面試官問我:什么是 “伸展樹” ?

學(xué)過數(shù)據(jù)結(jié)構(gòu)的小伙伴,一定都知道二叉查找樹,也叫二叉排序樹,英文縮寫是BST。
為了維持二叉查找樹的高效率查找,就需要對二叉查找樹進(jìn)行平衡調(diào)整。在數(shù)據(jù)結(jié)構(gòu)當(dāng)中大名鼎鼎的紅黑樹、AVL,就是典型的自平衡二叉查找樹。
今天,我們來介紹一種更有意思的自平衡二叉樹:伸展樹。它的英文名字是Splay Tree。
Part 1 為什么要伸展
我們來回顧一下,二叉搜索樹滿足:
左子結(jié)點(diǎn) < 當(dāng)前結(jié)點(diǎn) < 右子結(jié)點(diǎn)
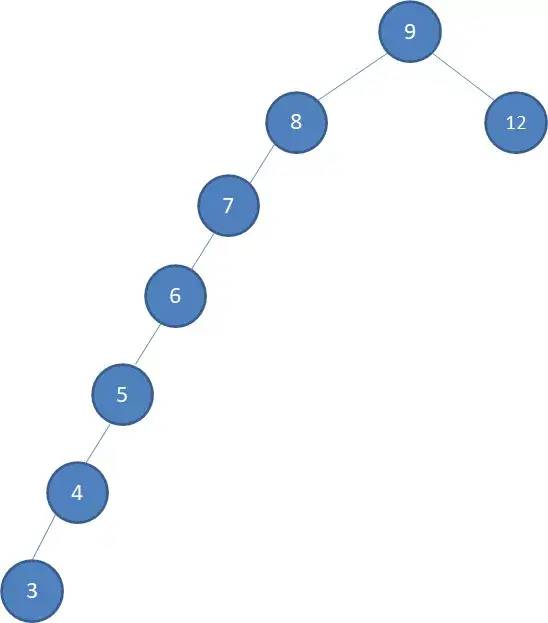
為什么要有平衡樹呢?因?yàn)楫?dāng)二叉搜索樹如下圖“瘸腿”時(shí),搜索左側(cè)的結(jié)點(diǎn),原來的速度 會(huì)掉到 ,與鏈表一個(gè)速度,失去了價(jià)值。為了避免樹瘸腿,我們可以通過適當(dāng)?shù)男D(zhuǎn)來調(diào)整樹的結(jié)構(gòu)。
伸展樹的核心,是通過不斷的將結(jié)點(diǎn)旋轉(zhuǎn)到根結(jié)點(diǎn)(即為splay操作),來保證整棵樹不會(huì)跟鏈表一樣。它由 Daniel Sleator 和 Robert Tarjan 發(fā)明 。
1.1 結(jié)點(diǎn)
node中記錄的信息:
parent:父結(jié)點(diǎn)的指針。child[0/1]:child[0]為左子結(jié)點(diǎn)的指針,child[1]為右子結(jié)點(diǎn)的指針。value:這個(gè)結(jié)點(diǎn)存了啥。count:二叉樹中不存在兩個(gè)值相同的結(jié)點(diǎn),如果需要記錄多個(gè)就需要一個(gè)變量來記錄這個(gè)數(shù)值出現(xiàn)了多少次。(count就是來干這個(gè)活的)size:這個(gè)結(jié)點(diǎn)為根結(jié)點(diǎn)的子樹中有多少個(gè)結(jié)點(diǎn)。
基礎(chǔ)操作:
maintain:更新結(jié)點(diǎn)的size。(更新要自底向上)get:獲取自己的類型,0為左子結(jié)點(diǎn),1為右子結(jié)點(diǎn)。connect: 連接兩個(gè)結(jié)點(diǎn)。
class node {
public:
node *parent; // 父結(jié)點(diǎn)的指針
node *child[2]; // child[0]為左子結(jié)點(diǎn)的指針,child[1]為右子結(jié)點(diǎn)的指針。
int value, count, size; // 數(shù)據(jù),出現(xiàn)次數(shù),子樹大小
node(int _value) {
value = _value;
parent = child[0] = child[1] = NULL;
count = size = 1;
}
};
我們把對指針是否為NULL提到了兩個(gè)基礎(chǔ)操作中,所以只能放在伸展樹的類中。
destroy:銷毀整個(gè)樹。因?yàn)榻Y(jié)點(diǎn)使用的是堆空間(new出來的),所以必須要銷毀(delete),否則會(huì)內(nèi)存泄漏。
class splayTree {
public:
node *root;
splayTree() {
root = NULL;
}
~splayTree() {
destroy(root); // 從root開始銷毀
}
void destroy(node *current) { // 銷毀結(jié)點(diǎn)
if (current) {
destroy(current->child[0]); // 后序遍歷
destroy(current->child[1]);
delete current;
}
}
void maintain(node *current) { // 更新size
if (current == NULL) { // 可能傳入的是一個(gè)空指針
return;
}
current->size = current->count; // 先將自己加上
if (current->child[0]) { // 防止沒兒子,NULL,報(bào)錯(cuò)
current->size += current->child[0]->size; // 加上兒子
}
if (current->child[1]) {
current->size += current->child[1]->size;
}
}
int get(node *current) { // 獲得結(jié)點(diǎn)是左結(jié)點(diǎn)還是右結(jié)點(diǎn),0左1右
if (current == NULL || current->parent == NULL) { // 傳入空指針;根結(jié)點(diǎn)沒有父親,特判一下
return -1;
}
return current->parent->child[1] == current; // 父親的右子結(jié)點(diǎn) 是不是 自己
}
void connect(node *parent, node *current, int type) { // 父結(jié)點(diǎn)指針,當(dāng)前結(jié)點(diǎn)指針,類型(0左1右)
if (parent) { // parent 可能為NULL
parent->child[type] = current;
}
if (current) { // current 也可能為NULL
current->parent = parent;
}
}
};
可能會(huì)有讀者好奇:這個(gè)size是用來干什么的呢?別急,等到查詢排名時(shí)就會(huì)用到。
1.2 左旋 & 右旋
通過旋轉(zhuǎn),我們能在保證旋轉(zhuǎn)可以保證左子結(jié)點(diǎn) < 當(dāng)前結(jié)點(diǎn) < 右子結(jié)點(diǎn)的情況下調(diào)整結(jié)點(diǎn)之間的關(guān)系。
旋轉(zhuǎn)有兩種定義:
對以x為根的子樹進(jìn)行旋轉(zhuǎn)。 把x向上旋轉(zhuǎn)。
1.2.1 以x為根的子樹進(jìn)行旋轉(zhuǎn)
1.2.2 把x向上旋轉(zhuǎn)
上面的動(dòng)畫使用文字?jǐn)⑹黾礊椋?/p>
左旋
將被旋轉(zhuǎn)結(jié)點(diǎn)的左結(jié)點(diǎn)變?yōu)楦附Y(jié)點(diǎn)的右結(jié)點(diǎn)。 父結(jié)點(diǎn)變?yōu)楸恍D(zhuǎn)結(jié)點(diǎn)的左子結(jié)點(diǎn) 原父結(jié)點(diǎn)的父結(jié)點(diǎn)(爺爺)變?yōu)楸恍D(zhuǎn)結(jié)點(diǎn)的父結(jié)點(diǎn)。 右旋
將被旋轉(zhuǎn)結(jié)點(diǎn)的右結(jié)點(diǎn)變?yōu)楦附Y(jié)點(diǎn)的左結(jié)點(diǎn)。 父結(jié)點(diǎn)變?yōu)楸恍D(zhuǎn)結(jié)點(diǎn)的右子結(jié)點(diǎn) 原父結(jié)點(diǎn)的父結(jié)點(diǎn)(爺爺)變?yōu)楸恍D(zhuǎn)結(jié)點(diǎn)的父結(jié)點(diǎn)。
雖然1、2兩種旋轉(zhuǎn)定義不同,但是只看移動(dòng)這分明就是一種嘛。
有細(xì)心的讀者發(fā)現(xiàn):左右旋的方式與AVL、紅黑樹等其他二叉樹相同。
因?yàn)檫@是唯一一種不改變中序遍歷的旋轉(zhuǎn)方式。
左旋與右旋都不會(huì)改變中序遍歷的結(jié)果,如上方動(dòng)圖,中序遍歷始終為1 y 2 x 3
除了舉例論證,你也可以這樣理解:
這是因?yàn)樽笮陀倚龝?huì)保證旋轉(zhuǎn)后的二叉樹
左子結(jié)點(diǎn) < 當(dāng)前結(jié)點(diǎn) < 右子結(jié)點(diǎn),因?yàn)樾D(zhuǎn)沒有插入或刪除結(jié)點(diǎn),所以二叉樹的中序遍歷沒變。
1.2.3 合并左右旋
想要合并左右旋,只能使用定義二:把x向上旋轉(zhuǎn)。(原因見下)
左旋和右旋雖然屬于兩種操作,但是細(xì)想想:
一個(gè)結(jié)點(diǎn)不是左子結(jié)點(diǎn),就是右子結(jié)點(diǎn)。因?yàn)槲覀円獙⒔Y(jié)點(diǎn)向上旋轉(zhuǎn),所以每一個(gè)結(jié)點(diǎn)(除了根結(jié)點(diǎn)),只能朝一個(gè)方向旋轉(zhuǎn),也就是父結(jié)點(diǎn)的方向。
所以可以將兩種操作整合為一種:
當(dāng)被旋轉(zhuǎn)的結(jié)點(diǎn)的類型為左子結(jié)點(diǎn)時(shí),進(jìn)行右旋。
當(dāng)被旋轉(zhuǎn)的結(jié)點(diǎn)的類型為右子結(jié)點(diǎn)時(shí),進(jìn)行左旋。
那么如何用一組代碼來表達(dá)兩種旋轉(zhuǎn)呢?
我們之前對child定義為數(shù)組,那么可以使用child[數(shù)值]來決定訪問的是左結(jié)點(diǎn)還是右結(jié)點(diǎn)。在內(nèi)嵌套get(...),可以得到與被旋轉(zhuǎn)結(jié)點(diǎn)類型相同的子結(jié)點(diǎn)。
如果get(...)得到的為0(左),怎樣讓其變成1(右),來訪問右結(jié)點(diǎn)呢?
這個(gè)問題等同于將get(...)取反。
x ^ 1可以將0變1,1變0。!x,疑似可以,但get(...)的返回值為int型,不建議使用!。
下面這個(gè)動(dòng)畫對應(yīng)左旋:
由于旋轉(zhuǎn)改變了父子關(guān)系,所以當(dāng)前結(jié)點(diǎn)與父結(jié)點(diǎn)的size會(huì)發(fā)生變化,需要重新更新。
旋轉(zhuǎn)之后,父親變?yōu)閮鹤樱砸?strong style="line-height: 1.75em;">先更新原父親(被旋轉(zhuǎn)結(jié)點(diǎn)在旋轉(zhuǎn)前的父結(jié)點(diǎn)),后更新原兒子(被旋轉(zhuǎn)結(jié)點(diǎn))。
代碼實(shí)現(xiàn),注釋中也藏了一些知識點(diǎn)(關(guān)于maintain的順序):
void rotate(node *current) {
if (current == root || current == NULL) { // 根結(jié)點(diǎn)沒有父結(jié)點(diǎn),旋轉(zhuǎn)不了;防止傳入空指針后報(bào)錯(cuò)
return;
}
node *parent = current->parent; // 爹爹
node *grandParent = parent->parent; // 爺爺,可能是NULL
int type = get(current); // 被旋轉(zhuǎn)結(jié)點(diǎn)的類型,0為右旋,1為左旋
int parentType = get(parent); // 爹爹的類型
connect(parent, current->child[type ^ 1], type); // 將三角形的結(jié)點(diǎn)掛到父結(jié)點(diǎn)
connect(current, parent, type ^ 1); // 兒子變父親
if (parent == root) { // 如果父結(jié)點(diǎn)為根結(jié)點(diǎn),需要將根結(jié)點(diǎn)指針更新
root = current;
}
connect(grandParent, current, parentType); // 爺爺認(rèn)孫子為兒子
maintain(parent); // 此時(shí)parent(父親)變?yōu)樽畹讓拥慕Y(jié)點(diǎn)了,對其先進(jìn)行更新
maintain(current); // parent結(jié)點(diǎn)更新之后,位于parent父親位置的current進(jìn)行更新
// 為啥不更新 grandParent 呢?是因?yàn)樾D(zhuǎn)是在 grandParent 以下的位置進(jìn)行的,子樹大小無變化。
}
下面的splay采用定義2,也就是上面的實(shí)現(xiàn)。
1.3 splay
splay名字很高大上,其實(shí)很簡單。splay其實(shí)就是將某一個(gè)結(jié)點(diǎn)經(jīng)過幾次旋轉(zhuǎn)后達(dá)到根結(jié)點(diǎn)位置。
當(dāng)前結(jié)點(diǎn)、父結(jié)點(diǎn)與爺爺結(jié)點(diǎn)的位置不同,向上旋轉(zhuǎn)的方式也不同。
前文,我們將左旋與右旋寫到了一起,使用的定義是把x向上旋轉(zhuǎn),此時(shí)
splay的邏輯如下:
當(dāng)前結(jié)點(diǎn)為x
如果x的父結(jié)點(diǎn)為根結(jié)點(diǎn),直接對x進(jìn)行旋轉(zhuǎn)。 如果父結(jié)點(diǎn)不是根結(jié)點(diǎn),且x與父結(jié)點(diǎn)的類型相同,對父結(jié)點(diǎn)進(jìn)行旋轉(zhuǎn)。 如果父結(jié)點(diǎn)不是根結(jié)點(diǎn),且x與父結(jié)點(diǎn)的類型不同,對x進(jìn)行旋轉(zhuǎn)。
void splay(node *current) {
if (current == NULL || current->parent == NULL) { // 根結(jié)點(diǎn)沒有父結(jié)點(diǎn),會(huì)形成死循環(huán);為current傳入NULL以防萬一
return;
}
while (current->parent->parent) { // 父結(jié)點(diǎn)不是根結(jié)點(diǎn)(是根結(jié)點(diǎn)的話get(current->parent)無法正常執(zhí)行)
if (get(current) == get(current->parent)) { // 類型相同
rotate(current->parent);
} else {
rotate(current);
}
}
rotate(current); // 父親為根結(jié)點(diǎn),旋轉(zhuǎn)自己篡位
}
1.4 查找
find(value)用于查找一個(gè)結(jié)點(diǎn),其數(shù)據(jù)與value相同。
由于平衡樹終究是在BST(二叉搜索樹)之上進(jìn)行變換,查找方式大體與BST相同:
如果 當(dāng)前結(jié)點(diǎn)的值小于要搜索的值:向右結(jié)點(diǎn)查找(右結(jié)點(diǎn)比當(dāng)前結(jié)點(diǎn)大)如果 當(dāng)前結(jié)點(diǎn)的值大于要搜索的值:向左結(jié)點(diǎn)查找(左結(jié)點(diǎn)比當(dāng)前結(jié)點(diǎn)小)如果兩個(gè)值相等:恭喜你,找到結(jié)點(diǎn)了。 其中,如果在向子結(jié)點(diǎn)查找時(shí),發(fā)現(xiàn)子結(jié)點(diǎn)為空,那么必然找不到結(jié)點(diǎn)了。(1、2都是對目標(biāo)值進(jìn)行逼近,不存在結(jié)點(diǎn)存在只是沒有被搜索的情況)
可是伸展樹有一個(gè)特性:在每執(zhí)行完一次操作(查找、插入、刪除等等)后都要對結(jié)點(diǎn)進(jìn)行splay
在查找這種操作中,被查找的結(jié)點(diǎn)需要在查找到后進(jìn)行splay
node* find(int value) {
node *current = root; // 從根結(jié)點(diǎn)開始搜索
while (current) {
if (current->value < value) {
current = current->child[1]; // 小了,往大了走
} else if (current ->value > value) {
current = current->child[0]; // 大了,往小了走
} else { // 不大也不小不就是找到了嗎?
splay(current);
return current;
}
}
return NULL; // 找不到結(jié)點(diǎn),退出。(找到得到結(jié)點(diǎn)的話會(huì)在while循環(huán)就退出)
}
1.5 查詢排名
rank(value),值為value的結(jié)點(diǎn)的排名,為這個(gè)結(jié)點(diǎn)在中序遍歷中排第幾位。
雖然排名為中序遍歷的排名,但是我們并不需要對整個(gè)樹進(jìn)行中序遍歷。
排名可以看做:結(jié)點(diǎn)左面的結(jié)點(diǎn)個(gè)數(shù) + 1(這個(gè)1對應(yīng)它自己)由于我們事先不知道值
value對應(yīng)哪一個(gè)結(jié)點(diǎn),所以我們需要將上文的find整合進(jìn)來。
維護(hù)一個(gè)變量leftSize,用于記錄結(jié)點(diǎn)左側(cè)共多少個(gè)結(jié)點(diǎn),
如果當(dāng)前結(jié)點(diǎn)的值大于要搜索的值:向左結(jié)點(diǎn)查找(左邊沒有結(jié)點(diǎn), leftSize不改變)這個(gè)時(shí)候果斷將 leftSize += 左子樹大小,因?yàn)槟繕?biāo)結(jié)點(diǎn)不是在當(dāng)前結(jié)點(diǎn)就是在右結(jié)點(diǎn),這兩種情況都約過了左子樹。
如果兩個(gè)值相等,那么就是找到了,將leftSize += 1,對找到的結(jié)點(diǎn)進(jìn)行splay,返回leftSize。(+ 1是自己的)2沒有返回目標(biāo)結(jié)點(diǎn)必然在右子樹, leftSize += 當(dāng)前結(jié)點(diǎn)的count向右結(jié)點(diǎn)查找吧。
int rankOfNode(int value) {
// 這里傳入的value為被查詢排名的結(jié)點(diǎn)的value
node *current = root; // 從根結(jié)點(diǎn)開始搜索
int leftSize = 0; // 左側(cè)的所有結(jié)點(diǎn)總和
while (current) {
if (value < current->value) { // 目標(biāo)結(jié)點(diǎn)小于當(dāng)前結(jié)點(diǎn),向左走
current = current->child[0];
} else {
// 無論是目標(biāo)結(jié)點(diǎn)為當(dāng)前結(jié)點(diǎn),還是在右子樹,都跨過了左子樹
if (current->child[0]) { // 可能沒有左子樹
leftSize += current->child[0]->size;
}
if (value == current->value) {
leftSize += 1; // 加上自己的。你就想最左邊結(jié)點(diǎn)leftSize = 0,可是排名是1
splay(current);
return leftSize;
}
// 找到結(jié)點(diǎn)的話會(huì)return,所以這里必然是目標(biāo)結(jié)點(diǎn)大,向右走
leftSize += current->count; // 把當(dāng)前結(jié)點(diǎn)越過,加上
current = current->child[1]; // 這個(gè)current變到右子結(jié)點(diǎn)是必須放在最后的,否則前面會(huì)亂
}
}
return -1; // 找不到結(jié)點(diǎn),輸出-1
}
1.6 查詢排名為rank的結(jié)點(diǎn)
當(dāng)我們知道了排名,怎樣找對應(yīng)的結(jié)點(diǎn)呢?
勘誤:動(dòng)畫中判斷應(yīng)為
rank <= 0,而非rank == 0。由于例子中所有結(jié)點(diǎn)的count都為1,所以表面看來沒有問題。
我們設(shè) 以當(dāng)前結(jié)點(diǎn)為根結(jié)點(diǎn)的樹中,需要查詢排名為
rank。1.如果
rank > 左子樹的size:
那么目標(biāo)結(jié)點(diǎn)只能存在于當(dāng)前結(jié)點(diǎn)與右子樹之間。我們對 rank -= 左子樹的size + 當(dāng)前結(jié)點(diǎn)的count。
如果此時(shí) rank <= 0,那么目標(biāo)結(jié)點(diǎn)就在根結(jié)點(diǎn)。(一個(gè)極端例子,第一個(gè)結(jié)點(diǎn)的count為999,1 ~ 999都對應(yīng)了這一個(gè)結(jié)點(diǎn),rank -= count就會(huì)出現(xiàn)負(fù)數(shù))如果此時(shí) rank > 0,那么目標(biāo)結(jié)點(diǎn)還在右結(jié)點(diǎn),把當(dāng)前結(jié)點(diǎn)設(shè)置為右結(jié)點(diǎn),整個(gè)過程再來一遍。2.如果
rank <= 左子樹的size:
那么目標(biāo)結(jié)點(diǎn)肯定藏匿于左子樹,將目標(biāo)結(jié)點(diǎn)設(shè)置為左結(jié)點(diǎn),再來一遍。 向右走,越過了左子樹的所有結(jié)點(diǎn)與當(dāng)前結(jié)點(diǎn),所以要對
rank減越過的結(jié)點(diǎn)。
向左走,越過了空氣什么也沒有越過,故rank不動(dòng)。
因?yàn)?code style="font-size: 14px;overflow-wrap: break-word;padding: 2px 4px;border-radius: 4px;margin-right: 2px;margin-left: 2px;background-color: rgba(27, 31, 35, 0.05);font-family: "Operator Mono", Consolas, Monaco, Menlo, monospace;word-break: break-all;color: rgb(60, 112, 198);">rank在做完減法后就會(huì)判斷是否為小于0,小于0就退出了。所以其余時(shí)間里
rank > 0。
node* nodeOfRank(int rank) {
node *current = root; // 從根結(jié)點(diǎn)查找
while (current) {
if ((current->child[0] && rank > current->child[0]->size) || current->child[0] == NULL) {
// 1. 左子樹存在,rank > 且左子樹大小
// 2. 左子樹不存在,大小可看做0。因?yàn)閞ank > 0,所以無需判斷可知 rank > 左子樹大小。
if (current->child[0]) {
rank -= current->child[0]->size;
}
rank -= current->count;
if (rank <= 0) {
splay(current);
return current;
}
current = current->child[1]; // 不是在左子樹、當(dāng)前結(jié)點(diǎn),就是在右子樹唄
} else {
current = current->child[0]; // 目標(biāo)結(jié)點(diǎn)在左子樹
}
}
return NULL;
}
1.7 前趨后繼
前趨pre:比查詢結(jié)點(diǎn)小的最大結(jié)點(diǎn)。
后繼next:比查詢結(jié)點(diǎn)大的最小結(jié)點(diǎn)。
由于結(jié)點(diǎn)的左子樹任意一個(gè)結(jié)點(diǎn)都比當(dāng)前結(jié)點(diǎn)小,在左子樹中取最大的結(jié)點(diǎn)即為前趨。
后繼同理,右子樹任意一個(gè)結(jié)點(diǎn)都比當(dāng)前結(jié)點(diǎn)大,在右子樹中取最小的結(jié)點(diǎn)即為后繼。
取最大值最小值與BST相同:
最大:找樹的最右側(cè)結(jié)點(diǎn)。(右 > 中 > 左)
最小:找樹的最左側(cè)結(jié)點(diǎn)。(左 < 中 < 右)
node* preNext(int type, node *current) { // 0為前趨,1為后繼
if (current == NULL) {
return NULL;
}
splay(current);
current = current->child[type]; // 如果current沒有左結(jié)點(diǎn),那么current會(huì)變?yōu)镹ULL
while (current && current->child[type ^ 1]) { // current->child[1]用來避免current為NULL
current = current->child[type ^ 1];
}
splay(current);
return current;
}
1.8 插入
插入有三種情況:
整棵樹是空的, root為NULL,這種情況下我們直接將結(jié)點(diǎn)放在root的位置即可。在樹的已有結(jié)點(diǎn)中存在新插入的值,由于二叉搜索樹中不能出現(xiàn)兩個(gè)值一樣的結(jié)點(diǎn),所以對已有的結(jié)點(diǎn)的 count加1即可。樹中沒有這個(gè)新插入的值,那么我們需要找到合適的位置,在插入后進(jìn)行 splay
第三種情況:
像 find的過程一樣,當(dāng)前結(jié)點(diǎn)小于插入值向右子樹查找,當(dāng)前結(jié)點(diǎn)大于插入值向左查找(等于就屬于第二種情況了),直到當(dāng)前結(jié)點(diǎn)為NULL,找到一個(gè)空位置。(這里我們需要記錄當(dāng)前結(jié)點(diǎn)的parent,因?yàn)镹ULL結(jié)點(diǎn)是記錄不了信息的)連接 NULL位置的父結(jié)點(diǎn) 與 插入的結(jié)點(diǎn)。 splay插入結(jié)點(diǎn)。
node* insert(int value) {
if (root == NULL) {
root = new node(value);
return root;
}
node *current = root;
node *parent = current->parent;
int type; // 類型
while (current) { // 和查找一模一樣
if (current->value < value) {
parent = current;
current = current->child[1];
type = 1;
} else if (current->value > value) {
parent = current;
current = current->child[0];
type = 0;
} else { // 已經(jīng)有相同結(jié)點(diǎn)了,將其count++即可。
current->count ++;
splay(current);
return current;
}
}
current = new node(value);
connect(parent, current, type);
splay(current);
return current;
}
1.9 合并兩棵樹
合并兩棵樹,我們設(shè)它們的根結(jié)點(diǎn)分別為x和y。
要使兩棵樹能夠合并,x中的最大值要小于y中的最小值。
合并過程:
x或y有一個(gè)樹是空的,返回不是空的那個(gè)。x和y均不為空。splayx中的最大值。此時(shí) x的根結(jié)點(diǎn)的右子樹為空,將y作為x的右子樹(因?yàn)?code style="font-size: 14px;overflow-wrap: break-word;padding: 2px 4px;border-radius: 4px;margin-right: 2px;margin-left: 2px;background-color: rgba(27, 31, 35, 0.05);font-family: "Operator Mono", Consolas, Monaco, Menlo, monospace;word-break: break-all;color: rgb(60, 112, 198);">右 > 中 > 左,x的最大值還在根結(jié)點(diǎn),沒有比最大值還有大的了,所有右側(cè)沒有結(jié)點(diǎn))
合并操作需要在刪除中遇到,動(dòng)畫與實(shí)現(xiàn)均在刪除中。
1.10 刪除
刪除過程:
我們首先將被刪除的結(jié)點(diǎn)進(jìn)行 splay。銷毀被刪除結(jié)點(diǎn),與左右子樹斷開聯(lián)系。 合并兩棵樹(右合并到左)
// 求以current為根的樹的最大與最小值
node* minMax(int type, node *current) { // type == 0為min,type == 1為max
while (current->child[type]) {
current = current->child[type];
}
splay(current);
return current;
}
void remove(node *current) {
splay(current);
if (current->count >= 2) {
current->count --;
return;
}
node *left = current->child[0];
node *right = current->child[1];
if (left) {
left->parent = NULL;
}
if (right) {
right->parent = NULL;
}
delete current;
if (left && right) { // 兩個(gè)都有
left = minMax(1, left); // 求最大值最小值時(shí)默認(rèn)進(jìn)行了splay
right = minMax(0, right);
connect(left, right, 1);
root = left;
} else {
if (left) { // 只有左結(jié)點(diǎn)
root = left;
} else { // 只有右結(jié)點(diǎn),或者兩個(gè)都沒有。兩個(gè)都沒有right為NULL,root就變成NULL了
root = right;
}
}
}
1.11 代碼
LOJ上的普通平衡樹[2]
我們上述的幾種操作個(gè)個(gè)對應(yīng)題目需要。但是當(dāng)我們仔細(xì)讀題:
求 的前趨(前趨定義為小于 ,且最大的數(shù));
求 的后繼(后繼定義為大于 ,且最小的數(shù))。
本文中的前趨后繼為結(jié)點(diǎn)的前一個(gè)與后一個(gè),而題目中 可能不存在,怎么辦呢?
簡單!將x插入到樹中,進(jìn)行查詢,隨后再刪除不就行了嗎?
完整代碼如下,LOJ中不開優(yōu)化測評記錄[3]:
//
// Created by Cat-shao on 2021/5/8.
//
#include <cstdio>
#include <algorithm>
#include <deque>
using namespace std;
class splayTree {
public:
class node {
public:
node *parent; // 父結(jié)點(diǎn)的指針
node *child[2]; // child[0]為左子結(jié)點(diǎn)的指針,child[1]為右子結(jié)點(diǎn)的指針。
int value, count, size; // 數(shù)據(jù),出現(xiàn)次數(shù),子樹大小
node(int _value) {
value = _value;
parent = child[0] = child[1] = NULL;
count = size = 1;
}
};
node *root;
splayTree() {
root = NULL;
}
~splayTree() {
destroy(root);
}
void destroy(node *current) {
if (current) {
destroy(current->child[0]);
destroy(current->child[1]);
delete current;
}
}
void maintain(node *current) { // 更新size
if (current == NULL) { // 可能傳入的是一個(gè)空指針
return;
}
current->size = current->count; // 先將自己加上
if (current->child[0]) { // 防止沒兒子,NULL,報(bào)錯(cuò)
current->size += current->child[0]->size; // 加上兒子
}
if (current->child[1]) {
current->size += current->child[1]->size;
}
}
int get(node *current) { // 獲得結(jié)點(diǎn)是左結(jié)點(diǎn)還是右結(jié)點(diǎn),0左1右
if (current == NULL || current->parent == NULL) { // 傳入空指針;根結(jié)點(diǎn)沒有父親,特判一下
return -1;
}
return current->parent->child[1] == current; // 父親的右子結(jié)點(diǎn) 是不是 自己
}
void connect(node *parent, node *current, int type) { // 父結(jié)點(diǎn)指針,當(dāng)前結(jié)點(diǎn)指針,類型(0左1右)
if (parent) { // parent 可能為NULL
parent->child[type] = current;
}
if (current) { // current 也可能為NULL
current->parent = parent;
}
}
void rotate(node *current) {
if (current == root || current == NULL) { // 根結(jié)點(diǎn)沒有父結(jié)點(diǎn),旋轉(zhuǎn)不了;防止傳入空指針后報(bào)錯(cuò)
return;
}
node *parent = current->parent; // 爹爹
node *grandParent = parent->parent; // 爺爺,可能是NULL
int type = get(current); // 被旋轉(zhuǎn)結(jié)點(diǎn)的類型,0為右旋,1為左旋
int parentType = get(parent); // 爹爹的類型
connect(parent, current->child[type ^ 1], type); // 將三角形的結(jié)點(diǎn)掛到父結(jié)點(diǎn)
connect(current, parent, type ^ 1); // 兒子變父親
if (parent == root) { // 如果父結(jié)點(diǎn)為根結(jié)點(diǎn),需要將根結(jié)點(diǎn)指針更新
root = current;
}
connect(grandParent, current, parentType); // 爺爺認(rèn)孫子為兒子
maintain(parent); // 此時(shí)parent(父親)變?yōu)樽畹讓拥慕Y(jié)點(diǎn)了,對其先進(jìn)行更新
maintain(current); // parent結(jié)點(diǎn)更新之后,位于parent父親位置的current進(jìn)行更新
// 為啥不更新 grandParent 呢?是因?yàn)樾D(zhuǎn)是在 grandParent 以下的位置進(jìn)行的,子樹大小無變化。
}
void splay(node *current) {
if (current == NULL || current->parent == NULL) { // 根結(jié)點(diǎn)沒有父結(jié)點(diǎn),會(huì)形成死循環(huán);為current傳入NULL以防萬一
return;
}
while (current->parent->parent) { // 父結(jié)點(diǎn)不是根結(jié)點(diǎn)(是根結(jié)點(diǎn)的話get(current->parent)無法正常執(zhí)行)
if (get(current) == get(current->parent)) { // 類型相同
rotate(current->parent);
} else {
rotate(current);
}
}
rotate(current); // 父親為根結(jié)點(diǎn),旋轉(zhuǎn)自己篡位
}
node* find(int value) {
node *current = root; // 從根結(jié)點(diǎn)開始搜索
while (current) {
if (current->value < value) {
current = current->child[1]; // 小了,往大了走
} else if (current->value > value) {
current = current->child[0]; // 大了,往小了走
} else { // 不大也不小不就是找到了嗎?
splay(current);
return current;
}
}
return NULL; // 找不到結(jié)點(diǎn),退出。(找到得到結(jié)點(diǎn)的話會(huì)在while循環(huán)就退出)
}
int rankOfNode(int value) {
// 這里傳入的value為被查詢排名的結(jié)點(diǎn)的value
node *current = root; // 從根結(jié)點(diǎn)開始搜索
int leftSize = 0; // 左側(cè)的所有結(jié)點(diǎn)總和
while (current) {
if (value < current->value) { // 目標(biāo)結(jié)點(diǎn)小于當(dāng)前結(jié)點(diǎn),向左走
current = current->child[0];
} else {
// 無論是目標(biāo)結(jié)點(diǎn)為當(dāng)前結(jié)點(diǎn),還是在右子樹,都跨過了左子樹
if (current->child[0]) { // 可能沒有左子樹
leftSize += current->child[0]->size;
}
if (value == current->value) {
leftSize += 1; // 加上自己的。你就想最左邊結(jié)點(diǎn)leftSize = 0,可是排名是1
splay(current);
return leftSize;
}
// 找到結(jié)點(diǎn)的話會(huì)return,所以這里必然是目標(biāo)結(jié)點(diǎn)大,向右走
leftSize += current->count; // 把當(dāng)前結(jié)點(diǎn)越過,加上
current = current->child[1]; // 這個(gè)current變到右子結(jié)點(diǎn)是必須放在最后的,否則前面會(huì)亂
}
}
return -1; // 找不到結(jié)點(diǎn),輸出-1
}
node* nodeOfRank(int rank) {
node *current = root; // 從根結(jié)點(diǎn)查找
while (current) {
if ((current->child[0] && rank > current->child[0]->size) || current->child[0] == NULL) {
// 1. 左子樹存在,rank > 且左子樹大小
// 2. 左子樹不存在,大小可看做0。因?yàn)閞ank > 0,所以無需判斷可知 rank > 左子樹大小。
if (current->child[0]) {
rank -= current->child[0]->size;
}
rank -= current->count;
if (rank <= 0) {
splay(current);
return current;
}
current = current->child[1]; // 不是在左子樹、當(dāng)前結(jié)點(diǎn),就是在右子樹唄
} else {
current = current->child[0]; // 目標(biāo)結(jié)點(diǎn)在左子樹
}
}
return NULL;
}
node* preNext(int type, node *current) { // 0為前趨,1為后繼
if (current == NULL) {
return NULL;
}
splay(current);
current = current->child[type]; // 如果current沒有左結(jié)點(diǎn),那么current會(huì)變?yōu)镹ULL
while (current && current->child[type ^ 1]) { // current->child[1]用來避免current為NULL
current = current->child[type ^ 1];
}
splay(current);
return current;
}
node* insert(int value) {
if (root == NULL) {
root = new node(value);
return root;
}
node *current = root;
node *parent = current->parent;
int type; // 類型
while (current) { // 和查找一模一樣
if (current->value < value) {
parent = current;
current = current->child[1];
type = 1;
} else if (current->value > value) {
parent = current;
current = current->child[0];
type = 0;
} else { // 已經(jīng)有相同結(jié)點(diǎn)了,將其count++即可。
current->count ++;
splay(current);
return current;
}
}
current = new node(value);
connect(parent, current, type);
splay(current);
return current;
}
node* minMax(int type, node *current) { // type == 0為min,type == 1為max
while (current->child[type]) {
current = current->child[type];
}
splay(current);
return current;
}
void remove(node *current) {
splay(current);
if (current->count >= 2) {
current->count --;
return;
}
node *left = current->child[0];
node *right = current->child[1];
if (left) {
left->parent = NULL;
}
if (right) {
right->parent = NULL;
}
delete current;
if (left && right) { // 兩個(gè)都有
left = minMax(1, left); // 求最大值最小值時(shí)默認(rèn)進(jìn)行了splay
right = minMax(0, right);
connect(left, right, 1);
root = left;
} else {
if (left) { // 只有左節(jié)點(diǎn)
root = left;
} else { // 只有右節(jié)點(diǎn),或者兩個(gè)都沒有。兩個(gè)都沒有right為NULL,root就變成NULL了
root = right;
}
}
}
};
void LOJ104()
{
int n, opt, x;
splayTree tree = splayTree();
scanf("%d", &n);
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
scanf("%d%d", &opt, &x);
switch (opt) {
case 1: tree.insert(x); break;
case 2: tree.remove(tree.find(x)); break;
case 3: printf("%d\n", tree.rankOfNode(x)); break;
case 4: printf("%d\n", tree.nodeOfRank(x)->value); break;
case 5:
tree.insert(x);
printf("%d\n", tree.preNext(0, tree.find(x))->value);
tree.remove(tree.find(x));
break;
case 6:
tree.insert(x);
printf("%d\n", tree.preNext(1, tree.find(x))->value);
tree.remove(tree.find(x));
break;
}
}
}
int main()
{
LOJ104();
}
1.12 時(shí)間復(fù)雜度
伸展樹可視化[4](需要將網(wǎng)址復(fù)制到瀏覽器中,網(wǎng)址見頁腳)
在學(xué)完了伸展樹的基礎(chǔ)操作之后,我們發(fā)現(xiàn)主要是splay來維護(hù)整個(gè)二叉樹平衡,然而splay后的樹并不平衡。
伸展樹的時(shí)間復(fù)雜度是均攤的 ,Tarjan是怎么將這個(gè)復(fù)雜度算出來的呢?
你百度一下,就會(huì)看見很多人使用了勢函數(shù)來證明。
身為一個(gè)蒟蒻,我無法證明。可是,經(jīng)過測試,伸展樹與其他平衡樹的速度大同小異。
1.13 與其他平衡樹比較
| 紅黑樹 | AVL | fhq treap | splay(伸展樹) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 速度最快 | 最平衡,查找最快 | 代碼最好打 | ? |
這么看伸展樹就一打醬油的,那這個(gè)東西到底有什么意義呢?
伸展樹的優(yōu)勢在于操作多
欲知后事如何,且聽下回分解!
參考與鳴謝
OI Wiki[5]:OIer的算法wiki,知識點(diǎn)全面但是小白看不懂,大家可以收藏。 KHIN[6]:問了KH很多問題,受益頗多。 manim幼兒園[7]:本文所有的動(dòng)畫皆為manim所做,manim幼兒園的視頻教程十分詳細(xì)。
伸展樹算法偏難,你若有什么問題,歡迎回復(fù),或者在LOJ的討論[8]中發(fā)出你的觀點(diǎn)。
討論中可能會(huì)跟進(jìn)一些內(nèi)容(如前趨后繼的更好實(shí)現(xiàn)、勘誤)。
參考資料
splay tree demo: https://www.link.cs.cmu.edu/splay/
[2]LOJ上的普通平衡樹: https://loj.ac/p/104
[3]LOJ中不開優(yōu)化測評記錄: https://loj.ac/s/1141137
[4]伸展樹可視化: https://www.cs.usfca.edu/~galles/visualization/SplayTree.html
[5]OI Wiki: https://oi-wiki.org/ds/splay/#_11
[6]KHIN: https://www.luogu.com.cn/user/236807
[7]manim幼兒園: https://manim.wiki/
[8]LOJ的討論: https://loj.ac/d/3181