詳解圈復(fù)雜度
點(diǎn)擊上方“程序員大白”,選擇“星標(biāo)”公眾號(hào)
重磅干貨,第一時(shí)間送達(dá)

詳解圈復(fù)雜度
圈復(fù)雜度概念
圈復(fù)雜度(Cyclomatic complexity,簡(jiǎn)寫(xiě)CC)也稱(chēng)為條件復(fù)雜度,是一種代碼復(fù)雜度的衡量標(biāo)準(zhǔn)。由托馬斯·J·麥凱布(Thomas J. McCabe, Sr.)于1976年提出,用來(lái)表示程序的復(fù)雜度,其符號(hào)為VG或是M。它可以用來(lái)衡量一個(gè)模塊判定結(jié)構(gòu)的復(fù)雜程度,數(shù)量上表現(xiàn)為獨(dú)立現(xiàn)行路徑條數(shù),也可理解為覆蓋所有的可能情況最少使用的測(cè)試用例數(shù)。圈復(fù)雜度大說(shuō)明程序代碼的判斷邏輯復(fù)雜,可能質(zhì)量低且難于測(cè)試和 維護(hù)。程序的可能錯(cuò)誤和高的圈復(fù)雜度有著很大關(guān)系。
圈復(fù)雜度計(jì)算方法
點(diǎn)邊計(jì)算法
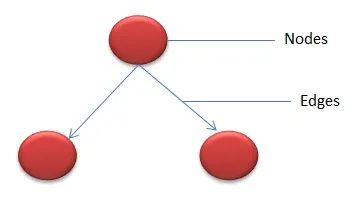
圈復(fù)雜度的計(jì)算方法很簡(jiǎn)單,計(jì)算公式為:
V(G) = E - N + 2
其中,e表示控制流圖中邊的數(shù)量,n表示控制流圖中節(jié)點(diǎn)的數(shù)量。
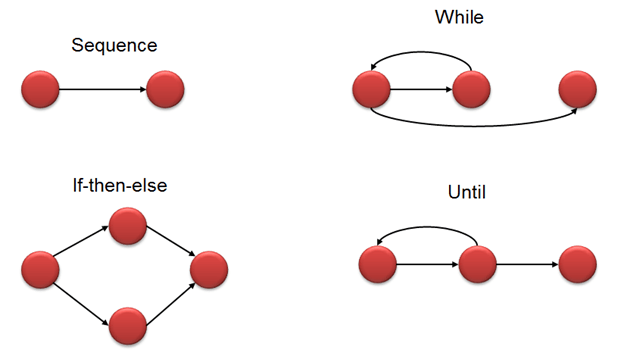
幾個(gè)節(jié)點(diǎn)通過(guò)邊連接。下面是典型的控制流程,如if-else,While,until和正常的流程順序:
節(jié)點(diǎn)判定法
其實(shí),圈復(fù)雜度的計(jì)算還有更直觀(guān)的方法,因?yàn)槿?fù)雜度所反映的是“判定條件”的數(shù)量,所以圈復(fù)雜度實(shí)際上就是等于判定節(jié)點(diǎn)的數(shù)量再加上1,也即控制流圖的區(qū)域數(shù),對(duì)應(yīng)的計(jì)算公式為:
V (G) = P + 1
其中P為判定節(jié)點(diǎn)數(shù),判定節(jié)點(diǎn)舉例:
if語(yǔ)句
while語(yǔ)句
for語(yǔ)句
case語(yǔ)句
catch語(yǔ)句
and和or布爾操作
?:三元運(yùn)算符
對(duì)于多分支的CASE結(jié)構(gòu)或IF-ELSEIF-ELSE結(jié)構(gòu),統(tǒng)計(jì)判定節(jié)點(diǎn)的個(gè)數(shù)時(shí)需要特別注意一點(diǎn),要求必須統(tǒng)計(jì)全部實(shí)際的判定節(jié)點(diǎn)數(shù),也即每個(gè)ELSEIF語(yǔ)句,以及每個(gè)CASE語(yǔ)句,都應(yīng)該算為一個(gè)判定節(jié)點(diǎn)。
判定節(jié)點(diǎn)在模塊的控制流圖中很容易被識(shí)別出來(lái),所以,針對(duì)程序的控制流圖計(jì)算圈復(fù)雜度V(G)時(shí),一般采用點(diǎn)邊計(jì)算法,也即V(G)=e-n+2;而針對(duì)模塊的控制流圖時(shí),可以直接使用統(tǒng)計(jì)判定節(jié)點(diǎn)數(shù),這樣更為簡(jiǎn)單。
圈復(fù)雜度計(jì)算練習(xí)
練習(xí)1:
1void?sort(int?*?A)
2{
3????int?i=0;
4???int?n=4;
5???int?j?=?0;
6???while(i?-1)
7???{
8???????j?=?i?+1
9???????while(j?10???????{
11???????????if?(A[i]?12????????????????swap(A[i],?A[j]);
13???????}
14???????i?=?i?+?1
15???}
16}
使用點(diǎn)邊計(jì)算法繪出控制流圖:
其圈復(fù)雜度為:V(G) = 9 - 7 + 2 = 4
練習(xí)2:
1U32?find?(string?match){
2?????????for(auto?var?:?list)
3?????????{
4?????????????if(var?==?match?&&?from?!=?INVALID_U32)?return?INVALID_U32;
5?????????}
6?????????//match?step1
7?????????if(session?==?getName()?&&?key?==?getKey())
8?????????{
9?????????????for?(auto&?kv?:?Map)
10?????????????{
11?????????????????if?(kv.second?==?last?&&?match?==?kv.first)
12?????????????????{
13?????????????????????return?last;
14?????????????????}
15?????????????}
16
17?????????}
18?????????//match?step2
19?????????auto?var?=?Map.find(match);
20?????????if(var?!=?Map.end()&&?(from?!=?var->second))?return?var->second;
21
22?????????//match?step3
23?????????for(auto?var:?Map)
24?????????{
25?????????????if((var.first,?match)?&&?from?!=?var.second)
26?????????????{
27?????????????????return?var.second;
28?????????????}
29?????????}
30?????????return?INVALID_U32;
31?????};
其圈復(fù)雜度為:V(G) = 1(for) + 2(if) + 2(if) + 1(for) + 2(if) + 2(if) + 1(for) + 2(if) + 1= 14
圈復(fù)雜度的意義
在缺陷成為缺陷之前捕獲它們。
圈復(fù)雜度與缺陷
一般來(lái)說(shuō)圈復(fù)雜度大于10的方法存在很大的出錯(cuò)風(fēng)險(xiǎn)。圈復(fù)雜度和缺陷個(gè)數(shù)有高度的正相關(guān):圈復(fù)雜度最高的模塊和方法,其缺陷個(gè)數(shù)也可能最多。
圈復(fù)雜度與結(jié)構(gòu)化測(cè)試
此外,它還為測(cè)試設(shè)計(jì)提供很好的參考。一個(gè)好的用例設(shè)計(jì)經(jīng)驗(yàn)是:創(chuàng)建數(shù)量與被測(cè)代碼圈復(fù)雜度值相等的測(cè)試用例,以此提升用例對(duì)代碼的分支覆蓋率。
圈復(fù)雜度與TDD
TDD(測(cè)試驅(qū)動(dòng)的開(kāi)發(fā),test-driven development)和低CC值之間存在著緊密聯(lián)系。在編寫(xiě)測(cè)試時(shí),開(kāi)發(fā)人員會(huì)考慮代碼的可測(cè)試性,傾向于編寫(xiě)簡(jiǎn)單的代碼,因?yàn)閺?fù)雜的代碼難以測(cè)試。因此TDD的“代碼、測(cè)試、代碼、測(cè)試” 循環(huán)將導(dǎo)致頻繁重構(gòu),驅(qū)使非復(fù)雜代碼的開(kāi)發(fā)。
圈復(fù)雜度與遺留代碼
對(duì)于遺留代碼的維護(hù)或重構(gòu),測(cè)量圈復(fù)雜度特別有價(jià)值。一般使用圈復(fù)雜度作為提升代碼質(zhì)量的切入點(diǎn)。
圈復(fù)雜度與CI
在持續(xù)集成環(huán)境中,可以基于時(shí)間變化維度來(lái)評(píng)估模塊或函數(shù)的復(fù)雜度和增長(zhǎng)值。如果CC值在不斷增長(zhǎng),那么應(yīng)該開(kāi)展兩項(xiàng)活動(dòng):
確保相關(guān)測(cè)試的有效性,減少故障風(fēng)險(xiǎn)。
評(píng)估重構(gòu)必要性和具體方式,以降低出現(xiàn)代碼維護(hù)問(wèn)題的可能性。
圈復(fù)雜度和軟件質(zhì)量
| 圈復(fù)雜度 | 代碼狀況 | 可測(cè)性 | 維護(hù)成本 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1-10 | 清晰、結(jié)構(gòu)化 | 高 | 低 |
| 10-20 | 復(fù)雜 | 中 | 中 |
| 20-30 | 非常復(fù)雜 | 低 | 高 |
| >30 | 不可讀 | 不可測(cè) | 非常高 |
降低圈復(fù)雜度的方法
重新組織你的函數(shù)
技巧1 提煉函數(shù)
有一段代碼可以被組織在一起并獨(dú)立出來(lái):
1void?Example(int?val)
2{
3????if(?val?>?MAX_VAL)
4????{
5????????val?=?MAX_VAL;
6????}
7
8????for(?int?i?=?0;?i? 9????{
10????????doSomething(i);
11????}
12}將這段代碼放進(jìn)一個(gè)獨(dú)立函數(shù)中,并讓函數(shù)名稱(chēng)解釋該函數(shù)的用途:
1int?getValidVal(int?val)
2{
3???????if(?val?>?MAX_VAL)
4????{
5????????return?MAX_VAL;
6????}?
7????return?val;
8}
9
10void?doSomethings(int?val)
11{
12????for(?int?i?=?0;?i?13????{
14????????doSomething(i);
15????}
16}
17
18void?Example(int?val)
19{
20????doSomethings(getValidVal(val));
21}最后還要重新審視函數(shù)內(nèi)容是否在統(tǒng)一層次上。
技巧2 替換算法
把某個(gè)算法替換為另一個(gè)更清晰的算法:
1string?foundPerson(const?vector<string>&?peoples){
2??for?(auto&?people?:?peoples)?
3??{
4????if?(people?==?"Don"){
5??????return?"Don";
6????}
7????if?(people?==?"John"){
8??????return?"John";
9????}
10????if?(people?==?"Kent"){
11??????return?"Kent";
12????}
13??}
14??return?"";
15}將函數(shù)實(shí)現(xiàn)替換為另一個(gè)算法:
1string?foundPerson(const?vector<string>&?people){
2??std::map<string,string>candidates{
3????????{?"Don",?"Don"},
4????????{?"John",?"John"},
5????????{?"Kent",?"Kent"},
6???????};
7??for?(auto&?people?:?peoples)?
8??{
9????auto&?it?=?candidates.find(people);
10????if(it?!=?candidates.end())
11????????return?it->second;
12??}
13}所謂的表驅(qū)動(dòng)。
簡(jiǎn)化條件表達(dá)式
技巧3 逆向表達(dá)
在代碼中可能存在條件表達(dá)如下:
1if?((condition1()?&&?condition2())?||?!condition1())
2{
3????return?true;
4}
5else
6{
7????return?false;
8}
應(yīng)用逆向表達(dá)調(diào)換表達(dá)順序后效果如下:
1if(condition1()?&&?!condition2())
2{
3????return?false;
4}
5
6return?true;技巧4 分解條件
在代碼中存在復(fù)雜的條件表達(dá):
1if(date.before?(SUMMER_START)?||?date.after(SUMMER_END))
2????charge?=?quantity?*?_winterRate?+?_winterServiceCharge;
3else?
4????charge?=?quantity?*?_summerRate;從if、then、else三個(gè)段落中分別提煉出獨(dú)立函數(shù):
1if(notSummer(date))
2????charge?=?winterCharge(quantity);
3else?
4????charge?=?summerCharge?(quantity);技巧5 合并條件
一系列條件判斷,都得到相同結(jié)果:
1double?disabilityAmount()?
2{
3????if?(_seniority?2)?return?0;
4????if?(_monthsDisabled?>?12)?return?0;
5????if?(_isPartTime)?return?0;
6????//?compute?the?disability?amount
7????......將這些判斷合并為一個(gè)條件式,并將這個(gè)條件式提煉成為一個(gè)獨(dú)立函數(shù):
1double?disabilityAmount()?
2{
3????if?(isNotEligableForDisability())?return?0;
4????//?compute?the?disability?amount
5????......技巧6 移除控制標(biāo)記
在代碼邏輯中,有時(shí)候會(huì)使用bool類(lèi)型作為邏輯控制標(biāo)記:
1void?checkSecurity(vector<string>&?peoples)?{
2????bool?found?=?false;
3????for?(auto&?people?:?peoples)?
4????{
5????????if?(!?found)?{
6????????????if?(people?==?"Don"){
7????????????????sendAlert();
8????????????????found?=?true;
9????????????}
10????????????if?(people?==?"John"){
11???????????????????sendAlert();
12???????????????????found?=?true;
13????????????}
14????????}
15????}
16}使用break和return取代控制標(biāo)記:
1void?checkSecurity(vector<string>&?peoples)?{
2????for?(auto&?people?:?peoples)
3????{?????
4????????if?(people?==?"Don"?||?people?==?"John")
5????????{
6????????????sendAlert();
7????????????break;
8????????}
9????}
10}技巧7 以多態(tài)取代條件式
條件式根據(jù)對(duì)象類(lèi)型的不同而選擇不同的行為:
1double?getSpeed()?
2{
3????switch?(_type)?{
4????????case?EUROPEAN:
5????????????return?getBaseSpeed();
6????????case?AFRICAN:
7????????????return?getBaseSpeed()?-?getLoadFactor()?*_numberOfCoconuts;
8????????case?NORWEGIAN_BLUE:
9????????????return?(_isNailed)???0?:?getBaseSpeed(_voltage);
10????}
11????throw?new?RuntimeException?("Should?be?unreachable");
12}
將整個(gè)條件式的每個(gè)分支放進(jìn)一個(gè)子類(lèi)的重載方法中,然后將原始函數(shù)聲明為抽象方法:
1class?Bird
2{
3public:
4????virtual?double?getSpeed()?=?0;
5
6protected:
7????double?getBaseSpeed();
8}
9
10class?EuropeanBird
11{
12public:
13????double?getSpeed()
14????{
15????????return?getBaseSpeed();
16????}
17}
18
19class?AfricanBird
20{
21public:
22????double?getSpeed()
23????{
24????????return?getBaseSpeed()?-?getLoadFactor()?*_numberOfCoconuts;
25????}
26
27private:
28????double?getLoadFactor();
29
30????double?_numberOfCoconuts;
31}
32
33class?NorwegianBlueBird
34{
35public:
36????double?getSpeed()
37????{
38????????return?(_isNailed)???0?:?getBaseSpeed(_voltage);
39????};
40
41private:
42????bool?_isNailed;
43}簡(jiǎn)化函數(shù)調(diào)用
技巧8 讀寫(xiě)分離
某個(gè)函數(shù)既返回對(duì)象狀態(tài)值,又修改對(duì)象狀態(tài):
1class?Customer
2{
3????int?getTotalOutstandingAndSetReadyForSummaries(int?number);
4}建立兩個(gè)不同的函數(shù),其中一個(gè)負(fù)責(zé)查詢(xún),另一個(gè)負(fù)責(zé)修改:
1class?Customer
2{
3????int?getTotalOutstanding();
4????void?SetReadyForSummaries(int?number);
5}技巧9 參數(shù)化方法
若干函數(shù)做了類(lèi)似的工作,但在函數(shù)本體中卻 包含了不同的值:
1Dollars?baseCharge()
2?{
3????double?result?=?Math.min(lastUsage(),100)?*?0.03;
4????if?(lastUsage()?>?100)
5????{
6????????result?+=?(Math.min?(lastUsage(),200)?-?100)?*?0.05;
7????}
8????if?(lastUsage()?>?200)
9????{
10????????result?+=?(lastUsage()?-?200)?*?0.07;
11????}
12????return?new?Dollars?(result);
13}
14
建立單一函數(shù),以參數(shù)表達(dá)那些不同的值:
1Dollars?baseCharge()?
2{
3????double?result?=?usageInRange(0,?100)?*?0.03;
4????result?+=?usageInRange?(100,200)?*?0.05;
5????result?+=?usageInRange?(200,?Integer.MAX_VALUE)?*?0.07;
6????return?new?Dollars?(result);
7}
8
9int?usageInRange(int?start,?int?end)?
10{
11????if?(lastUsage()?>?start)?
12????????return?Math.min(lastUsage(),end)?-start;
13
14????return?0;
15}技巧10 以明確函數(shù)取代參數(shù)
函數(shù)實(shí)現(xiàn)完全取決于參數(shù)值而采取不同反應(yīng):
1void?setValue?(string?name,?int?value)?
2{
3????if?(name?==?"height")
4????????_height?=?value;
5????else?if?(name?==?"width")
6????????_width?=?value;
7????Assert.shouldNeverReachHere();
8}
針對(duì)該參數(shù)的每一個(gè)可能值,建立一個(gè)獨(dú)立函數(shù):
1void?setHeight(int?arg)?
2{
3????_height?=?arg;
4}
5void?setWidth?(int?arg)?
6{
7????_width?=?arg;
8}實(shí)戰(zhàn)練習(xí)
還是以之前統(tǒng)計(jì)CC值的例子:
1?U32?find?(string?match){
2?????????for(auto?var?:?List)
3?????????{
4?????????????if(var?==?match?&&?from?!=?INVALID_U32)?
5????????????return?INVALID_U32;
6?????????}
7?????????//match?step1
8?????????if(session?==?getName()?&&?key?==?getKey())
9?????????{
10?????????????for?(auto&?kv?:?Map)
11?????????????{
12?????????????????if?(kv.second?==?last?&&?match?==?kv.first)
13?????????????????{
14?????????????????????return?last;
15?????????????????}
16?????????????}
17
18?????????}
19?????????//match?step2
20?????????auto?var?=?Map.find(match);
21?????????if(var?!=?Map.end()&&?(from?!=?var->second))?return?var->second;
22
23?????????//match?step3
24?????????for(auto?var:?Map)
25?????????{
26?????????????if((var.first,?match)?&&?from?!=?var.second)
27?????????????{
28?????????????????return?var.second;
29?????????????}
30?????????}
31?????????return?INVALID_U32;
32?????};綜合運(yùn)用降低CC值的技巧后:
1namespace
2{
3????struct?Matcher
4????{
5????????Matcher(string?name,?string?key);
6????????U32?find();
7
8????private:
9????????bool?except();
10????????U32?matchStep1();
11????????U32?matchStep2();
12????????U32?matchStep3();
13
14????????bool?isTheSameMatch();
15
16????????string?match;
17????????U32?from;
18????};
19
20????Matcher::Matcher(string?name,?string?key):
21????????match(name?+?key)
22????{
23????????from?=?GetFrom();
24????}
25
26????U32?Matcher::find()
27????{
28????????if?(except())
29????????????return?INVALID_U32;
30
31????????auto?result?=?matchStep1();
32????????if?(result?!=?INVALID_U32)
33????????????return?result;
34
35????????result?=?matchStep2();
36????????if?(result?!=?INVALID_U32)
37????????????return?result;
38
39????????return?matchStep3();
40????}
41
42????bool?Matcher::except()
43????{
44????????for(auto?var?:?List)
45????????{
46????????????if(var?==?match?&&?from?!=?INVALID_U32)
47????????????????return?true;
48????????}
49
50????????return?false;
51????}
52
53????U32?Matcher::matchStep1()
54????{
55????????if(!isTheSameMatch())
56????????{
57????????????return?INVALID_U32;
58????????}
59
60????????for?(auto&?kv?:?Map)
61????????{
62????????????if?(?last?==?kv.second?&&?match?==?kv.first)
63????????????{
64????????????????return?last;
65????????????}
66????????}
67
68????????return?INVALID_U32;
69????}
70
71????bool?Matcher::isTheSameMatch()
72????{
73????????return?match?==?getName()?+?getKey();
74????}
75
76????U32?Matcher::matchStep2()
77????{
78????????auto?var?=?Map.find(match);
79????????if(var?!=?Map.end()&&?(from?!=?var->second))
80????????{
81????????????return?var->second;
82????????}
83
84????????return?INVALID_U32;
85????}
86
87????U32?Matcher::matchStep3()
88????{
89????????for(auto?var:?Map)
90????????{
91????????????if(keyMatch(var.first,?match)?&&?from?!=?var.second)
92????????????{
93????????????????return?var.second;
94????????????}
95????????}
96
97????????return?INVALID_U32;
98????}
99}
100
101U32?find?(string?match)
102{
103????Matcher?matcher;
104
105????return?matcher.find(match);
106}
107
該例子將匹配算法都封裝到Matcher類(lèi)中,并將原有邏輯通過(guò)提煉函數(shù)(技巧1)和合并條件(技巧6)將匹配邏輯抽象成能力查詢(xún)、粘滯、精確匹配及模糊匹配四個(gè)步驟,這樣將循環(huán)和條件分支封入小函數(shù)中,從而降低接口函數(shù)(findPno)的圈復(fù)雜度,函數(shù)職責(zé)也更加單一和清晰。整體圈復(fù)雜度從單個(gè)函數(shù)的14降到多個(gè)函數(shù)最高的5。
圈復(fù)雜度思辨
思辨1 高復(fù)雜度的代碼是否可維護(hù)性差
在實(shí)際項(xiàng)目中為了調(diào)試方便,經(jīng)常會(huì)把消息號(hào)對(duì)應(yīng)的名稱(chēng)打印出來(lái):
1string?getMessageName(Message?msg)
2{
3????switch(msg)
4????{
5????????case?MSG_1:
6????????????return?"MSG_1";
7????????case?MSG_2:
8????????????return?"MSG_2";
9????????case?MSG_3:
10????????????return?"MSG_3";
11????????case?MSG_4:
12????????????return?"MSG_4";
13????????case?MSG_5:
14????????????return?"MSG_5";
15????????case?MSG_6:
16????????????return?"MSG_6";
17????????case?MSG_7:
18????????????return?"MSG_7";
19????????case?MSG_8:
20????????????return?"MSG_8";
21????????default:
22????????????return?"MSG_UNKNOWN"
23????}
24}這段代碼無(wú)論從可讀性來(lái)說(shuō),還是從可維護(hù)性來(lái)說(shuō)都是可以接收的。因此,當(dāng)因?yàn)椤备摺睆?fù)雜度就進(jìn)行重構(gòu)的話(huà)(例如:技巧2或技巧6),在降低圈復(fù)雜度的同時(shí)會(huì)帶來(lái)不必要的邏輯復(fù)雜度。
當(dāng)然,如果出現(xiàn)下面的情況的話(huà),還是有必要進(jìn)一步降低圈復(fù)雜度的:
消息數(shù)過(guò)多。
switch…case…多處重復(fù)。對(duì)于消息過(guò)多的情況,可以考慮將消息進(jìn)行分類(lèi),然后采用技巧1進(jìn)行重構(gòu)。對(duì)于出現(xiàn)多處重復(fù)的情況,可以通過(guò)技巧6將同樣case的內(nèi)容內(nèi)聚到一個(gè)具體的類(lèi)的方法中,然后通過(guò)多態(tài)的方式來(lái)使用。
思辨2 復(fù)雜度相同的代碼是否是一致的
例如下面兩個(gè)代碼片段的圈復(fù)雜度都是6。代碼片段1:
1string?getWeight(int?i)?{
2????????if?(i?<=?0)?
3????????{
4????????????????return?"no?weight";
5????????}
6????????if?(i?10)?
7????????{
8????????????????return?"light";
9????????}
10????????if?(i?20)?
11????????{
12????????????????return?"medium";
13????????}
14????????if?(i?30)?
15????????{
16????????????????return?"heavy";
17????????}
18????????if?(i?40)
19????????{
20????????????return?"very?heavy";
21????????}
22
23????????return?"super?heavy"
24}
代碼片段2
1int?sumOfNonPrimes(int?limit)?{
2????????bool?bAdd?=?false;
3????????int?sum?=?0;
4????????for?(int?i?=?0;?i? 5????????????????if?(i?<=?2)?
6????????????????????continue;
7
8????????????????for?(int?j?=?2;?j? 9????????????????{
10????????????????????if?(i?%?j?==?0)?
11????????????????????{
12????????????????????????????bAdd?=?false;
13????????????????????????????break;
14????????????????????}
15????????????????????bAdd?=?true;
16????????????????}
17????????????????if?(bAdd)
18????????????????????sum?+=?i;
19????????}
20????????return?sum;
21}
但是它們的代碼無(wú)論從可讀性上來(lái)說(shuō),還是從可維護(hù)性來(lái)說(shuō),代碼片段1應(yīng)該都優(yōu)于代碼片段2,代碼片段2的壞味道更加濃郁。因此,圈復(fù)雜度還需要具體情況具體分析,其只能作為重構(gòu)的一個(gè)度量指標(biāo),作為決策的一個(gè)參考依據(jù)。
圈復(fù)雜度工具
圈復(fù)雜度的工具有很多,大致有三類(lèi):
| 類(lèi)型 | 名稱(chēng) | 說(shuō)明 |
|---|---|---|
| 專(zhuān)用工具(單語(yǔ)言) | OCLint | C語(yǔ)言相關(guān) |
| GMetrics | Java | |
| PyMetrics | python | |
| JSComplexity | js | |
| 通用工具(多語(yǔ)言) | lizard | 支持多種語(yǔ)言:C/C++ (works with C++14)、Java、C#、JavaScript、Objective C、Swift、Python、Ruby、PHP、Scala等。 |
| sourcemonitor | 免費(fèi)、Windows平臺(tái)。支持語(yǔ)言包括C、C++、C#、Java、VB、Delphi和HTML。 | |
| 通用平臺(tái) | sonarqube | 一個(gè)用于代碼質(zhì)量管理的開(kāi)源平臺(tái),支持20多種語(yǔ)言。通過(guò)插件機(jī)制可集成不同的測(cè)試工具,代碼分析工具及持續(xù)集成工具 |
source: //kaelzhang81.github.io/2017/06/18/詳解圈復(fù)雜度
推薦閱讀
關(guān)于程序員大白
程序員大白是一群哈工大,東北大學(xué),西湖大學(xué)和上海交通大學(xué)的碩士博士運(yùn)營(yíng)維護(hù)的號(hào),大家樂(lè)于分享高質(zhì)量文章,喜歡總結(jié)知識(shí),歡迎關(guān)注[程序員大白],大家一起學(xué)習(xí)進(jìn)步!

