使用 MongoTemplate 對 MongoDB 進(jìn)行 CRUD
早期文章
MongoDB 是一個基于分布式文件存儲的數(shù)據(jù)庫,由 C++ 編寫,它是可擴(kuò)展的高性能數(shù)據(jù)存儲解決方案。來看一下 MongoDB 官網(wǎng)對于 MongoDB 的簡單介紹。

一、MongoDB 使用簡介
在 MongoDB 中,它的一些名詞與關(guān)系型數(shù)據(jù)庫的名詞不太相同,我引入一張圖供大家進(jìn)行參考,如下圖所示。
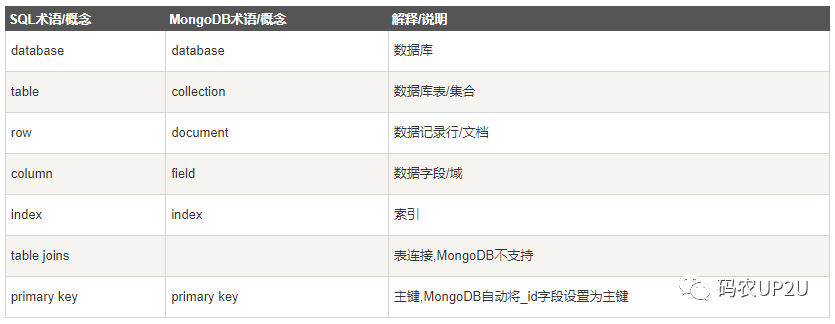
該圖片來自如下網(wǎng)址:
https://www.runoob.com/mongodb/mongodb-databases-documents-collections.html
在 MongoDB 中,集合就相當(dāng)于關(guān)系型數(shù)據(jù)庫中表的概念,但是它和表又不一樣。因為同一個集合下可以存儲不同的數(shù)據(jù),且集合與集合之間不存在關(guān)聯(lián)關(guān)系。它也沒有列的概念,在使用 MongoDB 時無需提前定義它的列與數(shù)據(jù)類型(盡管實際使用中還是會通過實體類定義一下),沒有列的概念,那么每一行的數(shù)據(jù)可以存儲意義上完全不同的數(shù)據(jù),比如商品詳情信息,可以把手機和電腦放入一個集合,但是手機和電腦的參數(shù)詳情完全不同,對于 MongoDB 而言是沒有問題的。
在對 MongoDB 做完簡單的介紹后,再介紹幾個 MongoDB 常用的命令:
1.查看 MongoDB 中的數(shù)據(jù)庫
show dbs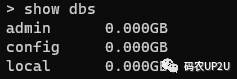
2.選擇數(shù)據(jù)庫
use local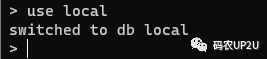
3.查看數(shù)據(jù)庫中的集合
show collections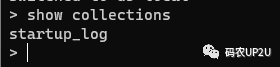
4.查看集合中的全部數(shù)據(jù)
db.startup_log.find()更多的使用命令,可以參考 MongoDB 的文件進(jìn)行學(xué)習(xí)了解。
二、在 SpringBoot 中引入依賴
在 SpringBoot 項目中使用 MongoDB,首先需要引入 MongoDB 的依賴,通過在 POM 文件中引入 MongoDB 的依賴坐標(biāo),即可將操作 MongoDB 的類庫整合入 SpringBoot 項目當(dāng)中,相關(guān)依賴如下:
<dependency><groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId><artifactId>spring-boot-starter-data-mongodb</artifactId></dependency>
三、添加配置
引入依賴之后,需要在配置文件中添加 MongoDB 的地址,如同我們使用 MySQL 一樣需要給出它的地址。
spring:data:mongodb:uri: mongodb://127.0.0.1:27017/test
在上面的 uri 中,test 指定了我們 Demo 中要操作的數(shù)據(jù)庫。
四、定義對應(yīng) MongoDB 中集合的實體類
操作 MySQL 時,我們會將 MySQL 的表在項目中定義一個對應(yīng)的實體類,操作 MongoDB 的集合也需要定義一個對應(yīng)的實體類。這里定義一個 Student 的實體類作為 Demo 中的實體類來進(jìn)行操作。
@Data@Document("Student")public class Student {@Idprivate String id;private String name;private Integer age;private String email;}
在實體類上添加注解 @Document,@Document 中給出的是集合的名稱。注解 @Id 會將該字段與 MongoDB 生成的 _id 進(jìn)行關(guān)聯(lián)。
在具體操作 MongoDB 時可以通過 MongoTemplate 來進(jìn)行操作,也可以通過 MongoRepository 來進(jìn)行操作。下面我們將介紹如何使用 MongoTemplate 來完成對 MongoDB 的 CRUD 操作。
五、使用 MongoTemplate 完成 CRUD
MongoTemplate 基于 Spring 容器提供了一組對 MongoDB 操作的基本方法,只要將 MongoTemplate 注入到需要使用的類中,即可直接使用。
1.注入 MongoTemplate
創(chuàng)建一個測試類,通過 @Autowired 將 MongoTemplate 進(jìn)行注入,代碼如下。
@Autowiredprivate MongoTemplate mongoTemplate;
2.添加操作
在注入 MongoTemplate 后,我們即可在測試類中完成 CRUD 的操作,先來完成一個添加數(shù)據(jù)的操作,代碼如下:
/*** 添加操作*/@Testvoid create() {for (int i = 0; i < 10; i ++) {Student student = new Student();student.setAge(20 + i);student.setName("test" + i);student.setEmail(i + "[email protected]");Student insert = mongoTemplate.insert(student);System.out.println(insert);}}
通過 MongoTemplate 的 insert 方法,即可完成數(shù)據(jù)的插入操作。
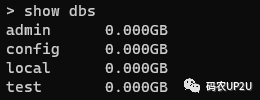
執(zhí)行上面的測試代碼后,我們通過 MongoDB 的客戶端來查看一下我們添加的數(shù)據(jù)。首先通過 show dbs 命令來查看 MongoDB 中的數(shù)據(jù)庫,可以看到多了一個 test 數(shù)據(jù)庫,如下圖所示:
然后,使用 use 選擇該數(shù)據(jù)庫,使用 show collections 查看 test 下的集合,可以看到在 test 數(shù)據(jù)庫下自動創(chuàng)建了一個 Student 的集合,如下圖所示:
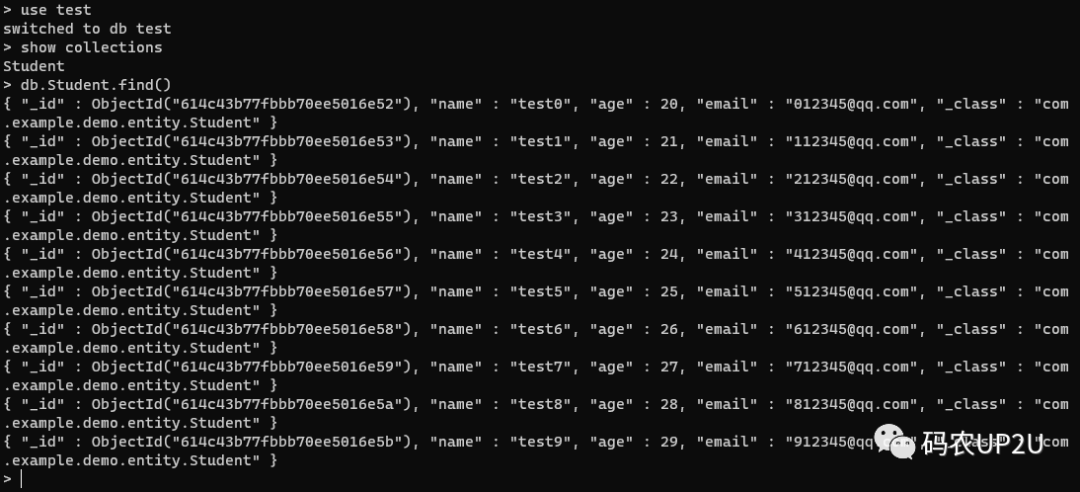
可以看到,在我們執(zhí)行上面的方法之前,并沒有去創(chuàng)建 test 數(shù)據(jù)庫,也沒有創(chuàng)建 Student 集合。執(zhí)行了上面的代碼后,會自動創(chuàng)建 test 數(shù)據(jù)庫和 Student 集合,并且在 Student 集合中插入了 10 條文檔。
3.查詢集合中的所有記錄
上面完成了文檔數(shù)據(jù)插入的操作,現(xiàn)在通過 MongoTemplate 來將其全部查出,代碼如下:
/*** 查詢表中所有記錄*/@Testvoid findAll() {List<Student> all = mongoTemplate.findAll(Student.class);all.forEach(System.out::println);}
通過 MongoTemplate 的 findAll 方法可以查詢指定集合下的所有文檔。
執(zhí)行上面的代碼后,在控制臺會輸出 Student 集合中的全部文檔,輸出內(nèi)容如下所示。
Student(id=614c43b77fbbb70ee5016e52, name=test0, age=20, [email protected])Student(id=614c43b77fbbb70ee5016e53, name=test1, age=21, [email protected])Student(id=614c43b77fbbb70ee5016e54, name=test2, age=22, [email protected])Student(id=614c43b77fbbb70ee5016e55, name=test3, age=23, [email protected])Student(id=614c43b77fbbb70ee5016e56, name=test4, age=24, [email protected])Student(id=614c43b77fbbb70ee5016e57, name=test5, age=25, [email protected])Student(id=614c43b77fbbb70ee5016e58, name=test6, age=26, [email protected])Student(id=614c43b77fbbb70ee5016e59, name=test7, age=27, [email protected])Student(id=614c43b77fbbb70ee5016e5a, name=test8, age=28, [email protected])Student(id=614c43b77fbbb70ee5016e5b, name=test9, age=29, [email protected])
從輸出中可以看出,MongoDB 為我們生成了 id,通過這個 id 我們可以唯一的確定一條數(shù)據(jù)。
4.通過 id 查詢指定的文檔
通常,我們在查詢指定的某條數(shù)據(jù)時會通過 id 進(jìn)行查詢,在添加數(shù)據(jù)時,可以看到 MongoDB 為我們自動生成了 id,名為 _id,只要通過 MongoTemplate 的 findById 方法,并傳入相應(yīng)的 id 值即可進(jìn)行查詢,代碼如下:
/*** 根據(jù) id查詢*/@Testvoid findById() {Student byId = mongoTemplate.findById("614c43b77fbbb70ee5016e52", Student.class);System.out.println(byId);}
從上面的代碼中可以看到,通過 MongoTemplate 的 findById 可以獲取指定 id 的文檔。
5.條件查詢
MongoDB 支持非常強大的查詢功能,這里簡單的完成一個條件查詢。代碼如下:
/*** 條件查詢*/@Testvoid findUserList() {// name = test0 and age = 20Query query = new Query(Criteria.where("name").is("test0").and("age").is(20));List<Student> users = mongoTemplate.find(query, Student.class);users.forEach(System.out::println);}
在上面的代碼中,Criteria 是 MongoTemplate 的標(biāo)準(zhǔn)查詢接口,它可以把多個查詢條件通過鏈?zhǔn)讲僮鬟M(jìn)行拼接,然后通過 Query 可以構(gòu)建查詢語句,上面的查詢相當(dāng)于如下 SQL 語句:
select * from student where name = 'test0' and age = 20 再來完成一個 or 的查詢,代碼如下:
/*** 條件查詢*/@Testvoid findUserList() {Query query = new Query(new Criteria().orOperator(Criteria.where("name").is("test0").and("age").is(20),Criteria.where("age").gt(25)));List<Student> users = mongoTemplate.find(query, Student.class);users.forEach(System.out::println);}
注意上面代碼中關(guān)于 Criteria 的寫法,上面的代碼,相當(dāng)于如下 SQL 語句:
select * from student where (name = 'test0' and age = 20) or (age > 25) or 查詢的輸出結(jié)果如下:
Student(id=614c43b77fbbb70ee5016e52, name=test0, age=20, [email protected])Student(id=614c43b77fbbb70ee5016e58, name=test6, age=26, [email protected])Student(id=614c43b77fbbb70ee5016e59, name=test7, age=27, [email protected])Student(id=614c43b77fbbb70ee5016e5a, name=test8, age=28, [email protected])Student(id=614c43b77fbbb70ee5016e5b, name=test9, age=29, [email protected])
通過上面的輸出可以驗證 or 查詢的寫法是正確的。
6.模糊查詢
MongoDB 的模糊查詢可以使用正則表達(dá)式來進(jìn)行完成,代碼如下:
/*** 模糊查詢*/@Testvoid findLikeUserList() {// name like test and age = 20String name = "est";String regex = String.format("%s%s%s", "^.*", name, ".*$");Pattern pattern = Pattern.compile(regex, Pattern.CASE_INSENSITIVE);Query query = new Query(Criteria.where("name").regex(pattern).and("age").is(20));List<Student> users = mongoTemplate.find(query, Student.class);users.forEach(System.out::println);}
上面的代碼中,在 Criteria.where 后面使用了 regex,而不是 is,就可以使用正則表達(dá)式來進(jìn)行查詢。上面的模糊查詢相當(dāng)于是 SQL 語句中的 like,由于我們的 name 字段中都能匹配到 est 字符串,這個例子也就沒有太多的意義了。
7.分頁查詢
在 MySQL 中進(jìn)行數(shù)據(jù)的分頁查詢,一般需要給接口傳入頁碼和每頁記錄的條數(shù),當(dāng)然也需要傳入一些查詢條件。對于 MongoDB 而言,傳入接口的數(shù)據(jù)也是一樣的。
/*** 分頁查詢*/@Testvoid findPageUserList() {int pageNo = 2;int pageSize = 3;// 條件構(gòu)件Query query = new Query(Criteria.where("age").gt(23));// 分頁構(gòu)件// 查詢記錄數(shù)long count = mongoTemplate.count(query, Student.class);// 分頁List<Student> users = mongoTemplate.find(query.skip((pageNo - 1) * pageSize).limit(pageSize),Student.class);System.out.println(count);users.forEach(System.out::println);}
分頁查詢通過 query 的 skip 和 limit 進(jìn)行完成,此處也類似于 MySQL 的 limit 的用法。上面的代碼中,我們的分頁每頁顯示 3 條,當(dāng)前頁是第 2 頁。在代碼的第 16 行,通過 MongoTemplate 的 count 獲取了滿足條件的記錄總數(shù),以上代碼輸出的數(shù)據(jù)如下:
6Student(id=614c43b77fbbb70ee5016e59, name=test7, age=27, [email protected])Student(id=614c43b77fbbb70ee5016e5a, name=test8, age=28, [email protected])Student(id=614c43b77fbbb70ee5016e5b, name=test9, age=29, [email protected])
在我們的條件中,我們查詢 age 大于 23 的,也就是從 24 到 29,一共有 6 條數(shù)據(jù)。前 3 條是 24 到 26,那么此處的數(shù)據(jù)顯示是正確的。
8.修改數(shù)據(jù)
修改數(shù)據(jù)時首先對數(shù)據(jù)進(jìn)行查詢,然后設(shè)置需要修改的值,進(jìn)行數(shù)據(jù)的更新。
/*** 修改*/@Testvoid updateUser() {// 根據(jù)id查詢Student user = mongoTemplate.findById("614c43b77fbbb70ee5016e59", Student.class);// 設(shè)置修改值assert user != null;user.setName("zhangsan");user.setAge(30);user.setEmail("[email protected]");Query query = new Query(Criteria.where("_id").is(user.getId()));Update update = new Update();update.set("name", user.getName());update.set("age", user.getAge());update.set("email", user.getEmail());// 調(diào)用方法實現(xiàn)修改UpdateResult upsert = mongoTemplate.upsert(query, update, Student.class);System.out.println(upsert.getModifiedCount());}
通過 MongoTemplate 的 upsert 方法可以對數(shù)據(jù)進(jìn)行修改,修改后的數(shù)據(jù)如下圖:
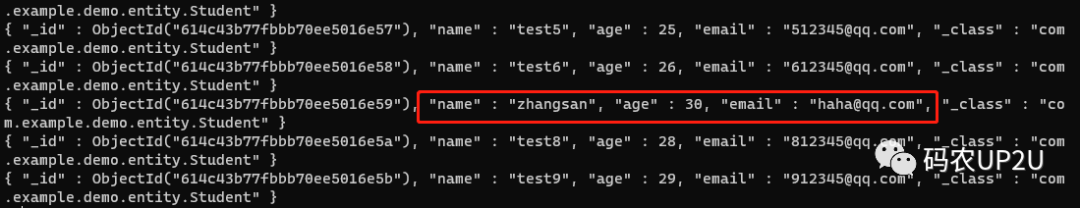
在上面的代碼中,如果只需要更新 name 或 age 或 email 中的一個,那么只需要設(shè)置其中一個值即可,無需全部進(jìn)行 set。
9.刪除數(shù)據(jù)
刪除操作同樣通過 Query 類構(gòu)造要刪除的條件,然后調(diào)用 remove 方法進(jìn)行刪除即可。
/*** 刪除操作*/@Testvoid deleteUser(){Query query = new Query(Criteria.where("_id").is("614c43b77fbbb70ee5016e59"));DeleteResult remove = mongoTemplate.remove(query, Student.class);System.out.println(remove.getDeletedCount());}
通過 MongoTemplate 的 remove 方法,我們刪除了一條數(shù)據(jù),通過 db.Student.find() 命令進(jìn)行查看,可以看到剛才更新過的 zhangsan 那條數(shù)據(jù)已經(jīng)被刪除了。調(diào)用 remove 方法后,會返回 DeleteResult 對象,通過該對象調(diào)用 getDeletedCount 方法可以獲得刪除的記錄數(shù)。
六、總結(jié)
MongoDB 已經(jīng)被越來越多的使用,它適合于對大量的、無固定數(shù)據(jù)結(jié)構(gòu)的數(shù)據(jù)進(jìn)行存儲。本文簡單的介紹了通過使用 MongoTemplate 來對 MongoDB 進(jìn)行 CRUD 的操作。下次來介紹通過 MongoRepository 對 MongoDB 的 CRUD 操作。
更多文章
