推薦收藏!14 種異常檢測方法總結(jié)!
↓推薦關(guān)注↓

一、基于分布的方法
1. 3sigma
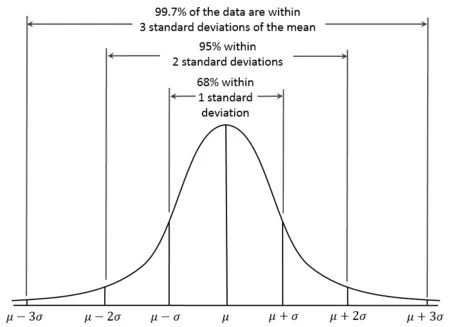
def three_sigma(s):
mu, std = np.mean(s), np.std(s)
lower, upper = mu-3*std, mu+3*std
return lower, upper
2. Z-score
def z_score(s):
z_score = (s - np.mean(s)) / np.std(s)
return z_score
3. boxplot
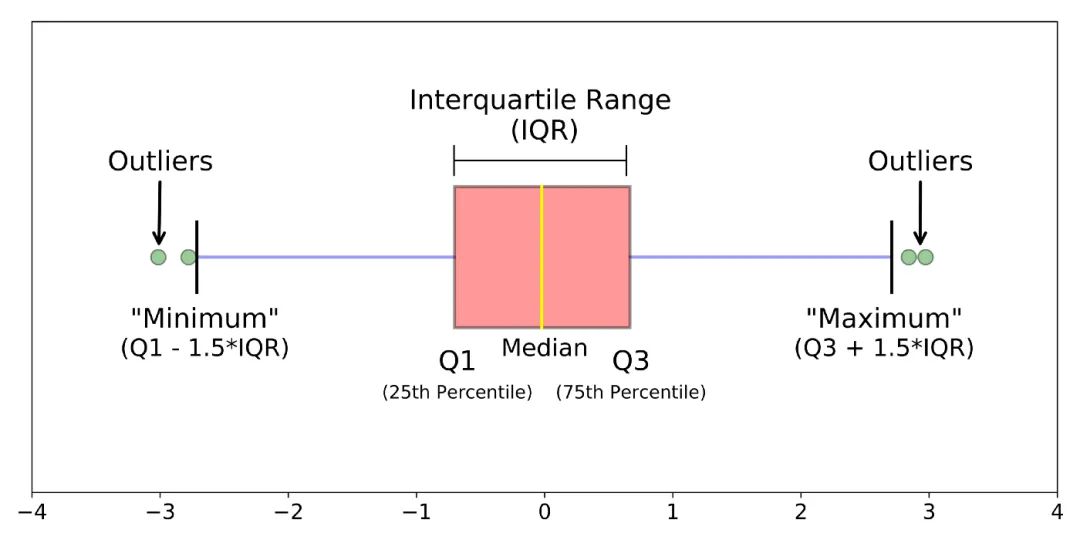
def boxplot(s):
q1, q3 = s.quantile(.25), s.quantile(.75)
iqr = q3 - q1
lower, upper = q1 - 1.5*iqr, q3 + 1.5*iqr
return lower, upper
4. Grubbs假設(shè)檢驗(yàn)
[1] 時(shí)序預(yù)測競賽之異常檢測算法綜述 - 魚遇雨欲語與余,知乎:https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/336944097 [2] 剔除異常值柵格計(jì)算器_數(shù)據(jù)分析師所需的統(tǒng)計(jì)學(xué):異常檢測 - weixin_39974030,CSDN:https://blog.csdn.net/weixin_39974030/article/details/112569610
-
H0: 數(shù)據(jù)集中沒有異常值
-
H1: 數(shù)據(jù)集中有一個(gè)異常值
from outliers import smirnov_grubbs as grubbs
print(grubbs.test([8, 9, 10, 1, 9], alpha=0.05))
print(grubbs.min_test_outliers([8, 9, 10, 1, 9], alpha=0.05))
print(grubbs.max_test_outliers([8, 9, 10, 1, 9], alpha=0.05))
print(grubbs.max_test_indices([8, 9, 10, 50, 9], alpha=0.05))
二、基于距離的方法
1. KNN
[3] 異常檢測算法之(KNN)-K Nearest Neighbors - 小伍哥聊風(fēng)控,知乎:https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/501691799
from pyod.models.knn import KNN
# 初始化檢測器clf
clf = KNN( method='mean', n_neighbors=3, )
clf.fit(X_train)
# 返回訓(xùn)練數(shù)據(jù)上的分類標(biāo)簽 (0: 正常值, 1: 異常值)
y_train_pred = clf.labels_
# 返回訓(xùn)練數(shù)據(jù)上的異常值 (分值越大越異常)
y_train_scores = clf.decision_scores_
三、基于密度的方法
1. Local Outlier Factor (LOF)
[4] 一文讀懂異常檢測 LOF 算法(Python代碼)- 東哥起飛,知乎:https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/448276009

-
對于每個(gè)數(shù)據(jù)點(diǎn),計(jì)算它與其他所有點(diǎn)的距離,并按從近到遠(yuǎn)排序;
-
對于每個(gè)數(shù)據(jù)點(diǎn),找到它的K-Nearest-Neighbor,計(jì)算LOF得分。
from sklearn.neighbors import LocalOutlierFactor as LOF
X = [[-1.1], [0.2], [100.1], [0.3]]
clf = LOF(n_neighbors=2)
res = clf.fit_predict(X)
print(res)
print(clf.negative_outlier_factor_)
2. Connectivity-Based Outlier Factor (COF)
[5] Nowak-Brzezińska, A., & Horyń, C. (2020). Outliers in rules-the comparision of LOF, COF and KMEANS algorithms. *Procedia Computer Science*, *176*, 1420-1429. [6] 機(jī)器學(xué)習(xí)_學(xué)習(xí)筆記系列(98):基於連接異常因子分析(Connectivity-Based Outlier Factor) - 劉智皓 (Chih-Hao Liu)
# https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/362358580
from pyod.models.cof import COF
cof = COF(contamination = 0.06, ## 異常值所占的比例
n_neighbors = 20, ## 近鄰數(shù)量
)
cof_label = cof.fit_predict(iris.values) # 鳶尾花數(shù)據(jù)
print("檢測出的異常值數(shù)量為:",np.sum(cof_label == 1))
3. Stochastic Outlier Selection (SOS)
[7] 異常檢測之SOS算法 - 呼廣躍,知乎:https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/34438518

-
計(jì)算相異度矩陣D;
-
計(jì)算關(guān)聯(lián)度矩陣A;
-
計(jì)算關(guān)聯(lián)概率矩陣B;
-
算出異常概率向量。

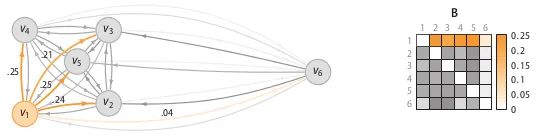
# Ref: https://github.com/jeroenjanssens/scikit-sos
import pandas as pd
from sksos import SOS
iris = pd.read_csv("http://bit.ly/iris-csv")
X = iris.drop("Name", axis=1).values
detector = SOS()
iris["score"] = detector.predict(X)
iris.sort_values("score", ascending=False).head(10)
四、基于聚類的方法
1. DBSCAN
-
輸入:數(shù)據(jù)集,鄰域半徑Eps,鄰域中數(shù)據(jù)對象數(shù)目閾值MinPts;
-
輸出:密度聯(lián)通簇。

-
從數(shù)據(jù)集中任意選取一個(gè)數(shù)據(jù)對象點(diǎn)p;
-
如果對于參數(shù)Eps和MinPts,所選取的數(shù)據(jù)對象點(diǎn)p為核心點(diǎn),則找出所有從p密度可達(dá)的數(shù)據(jù)對象點(diǎn),形成一個(gè)簇;
-
如果選取的數(shù)據(jù)對象點(diǎn) p 是邊緣點(diǎn),選取另一個(gè)數(shù)據(jù)對象點(diǎn);
-
重復(fù)以上2、3步,直到所有點(diǎn)被處理。
# Ref: https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/515268801
from sklearn.cluster import DBSCAN
import numpy as np
X = np.array([[1, 2], [2, 2], [2, 3],
[8, 7], [8, 8], [25, 80]])
clustering = DBSCAN(eps=3, min_samples=2).fit(X)
clustering.labels_
array([ 0, 0, 0, 1, 1, -1])
# 0,,0,,0:表示前三個(gè)樣本被分為了一個(gè)群
# 1, 1:中間兩個(gè)被分為一個(gè)群
# -1:最后一個(gè)為異常點(diǎn),不屬于任何一個(gè)群
五、基于樹的方法
1. Isolation Forest (iForest)
[8] 異常檢測算法 -- 孤立森林(Isolation Forest)剖析 - 風(fēng)控大魚,知乎:https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/74508141 [9] 孤立森林(isolation Forest)-一個(gè)通過瞎幾把亂分進(jìn)行異常檢測的算法 - 小伍哥聊風(fēng)控,知乎:https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/484495545 [10] 孤立森林閱讀 - Mark_Aussie,博文:https://blog.csdn.net/MarkAustralia/article/details/120181899
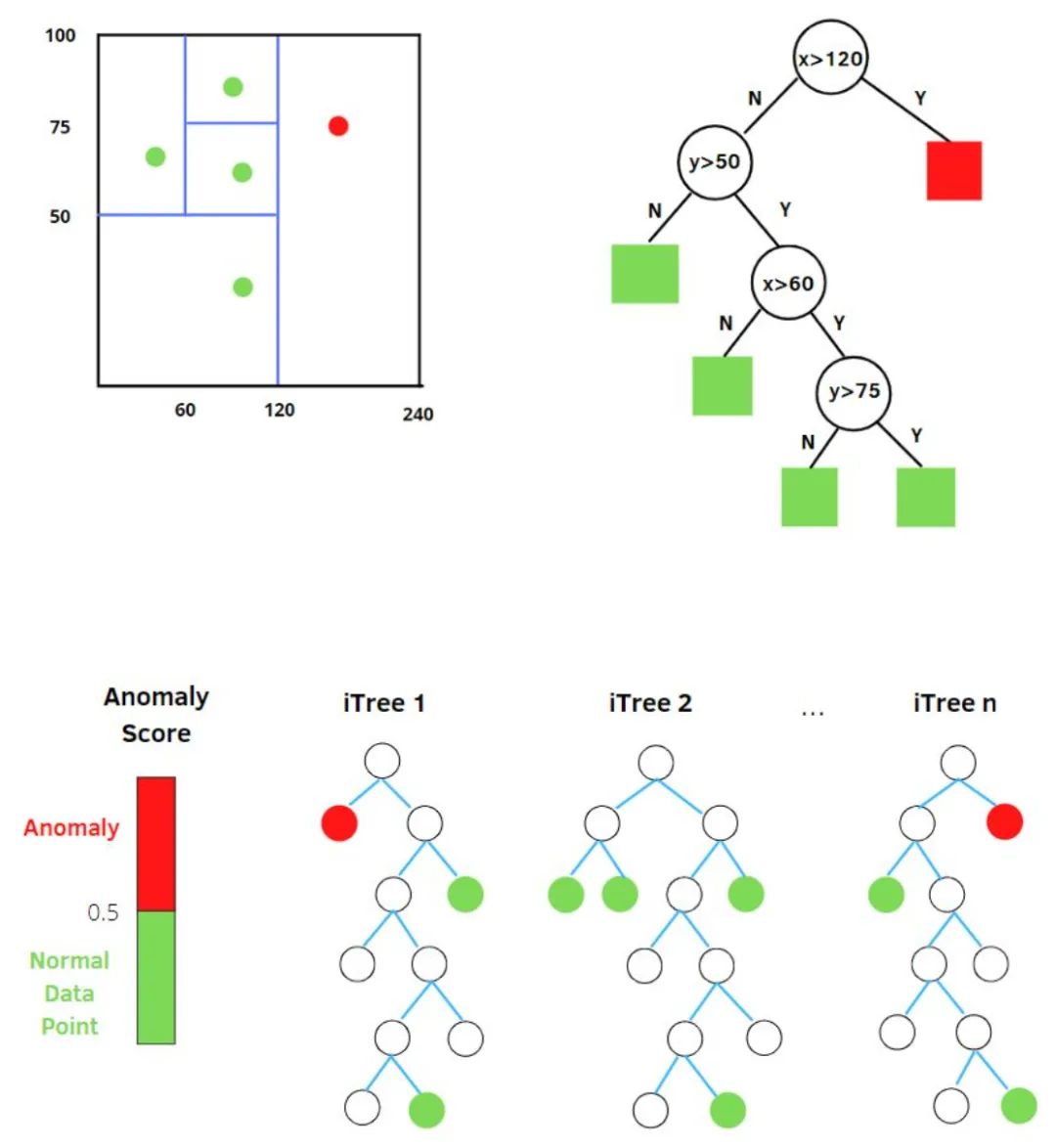
-
h(x):為樣本在iTree上的PathLength;
-
E(h(x)):為樣本在t棵iTree的PathLength的均值;
-
: 為 個(gè)樣本構(gòu)建一個(gè)二叉搜索樹BST中的末成功搜索平均路徑長度 (均值h(x)對外部節(jié)點(diǎn)終端的估計(jì)等同于BST中的末成功搜索)。 是對樣本x的路徑長度 進(jìn)行標(biāo)準(zhǔn)化處理。 是調(diào)和數(shù), 可使用 (歐拉常數(shù)) 估算。
# Ref:https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/484495545
from sklearn.datasets import load_iris
from sklearn.ensemble import IsolationForest
data = load_iris(as_frame=True)
X,y = data.data,data.target
df = data.frame
# 模型訓(xùn)練
iforest = IsolationForest(n_estimators=100, max_samples='auto',
contamination=0.05, max_features=4,
bootstrap=False, n_jobs=-1, random_state=1)
# fit_predict 函數(shù) 訓(xùn)練和預(yù)測一起 可以得到模型是否異常的判斷,-1為異常,1為正常
df['label'] = iforest.fit_predict(X)
# 預(yù)測 decision_function 可以得出 異常評分
df['scores'] = iforest.decision_function(X)
六、基于降維的方法
1. Principal Component Analysis (PCA)
[11] 機(jī)器學(xué)習(xí)-異常檢測算法(三):Principal Component Analysis - 劉騰飛,知乎:https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/29091645 [12] Anomaly Detection異常檢測--PCA算法的實(shí)現(xiàn) - CC思SS,知乎:https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/48110105
-
特征向量:反應(yīng)了原始數(shù)據(jù)方差變化程度的不同方向;
-
特征值:數(shù)據(jù)在對應(yīng)方向上的方差大小。
-
考慮在前k個(gè)特征向量方向上的偏差:前k個(gè)特征向量往往直接對應(yīng)原始數(shù)據(jù)里的某幾個(gè)特征,在前幾個(gè)特征向量方向上偏差比較大的數(shù)據(jù)樣本,往往就是在原始數(shù)據(jù)中那幾個(gè)特征上的極值點(diǎn)。
-
考慮后r個(gè)特征向量方向上的偏差:后r個(gè)特征向量通常表示某幾個(gè)原始特征的線性組合,線性組合之后的方差比較小反應(yīng)了這幾個(gè)特征之間的某種關(guān)系。在后幾個(gè)特征方向上偏差比較大的數(shù)據(jù)樣本,表示它在原始數(shù)據(jù)里對應(yīng)的那幾個(gè)特征上出現(xiàn)了與預(yù)計(jì)不太一致的情況。
# Ref: [https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/48110105](https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/48110105)
from sklearn.decomposition import PCA
pca = PCA()
pca.fit(centered_training_data)
transformed_data = pca.transform(training_data)
y = transformed_data
# 計(jì)算異常分?jǐn)?shù)
lambdas = pca.singular_values_
M = ((y*y)/lambdas)
# 前k個(gè)特征向量和后r個(gè)特征向量
q = 5
print "Explained variance by first q terms: ", sum(pca.explained_variance_ratio_[:q])
q_values = list(pca.singular_values_ < .2)
r = q_values.index(True)
# 對每個(gè)樣本點(diǎn)進(jìn)行距離求和的計(jì)算
major_components = M[:,range(q)]
minor_components = M[:,range(r, len(features))]
major_components = np.sum(major_components, axis=1)
minor_components = np.sum(minor_components, axis=1)
# 人為設(shè)定c1、c2閾值
components = pd.DataFrame({'major_components': major_components,
'minor_components': minor_components})
c1 = components.quantile(0.99)['major_components']
c2 = components.quantile(0.99)['minor_components']
# 制作分類器
def classifier(major_components, minor_components):
major = major_components > c1
minor = minor_components > c2
return np.logical_or(major,minor)
results = classifier(major_components=major_components, minor_components=minor_components)
2. AutoEncoder
[13] 利用Autoencoder進(jìn)行無監(jiān)督異常檢測(Python) - SofaSofa.io,知乎:https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/46188296 [14] 自編碼器AutoEncoder解決異常檢測問題(手把手寫代碼) - 數(shù)據(jù)如琥珀,知乎:https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/260882741

# Ref: [https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/260882741](https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/260882741)
import tensorflow as tf
from keras.models import Sequential
from keras.layers import Dense
# 標(biāo)準(zhǔn)化數(shù)據(jù)
scaler = preprocessing.MinMaxScaler()
X_train = pd.DataFrame(scaler.fit_transform(dataset_train),
columns=dataset_train.columns,
index=dataset_train.index)
# Random shuffle training data
X_train.sample(frac=1)
X_test = pd.DataFrame(scaler.transform(dataset_test),
columns=dataset_test.columns,
index=dataset_test.index)
tf.random.set_seed(10)
act_func = 'relu'
# Input layer:
model=Sequential()
# First hidden layer, connected to input vector X.
model.add(Dense(10,activation=act_func,
kernel_initializer='glorot_uniform',
kernel_regularizer=regularizers.l2(0.0),
input_shape=(X_train.shape[1],)
)
)
model.add(Dense(2,activation=act_func,
kernel_initializer='glorot_uniform'))
model.add(Dense(10,activation=act_func,
kernel_initializer='glorot_uniform'))
model.add(Dense(X_train.shape[1],
kernel_initializer='glorot_uniform'))
model.compile(loss='mse',optimizer='adam')
print(model.summary())
# Train model for 100 epochs, batch size of 10:
NUM_EPOCHS=100
BATCH_SIZE=10
history=model.fit(np.array(X_train),np.array(X_train),
batch_size=BATCH_SIZE,
epochs=NUM_EPOCHS,
validation_split=0.05,
verbose = 1)
plt.plot(history.history['loss'],
'b',
label='Training loss')
plt.plot(history.history['val_loss'],
'r',
label='Validation loss')
plt.legend(loc='upper right')
plt.xlabel('Epochs')
plt.ylabel('Loss, [mse]')
plt.ylim([0,.1])
plt.show()
# 查看訓(xùn)練集還原的誤差分布如何,以便制定正常的誤差分布范圍
X_pred = model.predict(np.array(X_train))
X_pred = pd.DataFrame(X_pred,
columns=X_train.columns)
X_pred.index = X_train.index
scored = pd.DataFrame(index=X_train.index)
scored['Loss_mae'] = np.mean(np.abs(X_pred-X_train), axis = 1)
plt.figure()
sns.distplot(scored['Loss_mae'],
bins = 10,
kde= True,
color = 'blue')
plt.xlim([0.0,.5])
# 誤差閾值比對,找出異常值
X_pred = model.predict(np.array(X_test))
X_pred = pd.DataFrame(X_pred,
columns=X_test.columns)
X_pred.index = X_test.index
threshod = 0.3
scored = pd.DataFrame(index=X_test.index)
scored['Loss_mae'] = np.mean(np.abs(X_pred-X_test), axis = 1)
scored['Threshold'] = threshod
scored['Anomaly'] = scored['Loss_mae'] > scored['Threshold']
scored.head()
七、基于分類的方法
1. One-Class SVM
[15] Python機(jī)器學(xué)習(xí)筆記:One Class SVM - zoukankan,博文:http://t.zoukankan.com/wj-1314-p-10701708.html [16] 單類SVM: SVDD - 張義策,知乎:https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/65617987
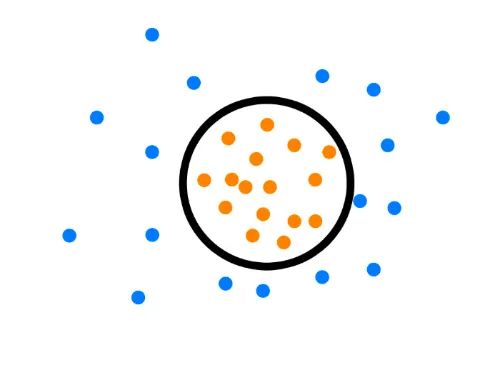
from sklearn import svm
# fit the model
clf = svm.OneClassSVM(nu=0.1, kernel='rbf', gamma=0.1)
clf.fit(X)
y_pred = clf.predict(X)
n_error_outlier = y_pred[y_pred == -1].size
八、基于預(yù)測的方法
[17] 【TS技術(shù)課堂】時(shí)間序列異常檢測 - 時(shí)序人,文章:https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s/9TimTB_ccPsme2MNPuy6uA
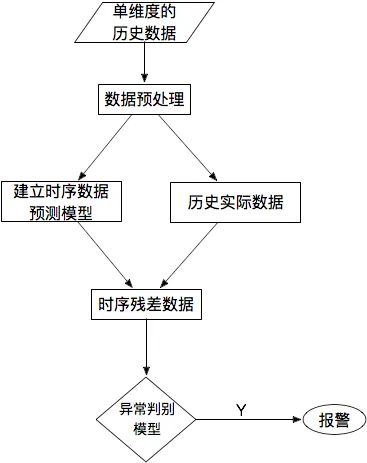
九、總結(jié)

參考資料
[1] 時(shí)序預(yù)測競賽之異常檢測算法綜述 - 魚遇雨欲語與余,知乎:https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/336944097
[2] 剔除異常值柵格計(jì)算器_數(shù)據(jù)分析師所需的統(tǒng)計(jì)學(xué):異常檢測 - weixin_39974030,CSDN:https://blog.csdn.net/weixin_39974030/article/details/112569610
[3] 異常檢測算法之(KNN)-K Nearest Neighbors - 小伍哥聊風(fēng)控,知乎:https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/501691799
[4] 一文讀懂異常檢測 LOF 算法(Python代碼)- 東哥起飛,知乎:https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/448276009
[5] Nowak-Brzezińska, A., & Horyń, C. (2020). Outliers in rules-the comparision of LOF, COF and KMEANS algorithms. *Procedia Computer Science*, *176*, 1420-1429.
[6] 機(jī)器學(xué)習(xí)_學(xué)習(xí)筆記系列(98):基於連接異常因子分析(Connectivity-Based Outlier Factor) - 劉智皓 (Chih-Hao Liu)
[7] 異常檢測之SOS算法 - 呼廣躍,知乎:https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/34438518
[8] 異常檢測算法 -- 孤立森林(Isolation Forest)剖析 - 風(fēng)控大魚,知乎:https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/74508141
[9] 孤立森林(isolation Forest)-一個(gè)通過瞎幾把亂分進(jìn)行異常檢測的算法 - 小伍哥聊風(fēng)控,知乎:https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/484495545
[10] 孤立森林閱讀 - Mark_Aussie,博文:https://blog.csdn.net/MarkAustralia/article/details/12018189
[11] 機(jī)器學(xué)習(xí)-異常檢測算法(三):Principal Component Analysis - 劉騰飛,知乎:https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/29091645
[12] Anomaly Detection異常檢測--PCA算法的實(shí)現(xiàn) - CC思SS,知乎:https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/48110105
[13] 利用Autoencoder進(jìn)行無監(jiān)督異常檢測(Python) - SofaSofa.io,知乎:https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/46188296
[14] 自編碼器AutoEncoder解決異常檢測問題(手把手寫代碼) - 數(shù)據(jù)如琥珀,知乎:https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/260882741
[15] Python機(jī)器學(xué)習(xí)筆記:One Class SVM - zoukankan,博文:http://t.zoukankan.com/wj-1314-p-10701708.html
[16] 單類SVM: SVDD - 張義策,知乎:https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/65617987[17] 【TS技術(shù)課堂】時(shí)間序列異常檢測 - 時(shí)序人,文章:https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s/9TimTB_ccPsme2MNPuy6uA
- EOF -
作者簡介
城哥,公眾號9年博主,一線互聯(lián)網(wǎng)工作10年(目前在職)、公司校招和社招技術(shù)面試官,主導(dǎo)多個(gè)公司級實(shí)戰(zhàn)項(xiàng)目(數(shù)據(jù)分析挖掘、算法、AI平臺建設(shè)等)。
關(guān)注我,陪你一起成長,遇見更好的自己。
星球服務(wù)
加入知識星球,可以享受7大福利與服務(wù):免費(fèi)獲取海量技術(shù)資料、向我 1 對 1 技術(shù)咨詢、求職指導(dǎo),簡歷優(yōu)化、歷史文章答疑(源碼+數(shù)據(jù))、綜合&專業(yè)技術(shù)交流社群、前沿技術(shù)分享(包含ChatGPT使用技巧)、定制專屬學(xué)習(xí)路線,幫你快速成長、告別迷茫。
原創(chuàng)不易,技術(shù)學(xué)習(xí)資料如下,星球成員可免費(fèi)獲取,非星球成員,添加城哥微信:dkl88191,請城哥喝杯星巴克。





