實踐教程 | OpenCV中直線擬合方法解密

極市導讀
如題,本文將解密OpenCV中直線擬合方法:通過OpenCV的距離變換,骨架提取,然后再直線擬合,使用DIST_L1得到的結果。 >>加入極市CV技術交流群,走在計算機視覺的最前沿
直線擬合原理
給出多個點,然后根據(jù)這些點擬合出一條直線,這個最常見的算法是多約束方程的最小二乘擬合,如下圖所示:
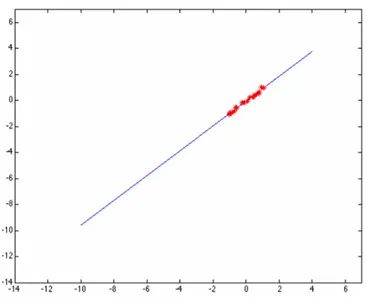
但是當這些點當中有一個或者幾個離群點(outlier)時候,最小二乘擬合出來的直線就直接翻車成這樣了:
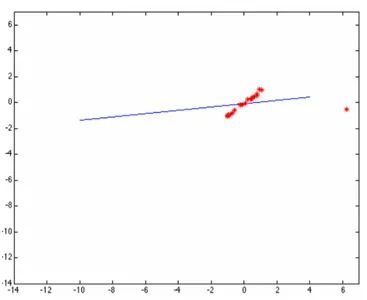
原因是最小二乘無法在估算擬合的時候剔除或者降低離群點的影響,于是一個聰明的家伙出現(xiàn)了,提出了基于權重的最小二乘擬合估算方法,這樣就避免了翻車。
根據(jù)高斯分布,離群點權重應該盡可能的小,這樣就可以降低它的影響,OpenCV中的直線擬合就是就權重最小二乘完成的,在生成權重時候OpenCV支持幾種不同的距離計算方法,分別如下:
DIST_L2
DIST_L1
DIST_L12
DIST_FAIR
DIST_WELSCH
DIST_HUBER
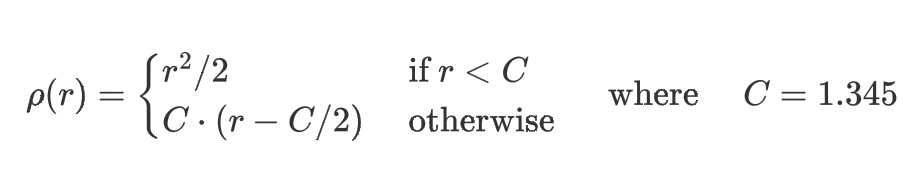
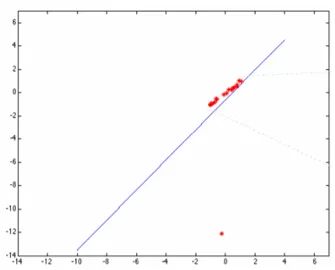
其中DIST_L2是最原始的最小二乘,最容易翻車的一種擬合方式,雖然速度快點。然后用基于權重的最小二乘估算擬合結果如下:
函數(shù)與實現(xiàn)源碼分析
OpenCV中直線擬合函數(shù)支持上述六種距離計算方式,函數(shù)與參數(shù)解釋如下:
void cv::fitLine(
InputArray points,
OutputArray line,
int distType,
double param,
double reps,
double aeps
)
points是輸入點集合
line是輸出的擬合參數(shù),支持2D與3D
distType是選擇距離計算方式
param 是某些距離計算時生成權重需要的參數(shù)
reps 是前后兩次原點到直線的距離差值,可以看成擬合精度高低
aeps是前后兩次角度差值,表示的是擬合精度
六種權重的計算更新實現(xiàn)如下:
static void weightL1( float *d, int count, float *w )
{
int i;
for( i = 0; i < count; i++ )
{
double t = fabs( (double) d[i] );
w[i] = (float)(1. / MAX(t, eps));
}
}
static void weightL12( float *d, int count, float *w )
{
int i;
for( i = 0; i < count; i++ )
{
w[i] = 1.0f / (float) std::sqrt( 1 + (double) (d[i] * d[i] * 0.5) );
}
}
static void weightHuber( float *d, int count, float *w, float _c )
{
int i;
const float c = _c <= 0 ? 1.345f : _c;
for( i = 0; i < count; i++ )
{
if( d[i] < c )
w[i] = 1.0f;
else
w[i] = c/d[i];
}
}
static void weightFair( float *d, int count, float *w, float _c )
{
int i;
const float c = _c == 0 ? 1 / 1.3998f : 1 / _c;
for( i = 0; i < count; i++ )
{
w[i] = 1 / (1 + d[i] * c);
}
}
static void weightWelsch( float *d, int count, float *w, float _c )
{
int i;
const float c = _c == 0 ? 1 / 2.9846f : 1 / _c;
for( i = 0; i < count; i++ )
{
w[i] = (float) std::exp( -d[i] * d[i] * c * c );
}
}
擬合計算的代碼實現(xiàn):
static void fitLine2D_wods( const Point2f* points, int count, float *weights, float *line )
{
CV_Assert(count > 0);
double x = 0, y = 0, x2 = 0, y2 = 0, xy = 0, w = 0;
double dx2, dy2, dxy;
int i;
float t;
// Calculating the average of x and y...
if( weights == 0 )
{
for( i = 0; i < count; i += 1 )
{
x += points[i].x;
y += points[i].y;
x2 += points[i].x * points[i].x;
y2 += points[i].y * points[i].y;
xy += points[i].x * points[i].y;
}
w = (float) count;
}
else
{
for( i = 0; i < count; i += 1 )
{
x += weights[i] * points[i].x;
y += weights[i] * points[i].y;
x2 += weights[i] * points[i].x * points[i].x;
y2 += weights[i] * points[i].y * points[i].y;
xy += weights[i] * points[i].x * points[i].y;
w += weights[i];
}
}
x /= w;
y /= w;
x2 /= w;
y2 /= w;
xy /= w;
dx2 = x2 - x * x;
dy2 = y2 - y * y;
dxy = xy - x * y;
t = (float) atan2( 2 * dxy, dx2 - dy2 ) / 2;
line[0] = (float) cos( t );
line[1] = (float) sin( t );
line[2] = (float) x;
line[3] = (float) y;
}
案例:直線擬合
有如下的原圖:
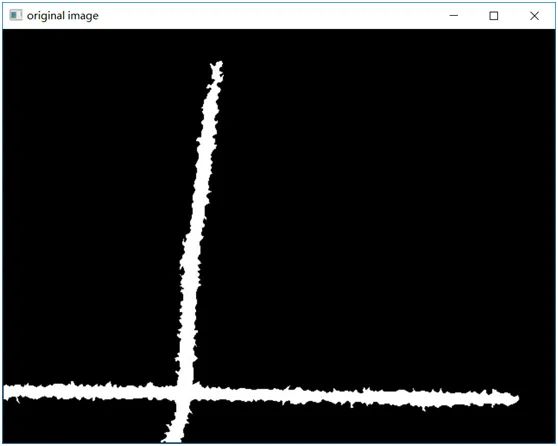
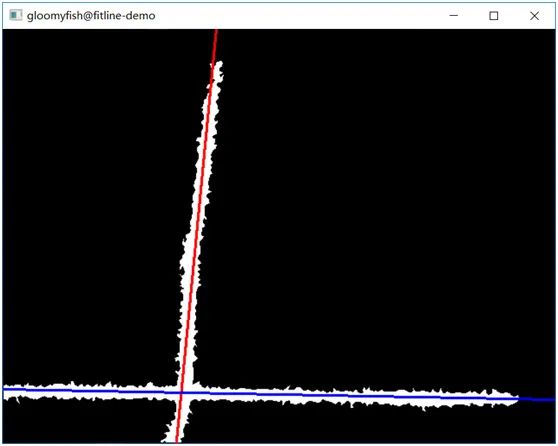
通過OpenCV的距離變換,骨架提取,然后再直線擬合,使用DIST_L1得到的結果如下:
OpenCV-C++/Python視頻教程30課時,請看B站:
https://www.bilibili.com/video/BV1hM4y1M7vQ (python版本)
https://www.bilibili.com/video/BV1i54y1m7tw (C++版本)
如果覺得有用,就請分享到朋友圈吧!
公眾號后臺回復“小目標檢測”獲取2021年小目標檢測綜述PDF~

# CV技術社群邀請函 #

備注:姓名-學校/公司-研究方向-城市(如:小極-北大-目標檢測-深圳)
即可申請加入極市目標檢測/圖像分割/工業(yè)檢測/人臉/醫(yī)學影像/3D/SLAM/自動駕駛/超分辨率/姿態(tài)估計/ReID/GAN/圖像增強/OCR/視頻理解等技術交流群
每月大咖直播分享、真實項目需求對接、求職內(nèi)推、算法競賽、干貨資訊匯總、與 10000+來自港科大、北大、清華、中科院、CMU、騰訊、百度等名校名企視覺開發(fā)者互動交流~