使用Pytorch實現(xiàn)風格遷移(Neural-Transfer)
# 前言
本文主要向大家分享一個小編剛剛學習的神經(jīng)網(wǎng)絡應用的實例:風格遷移(Neural-Transfer)。這是一個由 Leon A. Gatys,Alexander S. Ecker和Matthias Bethge提出的算法。通過這個算法,我們可以用一種新的風格對指定圖片進行重構(gòu),更通俗一點即:風格圖片+內(nèi)容圖片=輸出圖片,即:
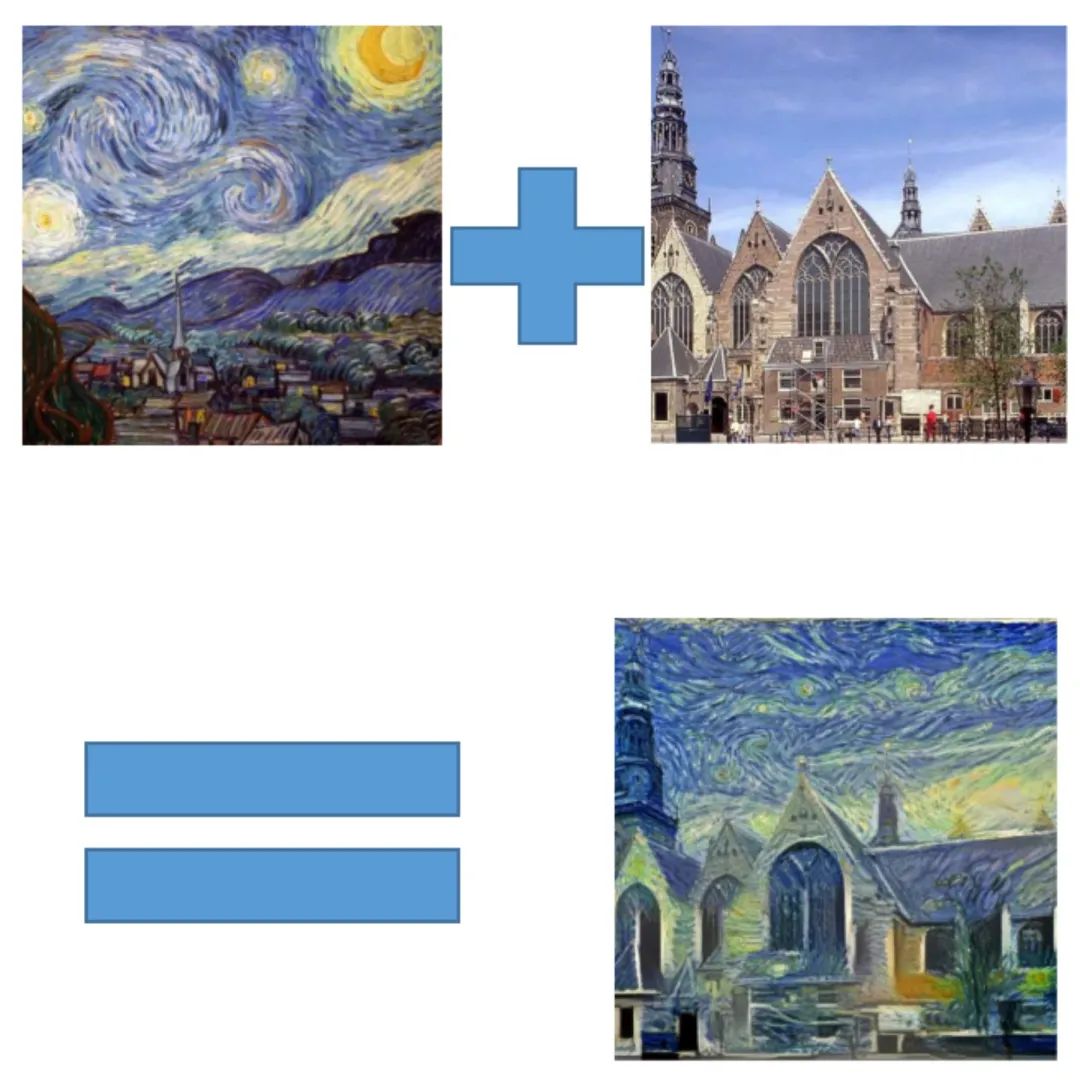

如上圖所示,神經(jīng)風格遷移可以將內(nèi)容圖像的內(nèi)容、風格圖像的風格混合在一起,使得輸出的圖片看起來像內(nèi)容圖像,但采用了風格圖像的風格。這就生成了一個帶有《星空》風格的風景圖,是不是很有趣呢?下面讓我們一起來看看它是怎么實現(xiàn)的吧!
01
基本原理
原理很簡單:我們定義了兩個距離,一個為內(nèi)容D_c和一個用于樣式D_s。D_c 測量兩個圖像之間的內(nèi)容有多大不同,而?D_s衡量兩個圖像之間風格的差異。然后,我們生成第三張圖片,并利用D_c和D_s來優(yōu)化這張圖片,使其與內(nèi)容圖片的內(nèi)容差別和風格圖片的風格差別最小化。當然,我們的第一步是利用卷積神經(jīng)網(wǎng)絡提取出圖片的特征,如圖所示:
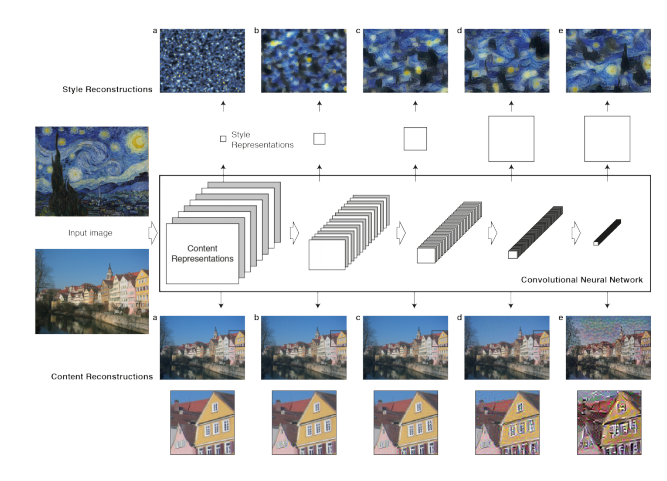
02
讀入圖片
現(xiàn)在我們導入content和style的原圖,我們需要使用PIL中的Image來讀取內(nèi)存中的圖片(PS:opencv也可以,但PIL的效果更好一點),再用torchvision中的transforms將讀入圖片轉(zhuǎn)化為tensor以便之后的操作。另外,我們還需要定義一個用于輸出圖像的函數(shù),以便輸出最終所得到的圖片,該函數(shù)會將tensor轉(zhuǎn)化為圖像。
代碼如下:
# load_img模塊import PIL.Image as Imageimport torchimport torchvision.transforms as transformsimg_size = 512 if torch.cuda.is_available() else 128#根據(jù)設備選擇改變后項數(shù)大小def load_img(img_path):#圖像讀入? ?img = Image.open(img_path).convert('RGB')#將圖像讀入并轉(zhuǎn)換成RGB形式? ?img = img.resize(img_size, img_size)#調(diào)整讀入圖像像素大小? ?img = transforms.ToTensor()(img)#將圖像轉(zhuǎn)化為tensor? ?img = img.unsqueeze(0)#在0維上增加一個維度? ?return imgdef show_img(img):#圖像輸出? ?img = img.squeeze(0)#將多余的0維通道刪去? ?img = transforms.ToPILImage()(img)#將tensor轉(zhuǎn)化為圖像? ?img.show()
03
損失函數(shù)
下一步是定義我們的損失函數(shù),為了實現(xiàn)神經(jīng)風格遷移,我們需要定義一個關于生成圖像(Generated image)G的損失函數(shù),用于評價生成圖像的好壞。通過最小化損失函數(shù)的方式,來生成所要的圖像。損失函數(shù)需要分成兩部分,一個是內(nèi)容損失函數(shù),它是關于生成圖像G與內(nèi)容圖像C的函數(shù),用于衡量生成圖像與內(nèi)容圖像在內(nèi)容上有多相似;一個是風格損失函數(shù),關于生成圖像G與風格圖像S的函數(shù),用于衡量生成圖像與風格圖像在風格上的相似度。最后需要用兩個超參數(shù)α和β來確定兩個函數(shù)之間的權(quán)重,我們的總損失是它們兩個的加權(quán)和,即
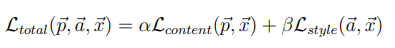
那么我們的關鍵就在于先單獨求出內(nèi)容損失和風格損失,計算它們的損失也很簡單,首先我們看一下內(nèi)容損失,我們使用最簡單的均方誤差:
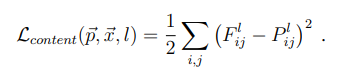
上式是內(nèi)容損失函數(shù)的定義。其中l(wèi)代表第l層的特征表示,p是原始內(nèi)容圖片特征圖,x是生成圖片特征圖。公式的含義就是對于每一層,原始圖片的特征圖(feature map)和生成圖片的特征圖的一一對應做差值平方和。
然后我們需要對損失梯度下降求導來優(yōu)化參數(shù)
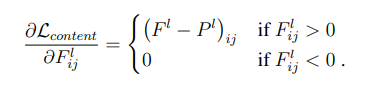
對于風格損失我們還需要引入Gram矩陣來幫助我們表示圖像的風格特征,我們讀入圖像卷積層的輸出形狀為C × H × W ,C是卷積核的通道數(shù),每個卷積核學習圖像不同特征,每個卷積核輸出H × W 代表這張圖像的一個feature map,讀入RGB圖像的三色通道相當于三個feature map,我們用Gram矩陣來計算feature map間的相似性,得到圖像的風格特征。
關于Gram矩陣
由于計算風格損失需要Gram矩陣,所以我們先來了解一下它吧。
Gram矩陣的定義:

Gram矩陣計算公式:
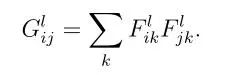
F表示生成圖像的feature map。上面式子的含義:第l層的Gram矩陣第i行,第j列的數(shù)值等于把生成圖像在第l層的第i個feature map與第j個feature map分別拉成一維后相乘求和,即Gram矩陣中的每個值都是每個通道 i 的feature map與每個通道 j 的feature map的內(nèi)積,由于內(nèi)積可以判斷兩個向量之間的夾角和方向關系(如:若a·b>0,則二者方向相同,夾角在0°到90°之間),所以Gram矩陣中的值可以反映出兩個feature map之間的某種關系。
Gram矩陣可以看是feature之間的偏心協(xié)方差矩陣,feature map中的每個數(shù)字都來自于一個特定濾波器在特定位置的卷積,因此每個數(shù)字代表一個特征的強度,而Gram計算的實際上是兩兩特征之間的相關性。Gram的對角線元素提供了不同特征圖各自的信息,而其余元素提供了不同特征圖之間的相關信息,因此,Gram有助于把握整個圖像的大體風格。有了表示風格的Gram矩陣,要度量兩個圖像風格的差異,只需比較他們Gram矩陣的差異即可。
然后我們就可以利用Gram矩陣提取的風格特征計算損失了,這里我們?nèi)匀皇褂镁秸`差,并進行歸一化操作。
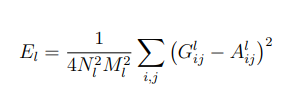
上面是第l層的風格損失函數(shù),N是指生成圖feature map數(shù)量,M是圖片寬乘高,G是生成圖像的Gram矩陣,A是風格圖像的Gram矩陣。
然后是梯度下降:
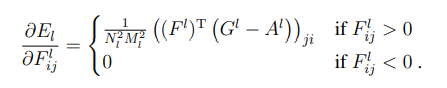
最終的風格損失函數(shù)為每一層的風格損失加權(quán)求和可得。式中,a是指風格圖像,x是指生成圖像,w是指權(quán)重:
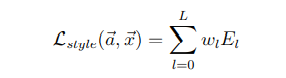
下面我們看看如何用代碼實現(xiàn)它:
# loss板塊import torch.nn as nnimport torchclass Content_Loss(nn.Module):#內(nèi)容損失? ?def __init__(self, target, weight):? ? ? ?super(Content_Loss, self).__init__()#繼承父類的初始化? ? ? ?self.weight = weight? ? ? ?self.target = target.detach() * self.weight? ? ? ?# 必須要用detach來分離出target,這時候target不再是一個Variable,這是為了動態(tài)計算梯度,否則forward會出錯,不能向前傳播? ? ? ?self.criterion = nn.MSELoss()#利用均方誤差計算損失? ? ? ?? ?def forward(self, input):#向前計算損失? ? ? ?self.loss = self.criterion(input * self.weight, self.target)? ? ? ?out = input.clone()? ? ? ?return out? ? ? ?? ?def backward(self, retain_graph=True):#反向求導? ? ? ?self.loss.backward(retain_graph=retain_graph)? ? ? ?return self.loss? ? ? ?? ? ? ?class Gram(nn.Module):#定義Gram矩陣? ?def __init__(self):? ? ? ?super(Gram, self).__init__()? ? ? ?? ?def forward(self, input):#向前計算Gram矩陣? ? ? ?a, b, c, d = input.size()#a為批量大小,b為feature map的數(shù)量,c*d為feature map的大小? ? ? ?feature = input.view(a * b, c * d)? ? ? ?gram = torch.mm(feature, feature.t())? ? ? ?gram /= (a * b * c * d)? ? ? ?return gram? ? ? ?? ? ? ?class Style_Loss(nn.Module):#風格損失? ?def __init__(self, target, weight):? ? ? ?super(Style_Loss, self).__init__()? ? ? ?self.weight = weight? ? ? ?self.target = target.detach() * self.weight? ? ? ?self.gram = Gram()? ? ? ?self.criterion = nn.MSELoss()? ? ? ?? ?def forward(self, input):? ? ? ?G = self.gram(input) * self.weight? ? ? ?self.loss = self.criterion(G, self.target)? ? ? ?out = input.clone()? ? ? ?return out? ? ? ?? ?def backward(self, retain_graph=True):? ? ? ?self.loss.backward(retain_graph=retain_graph)? ? ? ?return self.loss
04
模型構(gòu)建
接下來就該構(gòu)建我們的模型啦!雖然我們用的是已經(jīng)預訓練好的vgg框架,但我們還需要對它做一些“改造”:把我們之前構(gòu)造好的損失函數(shù)加進去。畢竟“白嫖”也是有限度的嘛!話不多說,上代碼!
# build_model模塊import torch.nn as nnimport torchimport torchvision.models as modelsimport loss ?# 指的是上文中已經(jīng)寫好的loss模塊device = torch.device("cuda" if torch.cuda.is_available() else "cpu")#選擇運行設備,如果你的電腦有g(shù)pu就在gpu上運行,否則在cpu上運行vgg = models.vgg19(pretrained=True).features.to(device)#這里我們使用預訓練好的vgg19模型'''所需的深度層來計算風格/內(nèi)容損失:'''content_layers_default = ['conv_4']style_layers_default = ['conv_1', 'conv_2', 'conv_3', 'conv_4', 'conv_5']def get_style_model_and_loss(style_img,? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? content_img,? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? cnn=vgg,? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? style_weight=1000,? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? content_weight=1,? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? content_layers=content_layers_default,? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? style_layers=style_layers_default):? ?content_loss_list = [] #內(nèi)容損失? ?style_loss_list = [] #風格損失? ?model = nn.Sequential() #創(chuàng)建一個model,按順序放入layer? ?model = model.to(device)? ?gram = loss.Gram().to(device)? ?? ?'''把vgg19中的layer、content_loss以及style_loss按順序加入到model中:'''? ?i = 1? ?for layer in cnn:? ? ? ?if isinstance(layer, nn.Conv2d):? ? ? ? ? ?name = 'conv_' + str(i)? ? ? ? ? ?model.add_module(name, layer)? ? ? ? ? ?if name in content_layers_default:? ? ? ? ? ? ? ?target = model(content_img)? ? ? ? ? ? ? ?content_loss = loss.Content_Loss(target, content_weight)? ? ? ? ? ? ? ?model.add_module('content_loss_' + str(i), content_loss)? ? ? ? ? ? ? ?content_loss_list.append(content_loss)? ? ? ? ? ?if name in style_layers_default:? ? ? ? ? ? ? ?target = model(style_img)? ? ? ? ? ? ? ?target = gram(target)? ? ? ? ? ? ? ?style_loss = loss.Style_Loss(target, style_weight)? ? ? ? ? ? ? ?model.add_module('style_loss_' + str(i), style_loss)? ? ? ? ? ? ? ?style_loss_list.append(style_loss)? ? ? ? ? ?i += 1? ? ? ?if isinstance(layer, nn.MaxPool2d):? ? ? ? ? ?name = 'pool_' + str(i)? ? ? ? ? ?model.add_module(name, layer)? ? ? ?if isinstance(layer, nn.ReLU):? ? ? ? ? ?name = 'relu' + str(i)? ? ? ? ? ?model.add_module(name, layer)? ? ? ? ? ?? ?return model, style_loss_list, content_loss_list
05
執(zhí)行
一切工作準備就緒,我們就可以開始定義我們的run_code模塊了,經(jīng)歷過這么多操作終于走到了最后一步,是不是有點小激動呢?我們的執(zhí)行模塊也很簡單,先定義一個LBFGS優(yōu)化器,然后就可以開始我們一次一次的訓練了。這里我們定義每訓練50次輸出一次我們的損失來評估學習效果。
# run_code模塊import torch.nn as nnimport torch.optim as optimfrom build_model import get_style_model_and_lossdef get_input_param_optimier(input_img):? ?"""input_img is a Variable"""? ?input_param = nn.Parameter(input_img.data)#獲取參數(shù)? ?optimizer = optim.LBFGS([input_param])#用LBFGS優(yōu)化參數(shù)? ?return input_param, optimizer? ?def run_style_transfer(content_img, style_img, input_img, num_epoches=300):? ?print('Building the style transfer model..')? ?model, style_loss_list, content_loss_list = get_style_model_and_loss(? ? ? ?style_img, content_img)? ?input_param, optimizer = get_input_param_optimier(input_img)? ?print('Opimizing...')? ?epoch = [0]? ?while epoch[0] < num_epoches:#每隔50次輸出一次loss? ? ? ?def closure():? ? ? ? ? ?input_param.data.clamp_(0, 1)#修正輸入圖像的值? ? ? ? ? ?model(input_param)? ? ? ? ? ?style_score = 0? ? ? ? ? ?content_score = 0? ? ? ? ? ?optimizer.zero_grad()? ? ? ? ? ?for sl in style_loss_list:? ? ? ? ? ? ? ?style_score += sl.backward()? ? ? ? ? ?for cl in content_loss_list:? ? ? ? ? ? ? ?content_score += cl.backward()? ? ? ? ? ?epoch[0] += 1? ? ? ? ? ?if epoch[0] % 50 == 0:? ? ? ? ? ? ? ?print('run {}'.format(epoch))? ? ? ? ? ? ? ?print('Style Loss: {:.4f} Content Loss: {:.4f}'.format(? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ?style_score.item(), content_score.item()))? ? ? ? ? ? ? ?print()? ? ? ? ? ?return style_score + content_score? ? ? ?optimizer.step(closure)? ? ? ?input_param.data.clamp_(0, 1)#再次修正? ?return input_param.data
06
運行
最最最最最激動人心的時刻就要到了!敲了這么多代碼,現(xiàn)在我們就可以開始驗證我們的成果了!現(xiàn)在我們只需要挑選一張中意的圖片,再為它尋找一個你想要的風格圖片,只需短短幾分鐘(甚至幾十秒),你,就創(chuàng)造出了屬于自己的藝術(shù)畫作(其實一般)!!!
# start模塊from torch.autograd import Variablefrom torchvision import transformsimport torchfrom run_code import run_style_transferfrom load_img import load_img, show_imgdevice = torch.device("cuda" if torch.cuda.is_available() else "cpu")style_img = load_img('./picture/style1.png')#風格圖片地址style_img = Variable(style_img).to(device)content_img = load_img('./picture/content5.png')#內(nèi)容圖片地址content_img = Variable(content_img).to(device)input_img = content_img.clone()out = run_style_transfer(content_img, style_img, input_img, num_epoches=200)#進行200次訓練save_pic = transforms.ToPILImage()(out.cpu().squeeze(0))save_pic.save('./picture/result4.png')#選擇你要保存的地址save_pic.show()
下面我們做幾組演示:
輸入:
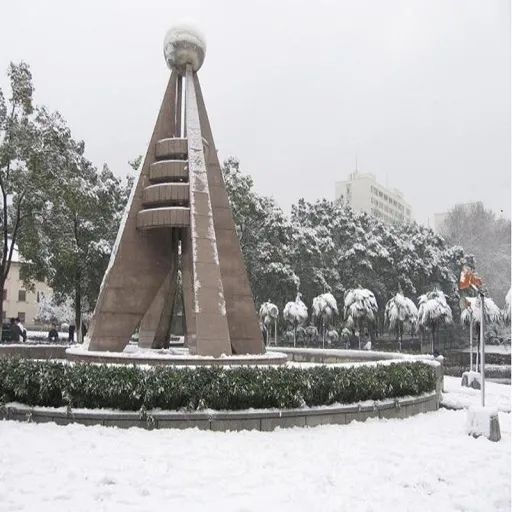
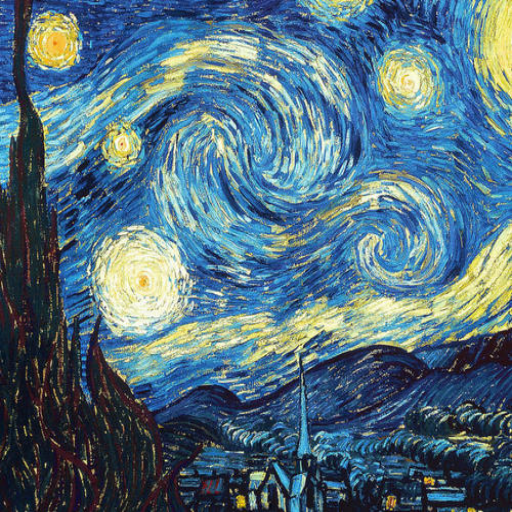


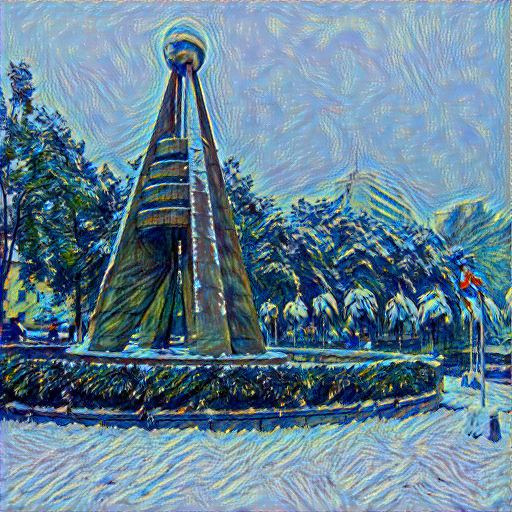
輸出:

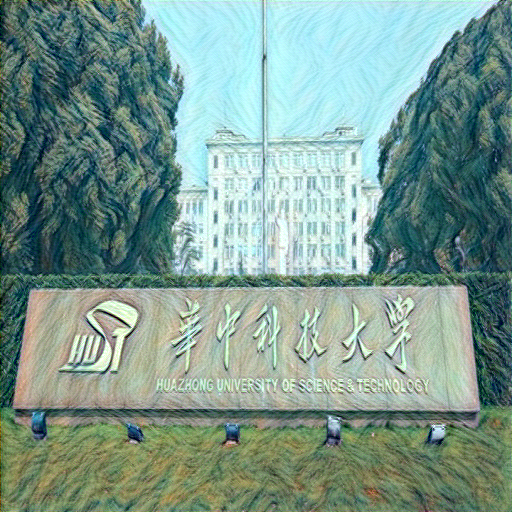
輸入:


輸出:

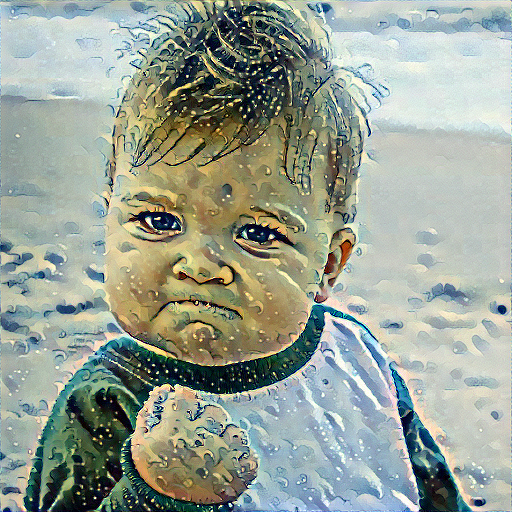
最后我們試一試人像:


輸出:

下面是其中一組loss的輸出:
Opimizing...run [50]Style Loss: 0.7299 Content Loss: 3.7480run [100]Style Loss: 0.3702 Content Loss: 3.3560run [150]Style Loss: 0.2747 Content Loss: 3.1843run [200]Style Loss: 0.2058 Content Loss: 3.0981
我們可以看出內(nèi)容損失還是挺大的,損失的大小不僅跟我們的模型有關,我們選擇的圖片也會對損失有很大的影響,不得不說有的圖片特征確實難以捕獲,小編曾經(jīng)還有過訓練1000次仍然有40多損失的慘痛經(jīng)歷,這種情況就不是單純增加訓練次數(shù)就能解決的了,我們需要更強大的模型去捕獲信息,大家也可以自己試試改進一下模型,也許會有意外的收獲呦!
reference
1] Gatys L A, Ecker A S, Bethge M. A neural algorithm of artistic style[J]. arXiv preprint arXiv:1508.06576, 2015.
2] https://pytorch.org/tutorials/advanced/neural_style_tutorial.html#importing-packages-and-selecting-a-device
1
END
1
文案&排版:王心怡(華中科技大學管理學院本科一年級)
? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? 潘云飛(華中科技大學管理學院本科一年級)
指導老師:秦虎老師(華中科技大學管理學院)
審稿:張宇(華中科技大學管理學院本科二年級)
如對文中內(nèi)容有疑問,歡迎交流。PS:部分資料來自網(wǎng)絡。
如有需求,可以聯(lián)系:
秦虎老師(華中科技大學管理學院:[email protected])
王心怡(華中科技大學管理學院本科一年級:[email protected])
潘云飛(華中科技大學管理學院本科一年級:[email protected])
張宇(華中科技大學管理學院本科二年級:[email protected])
