20 張圖讓你搞定 CompletableFuture 異步編程
前言
上一篇文章 不會用Java Future,我懷疑你泡茶沒我快 ?全面分析了 Future,通過它我們可以獲取線程的執(zhí)行結(jié)果,它雖然解決了 Runnable 的 “三無” 短板,但是它自身還是有短板:
不能手動完成計算
假設你使用 Future 運行子線程調(diào)用遠程 API 來獲取某款產(chǎn)品的最新價格,服務器由于洪災宕機了,此時如果你想手動結(jié)束計算,而是想返回上次緩存中的價格,這是 Future 做不到的
調(diào)用 get() 方法會阻塞程序
Future 不會通知你它的完成,它提供了一個get()方法,程序調(diào)用該方法會阻塞直到結(jié)果可用為止,沒有辦法利用回調(diào)函數(shù)附加到Future,并在Future的結(jié)果可用時自動調(diào)用它
不能鏈式執(zhí)行
燒水泡茶中,通過構造函數(shù)傳參做到多個任務的鏈式執(zhí)行,萬一有更多的任務,或是任務鏈的執(zhí)行順序有變,對原有程序的影響都是非常大的
整合多個 Future 執(zhí)行結(jié)果方式笨重
假設有多個 Future 并行執(zhí)行,需要在這些任務全部執(zhí)行完成之后做后續(xù)操作,F(xiàn)uture 本身是做不到的,需要借助工具類 Executors 的方法
?List>?invokeAll(Collection>?tasks)
?T?invokeAny(Collection>?tasks)
沒有異常處理
Future 同樣沒有提供很好的異常處理方案
上一篇文章看 Future 覺得是發(fā)現(xiàn)了新天地,這么一說有感覺回到了解放前
對于 Java 后端的同學,在 Java1.8 之前想實現(xiàn)異步編程,還想避開上述這些煩惱,ReactiveX 應該是一個常見解決方案(做Android 的應該會有了解)。如果熟悉前端同學, ES6 Promise(男朋友的承諾)也解決了異步編程的煩惱
天下語言都在彼此借鑒相應優(yōu)點,Java 作為老牌勁旅自然也要解決上述問題。又是那個男人,并發(fā)大師 Doug Lea 憂天下程序員之憂,解天下程序員之困擾,在 Java1.8 版本(Lambda 橫空出世)中,新增了一個并發(fā)工具類 CompletableFuture,它的出現(xiàn),讓人在泡茶過程中,品嘗到了不一樣的味道......
幾個重要 Lambda 函數(shù)
CompletableFuture 在 Java1.8 的版本中出現(xiàn),自然也得搭上 Lambda 的順風車,為了更好的理解 CompletableFuture,這里我需要先介紹一下幾個 Lambda 函數(shù),我們只需要關注它們的以下幾點就可以:
- 參數(shù)接受形式
- 返回值形式
- 函數(shù)名稱
Runnable
Runnable 我們已經(jīng)說過無數(shù)次了,無參數(shù),無返回值
@FunctionalInterface
public?interface?Runnable?{
????public?abstract?void?run();
}
Function
Function
@FunctionalInterface
public?interface?Function<T,?R>?{
????R?apply(T?t);
}
Consumer
Consumer接受一個參數(shù),沒有返回值
@FunctionalInterface
public?interface?Consumer<T>?{???
????void?accept(T?t);
}
Supplier
Supplier沒有參數(shù),有一個返回值
@FunctionalInterface
public?interface?Supplier<T>?{
????T?get();
}
BiConsumer
BiConsumer
@FunctionalInterface
public?interface?BiConsumer<T,?U>?{
????void?accept(T?t,?U?u);
好了,我們做個小匯總
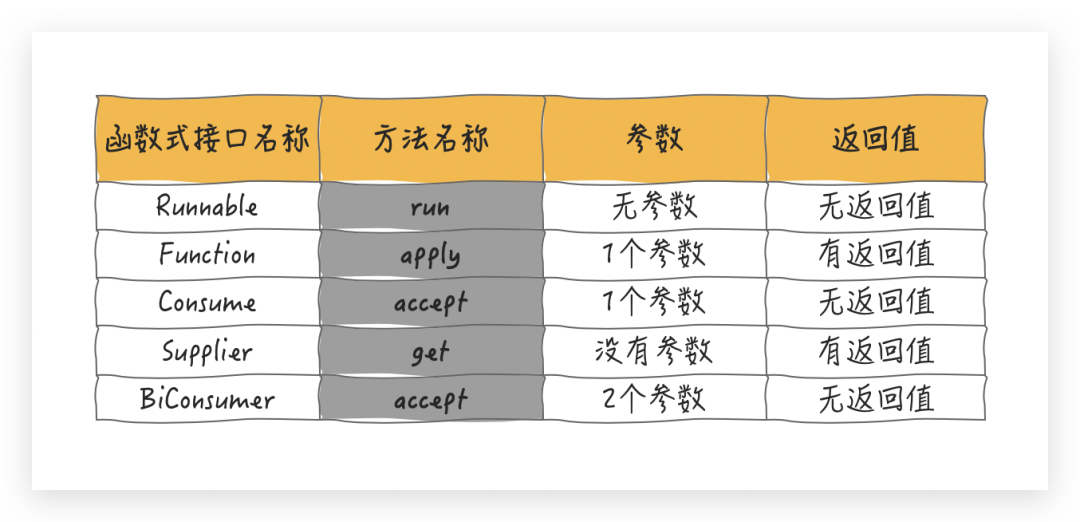
有些同學可能有疑問,為什么要關注這幾個函數(shù)式接口,因為 CompletableFuture 的函數(shù)命名以及其作用都是和這幾個函數(shù)式接口高度相關的,一會你就會發(fā)現(xiàn)了
前戲做足,終于可以進入正題了 CompletableFuture
CompletableFuture
類結(jié)構
老規(guī)矩,先從類結(jié)構看起:
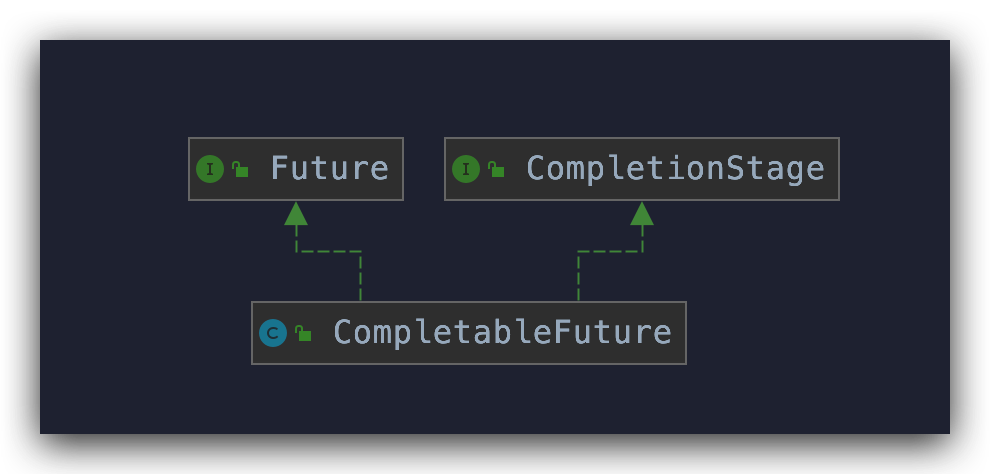
實現(xiàn)了 Future 接口
實現(xiàn)了 Future 接口,那就具有 Future 接口的相關特性,請腦補 Future 那少的可憐的 5 個方法,這里不再贅述,具體請查看 不會用Java Future,我懷疑你泡茶沒我快
實現(xiàn)了 CompletionStage 接口
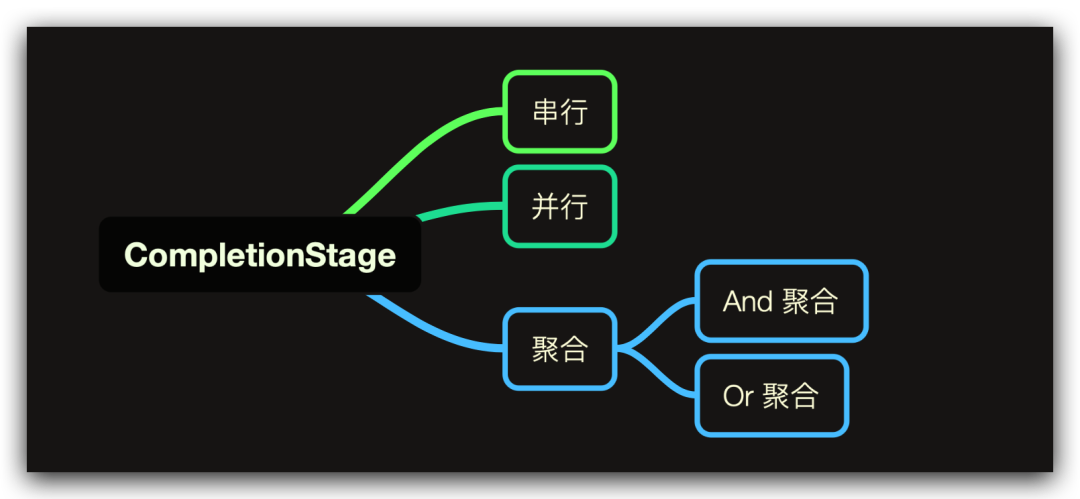
CompletionStage 這個接口還是挺陌生的,中文直譯過來是【竣工階段】,如果將燒水泡茶比喻成一項大工程,他們的竣工階段體現(xiàn)是不一樣的
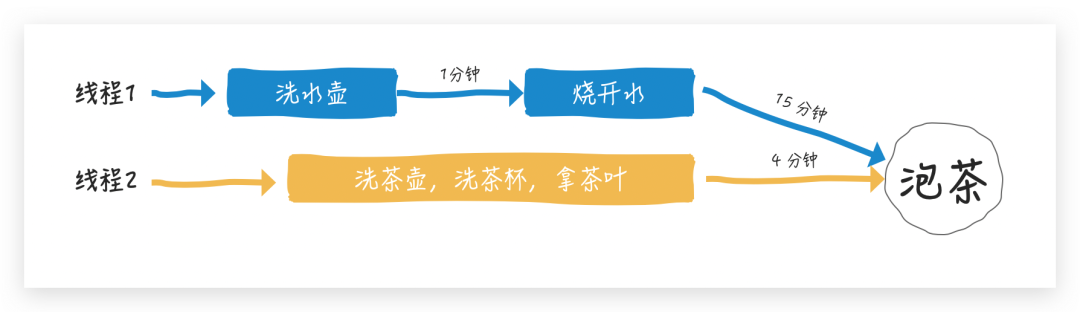
單看線程1 或單看線程 2 就是一種串行關系,做完一步之后做下一步
一起看線程1 和 線程 2,它們彼此就是并行關系,兩個線程做的事彼此獨立互補干擾
泡茶就是線程1 和 線程 2 的匯總/組合,也就是線程 1 和 線程 2 都完成之后才能到這個階段(當然也存在線程1 或 線程 2 任意一個線程竣工就可以開啟下一階段的場景)
所以,CompletionStage 接口的作用就做了這點事,所有函數(shù)都用于描述任務的時序關系,總結(jié)起來就是這個樣子:
CompletableFuture 既然實現(xiàn)了兩個接口,自然也就會實現(xiàn)相應的方法充分利用其接口特性,我們走進它的方法來看一看
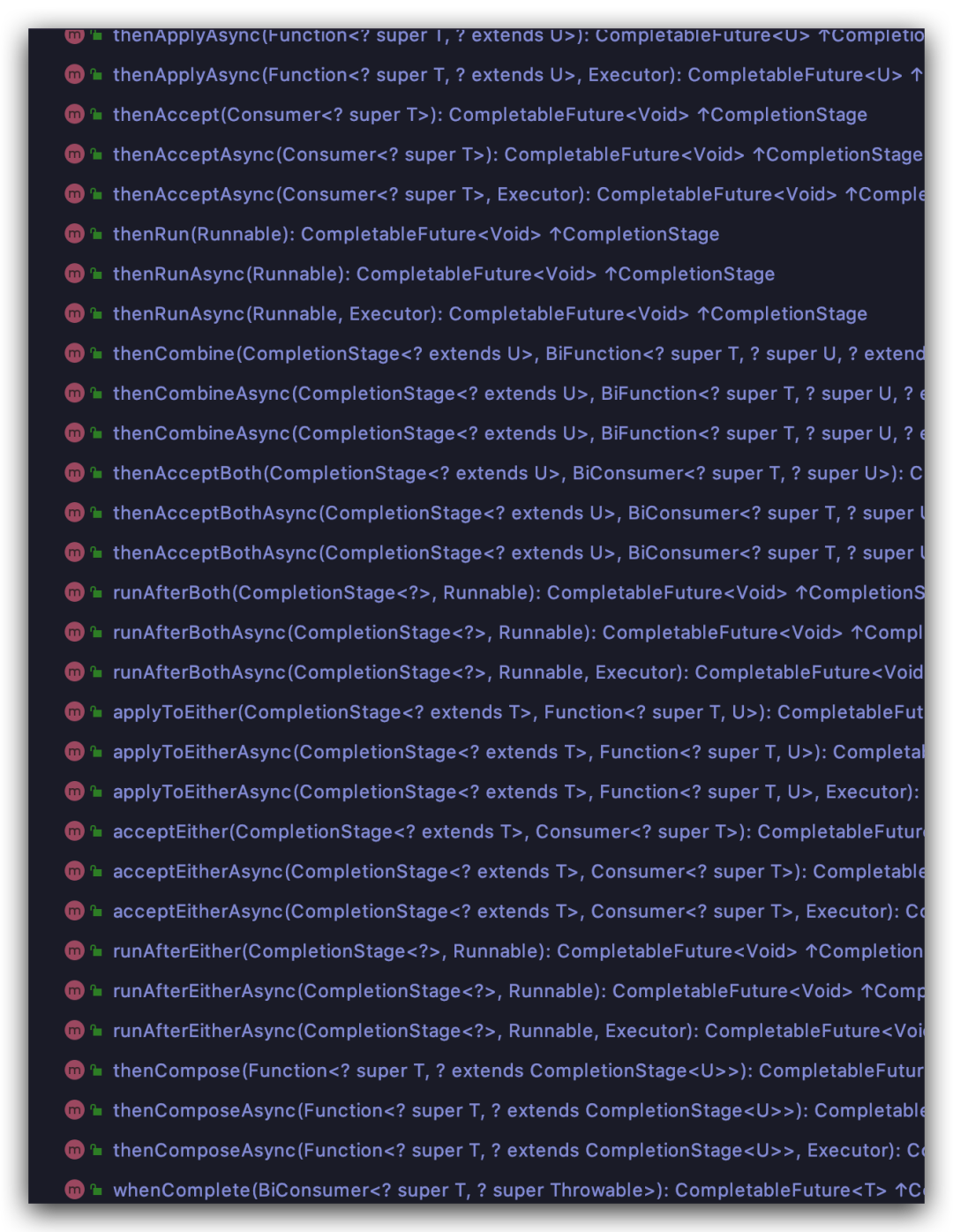
CompletableFuture 大約有50種不同處理串行,并行,組合以及處理錯誤的方法。小弟屏幕不爭氣,方法之多,一個屏幕裝不下,看到這么多方法,是不是瞬間要直接 收藏——>吃灰 2連走人?別擔心,我們按照相應的命名和作用進行分類,分分鐘搞定50多種方法
串行關系
then 直譯【然后】,也就是表示下一步,所以通常是一種串行關系體現(xiàn), then 后面的單詞(比如 run /apply/accept)就是上面說的函數(shù)式接口中的抽象方法名稱了,它的作用和那幾個函數(shù)式接口的作用是一樣一樣滴
CompletableFuture?thenRun(Runnable?action)
CompletableFuture?thenRunAsync(Runnable?action)
CompletableFuture?thenRunAsync(Runnable?action,?Executor?executor)
??
?CompletableFuture?thenApply(Functionsuper?T,??extends?U>?fn)
?CompletableFuture?thenApplyAsync(Functionsuper?T,??extends?U>?fn)
?CompletableFuture?thenApplyAsync(Functionsuper?T,??extends?U>?fn,?Executor?executor)
??
CompletableFuture?thenAccept(Consumersuper?T>?action)?
CompletableFuture?thenAcceptAsync(Consumersuper?T>?action)
CompletableFuture?thenAcceptAsync(Consumersuper?T>?action,?Executor?executor)
??
?CompletableFuture?thenCompose(Functionsuper?T,???extends?CompletionStage>?fn)??
?CompletableFuture?thenComposeAsync(Functionsuper?T,???extends?CompletionStage>?fn)
?CompletableFuture?thenComposeAsync(Functionsuper?T,???extends?CompletionStage>?fn,?Executor?executor)
聚合 And 關系
combine... with... 和 both...and... 都是要求兩者都滿足,也就是 and 的關系了
?CompletableFuture?thenCombine(CompletionStage?other,?BiFunctionsuper?T,??super?U,??extends?V>?fn)
?CompletableFuture?thenCombineAsync(CompletionStage?other,?BiFunctionsuper?T,??super?U,??extends?V>?fn)
?CompletableFuture?thenCombineAsync(CompletionStage?other,?BiFunctionsuper?T,??super?U,??extends?V>?fn,?Executor?executor)
?CompletableFuture?thenAcceptBoth(CompletionStage?other,?BiConsumersuper?T,???super?U>?action)
?CompletableFuture?thenAcceptBothAsync(CompletionStage?other,?BiConsumersuper?T,???super?U>?action)
?CompletableFuture?thenAcceptBothAsync(?CompletionStage?other,?BiConsumersuper?T,???super?U>?action,?Executor?executor)
??
CompletableFuture?runAfterBoth(CompletionStage?other,?Runnable?action)
CompletableFuture?runAfterBothAsync(CompletionStage?other,?Runnable?action)
CompletableFuture?runAfterBothAsync(CompletionStage?other,?Runnable?action,?Executor?executor)
聚合 Or 關系
Either...or... 表示兩者中的一個,自然也就是 Or 的體現(xiàn)了
?CompletableFuture?applyToEither(CompletionStage?other,?Functionsuper?T,?U>?fn)
?CompletableFuture?applyToEitherAsync(、CompletionStage?other,?Functionsuper?T,?U>?fn)
?CompletableFuture?applyToEitherAsync(CompletionStage?other,?Functionsuper?T,?U>?fn,?Executor?executor)
CompletableFuture?acceptEither(CompletionStage?other,?Consumersuper?T>?action)
CompletableFuture?acceptEitherAsync(CompletionStage?other,?Consumersuper?T>?action)
CompletableFuture?acceptEitherAsync(CompletionStage?other,?Consumersuper?T>?action,?Executor?executor)
CompletableFuture?runAfterEither(CompletionStage?other,?Runnable?action)
CompletableFuture?runAfterEitherAsync(CompletionStage?other,?Runnable?action)
CompletableFuture?runAfterEitherAsync(CompletionStage?other,?Runnable?action,?Executor?executor)
異常處理
CompletableFuture?exceptionally(Function?fn)
CompletableFuture?exceptionallyAsync(Function?fn)
CompletableFuture?exceptionallyAsync(Function?fn,?Executor?executor)
????????
CompletableFuture?whenComplete(BiConsumersuper?T,???super?Throwable>?action)
CompletableFuture?whenCompleteAsync(BiConsumersuper?T,???super?Throwable>?action)
CompletableFuture?whenCompleteAsync(BiConsumersuper?T,???super?Throwable>?action,?Executor?executor)
????????
???????
?CompletableFuture?handle(BiFunctionsuper?T,?Throwable,???extends?U>?fn)
?CompletableFuture?handleAsync(BiFunctionsuper?T,?Throwable,???extends?U>?fn)
?CompletableFuture?handleAsync(BiFunctionsuper?T,?Throwable,???extends?U>?fn,?Executor?executor)
這個異常處理看著還挺嚇人的,拿傳統(tǒng)的 try/catch/finally 做個對比也就瞬間秒懂了
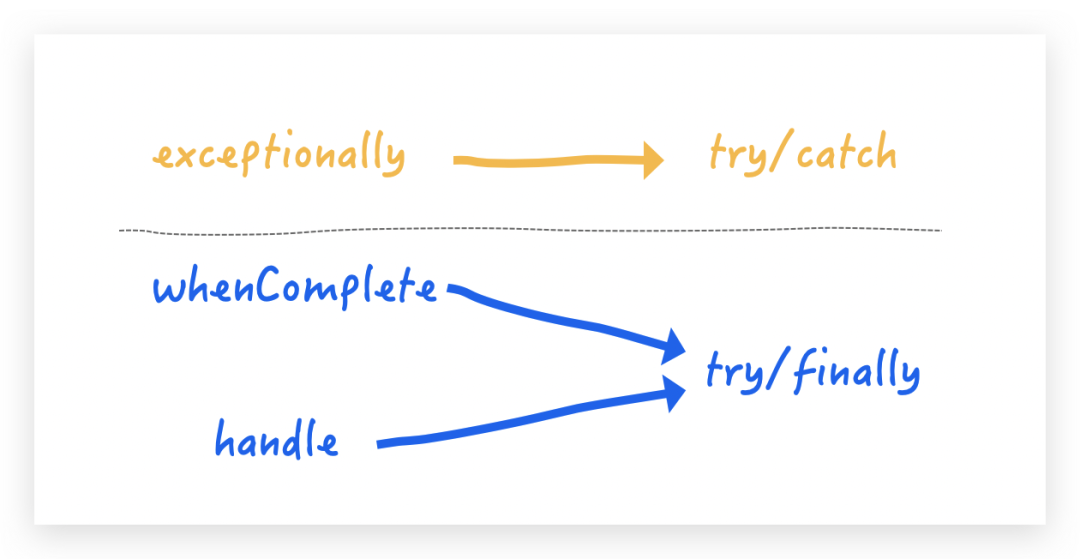
whenComplete 和 handle 的區(qū)別如果你看接受的參數(shù)函數(shù)式接口名稱你也就能看出差別了,前者使用Comsumer, 自然也就不會有返回值;后者使用 Function,自然也就會有返回值
這里并沒有全部列舉,不過相信很多同學已經(jīng)發(fā)現(xiàn)了規(guī)律:
CompletableFuture 提供的所有回調(diào)方法都有兩個異步(Async)變體,都像這樣
//?thenApply()?的變體
?CompletableFuture?thenApply(Functionsuper?T,??extends?U>?fn)
?CompletableFuture?thenApplyAsync(Functionsuper?T,??extends?U>?fn)
?CompletableFuture?thenApplyAsync(Functionsuper?T,??extends?U>?fn,?Executor?executor)
另外,方法的名稱也都與前戲中說的函數(shù)式接口完全匹配,按照這中規(guī)律分類之后,這 50 多個方法看起來是不是很輕松了呢?
基本方法已經(jīng)羅列的差不多了,接下來我們通過一些例子來實際演示一下:
案例演示
創(chuàng)建一個 CompletableFuture 對象
創(chuàng)建一個 CompletableFuture 對象并沒有什么稀奇的,依舊是通過構造函數(shù)構建
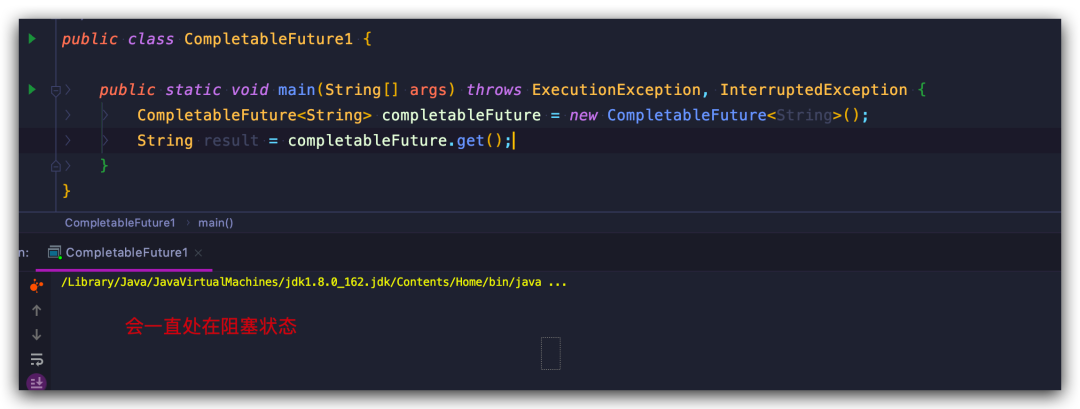
CompletableFuture?completableFuture?=?new?CompletableFuture();
這是最簡單的 CompletableFuture 對象創(chuàng)建方式,由于它實現(xiàn)了 Future 接口,所以自然就可以通過 get() 方法獲取結(jié)果
String?result?=?completableFuture.get();
文章開頭已經(jīng)說過,get()方法在任務結(jié)束之前將一直處在阻塞狀態(tài),由于上面創(chuàng)建的 Future 沒有返回,所以在這里調(diào)用 get() 將會永久性的堵塞
這時就需要我們調(diào)用 complete() 方法手動的結(jié)束一個 Future
completableFuture.complete("Future's?Result?Here?Manually");
這時,所有等待這個 Future 的 client 都會返回手動結(jié)束的指定結(jié)果
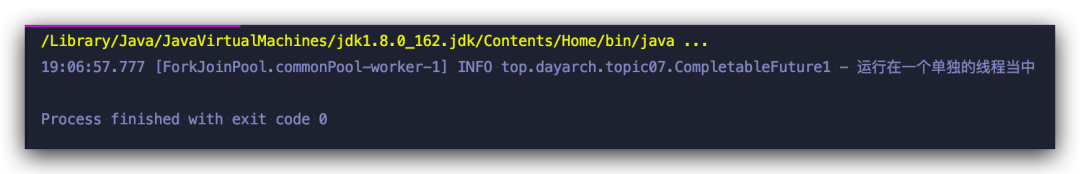
runAsync
使用 runAsync 進行異步計算
CompletableFuture?future?=?CompletableFuture.runAsync(()?->?{
????try?{
????????TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(3);
????}?catch?(InterruptedException?e)?{
????????throw?new?IllegalStateException(e);
????}
????System.out.println("運行在一個單獨的線程當中");
});
future.get();
由于使用的是 Runnable 函數(shù)式表達式,自然也不會獲取到結(jié)果
supplyAsync
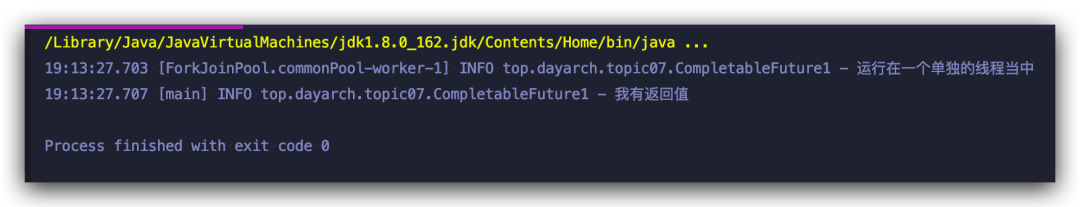
使用 runAsync 是沒有返回結(jié)果的,我們想獲取異步計算的返回結(jié)果需要使用 supplyAsync() 方法
??CompletableFuture?future?=?CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(()?->?{
???try?{
????TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(3);
???}?catch?(InterruptedException?e)?{
????throw?new?IllegalStateException(e);
???}
???log.info("運行在一個單獨的線程當中");
???return?"我有返回值";
??});
??log.info(future.get());
由于使用的是 Supplier 函數(shù)式表達式,自然可以獲得返回結(jié)果
我們已經(jīng)多次說過,get() 方法在Future 計算完成之前會一直處在 blocking 狀態(tài)下,對于真正的異步處理,我們希望的是可以通過傳入回調(diào)函數(shù),在Future 結(jié)束時自動調(diào)用該回調(diào)函數(shù),這樣,我們就不用等待結(jié)果
CompletableFuture?comboText?=?CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(()?->?{
????//可以注釋掉做快速返回?start
???try?{
????TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(3);
???}?catch?(InterruptedException?e)?{
????throw?new?IllegalStateException(e);
???}
???log.info("?");
????//可以注釋掉做快速返回?end
???return?"贊";
??})
????.thenApply(first?->?{
?????log.info("在看");
?????return?first?+?",?在看";
????})
????.thenApply(second?->?second?+?",?轉(zhuǎn)發(fā)");
??log.info("三連有沒有?");
??log.info(comboText.get());
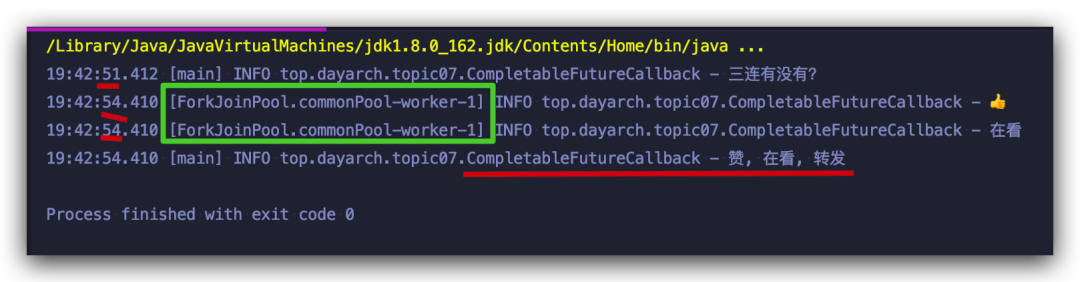
對 thenApply 的調(diào)用并沒有阻塞程序打印log,也就是前面說的通過回調(diào)通知機制, 這里你看到 thenApply ?使用的是supplyAsync所用的線程,如果將supplyAsync 做快速返回,我們再來看一下運行結(jié)果:
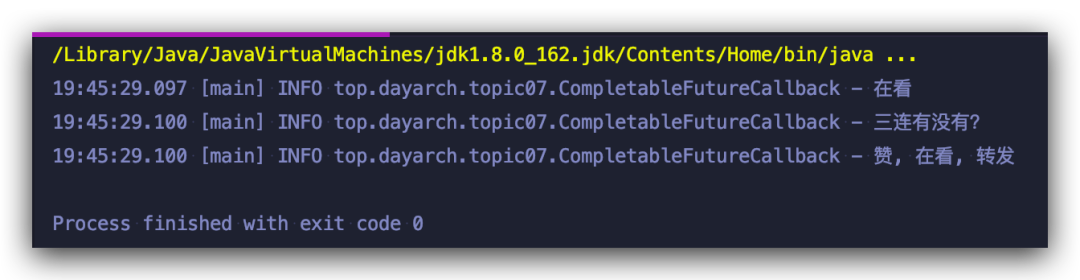
thenApply 此時使用的是主線程,所以:
串行的后續(xù)操作并不一定會和前序操作使用同一個線程
thenAccept
如果你不想從回調(diào)函數(shù)中返回任何結(jié)果,那可以使用 thenAccept
??final?CompletableFuture?voidCompletableFuture?=?CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(
????//?模擬遠端API調(diào)用,這里只返回了一個構造的對象
????()?->?Product.builder().id(12345L).name("頸椎/腰椎治療儀").build())
????.thenAccept(product?->?{
?????log.info("獲取到遠程API產(chǎn)品名稱?"?+?product.getName());
????});
??voidCompletableFuture.get();
thenRun
thenAccept 可以從回調(diào)函數(shù)中獲取前序執(zhí)行的結(jié)果,但thenRun 卻不可以,因為它的回調(diào)函數(shù)式表達式定義中沒有任何參數(shù)
CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(()?->?{
????//前序操作
}).thenRun(()?->?{
????//串行的后需操作,無參數(shù)也無返回值
});
我們前面同樣說過了,每個提供回調(diào)方法的函數(shù)都有兩個異步(Async)變體,異步就是另外起一個線程
??CompletableFuture?stringCompletableFuture?=?CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(()?->?{
???log.info("前序操作");
???return?"前需操作結(jié)果";
??}).thenApplyAsync(result?->?{
???log.info("后續(xù)操作");
???return?"后續(xù)操作結(jié)果";
??});
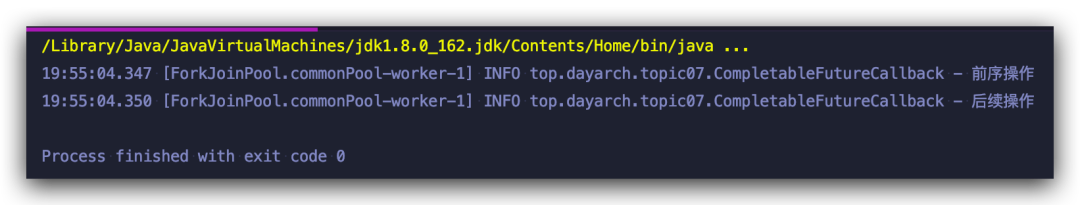
到這里,相信你串行的操作你已經(jīng)非常熟練了
thenCompose
日常的任務中,通常定義的方法都會返回 CompletableFuture 類型,這樣會給后續(xù)操作留有更多的余地,假如有這樣的業(yè)務(X唄是不是都有這樣的業(yè)務呢?):
//獲取用戶信息詳情
?CompletableFuture?getUsersDetail(String?userId)? {
??return?CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(()?->?User.builder().id(12345L).name("日拱一兵").build());
?}
?//獲取用戶信用評級
?CompletableFuture?getCreditRating(User?user)? {
??return?CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(()?->?CreditRating.builder().rating(7.5).build().getRating());
?}
這時,如果我們還是使用 thenApply() 方法來描述串行關系,返回的結(jié)果就會發(fā)生 CompletableFuture 的嵌套
??CompletableFuture>?result?=?completableFutureCompose.getUsersDetail(12345L)
????.thenApply(user?->?completableFutureCompose.getCreditRating(user));
顯然這不是我們想要的,如果想“拍平” 返回結(jié)果,thenCompose 方法就派上用場了
CompletableFuture?result?=?completableFutureCompose.getUsersDetail(12345L)
????.thenCompose(user?->?completableFutureCompose.getCreditRating(user));
這個和 Lambda 的map 和 flatMap 的道理是一樣一樣滴
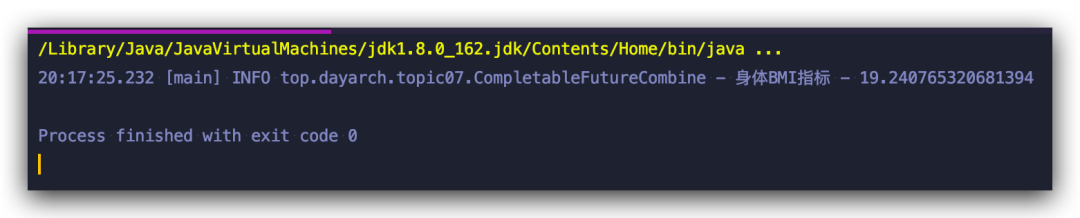
thenCombine
如果要聚合兩個獨立 Future 的結(jié)果,那么 thenCombine 就會派上用場了
??CompletableFuture?weightFuture?=?CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(()?->?65.0);
??CompletableFuture?heightFuture?=?CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(()?->?183.8);
??
??CompletableFuture?combinedFuture?=?weightFuture
????.thenCombine(heightFuture,?(weight,?height)?->?{
?????Double?heightInMeter?=?height/100;
?????return?weight/(heightInMeter*heightInMeter);
????});
??log.info("身體BMI指標?-?"?+?combinedFuture.get());
當然這里多數(shù)時處理兩個 Future 的關系,如果超過兩個Future,如何處理他們的一些聚合關系呢?
allOf | anyOf
相信你看到方法的簽名,你已經(jīng)明白他的用處了,這里就不再介紹了
static?CompletableFuture??allOf(CompletableFuture...?cfs)
static?CompletableFuture 接下來就是異常的處理了
exceptionally
??Integer?age?=?-1;
??CompletableFuture?maturityFuture?=?CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(()?->?{
???if(?age?0?)?{
????throw?new?IllegalArgumentException("何方神圣?");
???}
???if(age?>?18)?{
????return?"大家都是成年人";
???}?else?{
????return?"未成年禁止入內(nèi)";
???}
??}).thenApply((str)?->?{
???log.info("游戲開始");
???return?str;
??}).exceptionally(ex?->?{
???log.info("必有蹊蹺,來者"?+?ex.getMessage());
???return?"Unknown!";
??});
??log.info(maturityFuture.get());
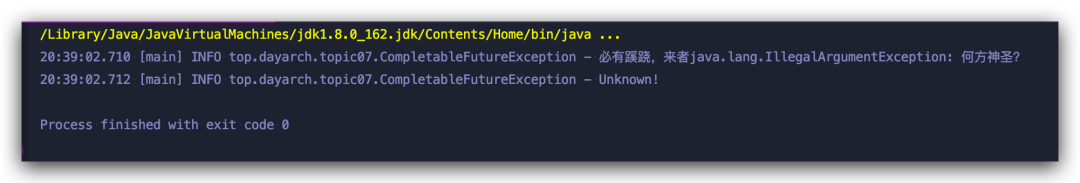
exceptionally 就相當于 catch,出現(xiàn)異常,將會跳過 thenApply 的后續(xù)操作,直接捕獲異常,進行一場處理
handle
用多線程,良好的習慣是使用 try/finally 范式,handle 就可以起到 finally 的作用,對上述程序做一個小小的更改, handle 接受兩個參數(shù),一個是正常返回值,一個是異常
注意:handle的寫法也算是范式的一種
??Integer?age?=?-1;
??CompletableFuture?maturityFuture?=?CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(()?->?{
???if(?age?0?)?{
????throw?new?IllegalArgumentException("何方神圣?");
???}
???if(age?>?18)?{
????return?"大家都是成年人";
???}?else?{
????return?"未成年禁止入內(nèi)";
???}
??}).thenApply((str)?->?{
???log.info("游戲開始");
???return?str;
??}).handle((res,?ex)?->?{
???if(ex?!=?null)?{
????log.info("必有蹊蹺,來者"?+?ex.getMessage());
????return?"Unknown!";
???}
???return?res;
??});
??log.info(maturityFuture.get());
到這里,關于 CompletableFuture 的基本使用你已經(jīng)了解的差不多了,不知道你是否注意,我們前面說的帶有 Sync 的方法是單獨起一個線程來執(zhí)行,但是我們并沒有創(chuàng)建線程,這是怎么實現(xiàn)的呢?
細心的朋友如果仔細看每個變種函數(shù)的第三個方法也許會發(fā)現(xiàn)里面都有一個 Executor 類型的參數(shù),用于指定線程池,因為實際業(yè)務中我們是嚴謹手動創(chuàng)建線程的,這在 我會手動創(chuàng)建線程,為什么要使用線程池?文章中明確說明過;如果沒有指定線程池,那自然就會有一個默認的線程池,也就是 ForkJoinPool
private?static?final?Executor?ASYNC_POOL?=?USE_COMMON_POOL??
????ForkJoinPool.commonPool()?:?new?ThreadPerTaskExecutor();
ForkJoinPool 的線程數(shù)默認是 CPU 的核心數(shù)。但是,在前序文章中明確說明過:
不要所有業(yè)務共用一個線程池,因為,一旦有任務執(zhí)行一些很慢的 I/O 操作,就會導致線程池中所有線程都阻塞在 I/O 操作上,從而造成線程饑餓,進而影響整個系統(tǒng)的性能
總結(jié)
CompletableFuture 的方法并沒有全部介紹完全,也沒必要全部介紹,相信大家按照這個思路來理解 CompletableFuture 也不會有什么大問題了,剩下的就交給實踐/時間以及自己的體會了
后記
你以為 JDK1.8 CompletableFuture 已經(jīng)很完美了是不是,但追去完美的道路上永無止境,Java 9 對CompletableFuture 又做了部分升級和改造
添加了新的工廠方法
支持延遲和超時處理
orTimeout()
completeOnTimeout()改進了對子類的支持
詳情可以查看:Java 9 CompletableFuture API Improvements. 怎樣快速的切換不同 Java 版本來嘗鮮?SDKMAN 統(tǒng)一靈活管理多版本Java 這篇文章的方法送給你
最后咱們再泡一壺茶,感受一下新變化吧
靈魂追問
- 聽說 ForkJoinPool 線程池效率更高,為什么呢?
- 如果批量處理異步程序,有什么可用的方案嗎?
參考
- Java 并發(fā)編程實戰(zhàn)
- Java 并發(fā)編程的藝術
- Java 并發(fā)編程之美
- https://www.baeldung.com/java-completablefuture
- https://www.callicoder.com/java-8-completablefuture-tutorial/
完
? ? ? ?
 ???●不會用 Java Future,我懷疑你泡茶都沒我快●深入了解 String、StringBuilder 和 StringBuffer 三兄弟
???●不會用 Java Future,我懷疑你泡茶都沒我快●深入了解 String、StringBuilder 和 StringBuffer 三兄弟●讀 Spring 源碼,我們可以從第一行讀起
覺得不錯,點個在看~