如何在 ASP.Net Core 中實(shí)現(xiàn) 健康檢查?
健康檢查 常用于判斷一個(gè)應(yīng)用程序能否對(duì) request 請(qǐng)求進(jìn)行響應(yīng),ASP.Net Core 2.2 中引入了 健康檢查 中間件用于報(bào)告應(yīng)用程序的健康狀態(tài)。
ASP.Net Core 中的 健康檢查 落地做法是暴露一個(gè)可配置的 Http 端口,你可以使用 健康檢查 去做一個(gè)最簡(jiǎn)單的活性檢測(cè),比如說(shuō):檢查網(wǎng)絡(luò)和系統(tǒng)的資源可用性,數(shù)據(jù)庫(kù)資源是否可用,應(yīng)用程序依賴的消息中間件或者 Azure cloud service 的可用性 等等,這篇文章我們就來(lái)討論如何使用這個(gè) 健康檢查中間件。
注冊(cè)健康檢查服務(wù)
要注冊(cè) 健康檢查 服務(wù),需要在 Startup.ConfigureServices 下調(diào)用 AddHealthChecks 方法,然后使用 UseHealthChecks 將其注入到 Request Pipeline 管道中,如下代碼所示:
public class Startup
{
// This method gets called by the runtime. Use this method to add services to the container.
public void ConfigureServices(IServiceCollection services)
{
services.AddControllersWithViews();
services.AddHealthChecks();
}
// This method gets called by the runtime. Use this method to configure the HTTP request pipeline.
public void Configure(IApplicationBuilder app, IWebHostEnvironment env)
{
app.UseHealthChecks("/health");
app.UseStaticFiles();
app.UseRouting();
app.UseEndpoints(endpoints =>
{
endpoints.MapControllerRoute(
name: "default",
pattern: "{controller=Home}/{action=Index}/{id?}");
});
}
}
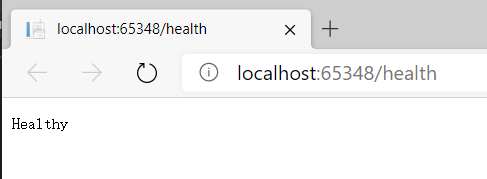
上圖的 /health 就是一個(gè)可供檢查此 web 是否存活的暴露端口。
其他服務(wù)的健康檢查
除了web的活性檢查,還可以檢查諸如:SQL Server, MySQL, MongoDB, Redis, RabbitMQ, Elasticsearch, Hangfire, Kafka, Oracle, Azure Storage 等一系列服務(wù)應(yīng)用的活性,每一個(gè)服務(wù)需要引用相關(guān)的 nuget 包即可,如下圖所示:

然后在 ConfigureServices 中添加相關(guān)服務(wù)即可,比如下面代碼的 AddSqlServer。
public void ConfigureServices(IServiceCollection services)
{
services.AddControllersWithViews();
services.AddHealthChecks().AddSqlServer("server=.;database=PYZ_L;Trusted_Connection=SSPI");
}
自定義健康檢查
除了上面的一些開(kāi)源方案,還可以自定義實(shí)現(xiàn) 健康檢查 類,比如自定義方式來(lái)檢測(cè) 數(shù)據(jù)庫(kù) 或 外部服務(wù) 的可用性,那怎么實(shí)現(xiàn)呢?只需要實(shí)現(xiàn)系統(tǒng)內(nèi)置的 IHealthCheck 接口并實(shí)現(xiàn) CheckHealthAsync() 即可,如下代碼所示:
public class MyCustomHealthCheck : IHealthCheck
{
public async Task<HealthCheckResult> CheckHealthAsync(HealthCheckContext context,
CancellationToken cancellationToken = default(CancellationToken))
{
bool canConnect = IsDBOnline();
if (canConnect)
return HealthCheckResult.Healthy();
return HealthCheckResult.Unhealthy();
}
}
這里的 IsDBOnline 方法用來(lái)判斷當(dāng)前數(shù)據(jù)庫(kù)是否是運(yùn)行狀態(tài),實(shí)現(xiàn)代碼如下:
private bool IsDBOnline()
{
string connectionString = "server=.;database=PYZ_L;Trusted_Connection=SSPI";
try
{
using (SqlConnection connection = new SqlConnection(connectionString))
{
if (connection.State != System.Data.ConnectionState.Open) connection.Open();
}
return true;
}
catch (System.Exception)
{
return false;
}
}
然后在 ConfigureServices 方法中進(jìn)行注入。
public void ConfigureServices(IServiceCollection services)
{
services.AddControllersWithViews();
services.AddHealthChecks().AddCheck<MyCustomHealthCheck>("sqlcheck");
}
public void Configure(IApplicationBuilder app, IWebHostEnvironment env)
{
app.UseRouting().UseEndpoints(config =>
{
config.MapHealthChecks("/health");
});
app.UseStaticFiles();
app.UseRouting();
app.UseEndpoints(endpoints =>
{
endpoints.MapControllerRoute(
name: "default",
pattern: "{controller=Home}/{action=Index}/{id?}");
});
}
接下來(lái)可以瀏覽下 /health 頁(yè)面,可以看出該端口自動(dòng)執(zhí)行了你的 MyCustomHealthCheck 方法,如下圖所示:
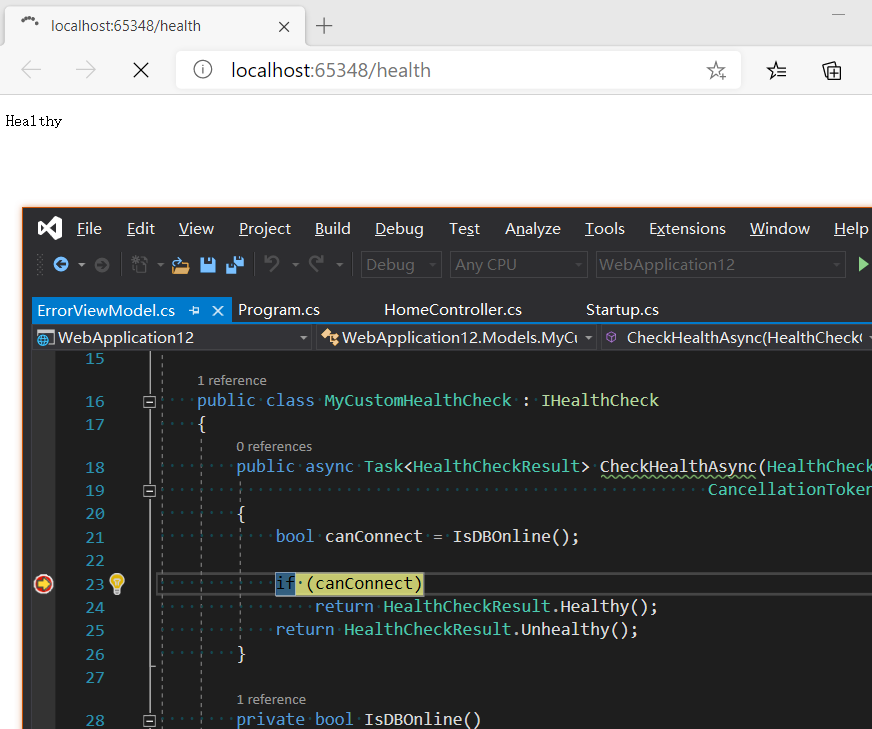
可視化健康檢查
上面的檢查策略雖然好,但并沒(méi)有一個(gè)好的可視化方案,要想實(shí)現(xiàn)可視化的話,還需要單獨(dú)下載 Nuget 包:AspNetCore.HealthChecks.UI , HealthChecks.UI.Client 和 AspNetCore.HealthChecks.UI.InMemory.Storage,命令如下:
Install-Package AspNetCore.HealthChecks.UI
Install-Package AspNetCore.HealthChecks.UI.Client
Install-Package AspNetCore.HealthChecks.UI.InMemory.Storage
一旦包安裝好之后,就可以在 ConfigureServices 和 Configure 方法下做如下配置。
public class Startup
{
// This method gets called by the runtime. Use this method to add services to the container.
public void ConfigureServices(IServiceCollection services)
{
services.AddControllersWithViews();
services.AddHealthChecks();
services.AddHealthChecksUI().AddInMemoryStorage();
}
// This method gets called by the runtime. Use this method to configure the HTTP request pipeline.
public void Configure(IApplicationBuilder app, IWebHostEnvironment env)
{
app.UseRouting().UseEndpoints(config =>
{
config.MapHealthChecks("/health", new HealthCheckOptions
{
Predicate = _ => true,
ResponseWriter = UIResponseWriter.WriteHealthCheckUIResponse
});
});
app.UseHealthChecksUI();
app.UseStaticFiles();
app.UseRouting();
app.UseEndpoints(endpoints =>
{
endpoints.MapControllerRoute(
name: "default",
pattern: "{controller=Home}/{action=Index}/{id?}");
});
}
}
最后還要在 appsettings.json 中配一下 HealthChecks-UI 中的檢查項(xiàng),如下代碼所示:
{
"Logging": {
"LogLevel": {
"Default": "Information",
"Microsoft": "Warning",
"Microsoft.Hosting.Lifetime": "Information"
}
},
"AllowedHosts": "*",
"HealthChecks-UI": {
"HealthChecks": [
{
"Name": "Local",
"Uri": "http://localhost:65348/health"
}
],
"EvaluationTimeOnSeconds": 10,
"MinimumSecondsBetweenFailureNotifications": 60
}
}
最后在瀏覽器中輸入 /healthchecks-ui 看一下 可視化UI 長(zhǎng)成啥樣。
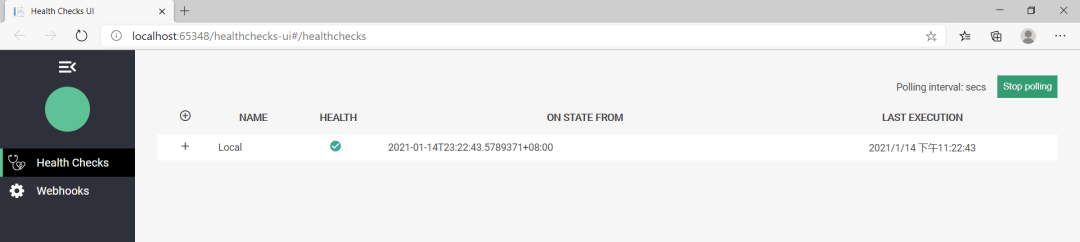
使用 ASP.Net Core 的 健康檢查中間件 可以非常方便的對(duì) 系統(tǒng)資源,數(shù)據(jù)庫(kù) 或者其他域外資源進(jìn)行監(jiān)控,你可以使用自定義檢查邏輯來(lái)判斷什么樣的情況算是 Healthy,什么樣的算是 UnHealthy,值得一提的是,當(dāng)檢測(cè)到失敗時(shí)還可以使用失敗通知機(jī)制,類似 github 發(fā)布鉤子。
譯文鏈接:https://www.infoworld.com/article/3379187/how-to-implement-health-checks-in-aspnet-core.html
回復(fù) 【關(guān)閉】學(xué)關(guān)閉微信朋友圈廣告 回復(fù) 【實(shí)戰(zhàn)】獲取20套實(shí)戰(zhàn)源碼 回復(fù) 【被刪】學(xué)查看你哪個(gè)好友刪除了你巧 回復(fù) 【訪客】學(xué)微信查看朋友圈訪客記錄 回復(fù) 【小程序】學(xué)獲取15套【入門+實(shí)戰(zhàn)+賺錢】小程序源碼 回復(fù) 【python】學(xué)微獲取全套0基礎(chǔ)Python知識(shí)手冊(cè) 回復(fù) 【2019】獲取2019 .NET 開(kāi)發(fā)者峰會(huì)資料PPT 回復(fù) 【加群】加入dotnet微信交流群 臥槽:微信可以這樣換個(gè)字體了!
.NET 5 中的隱藏特性,99%的人還不知道!



