從0梳理1場(chǎng)時(shí)間序列賽事!
一、賽題背景
賽題簡(jiǎn)介
比賽地址:https://tianchi.aliyun.com/competition/entrance/531871/information(復(fù)制粘貼或文末閱讀原文)
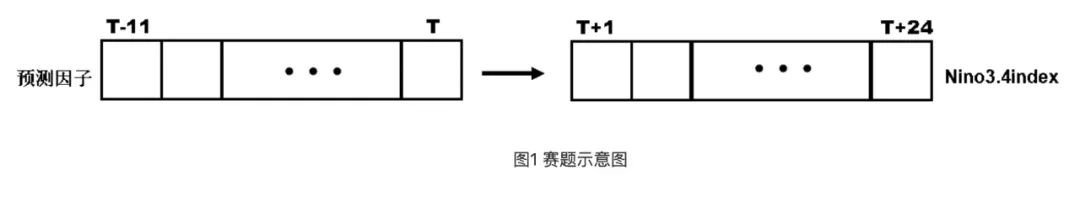
本次賽題是一個(gè)時(shí)間序列預(yù)測(cè)問(wèn)題。基于歷史氣候觀測(cè)和模式模擬數(shù)據(jù),利用T時(shí)刻過(guò)去12個(gè)月(包含T時(shí)刻)的時(shí)空序列(氣象因子),構(gòu)建預(yù)測(cè)ENSO的深度學(xué)習(xí)模型,預(yù)測(cè)未來(lái)1-24個(gè)月的Nino3.4指數(shù),如下圖所示:
背景數(shù)據(jù)描述
1. 數(shù)據(jù)簡(jiǎn)介
本次比賽使用的數(shù)據(jù)包括CMIP5/6模式的歷史模擬數(shù)據(jù)和美國(guó)SODA模式重建的近100多年歷史觀測(cè)同化數(shù)據(jù)。每個(gè)樣本包含以下氣象及時(shí)空變量:海表溫度異常(SST),熱含量異常(T300),緯向風(fēng)異常(Ua),經(jīng)向風(fēng)異常(Va),數(shù)據(jù)維度為(year,month,lat,lon)。對(duì)于訓(xùn)練數(shù)據(jù)提供對(duì)應(yīng)月份的Nino3.4 index標(biāo)簽數(shù)據(jù)。
2. 訓(xùn)練數(shù)據(jù)標(biāo)簽說(shuō)明
標(biāo)簽數(shù)據(jù)為Nino3.4 SST異常指數(shù),數(shù)據(jù)維度為(year,month)。
CMIP(SODA)_train.nc對(duì)應(yīng)的標(biāo)簽數(shù)據(jù)當(dāng)前時(shí)刻N(yùn)ino3.4 SST異常指數(shù)的三個(gè)月滑動(dòng)平均值,因此數(shù)據(jù)維度與維度介紹同訓(xùn)練數(shù)據(jù)一致。
注:三個(gè)月滑動(dòng)平均值為當(dāng)前月與未來(lái)兩個(gè)月的平均值。
3. 測(cè)試數(shù)據(jù)說(shuō)明
測(cè)試用的初始場(chǎng)(輸入)數(shù)據(jù)為國(guó)際多個(gè)海洋資料同化結(jié)果提供的隨機(jī)抽取的n段12個(gè)時(shí)間序列,數(shù)據(jù)格式采用NPY格式保存,維度為(12,lat,lon, 4),12為t時(shí)刻及過(guò)去11個(gè)時(shí)刻,4為預(yù)測(cè)因子,并按照SST,T300,Ua,Va的順序存放。
測(cè)試集文件序列的命名規(guī)則:test_編號(hào)_起始月份_終止月份.npy,如test_00001_01_12_.npy。
評(píng)估指標(biāo)
評(píng)分細(xì)則說(shuō)明:根據(jù)所提供的n個(gè)測(cè)試數(shù)據(jù),對(duì)模型進(jìn)行測(cè)試,得到n組未來(lái)1-24個(gè)月的序列選取對(duì)應(yīng)預(yù)測(cè)時(shí)效的n個(gè)數(shù)據(jù)與標(biāo)簽值進(jìn)行計(jì)算相關(guān)系數(shù)和均方根誤差,如下圖所示。并計(jì)算得分。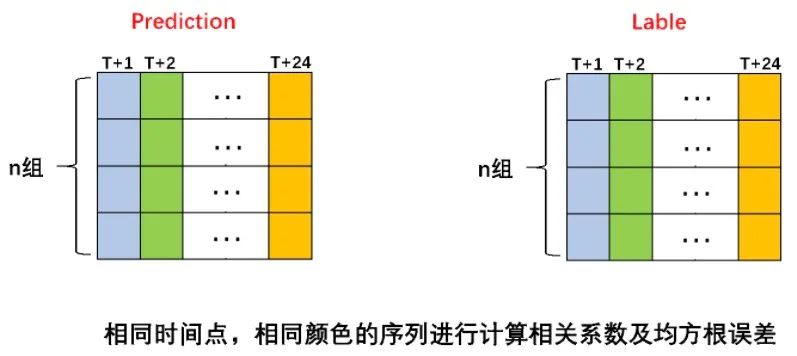 計(jì)算公式為:
計(jì)算公式為:
其中,
而:
二、線(xiàn)下數(shù)據(jù)轉(zhuǎn)換
將數(shù)據(jù)轉(zhuǎn)化為我們所熟悉的形式,每個(gè)人的風(fēng)格不一樣,此處可以作為如何將nc文件轉(zhuǎn)化為csv等文件
## 工具包導(dǎo)入&數(shù)據(jù)讀取
### 工具包導(dǎo)入
'''
安裝工具
# !pip install netCDF4
'''
import pandas as pd
import numpy as np
import tensorflow as tf
from tensorflow.keras.optimizers import Adam
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import scipy
from netCDF4 import Dataset
import netCDF4 as nc
import gc
%matplotlib inline
1. 數(shù)據(jù)讀取
1.1 SODA_label處理
標(biāo)簽含義
標(biāo)簽數(shù)據(jù)為Nino3.4 SST異常指數(shù),數(shù)據(jù)維度為(year,month)。
CMIP(SODA)_train.nc對(duì)應(yīng)的標(biāo)簽數(shù)據(jù)當(dāng)前時(shí)刻N(yùn)ino3.4 SST異常指數(shù)的三個(gè)月滑動(dòng)平均值,因此數(shù)據(jù)維度與維度介紹同訓(xùn)練數(shù)據(jù)一致
注:三個(gè)月滑動(dòng)平均值為當(dāng)前月與未來(lái)兩個(gè)月的平均值。
將標(biāo)簽轉(zhuǎn)化為我們熟悉的pandas形式
label_path = './data/SODA_label.nc'
label_trans_path = './data/'
nc_label = Dataset(label_path,'r')
years = np.array(nc_label['year'][:])
months = np.array(nc_label['month'][:])
year_month_index = []
vs = []
for i,year in enumerate(years):
for j,month in enumerate(months):
year_month_index.append('year_{}_month_{}'.format(year,month))
vs.append(np.array(nc_label['nino'][i,j]))
df_SODA_label = pd.DataFrame({'year_month':year_month_index})
df_SODA_label['year_month'] = year_month_index
df_SODA_label['label'] = vs
df_SODA_label.to_csv(label_trans_path + 'df_SODA_label.csv',index = None)
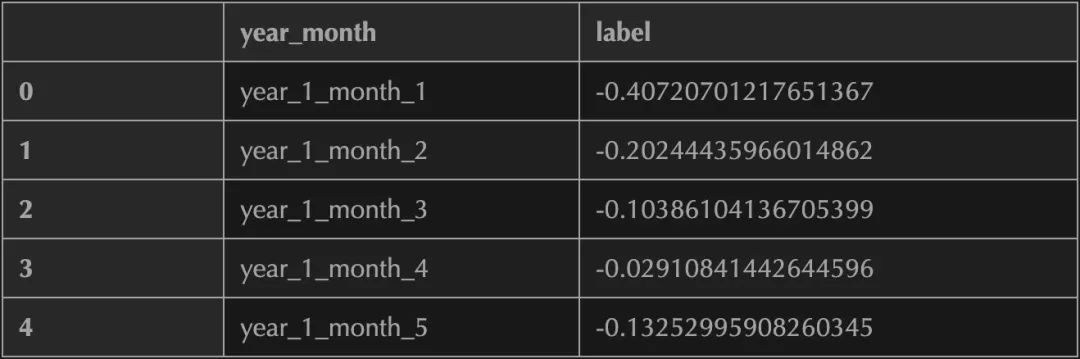
df_label.head()
2. 數(shù)據(jù)格式轉(zhuǎn)化
2.1 SODA_train處理
SODA_train.nc中[0,0:36,:,:]為第1-第3年逐月的歷史觀測(cè)數(shù)據(jù);
SODA_train.nc中[1,0:36,:,:]為第2-第4年逐月的歷史觀測(cè)數(shù)據(jù);
…,
SODA_train.nc中[99,0:36,:,:]為第100-102年逐月的歷史觀測(cè)數(shù)據(jù)。
SODA_path = './data/SODA_train.nc'
nc_SODA = Dataset(SODA_path,'r')
自定義抽取對(duì)應(yīng)數(shù)據(jù)&轉(zhuǎn)化為df的形式;
index為年月; columns為lat和lon的組合
def trans_df(df, vals, lats, lons, years, months):
'''
(100, 36, 24, 72) -- year, month,lat,lon
'''
for j,lat_ in enumerate(lats):
for i,lon_ in enumerate(lons):
c = 'lat_lon_{}_{}'.format(int(lat_),int(lon_))
v = []
for y in range(len(years)):
for m in range(len(months)):
v.append(vals[y,m,j,i])
df[c] = v
return df
year_month_index = []
years = np.array(nc_SODA['year'][:])
months = np.array(nc_SODA['month'][:])
lats = np.array(nc_SODA['lat'][:])
lons = np.array(nc_SODA['lon'][:])
for year in years:
for month in months:
year_month_index.append('year_{}_month_{}'.format(year,month))
df_sst = pd.DataFrame({'year_month':year_month_index})
df_t300 = pd.DataFrame({'year_month':year_month_index})
df_ua = pd.DataFrame({'year_month':year_month_index})
df_va = pd.DataFrame({'year_month':year_month_index})
%%time
df_sst = trans_df(df = df_sst, vals = np.array(nc_SODA['sst'][:]), lats = lats, lons = lons, years = years, months = months)
df_t300 = trans_df(df = df_t300, vals = np.array(nc_SODA['t300'][:]), lats = lats, lons = lons, years = years, months = months)
df_ua = trans_df(df = df_ua, vals = np.array(nc_SODA['ua'][:]), lats = lats, lons = lons, years = years, months = months)
df_va = trans_df(df = df_va, vals = np.array(nc_SODA['va'][:]), lats = lats, lons = lons, years = years, months = months)
label_trans_path = './data/'
df_sst.to_csv(label_trans_path + 'df_sst_SODA.csv',index = None)
df_t300.to_csv(label_trans_path + 'df_t300_SODA.csv',index = None)
df_ua.to_csv(label_trans_path + 'df_ua_SODA.csv',index = None)
df_va.to_csv(label_trans_path + 'df_va_SODA.csv',index = None)
2.2 CMIP_label處理
label_path = './data/CMIP_label.nc'
label_trans_path = './data/'
nc_label = Dataset(label_path,'r')
years = np.array(nc_label['year'][:])
months = np.array(nc_label['month'][:])
year_month_index = []
vs = []
for i,year in enumerate(years):
for j,month in enumerate(months):
year_month_index.append('year_{}_month_{}'.format(year,month))
vs.append(np.array(nc_label['nino'][i,j]))
df_CMIP_label = pd.DataFrame({'year_month':year_month_index})
df_CMIP_label['year_month'] = year_month_index
df_CMIP_label['label'] = vs
df_CMIP_label.to_csv(label_trans_path + 'df_CMIP_label.csv',index = None)
df_CMIP_label.head()
2.3 CMIP_train處理
CMIP_train.nc中[0,0:36,:,:]為CMIP6第一個(gè)模式提供的第1-第3年逐月的歷史模擬數(shù)據(jù);
…,
CMIP_train.nc中[150,0:36,:,:]為CMIP6第一個(gè)模式提供的第151-第153年逐月的歷史模擬數(shù)據(jù);
CMIP_train.nc中[151,0:36,:,:]為CMIP6第二個(gè)模式提供的第1-第3年逐月的歷史模擬數(shù)據(jù);
…,
CMIP_train.nc中[2265,0:36,:,:]為CMIP5第一個(gè)模式提供的第1-第3年逐月的歷史模擬數(shù)據(jù);
…,
CMIP_train.nc中[2405,0:36,:,:]為CMIP5第二個(gè)模式提供的第1-第3年逐月的歷史模擬數(shù)據(jù);
…,
CMIP_train.nc中[4644,0:36,:,:]為CMIP5第17個(gè)模式提供的第140-第142年逐月的歷史模擬數(shù)據(jù)。
其中每個(gè)樣本第三、第四維度分別代表經(jīng)緯度(南緯55度北緯60度,東經(jīng)0360度),所有數(shù)據(jù)的經(jīng)緯度范圍相同。
CMIP_path = './data/CMIP_train.nc'
CMIP_trans_path = './data'
nc_CMIP = Dataset(CMIP_path,'r')
nc_CMIP.variables.keys()
# dict_keys(['sst', 't300', 'ua', 'va', 'year', 'month', 'lat', 'lon'])
nc_CMIP['t300'][:].shape
# (4645, 36, 24, 72)
year_month_index = []
years = np.array(nc_CMIP['year'][:])
months = np.array(nc_CMIP['month'][:])
lats = np.array(nc_CMIP['lat'][:])
lons = np.array(nc_CMIP['lon'][:])
last_thre_years = 1000
for year in years:
'''
數(shù)據(jù)的原因,我們
'''
if year >= 4645 - last_thre_years:
for month in months:
year_month_index.append('year_{}_month_{}'.format(year,month))
df_CMIP_sst = pd.DataFrame({'year_month':year_month_index})
df_CMIP_t300 = pd.DataFrame({'year_month':year_month_index})
df_CMIP_ua = pd.DataFrame({'year_month':year_month_index})
df_CMIP_va = pd.DataFrame({'year_month':year_month_index})
因?yàn)閮?nèi)存限制,我們暫時(shí)取最后1000個(gè)year的數(shù)據(jù)
def trans_thre_df(df, vals, lats, lons, years, months, last_thre_years = 1000):
'''
(4645, 36, 24, 72) -- year, month,lat,lon
'''
for j,lat_ in (enumerate(lats)):
# print(j)
for i,lon_ in enumerate(lons):
c = 'lat_lon_{}_{}'.format(int(lat_),int(lon_))
v = []
for y_,y in enumerate(years):
'''
數(shù)據(jù)的原因,我們
'''
if y >= 4645 - last_thre_years:
for m_,m in enumerate(months):
v.append(vals[y_,m_,j,i])
df[c] = v
return df
%%time
df_CMIP_sst = trans_thre_df(df = df_CMIP_sst, vals = np.array(nc_CMIP['sst'][:]), lats = lats, lons = lons, years = years, months = months)
df_CMIP_sst.to_csv(CMIP_trans_path + 'df_CMIP_sst.csv',index = None)
del df_CMIP_sst
gc.collect()
df_CMIP_t300 = trans_thre_df(df = df_CMIP_t300, vals = np.array(nc_CMIP['t300'][:]), lats = lats, lons = lons, years = years, months = months)
df_CMIP_t300.to_csv(CMIP_trans_path + 'df_CMIP_t300.csv',index = None)
del df_CMIP_t300
gc.collect()
df_CMIP_ua = trans_thre_df(df = df_CMIP_ua, vals = np.array(nc_CMIP['ua'][:]), lats = lats, lons = lons, years = years, months = months)
df_CMIP_ua.to_csv(CMIP_trans_path + 'df_CMIP_ua.csv',index = None)
del df_CMIP_ua
gc.collect()
df_CMIP_va = trans_thre_df(df = df_CMIP_va, vals = np.array(nc_CMIP['va'][:]), lats = lats, lons = lons, years = years, months = months)
df_CMIP_va.to_csv(CMIP_trans_path + 'df_CMIP_va.csv',index = None)
del df_CMIP_va
gc.collect()
# (36036, 1729)
數(shù)據(jù)建模
工具包導(dǎo)入&數(shù)據(jù)讀取
1. 工具包導(dǎo)入
import pandas as pd
import numpy as np
import tensorflow as tf
from tensorflow.keras.optimizers import Adam
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import scipy
import joblib
from netCDF4 import Dataset
import netCDF4 as nc
from tensorflow.keras.callbacks import LearningRateScheduler, Callback
import tensorflow.keras.backend as K
from tensorflow.keras.layers import *
from tensorflow.keras.models import *
from tensorflow.keras.optimizers import *
from tensorflow.keras.callbacks import *
from tensorflow.keras.layers import Input
import gc
%matplotlib inline
2. 數(shù)據(jù)讀取
SODA_label處理
標(biāo)簽
標(biāo)簽數(shù)據(jù)為Nino3.4 SST異常指數(shù),數(shù)據(jù)維度為(year,month)。
CMIP(SODA)_train.nc對(duì)應(yīng)的標(biāo)簽數(shù)據(jù)當(dāng)前時(shí)刻N(yùn)ino3.4 SST異常指數(shù)的三個(gè)月滑動(dòng)平均值,因此數(shù)據(jù)維度與維度介紹同訓(xùn)練數(shù)據(jù)一致
注:三個(gè)月滑動(dòng)平均值為當(dāng)前月與未來(lái)兩個(gè)月的平均值。
label_path = './data/SODA_label.nc'
nc_label = Dataset(label_path,'r')
tr_nc_labels = nc_label['nino'][:]
2. 原始特征數(shù)據(jù)讀取
SODA_path = './data/SODA_train.nc'
nc_SODA = Dataset(SODA_path,'r')
nc_sst = np.array(nc_SODA['sst'][:])
nc_t300 = np.array(nc_SODA['t300'][:])
nc_ua = np.array(nc_SODA['ua'][:])
nc_va = np.array(nc_SODA['va'][:])
模型構(gòu)建
1. 神經(jīng)網(wǎng)絡(luò)框架
def RMSE(y_true, y_pred):
return tf.sqrt(tf.reduce_mean(tf.square(y_true - y_pred)))
def RMSE_fn(y_true, y_pred):
return np.sqrt(np.mean(np.power(np.array(y_true, float).reshape(-1, 1) - np.array(y_pred, float).reshape(-1, 1), 2)))
def build_model():
inp = Input(shape=(12,24,72,4))
x_4 = Dense(1, activation='relu')(inp)
x_3 = Dense(1, activation='relu')(tf.reshape(x_4,[-1,12,24,72]))
x_2 = Dense(1, activation='relu')(tf.reshape(x_3,[-1,12,24]))
x_1 = Dense(1, activation='relu')(tf.reshape(x_2,[-1,12]))
x = Dense(64, activation='relu')(x_1)
x = Dropout(0.25)(x)
x = Dense(32, activation='relu')(x)
x = Dropout(0.25)(x)
output = Dense(24, activation='linear')(x)
model = Model(inputs=inp, outputs=output)
adam = tf.optimizers.Adam(lr=1e-3,beta_1=0.99,beta_2 = 0.99)
model.compile(optimizer=adam, loss=RMSE)
return model
2. 訓(xùn)練集驗(yàn)證集劃分
### 訓(xùn)練特征,保證和訓(xùn)練集一致
tr_features = np.concatenate([nc_sst[:,:12,:,:].reshape(-1,12,24,72,1),nc_t300[:,:12,:,:].reshape(-1,12,24,72,1),\
nc_ua[:,:12,:,:].reshape(-1,12,24,72,1),nc_va[:,:12,:,:].reshape(-1,12,24,72,1)],axis=-1)
### 訓(xùn)練標(biāo)簽,取后24個(gè)
tr_labels = tr_nc_labels[:,12:]
### 訓(xùn)練集驗(yàn)證集劃分
tr_len = int(tr_features.shape[0] * 0.8)
tr_fea = tr_features[:tr_len,:].copy()
tr_label = tr_labels[:tr_len,:].copy()
val_fea = tr_features[tr_len:,:].copy()
val_label = tr_labels[tr_len:,:].copy()
3. 模型訓(xùn)練
#### 構(gòu)建模型
model_mlp = build_model()
#### 模型存儲(chǔ)的位置
model_weights = './model_baseline/model_mlp_baseline.h5'
checkpoint = ModelCheckpoint(model_weights, monitor='val_loss', verbose=0, save_best_only=True, mode='min',
save_weights_only=True)
plateau = ReduceLROnPlateau(monitor='val_loss', factor=0.5, patience=5, verbose=1, min_delta=1e-4, mode='min')
early_stopping = EarlyStopping(monitor="val_loss", patience=20)
history = model_mlp.fit(tr_fea, tr_label,
validation_data=(val_fea, val_label),
batch_size=4096, epochs=200,
callbacks=[plateau, checkpoint, early_stopping],
verbose=2)
4. 模型預(yù)測(cè)
prediction = model_mlp.predict(val_fea)
5. Metrics
from sklearn.metrics import mean_squared_error
def rmse(y_true, y_preds):
return np.sqrt(mean_squared_error(y_pred = y_preds, y_true = y_true))
def score(y_true, y_preds):
accskill_score = 0
rmse_scores = 0
a = [1.5] * 4 + [2] * 7 + [3] * 7 + [4] * 6
y_true_mean = np.mean(y_true,axis=0)
y_pred_mean = np.mean(y_preds,axis=0)
# print(y_true_mean.shape, y_pred_mean.shape)
for i in range(24):
fenzi = np.sum((y_true[:,i] - y_true_mean[i]) *(y_preds[:,i] - y_pred_mean[i]) )
fenmu = np.sqrt(np.sum((y_true[:,i] - y_true_mean[i])**2) * np.sum((y_preds[:,i] - y_pred_mean[i])**2) )
cor_i = fenzi / fenmu
accskill_score += a[i] * np.log(i+1) * cor_i
rmse_score = rmse(y_true[:,i], y_preds[:,i])
# print(cor_i, 2 / 3.0 * a[i] * np.log(i+1) * cor_i - rmse_score)
rmse_scores += rmse_score
return 2 / 3.0 * accskill_score - rmse_scores
print('score', score(y_true = val_label, y_preds = prediction))
三、模型預(yù)測(cè)
在上面的部分,我們已經(jīng)訓(xùn)練好了模型,接下來(lái)就是提交模型并在線(xiàn)上進(jìn)行預(yù)測(cè),這塊可以分為三步:
導(dǎo)入模型; 讀取測(cè)試數(shù)據(jù)并且進(jìn)行預(yù)測(cè); 生成提交所需的版本;
模型導(dǎo)入
import tensorflow as tf
import tensorflow.keras.backend as K
from tensorflow.keras.layers import *
from tensorflow.keras.models import *
from tensorflow.keras.optimizers import *
from tensorflow.keras.callbacks import *
from tensorflow.keras.layers import Input
import numpy as np
import os
import zipfile
def RMSE(y_true, y_pred):
return tf.sqrt(tf.reduce_mean(tf.square(y_true - y_pred)))
def build_model():
inp = Input(shape=(12,24,72,4))
x_4 = Dense(1, activation='relu')(inp)
x_3 = Dense(1, activation='relu')(tf.reshape(x_4,[-1,12,24,72]))
x_2 = Dense(1, activation='relu')(tf.reshape(x_3,[-1,12,24]))
x_1 = Dense(1, activation='relu')(tf.reshape(x_2,[-1,12]))
x = Dense(64, activation='relu')(x_1)
x = Dropout(0.25)(x)
x = Dense(32, activation='relu')(x)
x = Dropout(0.25)(x)
output = Dense(24, activation='linear')(x)
model = Model(inputs=inp, outputs=output)
adam = tf.optimizers.Adam(lr=1e-3,beta_1=0.99,beta_2 = 0.99)
model.compile(optimizer=adam, loss=RMSE)
return model
model = build_model()
model.load_weights('./user_data/model_data/model_mlp_baseline.h5')
模型預(yù)測(cè)
test_path = './tcdata/enso_round1_test_20210201/'
### 1. 測(cè)試數(shù)據(jù)讀取
files = os.listdir(test_path)
test_feas_dict = {}
for file in files:
test_feas_dict[file] = np.load(test_path + file)
### 2. 結(jié)果預(yù)測(cè)
test_predicts_dict = {}
for file_name,val in test_feas_dict.items():
test_predicts_dict[file_name] = model.predict(val).reshape(-1,)
# test_predicts_dict[file_name] = model.predict(val.reshape([-1,12])[0,:])
### 3.存儲(chǔ)預(yù)測(cè)結(jié)果
for file_name,val in test_predicts_dict.items():
np.save('./result/' + file_name,val)
預(yù)測(cè)結(jié)果打包
#打包目錄為zip文件(未壓縮)
def make_zip(source_dir='./result/', output_filename = 'result.zip'):
zipf = zipfile.ZipFile(output_filename, 'w')
pre_len = len(os.path.dirname(source_dir))
source_dirs = os.walk(source_dir)
print(source_dirs)
for parent, dirnames, filenames in source_dirs:
print(parent, dirnames)
for filename in filenames:
if '.npy' not in filename:
continue
pathfile = os.path.join(parent, filename)
arcname = pathfile[pre_len:].strip(os.path.sep) #相對(duì)路徑
zipf.write(pathfile, arcname)
zipf.close()
make_zip()
四、提升方向
模型角度:我們只使用了簡(jiǎn)單的MLP模型進(jìn)行建模,可以考慮使用其它的更加fancy的模型進(jìn)行嘗試; 數(shù)據(jù)層面:構(gòu)建一些特征或者對(duì)數(shù)據(jù)進(jìn)行一些數(shù)據(jù)變換等; 針對(duì)損失函數(shù)設(shè)計(jì)各種trick的提升技巧;
