ES 和 Clickhouse 查詢能力對比,實(shí)踐結(jié)果根本料不到……
點(diǎn)擊關(guān)注公眾號,Java干貨及時(shí)送達(dá)??
 來源:zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/353296392
來源:zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/353296392
架構(gòu)和設(shè)計(jì)的對比 查詢對比實(shí)戰(zhàn) 總結(jié)
Elasticsearch 是一個(gè)實(shí)時(shí)的分布式搜索分析引擎,它的底層是構(gòu)建在Lucene之上的。簡單來說是通過擴(kuò)展Lucene的搜索能力,使其具有分布式的功能。ES通常會和其它兩個(gè)開源組件logstash(日志采集)和Kibana(儀表盤)一起提供端到端的日志/搜索分析的功能,常常被簡稱為ELK。
Clickhouse是俄羅斯搜索巨頭Yandex開發(fā)的面向列式存儲的關(guān)系型數(shù)據(jù)庫。ClickHouse是過去兩年中OLAP領(lǐng)域中最熱門的,并于2016年開源。
ES是最為流行的大數(shù)據(jù)日志和搜索解決方案,但是近幾年來,它的江湖地位受到了一些挑戰(zhàn),許多公司已經(jīng)開始把自己的日志解決方案從ES遷移到了Clickhouse,這里就包括:攜程,快手等公司。
架構(gòu)和設(shè)計(jì)的對比
ES的底層是Lucenc,主要是要解決搜索的問題。搜索是大數(shù)據(jù)領(lǐng)域要解決的一個(gè)常見的問題,就是在海量的數(shù)據(jù)量要如何按照條件找到需要的數(shù)據(jù)。搜索的核心技術(shù)是倒排索引和布隆過濾器。ES通過分布式技術(shù),利用分片與副本機(jī)制,直接解決了集群下搜索性能與高可用的問題。
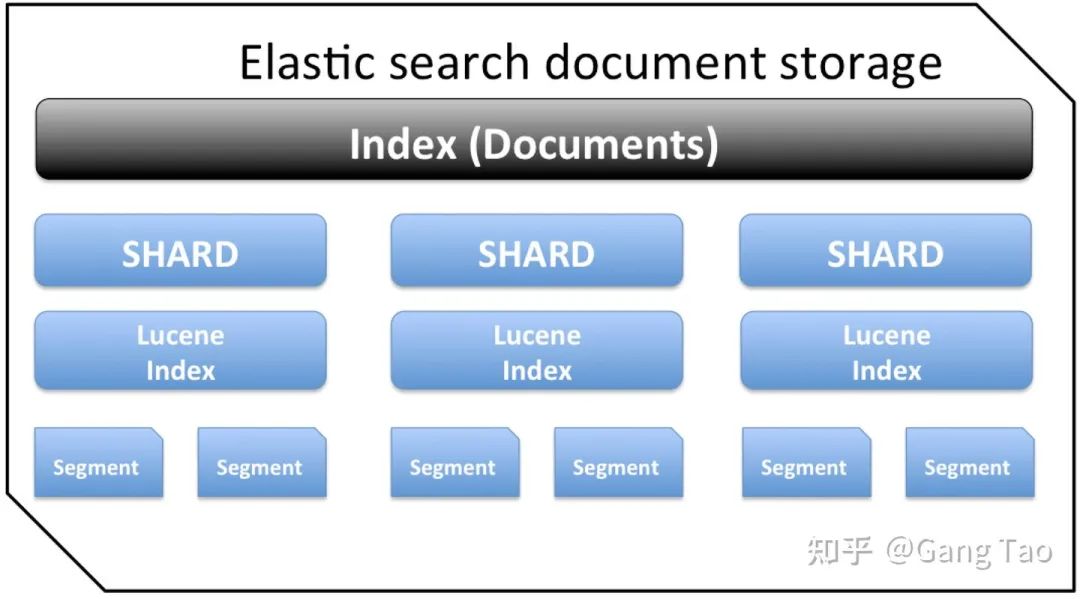
ElasticSearch是為分布式設(shè)計(jì)的,有很好的擴(kuò)展性,在一個(gè)典型的分布式配置中,每一個(gè)節(jié)點(diǎn)(node)可以配制成不同的角色,如下圖所示:
Client Node,負(fù)責(zé)API和數(shù)據(jù)的訪問的節(jié)點(diǎn),不存儲/處理數(shù)據(jù) Data Node,負(fù)責(zé)數(shù)據(jù)的存儲和索引 Master Node, 管理節(jié)點(diǎn),負(fù)責(zé)Cluster中的節(jié)點(diǎn)的協(xié)調(diào),不存儲數(shù)據(jù)。
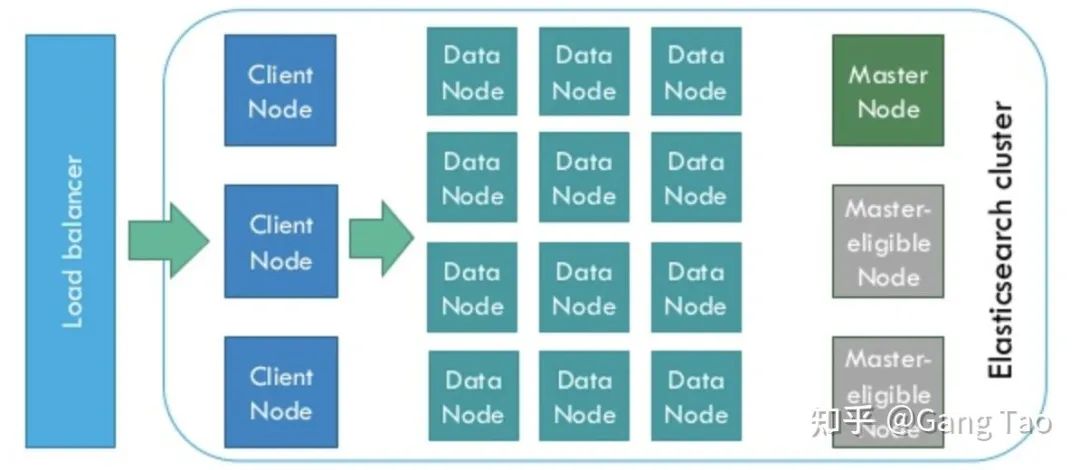
ClickHouse是基于MPP架構(gòu)的分布式ROLAP(關(guān)系OLAP)分析引擎。每個(gè)節(jié)點(diǎn)都有同等的責(zé)任,并負(fù)責(zé)部分?jǐn)?shù)據(jù)處理(不共享任何內(nèi)容)。ClickHouse 是一個(gè)真正的列式數(shù)據(jù)庫管理系統(tǒng)(DBMS)。在 ClickHouse 中,數(shù)據(jù)始終是按列存儲的,包括矢量(向量或列塊)執(zhí)行的過程。讓查詢變得更快,最簡單且有效的方法是減少數(shù)據(jù)掃描范圍和數(shù)據(jù)傳輸時(shí)的大小,而列式存儲和數(shù)據(jù)壓縮就可以幫助實(shí)現(xiàn)上述兩點(diǎn)。Clickhouse同時(shí)使用了日志合并樹,稀疏索引和CPU功能(如SIMD單指令多數(shù)據(jù))充分發(fā)揮了硬件優(yōu)勢,可實(shí)現(xiàn)高效的計(jì)算。Clickhouse 使用Zookeeper進(jìn)行分布式節(jié)點(diǎn)之間的協(xié)調(diào)。
為了支持搜索,Clickhouse同樣支持布隆過濾器。
查詢對比實(shí)戰(zhàn)
為了對比ES和Clickhouse的基本查詢能力的差異,我寫了一些代碼(https://github.com/gangtao/esvsch)來驗(yàn)證。
這個(gè)測試的架構(gòu)如下:
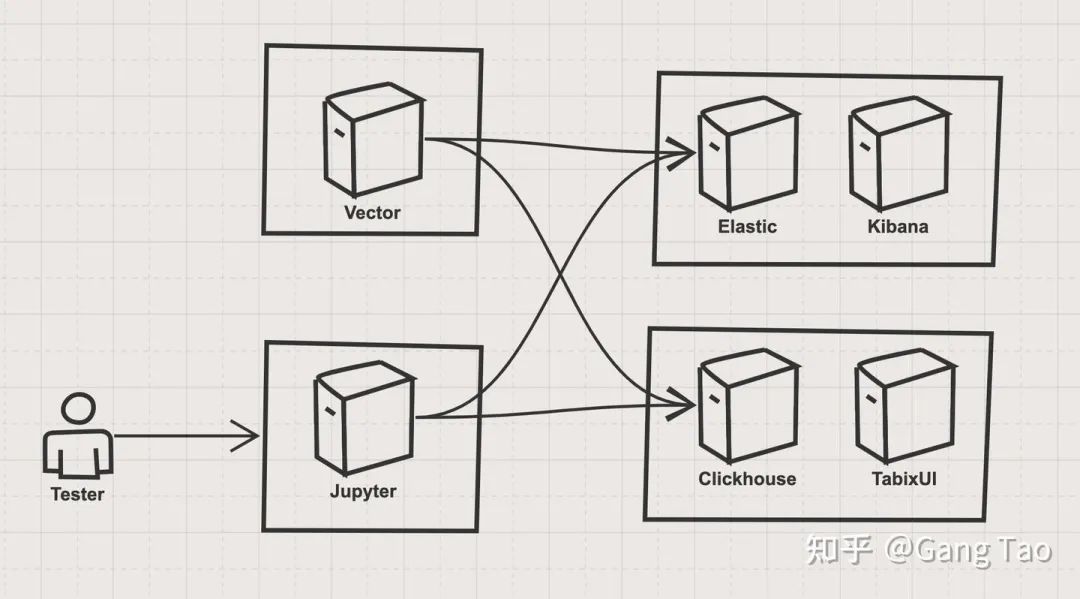
架構(gòu)主要有四個(gè)部分組成:
ES stack ES stack有一個(gè)單節(jié)點(diǎn)的Elastic的容器和一個(gè)Kibana容器組成,Elastic是被測目標(biāo)之一,Kibana作為驗(yàn)證和輔助工具。部署代碼如下:
version:?'3.7'
services:
??elasticsearch:
????image:?docker.elastic.co/elasticsearch/elasticsearch:7.4.0
????container_name:?elasticsearch
????environment:
??????-?xpack.security.enabled=false
??????-?discovery.type=single-node
????ulimits:
??????memlock:
????????soft:?-1
????????hard:?-1
??????nofile:
????????soft:?65536
????????hard:?65536
????cap_add:
??????-?IPC_LOCK
????volumes:
??????-?elasticsearch-data:/usr/share/elasticsearch/data
????ports:
??????-?9200:9200
??????-?9300:9300
????deploy:
??????resources:
????????limits:
??????????cpus:?'4'
??????????memory:?4096M
????????reservations:
??????????memory:?4096M
??kibana:
????container_name:?kibana
????image:?docker.elastic.co/kibana/kibana:7.4.0
????environment:
??????-?ELASTICSEARCH_HOSTS=http://elasticsearch:9200
????ports:
??????-?5601:5601
????depends_on:
??????-?elasticsearch
volumes:
??elasticsearch-data:
????driver:?local
Clickhouse stack Clickhouse stack有一個(gè)單節(jié)點(diǎn)的Clickhouse服務(wù)容器和一個(gè)TabixUI作為Clickhouse的客戶端。部署代碼如下:
version:?"3.7"
services:
??clickhouse:
????container_name:?clickhouse
????image:?yandex/clickhouse-server
????volumes:
??????-?./data/config:/var/lib/clickhouse
????ports:
??????-?"8123:8123"
??????-?"9000:9000"
??????-?"9009:9009"
??????-?"9004:9004"
????ulimits:
??????nproc:?65535
??????nofile:
????????soft:?262144
????????hard:?262144
????healthcheck:
??????test:?["CMD",?"wget",?"--spider",?"-q",?"localhost:8123/ping"]
??????interval:?30s
??????timeout:?5s
??????retries:?3
????deploy:
??????resources:
????????limits:
??????????cpus:?'4'
??????????memory:?4096M
????????reservations:
??????????memory:?4096M
??tabixui:
????container_name:?tabixui
????image:?spoonest/clickhouse-tabix-web-client
????environment:
??????-?CH_NAME=dev
??????-?CH_HOST=127.0.0.1:8123
??????-?CH_LOGIN=default
????ports:
??????-?"18080:80"
????depends_on:
??????-?clickhouse
????deploy:
??????resources:
????????limits:
??????????cpus:?'0.1'
??????????memory:?128M
????????reservations:
??????????memory:?128M
數(shù)據(jù)導(dǎo)入 stack 數(shù)據(jù)導(dǎo)入部分使用了Vector.dev開發(fā)的vector,該工具和fluentd類似,都可以實(shí)現(xiàn)數(shù)據(jù)管道式的靈活的數(shù)據(jù)導(dǎo)入。 測試控制 stack 測試控制我使用了Jupyter,使用了ES和Clickhouse的Python SDK來進(jìn)行查詢的測試。
用Docker compose啟動ES和Clickhouse的stack后,我們需要導(dǎo)入數(shù)據(jù),我們利用Vector的generator功能,生成syslog,并同時(shí)導(dǎo)入ES和Clickhouse,在這之前,我們需要在Clickhouse上創(chuàng)建表。ES的索引沒有固定模式,所以不需要事先創(chuàng)建索引。
創(chuàng)建表的代碼如下:
CREATE?TABLE?default.syslog(
????application?String,
????hostname?String,
????message?String,
????mid?String,
????pid?String,
????priority?Int16,
????raw?String,
????timestamp?DateTime('UTC'),
????version?Int16
)?ENGINE?=?MergeTree()
????PARTITION?BY?toYYYYMMDD(timestamp)
????ORDER?BY?timestamp
????TTL?timestamp?+?toIntervalMonth(1);
創(chuàng)建好表之后,我們就可以啟動vector,向兩個(gè)stack寫入數(shù)據(jù)了。vector的數(shù)據(jù)流水線的定義如下:
[sources.in]
??type?=?"generator"
??format?=?"syslog"
??interval?=?0.01
??count?=?100000
[transforms.clone_message]
??type?=?"add_fields"
??inputs?=?["in"]
??fields.raw?=?"{{?message?}}"
[transforms.parser]
??#?General
??type?=?"regex_parser"
??inputs?=?["clone_message"]
??field?=?"message"?#?optional,?default
??patterns?=?['^<(?P\d*)>(?P\d)?(?P\d{4}-\d{2}-\d{2}T\d{2}:\d{2}:\d{2}\.\d{3}Z)?(?P\w+\.\w+)?(?P\w+)?(?P\d+)?(?PID\d+)?-?(?P.*)$' ]
[transforms.coercer]
??type?=?"coercer"
??inputs?=?["parser"]
??types.timestamp?=?"timestamp"
??types.version?=?"int"
??types.priority?=?"int"
[sinks.out_console]
??#?General
??type?=?"console"
??inputs?=?["coercer"]
??target?=?"stdout"
??#?Encoding
??encoding.codec?=?"json"
[sinks.out_clickhouse]
??host?=?"http://host.docker.internal:8123"
??inputs?=?["coercer"]
??table?=?"syslog"
??type?=?"clickhouse"
??encoding.only_fields?=?["application",?"hostname",?"message",?"mid",?"pid",?"priority",?"raw",?"timestamp",?"version"]
??encoding.timestamp_format?=?"unix"
[sinks.out_es]
??#?General
??type?=?"elasticsearch"
??inputs?=?["coercer"]
??compression?=?"none"
??endpoint?=?"http://host.docker.internal:9200"
??index?=?"syslog-%F"
??#?Encoding
??#?Healthcheck
??healthcheck.enabled?=?true
這里簡單介紹一下這個(gè)流水線:
http://source.in 生成syslog的模擬數(shù)據(jù),生成10w條,生成間隔和0.01秒 transforms.clone_message 把原始消息復(fù)制一份,這樣抽取的信息同時(shí)可以保留原始消息 transforms.parser 使用正則表達(dá)式,按照syslog的定義,抽取出application,hostname,message ,mid ,pid ,priority ,timestamp ,version 這幾個(gè)字段 transforms.coercer 數(shù)據(jù)類型轉(zhuǎn)化 sinks.out_console 把生成的數(shù)據(jù)打印到控制臺,供開發(fā)調(diào)試 sinks.out_clickhouse 把生成的數(shù)據(jù)發(fā)送到Clickhouse sinks.out_es 把生成的數(shù)據(jù)發(fā)送到ES
運(yùn)行Docker命令,執(zhí)行該流水線:
docker?run?\
??-v?$(mkfile_path)/vector.toml:/etc/vector/vector.toml:ro?\
??-p?18383:8383?\
??timberio/vector:nightly-alpine
數(shù)據(jù)導(dǎo)入后,我們針對一下的查詢來做一個(gè)對比。ES使用自己的查詢語言來進(jìn)行查詢,Clickhouse支持SQL,我簡單測試了一些常見的查詢,并對它們的功能和性能做一些比較。
返回所有的記錄
>?基于微服務(wù)的思想,構(gòu)建在 B2C 電商場景下的項(xiàng)目實(shí)戰(zhàn)。核心技術(shù)棧,是 Spring Boot + Dubbo 。未來,會重構(gòu)成 Spring Cloud Alibaba 。
>
>?項(xiàng)目地址:
#?ES
{
??"query":{
????"match_all":{}
??}
}
#?Clickhouse
"SELECT?*?FROM?syslog"
匹配單個(gè)字段
#?ES
{
??"query":{
????"match":{
??????"hostname":"for.org"
????}
??}
}
#?Clickhouse
"SELECT?*?FROM?syslog?WHERE?hostname='for.org'"
匹配多個(gè)字段
#?ES
{
??"query":{
????"multi_match":{
??????"query":"up.com?ahmadajmi",
????????"fields":[
??????????"hostname",
??????????"application"
????????]
????}
??}
}
#?Clickhouse、
"SELECT?*?FROM?syslog?WHERE?hostname='for.org'?OR?application='ahmadajmi'"
單詞查找,查找包含特定單詞的字段
#?ES
{
??"query":{
????"term":{
??????"message":"pretty"
????}
??}
}
#?Clickhouse
"SELECT?*?FROM?syslog?WHERE?lowerUTF8(raw)?LIKE?'%pretty%'"
范圍查詢, 查找版本大于2的記錄
#?ES
{
??"query":{
????"range":{
??????"version":{
????????"gte":2
??????}
????}
??}
}
#?Clickhouse
"SELECT?*?FROM?syslog?WHERE?version?>=?2"
查找到存在某字段的記錄 ES是文檔類型的數(shù)據(jù)庫,每一個(gè)文檔的模式不固定,所以會存在某字段不存在的情況;而Clickhouse對應(yīng)為字段為空值
#?ES
{
??"query":{
????"exists":{
??????"field":"application"
????}
??}
}
#?Clickhouse
"SELECT?*?FROM?syslog?WHERE?application?is?not?NULL"
正則表達(dá)式查詢,查詢匹配某個(gè)正則表達(dá)式的數(shù)據(jù)
#?ES
{
??"query":{
????"regexp":{
??????"hostname":{
????????"value":"up.*",
??????????"flags":"ALL",
????????????"max_determinized_states":10000,
??????????????"rewrite":"constant_score"
??????}
????}
??}
}
#?Clickhouse
"SELECT?*?FROM?syslog?WHERE?match(hostname,?'up.*')"
聚合計(jì)數(shù),統(tǒng)計(jì)某個(gè)字段出現(xiàn)的次數(shù)
#?ES
{
??"aggs":{
????"version_count":{
??????"value_count":{
????????"field":"version"
??????}
????}
??}
}
#?Clickhouse
"SELECT?count(version)?FROM?syslog"
聚合不重復(fù)的值,查找所有不重復(fù)的字段的個(gè)數(shù)
#?ES
{
??"aggs":{
????"my-agg-name":{
??????"cardinality":{
????????"field":"priority"
??????}
????}
??}
}
#?Clickhouse
"SELECT?count(distinct(priority))?FROM?syslog?"
我用Python的SDK,對上述的查詢在兩個(gè)Stack上各跑10次,然后統(tǒng)計(jì)查詢的性能結(jié)果。
我們畫出出所有的查詢的響應(yīng)時(shí)間的分布:
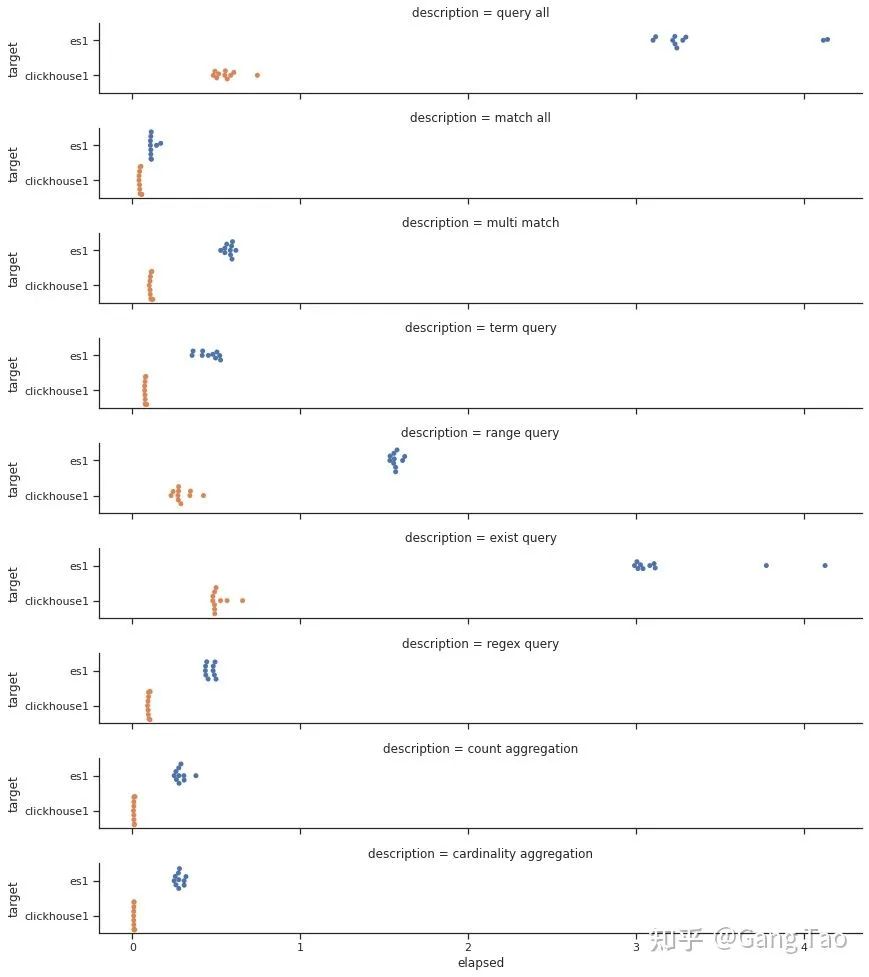
總查詢時(shí)間的對比如下:
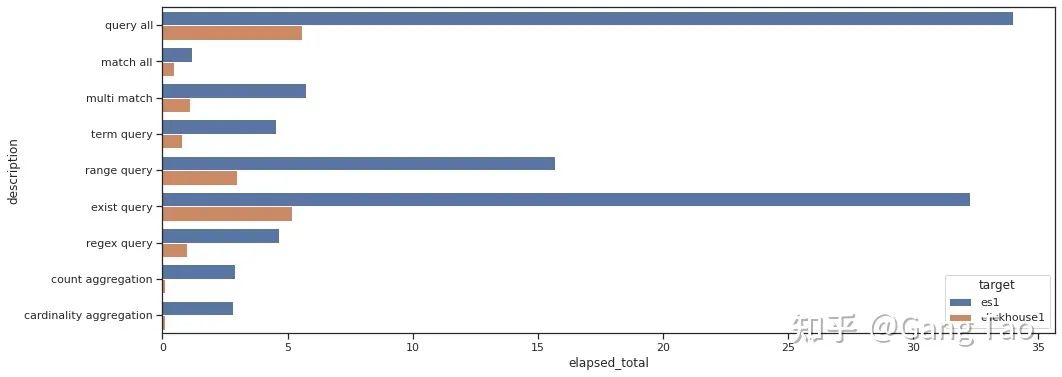
通過測試數(shù)據(jù)我們可以看出Clickhouse在大部分的查詢的性能上都明顯要優(yōu)于Elastic。在正則查詢(Regex query)和單詞查詢(Term query)等搜索常見的場景下,也并不遜色。
在聚合場景下,Clickhouse表現(xiàn)異常優(yōu)秀,充分發(fā)揮了列村引擎的優(yōu)勢。
注意,我的測試并沒有任何優(yōu)化,對于Clickhouse也沒有打開布隆過濾器。可見Clickhouse確實(shí)是一款非常優(yōu)秀的數(shù)據(jù)庫,可以用于某些搜索的場景。當(dāng)然ES還支持非常豐富的查詢功能,這里只有一些非常基本的查詢,有些查詢可能存在無法用SQL表達(dá)的情況。
總結(jié)
本文通過對于一些基本查詢的測試,對比了Clickhouse 和Elasticsearch的功能和性能,測試結(jié)果表明,Clickhouse在這些基本場景表現(xiàn)非常優(yōu)秀,性能優(yōu)于ES,這也解釋了為什么用很多的公司應(yīng)從ES切換到Clickhouse之上。
1.?任務(wù)調(diào)度框架 Quartz 用法指南(超詳細(xì))
最近面試BAT,整理一份面試資料《Java面試BATJ通關(guān)手冊》,覆蓋了Java核心技術(shù)、JVM、Java并發(fā)、SSM、微服務(wù)、數(shù)據(jù)庫、數(shù)據(jù)結(jié)構(gòu)等等。
獲取方式:點(diǎn)“在看”,關(guān)注公眾號并回復(fù)?Java?領(lǐng)取,更多內(nèi)容陸續(xù)奉上。
PS:因公眾號平臺更改了推送規(guī)則,如果不想錯(cuò)過內(nèi)容,記得讀完點(diǎn)一下“在看”,加個(gè)“星標(biāo)”,這樣每次新文章推送才會第一時(shí)間出現(xiàn)在你的訂閱列表里。
點(diǎn)“在看”支持小哈呀,謝謝啦??

