);
List<Student> students = new LinkedList<>();
Student stu1 = new Student();
stu1.setName("批量01");
stu1.setPhone("13888888881");
stu1.setLocked((byte) 0);
stu1.setEmail("[email protected]");
stu1.setSex((byte) 1);
students.add(stu1);
Student stu2 = new Student();
stu2.setName("批量02");
stu2.setPhone("13888888882");
stu2.setLocked((byte) 0);
stu2.setEmail("[email protected]");
stu2.setSex((byte) 0);
students.add(stu2);
System.out.println(studentMapper.insertList(students));
sqlSession.commit();
sqlSession.close();
}
結(jié)果

6 bind 標簽
bind 標簽是通過 OGNL 表達式去定義一個上下文的變量, 這樣方便我們使用。
如在 selectByStudentSelective 方法中, 有如下
<if test="name != null and name !=''">
and name like concat('%', #{name}, '%')
</if>
在 MySQL 中, 該函數(shù)支持多參數(shù), 但在 Oracle 中只支持兩個參數(shù)。那么我們可以使用 bind 來讓該 SQL 達到支持兩個數(shù)據(jù)庫的作用
<if test="name != null and name !=''">
<bind name="nameLike" value="'%'+name+'%'"/>
and name like #{nameLike}
</if>
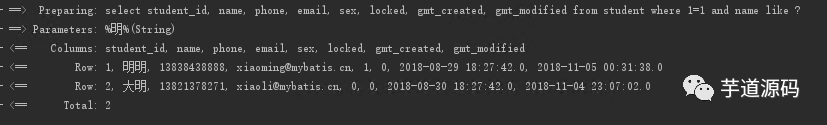
更改后的查詢結(jié)果如下
關注公眾號【Java技術江湖】后回復“PDF”即可領取200+頁的《Java工程師面試指南》
強烈推薦,幾乎涵蓋所有Java工程師必知必會的知識點,不管是復習還是面試,都很實用。


