從零開始漫談 | 多實例的狀態(tài)機(jī)
來源:裸機(jī)思維
作者:GorgonMeducer
【說在前面的話】
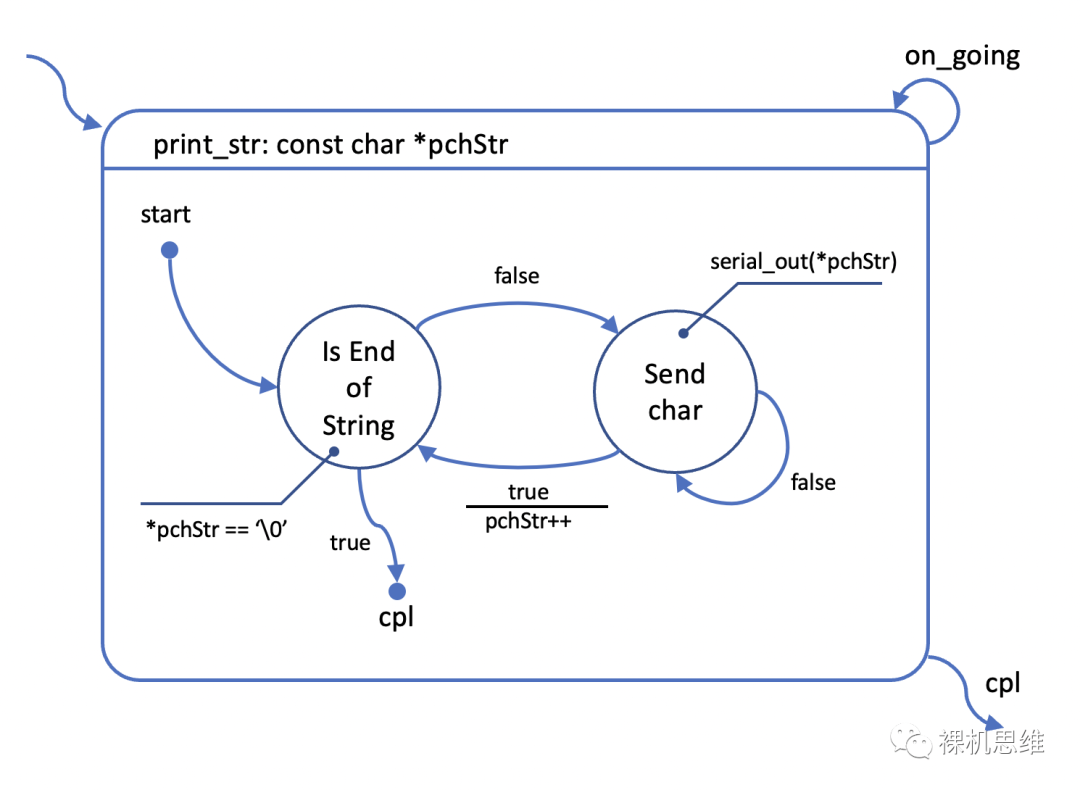
typedef enum {fsm_rt_err = -1,fsm_rt_on_going = 0,fsm_rt_cpl = 1,} fsm_rt_t;extern bool serial_out(uint8_t chByte);do { s_tState = START; } while(0)fsm_rt_t print_str(const char *pchStr){static enum {START = 0,IS_END_OF_STRING,SEND_CHAR,} s_tState = START;switch (s_tState) {case START:s_tState = IS_END_OF_STRING;break;case IS_END_OF_STRING:if (*pchStr == '\0') {PRINT_STR_RESET_FSM();return fsm_rt_cpl;}s_tState = SEND_CHAR;break;case SEND_CHAR:if (serial_out(*pchStr)) {pchStr++;s_tState = IS_END_OF_STRING;}break;}return fsm_rt_on_going;}
int main(void){...while(true) {static const char c_tDemoStr[] = {"Hello world!\r\n"};print_str(c_tDemoStr);}}
還沒看出問題么?
pchStr是一個局部變量,它保存了狀態(tài)機(jī)函數(shù) print_str 被調(diào)用時用戶所傳遞的字符串首地址;
該狀態(tài)機(jī)在執(zhí)行的過程中,不可避免的要多次出讓(Yield)處理器時間,以達(dá)到“非阻塞”的目的;
由于pchStr是一個局部變量,它的生命周期在退出print_str函數(shù)后就結(jié)束了;而每次重新進(jìn)入print_str函數(shù),它的值都會被復(fù)位成“hello world\r\n”的起始地址。
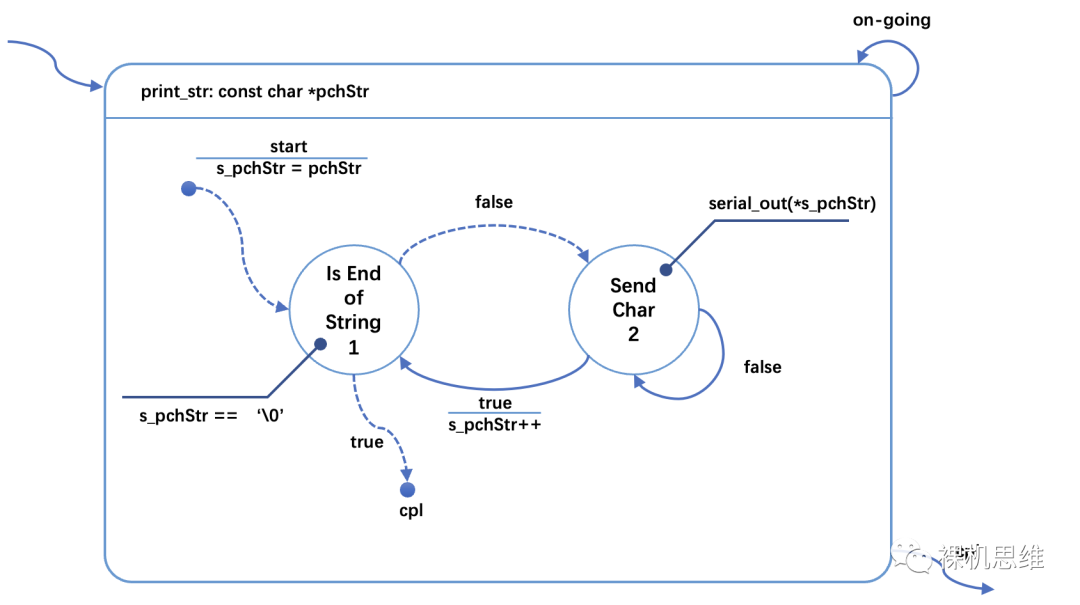
fsm_rt_t print_str(const char *pchStr){static enum {START = 0,IS_END_OF_STRING,SEND_CHAR,} s_tState = START;static const char *s_pchStr = NULL;switch (s_tState) {case START:s_pchStr = pchStr;s_tState = IS_END_OF_STRING;//break; //!< fall-throughcase IS_END_OF_STRING:if (*s_pchStr == '\0') {PRINT_STR_RESET_FSM();return fsm_rt_cpl;}s_tState = SEND_CHAR;//break; //!< fall-throughcase SEND_CHAR:if (serial_out(*s_pchStr)) {pchStr++;s_tState = IS_END_OF_STRING;}break;}return fsm_rt_on_going;}
【一系列似是而非的問題……】
狀態(tài)機(jī)print_str 使用了靜態(tài)變量來保存狀態(tài)(s_tState)和關(guān)鍵的上下文(s_pchStr),因此幾乎肯定是不可重入的;
狀態(tài)機(jī)print_str使用了共享函數(shù)serial_out(),即便該函數(shù)本身可以保證原子性,但它仍然是一個臨界資源——換句話說,即便拋開 print_str 的可重入性問題不談,當(dāng)有該狀態(tài)機(jī)存在多個實例時,你能保證每個字符串的打印都是完整的么?比如:
int main(void){...while(true) {print_str(“I have a pen...”);print_str("I have an apple...");}}
In computing, ... a reentrant procedure can be interrupted in the middle of its execution and then safely be called again ("re-entered") before its previous invocations complete execution.
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Reentrancy_(computing)
大體翻譯成中文就是:
可重入的函數(shù)不一定線程安全;
線程安全的函數(shù)也不一定可重入。
【多實例的狀態(tài)機(jī)】
為狀態(tài)機(jī)定義一個控制塊;
在控制塊里存放狀態(tài)變量;
在控制塊里存放狀態(tài)機(jī)的上下文;
建立狀態(tài)機(jī)實例時,首先要建立一個控制塊,并對其進(jìn)行必要的初始化;
在隨后調(diào)用狀態(tài)機(jī)時,應(yīng)該首先傳遞狀態(tài)機(jī)的控制塊給狀態(tài)機(jī)函數(shù)。
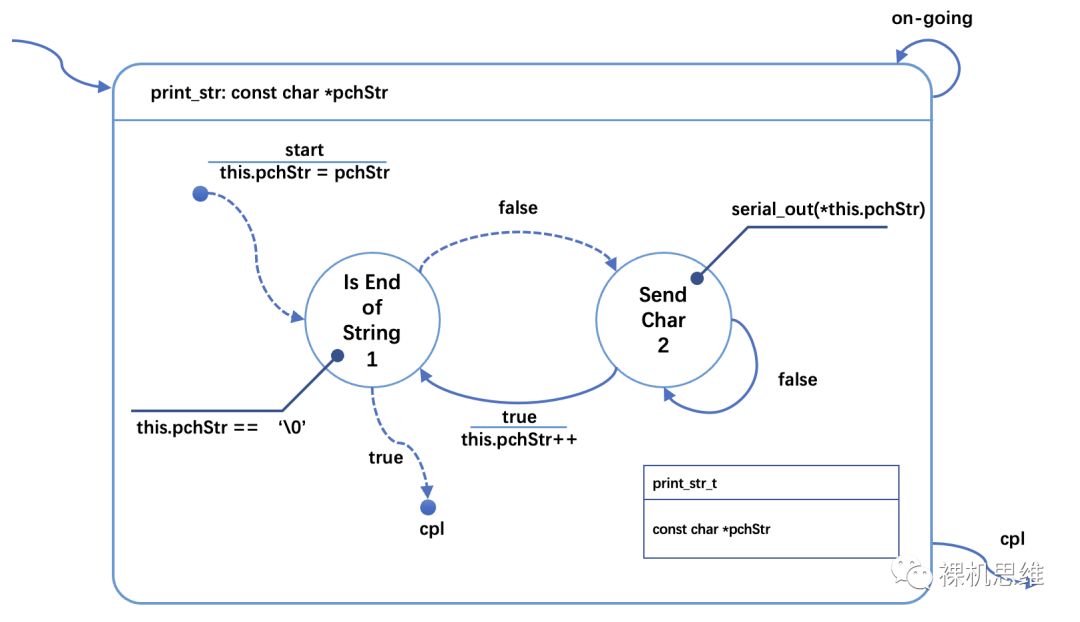
在圖的右下角,出現(xiàn)了一個帶標(biāo)題的矩形框。這里標(biāo)題print_str_t是狀態(tài)機(jī)控制塊的類型名稱;下面的列表中列舉了上下文的內(nèi)容,在本例中就是 pchStr,注意,它已經(jīng)去掉了"s_"前綴。
狀態(tài)圖中通過 "this.xxxx" 的方式來訪問狀態(tài)機(jī)上下文中的內(nèi)容。
【基本的翻譯方法】
typedef struct <控制塊類型名稱> {uint8_t chState; //!< 狀態(tài)變量<上下文列表>} <控制塊類型名稱>;
以print_str狀態(tài)圖為例:
typedef struct print_str_t {uint8_t chState; //!< 狀態(tài)變量const char *pchStr; //!< 上下文} print_str_t;
...int <狀態(tài)機(jī)名稱>_init(<狀態(tài)機(jī)類型名稱> *ptThis[, <形參列表>]){...this.chState = 0; //!< 復(fù)位狀態(tài)變量,這里固定用0/*! \note 這里根據(jù)需要可以初始化那些只需要初始化一次的上下文*//*! \note 這里也可以對輸入的參數(shù)進(jìn)行有效性檢測,如果發(fā)現(xiàn)錯誤,*! 就返回負(fù)數(shù)值。這里既可以自定義一套枚舉,也可以簡單*! 返回 -1 了事。*/return 0; //!< 如果一切順利返回0,表示正常}
int print_str_init(print_str_t *ptThis){if (NULL == ptThis) {return -1; //!< 是的,我偷懶了}this.chState = 0;//在這個例子中,this.pchStr 更適合在運(yùn)行時刻由用戶指定。return 0;}
fsm_rt_t <狀態(tài)機(jī)名稱>(<狀態(tài)機(jī)類型名> *ptThis[, <形參列表>]){//!< 這種事情就不適合在release版本的運(yùn)行時刻檢查assert(NULL != ptThis);enum {START = 0,<狀態(tài)列表>};...switch (this.chState) {...}return fsm_rt_on_going;}

最后,該圖的翻譯為:
#undef this#define this (*ptThis)#define PRINT_STR_RESET_FSM() \do { this.State = START; } while(0)fsm_rt_t print_str(print_str_t *ptThis, const char *pchStr){enum {START = 0,IS_END_OF_STRING,SEND_CHAR,};switch (this.chState) {case START:this.pchStr = pchStr;this.chState = IS_END_OF_STRING;//break; //!< fall-throughcase IS_END_OF_STRING:if (*(this.pchStr) == '\0') {PRINT_STR_RESET_FSM();return fsm_rt_cpl;}this.chState = SEND_CHAR;//break; //!< fall-throughcase SEND_CHAR:if (serial_out(*(this.pchStr))) {this.pchStr++;this.chState = IS_END_OF_STRING;}break;}return fsm_rt_on_going;}
此時,我們就可以“安全”的進(jìn)行多實例調(diào)用了:
static print_str_t s_tPrintTaskA;static print_str_t s_tPrintTaskB;int main(void){...print_str_init(&s_tPrintTaskA);print_str_init(&s_tPrintTaskB);while(true) {print_str(&s_tPrintTaskA, “I have a pen...”);print_str(&s_tPrintTaskB, "I have an apple...");}}
至此,我們就完成了狀態(tài)機(jī)print_str多實例的整個改造和部署過程。
【說在后面的話】
控制塊的定義就是狀態(tài)機(jī)的類(Class)定義;
狀態(tài)機(jī)函數(shù)是類的方法(Method);
初始化函數(shù)是類的構(gòu)造函數(shù)(Constructor);
實際上,狀態(tài)機(jī)函數(shù)中用 this 來訪問上下文,也已經(jīng)暴露其OO的本質(zhì)。
結(jié)合我在《真刀真槍模塊化(2.5)—— 君子協(xié)定》介紹的方法,我們還可以真正做到對狀態(tài)機(jī)的類進(jìn)行私有化保護(hù)——是不是格局越來越大了呢?
???????????????? END ???????????????? 關(guān)注我的微信公眾號,回復(fù)“加群”按規(guī)則加入技術(shù)交流群。
點(diǎn)擊“閱讀原文”查看更多分享,歡迎點(diǎn)分享、收藏、點(diǎn)贊、在看。
