PyTorch 源碼解讀之 nn.Module
? 點擊上方“AI算法與圖像處理”,選擇加"星標"或“置頂”
重磅干貨,第一時間送達
作者:OpenMMLab
知乎:https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/340453841
本文已獲作者授權(quán)轉(zhuǎn)載,不得擅自二次轉(zhuǎn)載編輯:AIWalker
本次解讀主要介紹 PyTorch 中的神經(jīng)網(wǎng)絡(luò)模塊,即 torch.nn,其中主要介紹 nn.Module,其他模塊的細節(jié)可以通過 PyTorch 的 API 文檔進行查閱,一些較重要的模塊如?DataParallel?和?BN/SyncBN?等,都有獨立的文章進行介紹。
0 設(shè)計
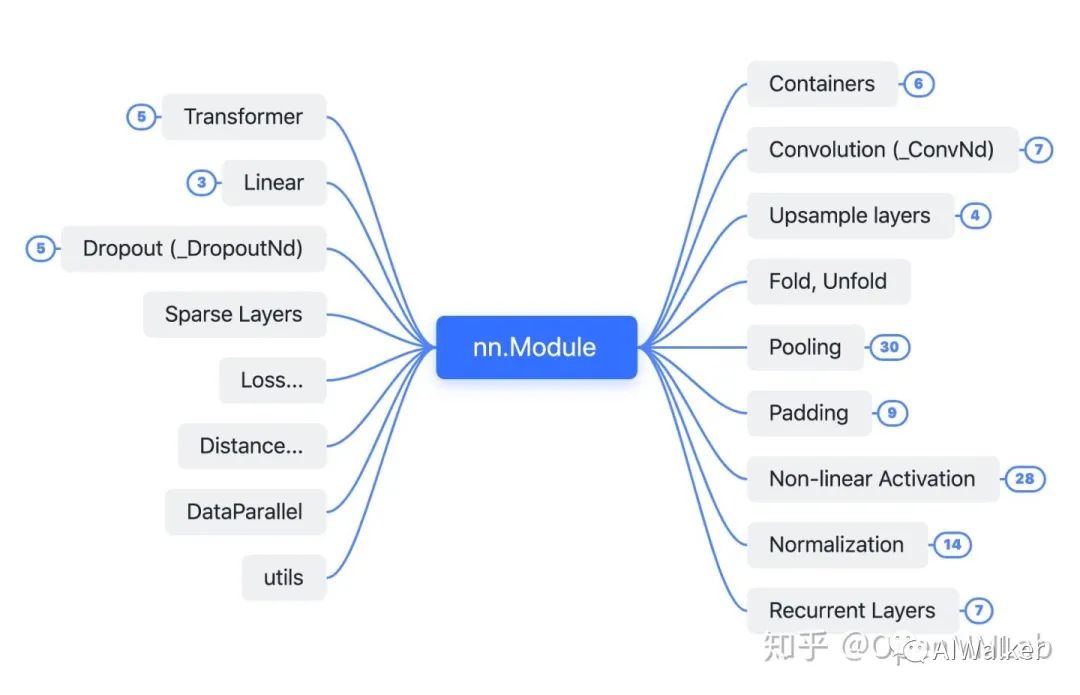
nn.Module 其實是 PyTorch 體系下所有神經(jīng)網(wǎng)絡(luò)模塊的基類,此處順帶梳理了一下 torch.nn 中的各個組件,他們的關(guān)系概覽如下圖所示。
展開各模塊后,模塊之間的繼承關(guān)系與層次結(jié)構(gòu)如下圖所示:
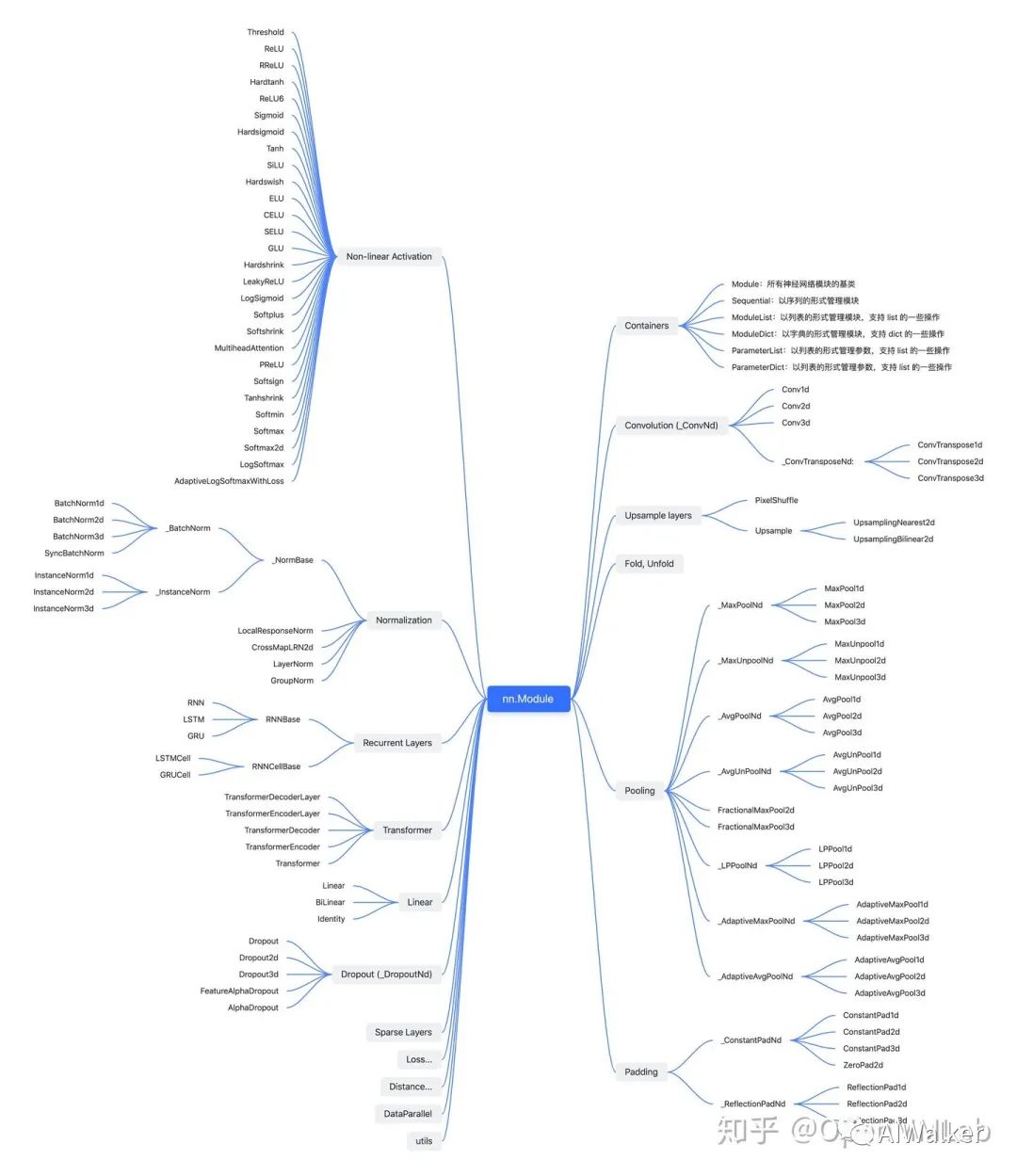
從各模塊的繼承關(guān)系來看,模塊的組織和實現(xiàn)有幾個常見的特點,供 PyTorch 代碼庫的開發(fā)者參考借鑒:
一般有一個基類來定義接口,通過繼承來處理不同維度的 input,如:
Conv1d,Conv2d,Conv3d,ConvTransposeNd 繼承自 _ConvNd
MaxPool1d,MaxPool2d,MaxPool3d 繼承自 _MaxPoolNd 等
每一個類都有一個對應(yīng)的 nn.functional 函數(shù),類定義了所需要的 arguments 和模塊的 parameters,在 forward 函數(shù)中將 arguments 和 parameters 傳給 nn.functional 的對應(yīng)函數(shù)來實現(xiàn) forward 功能。比如:
所有的非線性激活函數(shù),都是在 forward 中直接調(diào)用對應(yīng)的 nn.functional 函數(shù)
Normalization 層都是調(diào)用的如 F.layer_norm, F.group_norm 等函數(shù)
繼承 nn.Module 的模塊主要重載?init、 forward、 和 extra_repr 函數(shù),含有 parameters 的模塊還會實現(xiàn) reset_parameters 函數(shù)來初始化參數(shù)
1 nn.Module 實現(xiàn)
1.1 常用接口
1.1.1 __init__ 函數(shù)
在 nn.Module 的?__init__?函數(shù)中,會首先調(diào)用 torch._C._log_api_usage_once("python.nn_module"), 這一行代碼是 PyTorch 1.7 的新功能,用于監(jiān)測并記錄 API 的調(diào)用,詳細解釋可見?文檔。
在此之后,nn.Module 初始化了一系列重要的成員變量。這些變量初始化了在模塊 forward、 backward 和權(quán)重加載等時候會被調(diào)用的的 hooks,也定義了 parameters 和 buffers,如下面的代碼所示:
self.training = True # 控制 training/testing 狀態(tài)
self._parameters = OrderedDict() # 在訓(xùn)練過程中會隨著 BP 而更新的參數(shù)
self._buffers = OrderedDict() # 在訓(xùn)練過程中不會隨著 BP 而更新的參數(shù)
self._non_persistent_buffers_set = set()
self._backward_hooks = OrderedDict() # Backward 完成后會被調(diào)用的 hook
self._forward_hooks = OrderedDict() # Forward 完成后會被調(diào)用的 hook
self._forward_pre_hooks = OrderedDict() # Forward 前會被調(diào)用的 hook
self._state_dict_hooks = OrderedDict() # 得到 state_dict 以后會被調(diào)用的 hook
self._load_state_dict_pre_hooks = OrderedDict() # load state_dict 前會被調(diào)用的 hook
self._modules = OrderedDict() # 子神經(jīng)網(wǎng)絡(luò)模塊各個成員變量的功能在后面還會繼續(xù)提到,這里先在注釋中簡單解釋。由源碼的實現(xiàn)可見,繼承 nn.Module 的神經(jīng)網(wǎng)絡(luò)模塊在實現(xiàn)自己的 __init__ 函數(shù)時,一定要先調(diào)用?super().__init__()。只有這樣才能正確地初始化自定義的神經(jīng)網(wǎng)絡(luò)模塊,否則會缺少上面代碼中的成員變量而導(dǎo)致模塊被調(diào)用時出錯。實際上,如果沒有提前調(diào)用?super().__init__(),在增加模塊的 parameter 或者 buffer 的時候,被調(diào)用的?__setattr__?函數(shù)也會檢查出父類 nn.Module 沒被正確地初始化并報錯。(在面試的過程中,我們經(jīng)常發(fā)現(xiàn)面試者在寫自定義神經(jīng)網(wǎng)絡(luò)模塊的時候會忽略掉這一點,看了這篇文章以后可要千萬記得哦~)
1.1.2 狀態(tài)的轉(zhuǎn)換
訓(xùn)練與測試
nn.Module 通過?self.training?來區(qū)分訓(xùn)練和測試兩種狀態(tài),使得模塊可以在訓(xùn)練和測試時有不同的 forward 行為(如 Batch Normalization)。nn.Module 通過 self.train() 和 self.eval() 來修改訓(xùn)練和測試狀態(tài),其中 self.eval 直接調(diào)用了 self.train(False),而?self.train() 會修改 self.training 并通過 self.children() 來調(diào)整所有子模塊的狀態(tài)。關(guān)于 self.children() 的介紹可見下文的?常見的屬性訪問?章節(jié)。
def train(self: T, mode: bool = True) -> T:
self.training = mode
for module in self.children():
module.train(mode)
return selfExample: freeze 部分模型參數(shù)
在目標檢測等任務(wù)中,常見的 training practice 會將 backbone 中的所有 BN 層保留為 eval 狀態(tài),即 freeze BN 層中的 running_mean 和 running_var,并且將淺層的模塊 freeze。此時就需要重載 detector 類的 train 函數(shù),MMDetection 中 ResNet 的 train 函數(shù)實現(xiàn)如下:
def train(self, mode=True):
super(ResNet, self).train(mode)
self._freeze_stages()
if mode and self.norm_eval:
for m in self.modules():
# trick: eval have effect on BatchNorm only
if isinstance(m, _BatchNorm):
m.eval()梯度的處理
對于梯度的處理 nn.Module 有兩個相關(guān)的函數(shù)實現(xiàn),分別是 requires_grad_ 和 zero_grad 函數(shù),他們都調(diào)用了 self.parameters() 來訪問所有的參數(shù),并修改參數(shù)的 requires_grad 狀態(tài) 或者 清理參數(shù)的梯度。
def requires_grad_(self: T, requires_grad: bool = True) -> T:
for p in self.parameters():
p.requires_grad_(requires_grad)
return self
def zero_grad(self, set_to_none: bool = False) -> None:
if getattr(self, '_is_replica', False):
warnings.warn(
"Calling .zero_grad() from a module created with nn.DataParallel() has no effect. "
"The parameters are copied (in a differentiable manner) from the original module. "
"This means they are not leaf nodes in autograd and so don't accumulate gradients. "
"If you need gradients in your forward method, consider using autograd.grad instead.")
for p in self.parameters():
if p.grad is not None:
if set_to_none:
p.grad = None
else:
if p.grad.grad_fn is not None:
p.grad.detach_()
else:
p.grad.requires_grad_(False)
p.grad.zero_()1.1.3 參數(shù)的轉(zhuǎn)換或轉(zhuǎn)移
nn.Module 實現(xiàn)了如下 8 個常用函數(shù)將模塊轉(zhuǎn)變成 float16 等類型、轉(zhuǎn)移到 CPU/ GPU上。
CPU:將所有 parameters 和 buffer 轉(zhuǎn)移到 CPU 上
type:將所有 parameters 和 buffer 轉(zhuǎn)變成另一個類型
CUDA:將所有 parameters 和 buffer 轉(zhuǎn)移到 GPU 上
float:將所有浮點類型的 parameters 和 buffer 轉(zhuǎn)變成 float32 類型
double:將所有浮點類型的 parameters 和 buffer 轉(zhuǎn)變成 double 類型
half:將所有浮點類型的 parameters 和 buffer 轉(zhuǎn)變成 float16 類型
bfloat16:將所有浮點類型的 parameters 和 buffer 轉(zhuǎn)變成 bfloat16 類型
to:移動模塊或/和改變模塊的類型
這些函數(shù)的功能最終都是通過?self._apply(function)?來實現(xiàn)的, function 一般是 lambda 表達式或其他自定義函數(shù)。因此,用戶其實也可以通過 self._apply(function) 來實現(xiàn)一些特殊的轉(zhuǎn)換。self._apply() 函數(shù)實際上做了如下 3 件事情,最終將 function 完整地應(yīng)用于整個模塊。
通過 self.children() 進行遞歸的調(diào)用
對 self._parameters 中的參數(shù)及其 gradient 通過 function 進行處理
對 self._buffers 中的 buffer 逐個通過 function 來進行處理
def _apply(self, fn):
# 對子模塊進行遞歸調(diào)用
for module in self.children():
module._apply(fn)
# 為了 BC-breaking 而新增了一個 tensor 類型判斷
def compute_should_use_set_data(tensor, tensor_applied):
if torch._has_compatible_shallow_copy_type(tensor, tensor_applied):
# If the new tensor has compatible tensor type as the existing tensor,
# the current behavior is to change the tensor in-place using `.data =`,
# and the future behavior is to overwrite the existing tensor. However,
# changing the current behavior is a BC-breaking change, and we want it
# to happen in future releases. So for now we introduce the
# `torch.__future__.get_overwrite_module_params_on_conversion()`
# global flag to let the user control whether they want the future
# behavior of overwriting the existing tensor or not.
return not torch.__future__.get_overwrite_module_params_on_conversion()
else:
return False
# 處理參數(shù)及其gradint
for key, param in self._parameters.items():
if param is not None:
# Tensors stored in modules are graph leaves, and we don't want to
# track autograd history of `param_applied`, so we have to use
# `with torch.no_grad():`
with torch.no_grad():
param_applied = fn(param)
should_use_set_data = compute_should_use_set_data(param, param_applied)
if should_use_set_data:
param.data = param_applied
else:
assert isinstance(param, Parameter)
assert param.is_leaf
self._parameters[key] = Parameter(param_applied, param.requires_grad)
if param.grad is not None:
with torch.no_grad():
grad_applied = fn(param.grad)
should_use_set_data = compute_should_use_set_data(param.grad, grad_applied)
if should_use_set_data:
param.grad.data = grad_applied
else:
assert param.grad.is_leaf
self._parameters[key].grad = grad_applied.requires_grad_(param.grad.requires_grad)
# 處理 buffers
for key, buf in self._buffers.items():
if buf is not None:
self._buffers[key] = fn(buf)
return self1.1.4 Apply 函數(shù)
nn.Module 還實現(xiàn)了一個 apply 函數(shù),與 _apply() 函數(shù)不同的是,apply 函數(shù)只是簡單地遞歸調(diào)用了 self.children() 去處理自己以及子模塊,如下面的代碼所示。
def apply(self: T, fn: Callable[['Module'], None]) -> T:
for module in self.children():
module.apply(fn)
fn(self)
return selfapply 函數(shù)和 _apply 函數(shù)的區(qū)別在于,_apply() 是專門針對 parameter 和 buffer?而實現(xiàn)的一個“僅供內(nèi)部使用”的接口,但是 apply 函數(shù)是“公有”接口 (Python 對類的“公有”和“私有”區(qū)別并不是很嚴格,一般通過單前導(dǎo)下劃線來區(qū)分)。apply 實際上可以通過修改 fn 來實現(xiàn) _apply 能實現(xiàn)的功能,同時還可以實現(xiàn)其他功能,如下面給出的重新初始化參數(shù)的例子。
Example: 參數(shù)重新初始化
可以自定義一個 init_weights 函數(shù),通過?net.apply(init_weights)?來初始化模型權(quán)重。
@torch.no_grad()
def init_weights(m):
print(m)
if type(m) == nn.Linear:
m.weight.fill_(1.0)
print(m.weight)
net = nn.Sequential(nn.Linear(2, 2), nn.Linear(2, 2))
net.apply(init_weights)1.2 屬性的增刪改查
1.2.1 屬性設(shè)置
對 nn.Module 屬性的修改有一下三個函數(shù),函數(shù)以及對應(yīng)功能如下
add_module:增加子神經(jīng)網(wǎng)絡(luò)模塊,更新 self._modules
register_parameter:增加通過 BP 可以更新的 parameters (如 BN 和 Conv 中的 weight 和 bias ),更新 self._parameters
register_buffer:增加不通過 BP 更新的 buffer(如 BN 中的 running_mean 和 running_var),更新 self._buffers,如果 buffer 不是 persistant 的,還會同時更新到 self._non_persistent_buffers_set 中。buffer 是否 persistant 的區(qū)別在于這個 buffer 是否會能被放入 self.state_dict 中被保存下來。這 3 個函數(shù)都會先檢查?
self.__dict__?中是否包含對應(yīng)的屬性字典以確保?nn.Module 被正確初始化,然后檢查屬性的 name 是否合法,如不為空 string 且不包含“.”,同時還會檢查他們是否已經(jīng)存在于要修改的屬性字典中。
在日常的代碼開發(fā)過程中,更常見的用法是直接通過?self.xxx?= xxx 的方式來增加或修改子神經(jīng)網(wǎng)絡(luò)模塊、parameters、buffers 以及其他一般的 attribute。這種方式本質(zhì)上會調(diào)用 nn.Module 重載的函數(shù)?__setattr__?,詳細的代碼如下:
def __setattr__(self, name: str, value: Union[Tensor, 'Module']):
def remove_from(*dicts_or_sets):
for d in dicts_or_sets:
if name in d:
if isinstance(d, dict):
del d[name]
else:
d.discard(name)
params = self.__dict__.get('_parameters')
if isinstance(value, Parameter):
if params is None:
raise AttributeError(
"cannot assign parameters before Module.__init__() call")
remove_from(self.__dict__, self._buffers, self._modules, self._non_persistent_buffers_set)
self.register_parameter(name, value)
elif params is not None and name in params:
if value is not None:
raise TypeError("cannot assign '{}' as parameter '{}' "
"(torch.nn.Parameter or None expected)"
.format(torch.typename(value), name))
self.register_parameter(name, value)
else:
modules = self.__dict__.get('_modules')
if isinstance(value, Module):
if modules is None:
raise AttributeError(
"cannot assign module before Module.__init__() call")
remove_from(self.__dict__, self._parameters, self._buffers, self._non_persistent_buffers_set)
modules[name] = value
elif modules is not None and name in modules:
if value is not None:
raise TypeError("cannot assign '{}' as child module '{}' "
"(torch.nn.Module or None expected)"
.format(torch.typename(value), name))
modules[name] = value
else:
buffers = self.__dict__.get('_buffers')
if buffers is not None and name in buffers:
if value is not None and not isinstance(value, torch.Tensor):
raise TypeError("cannot assign '{}' as buffer '{}' "
"(torch.Tensor or None expected)"
.format(torch.typename(value), name))
buffers[name] = value
else:
object.__setattr__(self, name, value)從源碼中我們還有如下觀察:
在第 14 行和 28 行,函數(shù)檢查了繼承 nn.Module 的自定義模塊是否有正確地初始化父類 nn.Module,這也說明了?super().__init__()?的必要性
在增加 self._parameters,self._modules 的時候,會預(yù)先調(diào)用 remove_from 函數(shù) (15 和 29 行)從其余私有屬性中刪除對應(yīng)的 name,這說明 self.dict,self._buffers,self._parameters,self._modules 中的屬性應(yīng)該是互斥的
如果要給模塊增加 buffer,self.register_buffer 是唯一的方式,
__setattr__?只能將 self._buffers 中已有的 buffer 重新賦值為 None 或者 tensor 。這是因為 buffer 的初始化類型就是 torch.Tensor 或者 None,而不像 parameters 和 module 分別是 nn.Parameter 和 nn.Module 類型除了其他普通的 attribute,最終 parameters 還是會在?
__setattr__?中通過 register_parameter 來增加,但是子神經(jīng)網(wǎng)絡(luò)模塊和 buffer 是直接修改的 self._modules 和 self._buffers由第三點和前文所述的 _apply 實現(xiàn)可以得出?self.xxxx = torch.Tensor() 是一種不被推薦的行為,因為這樣新增的 attribute 既不屬于 self._parameters,也不屬于 self._buffers,而會被視為普通的 attribute ,在將模塊進行狀態(tài)轉(zhuǎn)換的時候,self.xxxx 會被遺漏進而導(dǎo)致 device 或者 type 不一樣的 bug
1.2.2 屬性刪除
屬性的刪除通過重載的?__delattr__?來實現(xiàn),詳細代碼如下:
def __delattr__(self, name):
if name in self._parameters:
del self._parameters[name]
elif name in self._buffers:
del self._buffers[name]
self._non_persistent_buffers_set.discard(name)
elif name in self._modules:
del self._modules[name]
else:
object.__delattr__(self, name)__delattr__?會挨個檢查 self._parameters、self._buffers、self._modules 和普通的 attribute 并將 name 從中刪除。
1.2.3 常見的屬性訪問
nn.Module 中的常用函數(shù)包括下面 8 個,他們都會返回一個迭代器用于訪問模塊中的 buffer,parameter,子模塊等。他們的功能與區(qū)別如下
parameters:調(diào)用 self.named_parameters 并返回模型參數(shù),被應(yīng)用于 self.requires_grad_ 和 self.zero_grad 函數(shù)中
named_parameters:返回 self._parameters 中的 name 和 parameter 元組,如果 recurse=True 還會返回子模塊中的模型參數(shù)
buffers:調(diào)用 self.named_buffers 并返回模型參數(shù)
named_buffers:返回 self._buffers 中的 name 和 buffer 元組,如果 recurse=True 還會返回子模塊中的模型 buffer
children:調(diào)用 self.named_children,只返回 self._modules 中的模塊,被應(yīng)用于 self.train 函數(shù)中
named_children:只返回 self._modules 中的 name 和 module 元組
modules:調(diào)用 self.named_modules 并返回各個 module 但不返回 name
named_modules:返回 self._modules 下的 name 和 module 元組,并遞歸調(diào)用和返回 module.named_modules
def _named_members(self, get_members_fn, prefix='', recurse=True):
memo = set()
modules = self.named_modules(prefix=prefix) if recurse else [(prefix, self)]
for module_prefix, module in modules:
members = get_members_fn(module)
for k, v in members:
if v is None or v in memo:
continue
memo.add(v)
name = module_prefix + ('.' if module_prefix else '') + k
yield name, v
def parameters(self, recurse: bool = True) -> Iterator[Parameter]:
for name, param in self.named_parameters(recurse=recurse):
yield param
def named_parameters(self, prefix: str = '', recurse: bool = True) -> Iterator[Tuple[str, Tensor]]:
gen = self._named_members(
lambda module: module._parameters.items(),
prefix=prefix, recurse=recurse)
for elem in gen:
yield elem
def buffers(self, recurse: bool = True) -> Iterator[Tensor]:
for name, buf in self.named_buffers(recurse=recurse):
yield buf
def named_buffers(self, prefix: str = '', recurse: bool = True) -> Iterator[Tuple[str, Tensor]]:
gen = self._named_members(
lambda module: module._buffers.items(),
prefix=prefix, recurse=recurse)
for elem in gen:
yield elem
def children(self) -> Iterator['Module']:
for name, module in self.named_children():
yield module
def named_children(self) -> Iterator[Tuple[str, 'Module']]:
memo = set()
for name, module in self._modules.items():
if module is not None and module not in memo:
memo.add(module)
yield name, module
def modules(self) -> Iterator['Module']:
for name, module in self.named_modules():
yield module
def named_modules(self, memo: Optional[Set['Module']] = None, prefix: str = ''):
if memo is None:
memo = set()
if self not in memo:
memo.add(self)
yield prefix, self
for name, module in self._modules.items():
if module is None:
continue
submodule_prefix = prefix + ('.' if prefix else '') + name
for m in module.named_modules(memo, submodule_prefix):
yield mnamed_parameters 和 named_buffers 都是調(diào)用的 self._named_members 實現(xiàn)的,named_modules 和 named_children 雖然有自己的實現(xiàn),但和 self._named_members 一樣,都是通過 set 類型的 memo 來記錄已經(jīng)拋出的模塊,如果 member 不在 memo 中,才會將 member 拋出并將 member 放入 memo 中,因此 named_parameters、named_buffers、named_modules 和named_children 都不會返回重復(fù)的 parameter、 buffer 或 module。
nn.Module 重載了?__dir__?函數(shù),重載的?__dir__?函數(shù)會將 self._modules、self._parameters 和 self._buffers 中的 attributes 給暴露出來。
def __dir__(self):
module_attrs = dir(self.__class__)
attrs = list(self.__dict__.keys())
parameters = list(self._parameters.keys())
modules = list(self._modules.keys())
buffers = list(self._buffers.keys())
keys = module_attrs + attrs + parameters + modules + buffers
# Eliminate attrs that are not legal Python variable names
keys = [key for key in keys if not key[0].isdigit()]
return sorted(keys)還有一種常見的屬性訪問是通過 module.attribute 來進行的。這種調(diào)用等價于?getattr(module, 'attribute')。和 nn.Module 對?__delattr__?以及?__setattr__?的重載類似,為了確保 getattr 能訪問到所有的屬性,nn.Module 也重載了?__getattr__?函數(shù),以訪問 self._parameters,self._buffers,self._modules 中的屬性。
根據(jù) Python 對實例屬性的查找規(guī)則,當我們調(diào)用 module.attribute 的時候,Python 會首先查找 module 的 類及其基類的?__dict__,然后查找這個 object 的?__dict__,最后查找?__getattr__?函數(shù)。因此,雖然 nn.Module 的?__getattr__?只查找了 self._parameters,self._buffers,self._modules 三個成員變量,但是?getattr(module, 'attribute') 覆蓋的范圍和?__dir__?暴露的范圍是一致的。
def __getattr__(self, name: str) -> Union[Tensor, 'Module']:
if '_parameters' in self.__dict__:
_parameters = self.__dict__['_parameters']
if name in _parameters:
return _parameters[name]
if '_buffers' in self.__dict__:
_buffers = self.__dict__['_buffers']
if name in _buffers:
return _buffers[name]
if '_modules' in self.__dict__:
modules = self.__dict__['_modules']
if name in modules:
return modules[name]
raise ModuleAttributeError("'{}' object has no attribute '{}'".format(
type(self).__name__, name))1.3 Forward & Backward
1.3.1 Hooks
在 nn.Module 的實現(xiàn)文件中,首先實現(xiàn)了 3 個通用的 hook 注冊函數(shù),用于注冊被應(yīng)用于全局的 hook。這 3 個函數(shù)會將 hook 分別注冊進 3 個全局的 OrderedDict,使得所有的 nn.Module 的子類實例在運行的時候都會觸發(fā)這些 hook。每個 hook 修改的 OrderedDict 如下所示:
register_module_backward_hook:_global_backward_hooks
register_module_forward_pre_hook:_global_forward_pre_hooks
register_module_forward_hook:_global_forward_hooks
同樣的,nn.Module 也支持注冊只被應(yīng)用于自己的 forward 和 backward hook,通過 3 個函數(shù) 來管理 自己的 3 個屬性并維護 3 個 attribute,他們的類型也是 OrderedDict,每個 hook 修改的 OrderedDict 如下所示:
self.register_backward_hook: self._backward_hooks
self.register_forward_pre_hook: self._forward_pre_hooks
self.register_forward_hook: self._forward_hooks
1.3.2 運行邏輯
nn.Module 在被調(diào)用的時候,一般是以 module(input) 的形式,此時會首先調(diào)用?self.__call__,接下來這些 hooks 在模塊被調(diào)用時候的執(zhí)行順序如下圖所示:

_call_impl 的代碼實現(xiàn)如下。注意到 _call_impl 在定義以后被直接賦值給了?__call__?。同時我們注意到在 torch._C._get_tracing_state() 為 True 的時候,nn.Module 會通過 _slow_forward() 來調(diào)用 forward 函數(shù)而非直接調(diào)用 forward 函數(shù),這一功能主要用于 JIT。
def _call_impl(self, *input, **kwargs):
for hook in itertools.chain(
_global_forward_pre_hooks.values(),
self._forward_pre_hooks.values()):
result = hook(self, input)
if result is not None:
if not isinstance(result, tuple):
result = (result,)
input = result
if torch._C._get_tracing_state():
result = self._slow_forward(*input, **kwargs)
else:
result = self.forward(*input, **kwargs)
for hook in itertools.chain(
_global_forward_hooks.values(),
self._forward_hooks.values()):
hook_result = hook(self, input, result)
if hook_result is not None:
result = hook_result
if (len(self._backward_hooks) > 0) or (len(_global_backward_hooks) > 0):
var = result
while not isinstance(var, torch.Tensor):
if isinstance(var, dict):
var = next((v for v in var.values() if isinstance(v, torch.Tensor)))
else:
var = var[0]
grad_fn = var.grad_fn
if grad_fn is not None:
for hook in itertools.chain(
_global_backward_hooks.values(),
self._backward_hooks.values()):
wrapper = functools.partial(hook, self)
functools.update_wrapper(wrapper, hook)
grad_fn.register_hook(wrapper)
return result
__call__ : Callable[..., Any] = _call_impl1.4 模塊存取
1.4.1 Hooks
nn.Module 還有兩個相關(guān)的 hook 是關(guān)于模型參數(shù)的加載和存儲的,分別是:
_register_state_dict_hook:在self.state_dict()的最后對模塊導(dǎo)出的 state_dict 進行修改
_register_load_state_dict_pre_hook:在 _load_from_state_dict 中最先執(zhí)行
1.4.2 功能實現(xiàn)
nn.Module 使用 state_dict() 函數(shù)來進行獲得當前的完整狀態(tài),用于在模型訓(xùn)練中儲存 checkpoint。模塊的 _version 信息會首先存入 metadata 中,用于模型的版本管理,然后會通過 _save_to_state_dict() 將 self._parameters 以及 self._buffers 中的 persistent buffer 進行保存。?用戶可以通過重載 _save_to_state_dict 函數(shù)來滿足特定的需求。
nn.Module 使用 load_state_dict() 函數(shù)來讀取 checkpoint。load_state_dict() 會通過調(diào)用每個子模塊的_load_from_state_dict 函數(shù)來加載他們所需的權(quán)重,如下面代碼的 55-63 行所示。而 _load_from_state_dict 才是真正負責(zé)加載 parameter 和 buffer 的函數(shù)。這也說明了每個模塊可以自行定義他們的 _load_from_state_dict 函數(shù)來滿足特殊需求,實際上這也是 PyTorch 官方推薦的做法。在后面的兩個例子中,我們也給出了 _load_from_state_dict 的使用例子。
def _load_from_state_dict(self, state_dict, prefix, local_metadata, strict,
missing_keys, unexpected_keys, error_msgs):
for hook in self._load_state_dict_pre_hooks.values():
hook(state_dict, prefix, local_metadata, strict, missing_keys, unexpected_keys, error_msgs)
persistent_buffers = {k: v for k, v in self._buffers.items() if k not in self._non_persistent_buffers_set}
local_name_params = itertools.chain(self._parameters.items(), persistent_buffers.items())
local_state = {k: v for k, v in local_name_params if v is not None}
for name, param in local_state.items():
key = prefix + name
if key in state_dict:
input_param = state_dict[key]
# Backward compatibility: loading 1-dim tensor from 0.3.* to version 0.4+
if len(param.shape) == 0 and len(input_param.shape) == 1:
input_param = input_param[0]
if input_param.shape != param.shape:
# local shape should match the one in checkpoint
error_msgs.append('size mismatch for {}: copying a param with shape {} from checkpoint, '
'the shape in current model is {}.'
.format(key, input_param.shape, param.shape))
continue
try:
with torch.no_grad():
param.copy_(input_param)
except Exception as ex:
error_msgs.append('While copying the parameter named "{}", '
'whose dimensions in the model are {} and '
'whose dimensions in the checkpoint are {}, '
'an exception occurred : {}.'
.format(key, param.size(), input_param.size(), ex.args))
elif strict:
missing_keys.append(key)
if strict:
for key in state_dict.keys():
if key.startswith(prefix):
input_name = key[len(prefix):]
input_name = input_name.split('.', 1)[0] # get the name of param/buffer/child
if input_name not in self._modules and input_name not in local_state:
unexpected_keys.append(key)
def load_state_dict(self, state_dict: Union[Dict[str, Tensor], Dict[str, Tensor]], strict: bool = True):
missing_keys = []
unexpected_keys = []
error_msgs = []
# copy state_dict so _load_from_state_dict can modify it
metadata = getattr(state_dict, '_metadata', None)
state_dict = state_dict.copy()
if metadata is not None:
state_dict._metadata = metadata
def load(module, prefix=''):
local_metadata = {} if metadata is None else metadata.get(prefix[:-1], {})
module._load_from_state_dict(
state_dict, prefix, local_metadata, True, missing_keys, unexpected_keys, error_msgs)
for name, child in module._modules.items():
if child is not None:
load(child, prefix + name + '.')
load(self)
load = None # break load->load reference cycle
if strict:
if len(unexpected_keys) > 0:
error_msgs.insert(
0, 'Unexpected key(s) in state_dict: {}. '.format(
', '.join('"{}"'.format(k) for k in unexpected_keys)))
if len(missing_keys) > 0:
error_msgs.insert(
0, 'Missing key(s) in state_dict: {}. '.format(
', '.join('"{}"'.format(k) for k in missing_keys)))
if len(error_msgs) > 0:
raise RuntimeError('Error(s) in loading state_dict for {}:\n\t{}'.format(
self.__class__.__name__, "\n\t".join(error_msgs)))
return _IncompatibleKeys(missing_keys, unexpected_keys)1.4.3 _load_from_state_dict 妙用
Example: 避免 BC-breaking
在模型迭代的過程中,module 很容易出現(xiàn) BC-breaking ,PyTorch 通過?_version?和?_load_from_state_dict?來處理的這類問題(這也是 PyTorch 推薦的方式)。下面的代碼是?_NormBase?類避免 BC-breaking 的方式。在 PyTorch 的開發(fā)過程中,Normalization layers 在某個新版本中 引入了 num_batches_tracked 這個 key,給 BN 記錄訓(xùn)練過程中經(jīng)歷的 batch 數(shù),為了兼容舊版本訓(xùn)練的模型,PyTorch 修改了?_version,并修改了?_load_from_state_dict。
def _load_from_state_dict(self, state_dict, prefix, local_metadata, strict,
missing_keys, unexpected_keys, error_msgs):
version = local_metadata.get('version', None)
if (version is None or version < 2) and self.track_running_stats:
# at version 2: added num_batches_tracked buffer
# this should have a default value of 0
num_batches_tracked_key = prefix + 'num_batches_tracked'
if num_batches_tracked_key not in state_dict:
state_dict[num_batches_tracked_key] = torch.tensor(0, dtype=torch.long)
super(_NormBase, self)._load_from_state_dict(
state_dict, prefix, local_metadata, strict,
missing_keys, unexpected_keys, error_msgs)這里再舉一個 MMCV 中的例子,DCN 經(jīng)歷了一次重構(gòu),屬性的名字經(jīng)過了重命名。
def _load_from_state_dict(self, state_dict, prefix, local_metadata, strict,
missing_keys, unexpected_keys, error_msgs):
version = local_metadata.get('version', None)
if version is None or version < 2:
# the key is different in early versions
# In version < 2, DeformConvPack loads previous benchmark models.
if (prefix + 'conv_offset.weight' not in state_dict
and prefix[:-1] + '_offset.weight' in state_dict):
state_dict[prefix + 'conv_offset.weight'] = state_dict.pop(
prefix[:-1] + '_offset.weight')
if (prefix + 'conv_offset.bias' not in state_dict
and prefix[:-1] + '_offset.bias' in state_dict):
state_dict[prefix +
'conv_offset.bias'] = state_dict.pop(prefix[:-1] +
'_offset.bias')
if version is not None and version > 1:
print_log(
f'DeformConv2dPack {prefix.rstrip(".")} is upgraded to '
'version 2.',
logger='root')
super()._load_from_state_dict(state_dict, prefix, local_metadata,
strict, missing_keys, unexpected_keys,
error_msgs)Example: 模型無痛遷移
如果在 MMDetection 中訓(xùn)練了一個 detector,MMDetection3D 中的多模態(tài)檢測器想要加載這個預(yù)訓(xùn)練的檢測器,很多權(quán)重名字對不上,又不想寫一個腳本手動來轉(zhuǎn),可以使用 _load_from_state_dict 來進行。通過這種方式,MMDetection3D 可以加載并使用 MMDetection 訓(xùn)練的任意一個檢測器。
def _load_from_state_dict(self, state_dict, prefix, local_metadata, strict,
missing_keys, unexpected_keys, error_msgs):
# override the _load_from_state_dict function
# convert the backbone weights pre-trained in Mask R-CNN
# use list(state_dict.keys()) to avoid
# RuntimeError: OrderedDict mutated during iteration
for key_name in list(state_dict.keys()):
key_changed = True
if key_name.startswith('backbone.'):
new_key_name = f'img_backbone{key_name[8:]}'
elif key_name.startswith('neck.'):
new_key_name = f'img_neck{key_name[4:]}'
elif key_name.startswith('rpn_head.'):
new_key_name = f'img_rpn_head{key_name[8:]}'
elif key_name.startswith('roi_head.'):
new_key_name = f'img_roi_head{key_name[8:]}'
else:
key_changed = False
if key_changed:
logger = get_root_logger()
print_log(
f'{key_name} renamed to be {new_key_name}', logger=logger)
state_dict[new_key_name] = state_dict.pop(key_name)
super()._load_from_state_dict(state_dict, prefix, local_metadata,
strict, missing_keys, unexpected_keys,
error_msgs)Reference
Pytorch nn.Module 文檔
MMCV 中 DCN 的實現(xiàn)
MMDetection3D
下載1:何愷明頂會分享
在「AI算法與圖像處理」公眾號后臺回復(fù):何愷明,即可下載。總共有6份PDF,涉及 ResNet、Mask RCNN等經(jīng)典工作的總結(jié)分析
下載2:終身受益的編程指南:Google編程風(fēng)格指南
在「AI算法與圖像處理」公眾號后臺回復(fù):c++,即可下載。歷經(jīng)十年考驗,最權(quán)威的編程規(guī)范!
下載3 CVPR2020 在「AI算法與圖像處理」公眾號后臺回復(fù):CVPR2020,即可下載1467篇CVPR?2020論文 個人微信(如果沒有備注不拉群!) 請注明:地區(qū)+學(xué)校/企業(yè)+研究方向+昵稱
覺得不錯就點亮在看吧