18 個(gè) Jupyter Notebook 小技巧,幫助你快速騰飛
作者丨周蘿卜
來源丨蘿卜大雜燴
Jupyter Notebook 是干嘛的就不再過多介紹了,這篇文章收集了一些頂級(jí)的 Jupyter Notebook 技巧,可以讓你迅速成為一個(gè) Jupyter 超級(jí)使用者!
作為一款完全免費(fèi)的產(chǎn)品,它的身上有太多值得探索的內(nèi)容了,這里整理了28個(gè),希望能夠?qū)δ阌兴鶐椭?/p>
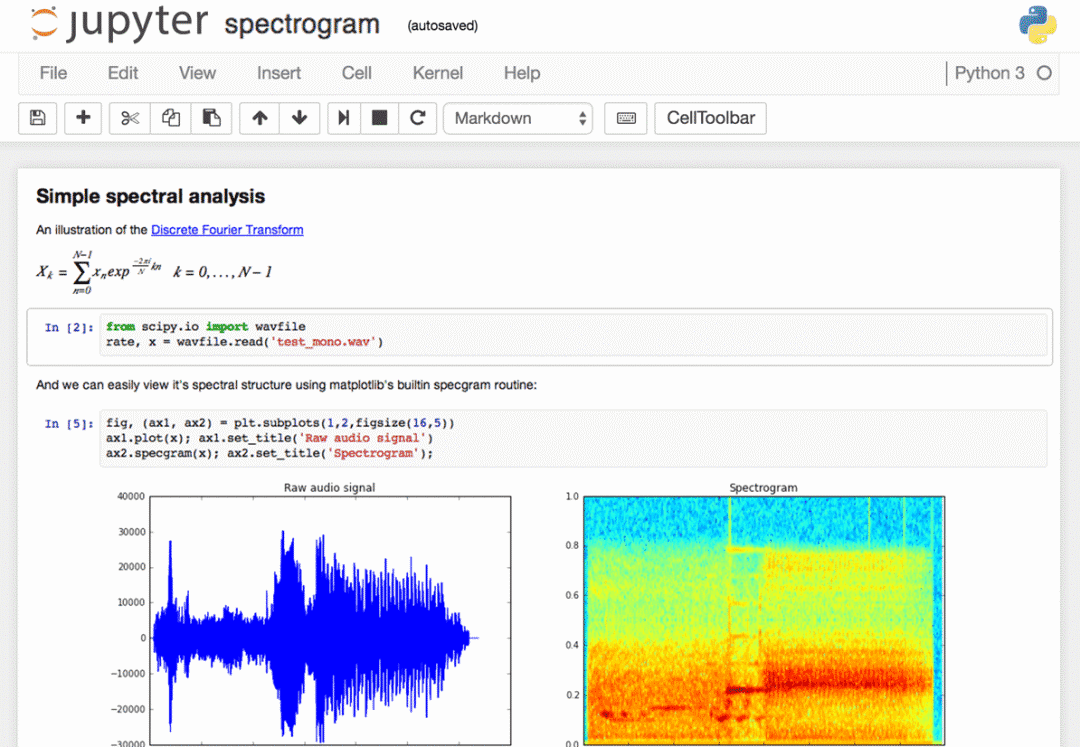
1、快捷鍵
任何重度用戶應(yīng)該都知道,鍵盤快捷鍵的有效使用可以節(jié)省大量時(shí)間。Jupyter 在頂部的菜單下存儲(chǔ)了一個(gè) keybord 快捷鍵列表:Help>Keyboard shortcuts,或者在命令模式下按H鍵也可以調(diào)出。我們每次更新 Jupyter 時(shí)都需要檢查一下快捷鍵的情況,因?yàn)楹芏鄷r(shí)候總是會(huì)添加更多的快捷方式。
另一種訪問快捷鍵的方法,也是學(xué)習(xí)快捷鍵的一種簡(jiǎn)便方法,就是使用命令面板:Cmd+Shift+P(在Linux和Windows上是Ctrl+Shift+P)。這個(gè)對(duì)話框可幫助我們按名稱運(yùn)行任何命令—如果我們不知道某個(gè)操作的鍵盤快捷鍵,或者想要執(zhí)行的操作沒有鍵盤快捷鍵,那么該對(duì)話框?qū)⑹欠浅S杏谩K墓δ茴愃朴?Mac 上的 Spotlight 搜索,一旦我們開始使用它,你就會(huì)依賴它,以至于會(huì)想沒有它你會(huì)怎么生活!
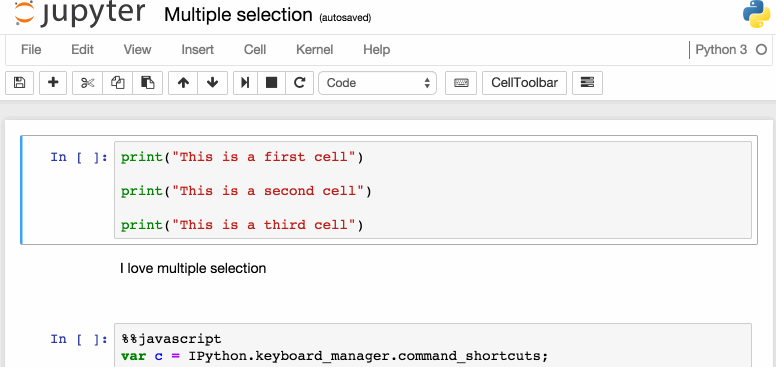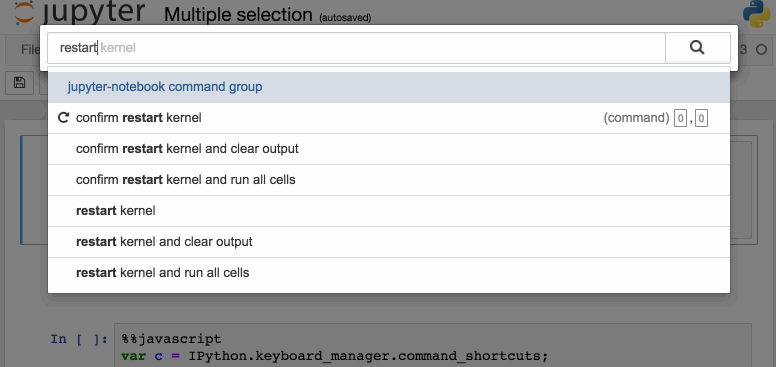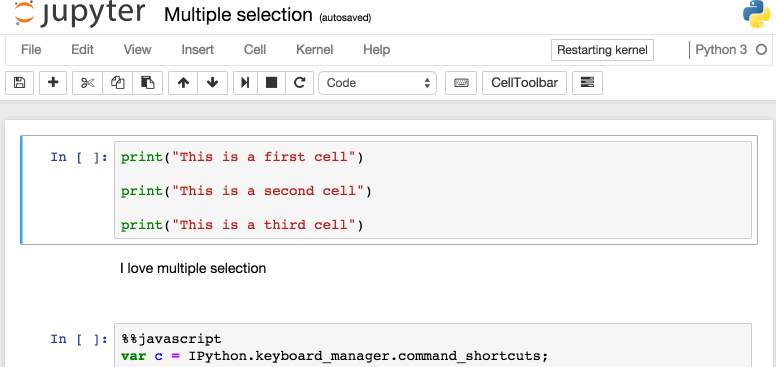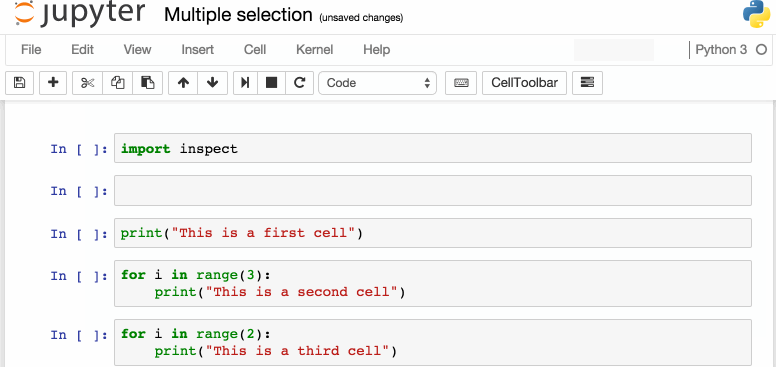
下面是一些我個(gè)人比較喜歡的快捷鍵:
Esc 進(jìn)入命令模式
在命令模式下:
A要在當(dāng)前單元格上方插入新單元格,B將在下面插入新單元格。
M要將當(dāng)前單元格更改為標(biāo)記,Y將其更改為代碼
D+D(按兩次鍵)刪除當(dāng)前單元格
Enter將使我們從命令模式返回到給定單元格的編輯模式。
Shift+Tab將顯示剛輸入代碼單元的對(duì)象的Docstring(文檔)——可以繼續(xù)按此鍵切換以循環(huán)使用幾種文檔模式。
Ctrl+Shift+-將當(dāng)前單元格從光標(biāo)所在的位置拆分為兩個(gè)。
Esc+F查找并替換代碼,但不是輸出。
Esc+O切換單元格輸出。
選擇多個(gè)單元格:
Shift+J或Shift+Down選擇下一個(gè)單元格,也可以使用Shift+K或Shift+Up選擇向上一個(gè)單元格。
一旦我們選擇了多個(gè)單元格,就可以對(duì)它們進(jìn)行批量的刪除/復(fù)制/剪切/粘貼/運(yùn)行,這個(gè)功能在需要修改部分腳本是是很有幫助的。
可以使用Shift+M合并多個(gè)單元格。
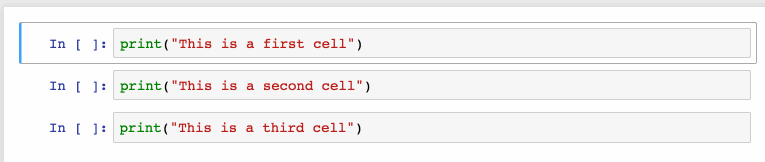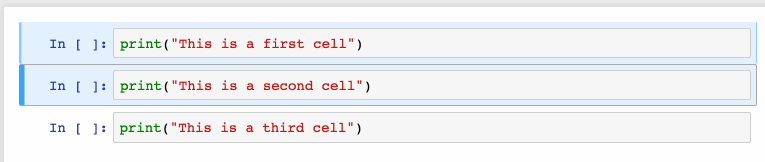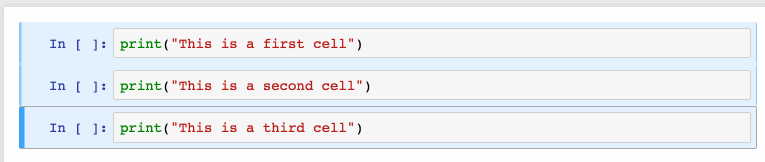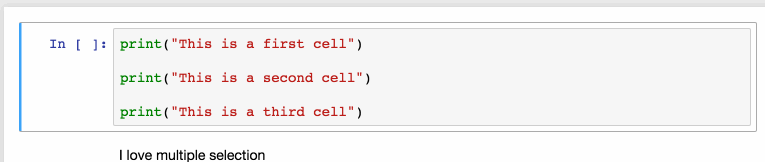
2、漂亮的顯示變量
我們都知道,通過使用變量名或語(yǔ)句的未賦值輸出完成Jupyter單元格,Jupyter將顯示該變量,而不需要print語(yǔ)句。這在處理數(shù)據(jù)幀時(shí)特別有用,因?yàn)檩敵霰徽R地格式化為一個(gè)表。
但是鮮為人知的是,我們可以修改一個(gè) ast_note_interactivity 選項(xiàng),使Jupyter對(duì)自己行中的任何變量或語(yǔ)句執(zhí)行此操作,這樣我們就可以一次看到多個(gè)語(yǔ)句的值。
from IPython.core.interactiveshell import InteractiveShell
InteractiveShell.ast_node_interactivity = "all"
from pydataset import data
quakes = data('quakes')
quakes.head()
quakes.tail()
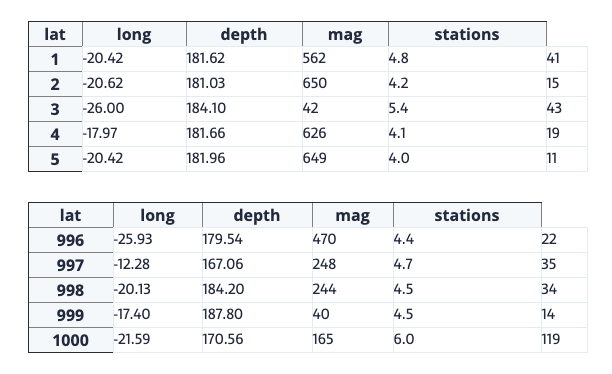
如果要為所有Jupyter實(shí)例(筆記本和控制臺(tái))設(shè)置這個(gè)行為,只需創(chuàng)建一個(gè)文件~/.ipython/profile_default/ipython_config.py,通過下面的代碼實(shí)現(xiàn)
c = get_config()
# Run all nodes interactively
c.InteractiveShell.ast_node_interactivity = "all"
3、文檔的簡(jiǎn)單鏈接
在“幫助”菜單中,可以找到指向常用庫(kù)(包括NumPy、Pandas、SciPy和Matplotlib)的聯(lián)機(jī)文檔鏈接。
但是我們也應(yīng)該知道,在庫(kù)、方法或變量前面加上?,也可以訪問Docstring以快速參考語(yǔ)法。
?str.replace()
Docstring:
S.replace(old, new[, count]) -> str
Return a copy of S with all occurrences of substring
old replaced by new. If the optional argument count is
given, only the first count occurrences are replaced.
Type: method_descriptor
4、繪圖
有許多方法可以在notebook中繪制圖片
matplotlib,用%matplotlib inline激活–大部分情況下,使用matplotlib繪圖是實(shí)際上的標(biāo)準(zhǔn)
%matplotlib notebook提供了交互性,但是速度可能有點(diǎn)慢,因?yàn)樗械匿秩径际窃诜?wù)器端完成的。
Seaborn是建立在Matplotlib之上的,它使得建造更具吸引力的圖片變得更加容易。只需導(dǎo)入Seaborn,matplotlib繪圖就變得“更漂亮”,無(wú)需任何代碼修改。
mpld3為matplotlib代碼提供了可選的呈現(xiàn)器(使用d3)。很好,可以選擇嘗試下。
bokeh是一個(gè)更好的選擇,可以建立互動(dòng)的場(chǎng)景。
ploy.ly可以繪制一些很棒的動(dòng)態(tài)圖表-雖然曾經(jīng)是一個(gè)付費(fèi)服務(wù),但是現(xiàn)在已經(jīng)開源了。
Altair是一個(gè)相對(duì)較新的Python可視化庫(kù)。很容易使用,并且可以生成非常好看的繪圖,但是定制這些繪圖的功能遠(yuǎn)不如Matplotlib強(qiáng)大。
5、IPython 魔法命令行
上面看到的%matplotlib就是IPython魔術(shù)命令的一個(gè)示例,基于IPython內(nèi)核,Jupyter可以訪問IPython內(nèi)核中的所有魔法,它們可以讓我們更輕松的使用 Jupyter!
# This will list all magic commands
%lsmagic
Available line magics:
%alias %alias_magic %autocall %automagic %autosave %bookmark %cat %cd %clear %colors %config %connect_info %cp %debug %dhist %dirs %doctest_mode %ed %edit %env %gui %hist %history %killbgscripts %ldir %less %lf %lk %ll %load %load_ext %loadpy %logoff %logon %logstart %logstate %logstop %ls %lsmagic %lx %macro %magic %man %matplotlib %mkdir %more %mv %notebook %page %pastebin %pdb %pdef %pdoc %pfile %pinfo %pinfo2 %popd %pprint %precision %profile %prun %psearch %psource %pushd %pwd %pycat %pylab %qtconsole %quickref %recall %rehashx %reload_ext %rep %rerun %reset %reset_selective %rm %rmdir %run %save %sc %set_env %store %sx %system %tb %time %timeit %unalias %unload_ext %who %who_ls %whos %xdel %xmode
Available cell magics:%%! %%HTML %%SVG %%bash %%capture %%debug %%file %%html %%javascript %%js %%latex %%perl %%prun %%pypy %%python %%python2 %%python3 %%ruby %%script %%sh %%svg %%sx %%system %%time %%timeit %%writefile
Automagic is ON, % prefix IS NOT needed for line magics.
6、IPython 魔法-%env 設(shè)置環(huán)境變量
我們可以管理notebook的環(huán)境變量,而無(wú)需重新啟動(dòng)jupyter服務(wù)器進(jìn)程。有些庫(kù)是(比如theano)使用環(huán)境變量來控制行為的,%env 就是最方便的方法。
# Running %env without any arguments
# lists all environment variables# The line below sets the environment
# variable
%env OMP_NUM_THREADS%env OMP_NUM_THREADS=4
env: OMP_NUM_THREADS=4
7、IPython 魔法-%run 執(zhí)行Python代碼
%run可以從.py文件執(zhí)行python代碼——這是一個(gè)有很好方法,但是卻很少有人知道,它還可以執(zhí)行其他jupyter notebook,這也非常有用。
需要注意的是,使用%run與導(dǎo)入python模塊不同。
# this will execute and show the output from
# all code cells of the specified notebook
%run ./two-histograms.ipynb
8、IPython 魔法-%load 從外部腳本插入代碼
這個(gè)魔法語(yǔ)言,可以用外部腳本替換單元格的內(nèi)容,可以使用計(jì)算機(jī)上的文件作為源,也可以使用URL。
# Before Running
%load ./hello_world.py
# After Running
# %load ./hello_world.py
if __name__ == "__main__":
print("Hello World!")
Hello World!
9、IPython 魔法-%store 在notebook之間傳遞變
%store命令允許我們?cè)趦蓚€(gè)不同的notebook之間傳遞變量。
data = 'this is the string I want to pass to different notebook'
%store data
del data # This has deleted the variable
Stored 'data' (str)
然后在一個(gè)新的notebook中
%store -r data
print(data)
this is the string I want to pass to different notebook
10、IPython 魔法-%who 列出全局范圍的所有變量
不帶任何參數(shù)的%who命令將列出全局范圍中存在的所有變量,傳遞類似str的參數(shù)將只列出該類型的變量。
one = "for the money"
two = "for the show"
three = "to get ready now go cat go"
%who str
one three two
11、IPython 魔法-計(jì)時(shí)功能
有兩個(gè)IPython魔術(shù)命令對(duì)計(jì)時(shí)很有用–%%time和%timeit,當(dāng)我們有一些慢代碼需要執(zhí)行并且試圖找出問題所在的時(shí)候,這就特別方便了。
%%time會(huì)給你關(guān)于代碼里一次代碼運(yùn)行的信息。
%%time
import time
for _ in range(1000):
time.sleep(0.01) # sleep for 0.01 seconds
CPU times: user 21.5 ms, sys: 14.8 ms, total: 36.3 ms Wall time: 11.6 s
%%timeit使用Python timeit模塊,該模塊運(yùn)行一條語(yǔ)句100000次(默認(rèn)情況下),然后提供最快三次的平均值。
import numpy
%timeit numpy.random.normal(size=100)
The slowest run took 7.29 times longer than the fastest. This could mean that an intermediate result is being cached.
100000 loops, best of 3: 5.5 μs per loop
12、IPython 魔法-%%writefile和%pycat 導(dǎo)出單元格的內(nèi)容/顯示外部腳本的內(nèi)容
使用%%writefile將該單元格的內(nèi)容保存到外部文件中,%pycat的作用正好相反,它(在彈出窗口中)可以顯示外部文件的內(nèi)容。
%%writefile
%%writefile pythoncode.py
import numpy
def append_if_not_exists(arr, x):
if x not in arr:
arr.append(x)def some_useless_slow_function():
arr = list()
for i in range(10000):
x = numpy.random.randint(0, 10000)
append_if_not_exists(arr, x)
Writing pythoncode.py
%%pycat
%pycat pythoncode.py
import numpy
def append_if_not_exists(arr, x):
if x not in arr:
arr.append(x)def some_useless_slow_function():
arr = list()
for i in range(10000):
x = numpy.random.randint(0, 10000)
append_if_not_exists(arr, x)
13、IPython 魔法-%prun 顯示程序在每個(gè)函數(shù)中花費(fèi)的時(shí)間
使用%prun statement_name將生產(chǎn)一個(gè)有序表,顯示在語(yǔ)句中調(diào)用每個(gè)內(nèi)部函數(shù)的次數(shù)、每次調(diào)用所占用的時(shí)間以及函數(shù)的所有運(yùn)行的累計(jì)時(shí)間。
%prun some_useless_slow_function()
26324 function calls in 0.556 seconds
Ordered by: internal time
ncalls tottime percall cumtime percall filename:lineno(function)
10000 0.527 0.000 0.528 0.000 :2(append_if_not_exists)
10000 0.022 0.000 0.022 0.000 {method 'randint' of 'mtrand.RandomState' objects}
1 0.006 0.006 0.556 0.556 :6(some_useless_slow_function)
6320 0.001 0.000 0.001 0.000 {method 'append' of 'list' objects}
1 0.000 0.000 0.556 0.556 :1()
1 0.000 0.000 0.556 0.556 {built-in method exec}
1 0.000 0.000 0.000 0.000 {method 'disable' of '_lsprof.Profiler' objects}
14、IPython 魔法-使用%pdb進(jìn)行調(diào)試
Jupyter有自己的Python調(diào)試器(pdb)接口,這樣就可以進(jìn)入函數(shù)內(nèi)部并調(diào)查那里發(fā)生了什么。
%pdb
def pick_and_take():
picked = numpy.random.randint(0, 1000)
raise NotImplementedError()
pick_and_take()
Automatic pdb calling has been turned ON
--------------------------------------------------------------------
NotImplementedError Traceback (most recent call last)
in ()
5 raise NotImplementedError()
6
----> 7 pick_and_take()
in pick_and_take()
3 def pick_and_take():
4 picked = numpy.random.randint(0, 1000)
----> 5 raise NotImplementedError()
6
7 pick_and_take()
NotImplementedError:
> (5)pick_and_take()
3 def pick_and_take():
4 picked = numpy.random.randint(0, 1000)
----> 5 raise NotImplementedError()
6
7 pick_and_take()
ipdb>
15、執(zhí)行Shell命令
從notebook內(nèi)部執(zhí)行shell命令很容易,可以使用此選項(xiàng)檢查工作文件夾中的可用數(shù)據(jù)集
!ls *.csv
nba_2016.csv titanic.csv pixar_movies.csv whitehouse_employees.csv
檢查安裝的庫(kù)
!pip install numpy !pip list | grep pandas
Requirement already satisfied (use --upgrade to upgrade): numpy in /Library/Frameworks/Python.framework/Versions/3.4/lib/python3.4/site-packages pandas (0.18.1)
16、使用LaTeX格式化
在markdown單元格中寫入LaTeX時(shí),將使用MathJax將其呈現(xiàn)為公式。
$P(A mid B) = frac{P(B mid A)P(A)}{P(B)}$
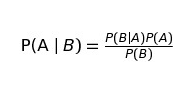
我們要時(shí)刻謹(jǐn)記,MarkDown 是 Jupyter 的非常重要的一部分,一定要好好利用
17、在一個(gè)notebook中使用不同的kernel運(yùn)行代碼
如果需要,可以將多個(gè)內(nèi)核中的代碼合并到一個(gè)notebook中。
只需在每個(gè)要使用內(nèi)核的單元格的開頭使用ipython magics和內(nèi)核名稱:
%%bash
%%HTML
%%python2
%%python3
%%ruby
%%perl
%%bash
for i in {1..5}
do echo "i is $i"
done
i is 1
i is 2
i is 3
i is 4
i is 5
18、在同一個(gè)notebook上運(yùn)行R和Python
最好的解決方案是安裝rpy2,這可以通過pip輕松完成:
pip install rpy2
接下來就是同時(shí)使用兩種語(yǔ)言了
%load_ext rpy2.ipython
%R require(ggplot2)
array([1], dtype=int32)
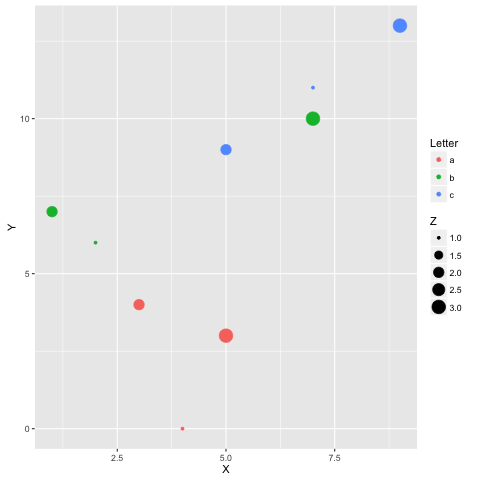
import pandas as pd df = pd.DataFrame({
'Letter': ['a', 'a', 'a', 'b', 'b', 'b', 'c', 'c', 'c'],
'X': [4, 3, 5, 2, 1, 7, 7, 5, 9],
'Y': [0, 4, 3, 6, 7, 10, 11, 9, 13],
'Z': [1, 2, 3, 1, 2, 3, 1, 2, 3]
})
%%R -i df ggplot(data = df) + geom_point(aes(x = X, y= Y, color = Letter, size = Z))
-End-
最近有一些小伙伴,讓我?guī)兔φ乙恍?nbsp;面試題 資料,于是我翻遍了收藏的 5T 資料后,匯總整理出來,可以說是程序員面試必備!所有資料都整理到網(wǎng)盤了,歡迎下載!
面試題】即可獲取