垃圾郵件識別:用機器學(xué)習(xí)做中文郵件內(nèi)容分類
隨著微信的迅速發(fā)展,工作和生活中的交流也更多依賴于此,但是由于郵件的正式性和規(guī)范性,其仍然不可被取代。但是不管是企業(yè)內(nèi)部工作郵箱,還是個人郵箱,總是收到各種各樣的垃圾郵件,包括商家的廣告、打折促銷信息、澳門博彩郵件、理財推廣信息等等,不管如何進行垃圾郵件分類,總有漏網(wǎng)之魚。最重要的是,不同用戶對于垃圾郵件的定義并不一致。
而且大部分用戶網(wǎng)絡(luò)安全意識比較一般,萬一誤點垃圾郵件上鉤,或者因為垃圾郵件淹沒了工作中的關(guān)鍵信件,則會給個人或者企業(yè)造成損失。
垃圾郵件識別一直以來都是痛點難點,雖然方法無非是基于貝葉斯學(xué)習(xí)或者是概率統(tǒng)計還是深度學(xué)習(xí)的方法,但是由于業(yè)務(wù)場景的多樣化,垃圾郵件花樣實在太多了,所以傳統(tǒng)垃圾郵件攔截器總是有點跟不上。
因此打算針對同一數(shù)據(jù)集,逐步嘗試各種方法,來進行垃圾郵件的識別分類——希望假以時日,這種定制化的垃圾郵件識別工具能大幅提升用戶的郵箱使用體驗。
一、整體思路總的來說,一封郵件可以分為發(fā)送人、接收人、抄送人、主題、時間、內(nèi)容等要素,所以很自然的可以認(rèn)為主要通過上述要素中的發(fā)送方、主題以及內(nèi)容來進行垃圾郵件判斷。
因此我們依次對上述要素進行分析:
垃圾郵件內(nèi)容分類(通過提取垃圾郵件內(nèi)容進行判斷)
- 中文垃圾郵件分類- 英文垃圾郵件分類 最終,我們可以根據(jù)這三個維度進行綜合評判,從而實現(xiàn)垃圾郵件的準(zhǔn)確分類。本文將根據(jù)**郵件內(nèi)容**進行垃圾郵件分類。
1.數(shù)據(jù)集介紹
首先我們選擇這一個公開的垃圾郵件語料庫。該語料庫由國際文本檢索會議提供,分為英文數(shù)據(jù)集(trec06p)和中文數(shù)據(jù)集(trec06c),其中所含的郵件均來源于真實郵件保留了郵件的原有格式和內(nèi)容。
文件目錄形式:delay和full分別是一種垃圾郵件過濾器的過濾機制,full目錄下,是理想的郵件分類結(jié)果,我們可以視為研究的標(biāo)簽。
trec06c │ └───data │ ? │ ? 000 │ ? │ ? 001 │ ? │ ? ... │ ? └───215 └───delay │ ? │ ? index └───full │ ? │ ? index
2.數(shù)據(jù)加載
2.1 從eml格式中提取郵件要素并且存儲成csv
由于目前數(shù)據(jù)集是存儲成郵件的形式,并且通過索引進行垃圾郵件標(biāo)注,所以我們先提取每一封郵件的發(fā)件人、收件人、抄送人、主題、發(fā)送時間、內(nèi)容以及是否垃圾郵件標(biāo)簽。
mailTable=pd.DataFrame(columns=('Sender','Receiver','CarbonCopy','Subject','Date','Body','isSpam'))
#?path='trec06p/full/../data/000/004'
#?emlContent=?emlAnayalyse(path)
#?print(emlContent)
f?=?open('trec06c/full/index',?'r')
csvfile=open('mailChinese.csv','w',newline='',encoding='utf-8')
writer=csv.writer(csvfile)
for?line?in?f:
????str_list?=?line.split("?")
????print(str_list[1])
????#?設(shè)置垃圾郵件的標(biāo)簽為0
????if?str_list[0]?==?'spam':
????????label?=?'0'
????#?設(shè)置正常郵件標(biāo)簽為1
????elif?str_list[0]?==?'ham':
????????label?=?'1'
????emlContent=?emlAnayalyse('trec06c/full/'?+?str(str_list[1].split("\n")[0]))
????if?emlContent?is?not?None:
????????writer.writerow([emlContent[0],emlContent[1],emlContent[2],emlContent[3],emlContent[4],emlContent[5],label])
其中emlAnayalyze函數(shù)利用flanker庫中的mime,可以將郵件中的發(fā)件人、收件人、抄送人、主題、發(fā)送時間、內(nèi)容等要素提取出來,具體可以參考我的這篇文章,然后存成csv,方便后續(xù)郵件分析。
2.2 從csv中提取郵件內(nèi)容進行分類
def?get_data(path):
????'''
????獲取數(shù)據(jù)
????:return:?文本數(shù)據(jù),對應(yīng)的labels
????'''
????maildf?=?pd.read_csv(path,header=None,?names=['Sender','Receiver','“CarbonCopy','Subject','Date','Body','isSpam'])
????filteredmaildf=maildf[maildf['Body'].notnull()]
????corpus=filteredmaildf['Body']
????
????labels=filteredmaildf['isSpam']
????corpus=list(corpus)
????labels=list(labels)
????return?corpus,?labels
通過get_data函數(shù)讀取csv格式數(shù)據(jù),并且提取出內(nèi)容不為空的數(shù)據(jù),和對應(yīng)的標(biāo)簽。
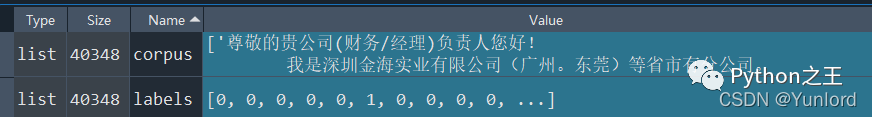
可以看到一共有40348個數(shù)據(jù)。
from?sklearn.model_selection?import?train_test_split
#?對數(shù)據(jù)進行劃分
train_corpus,?test_corpus,?train_labels,?test_labels?=?train_test_split(corpus,?labels,
??????????????????????????????????????????????????test_size=0.3,?random_state=0)
然后通過 sklearn.model_selection庫中的train_test_split函數(shù)劃分訓(xùn)練集、驗證集。
#?進行歸一化
norm_train_corpus?=?normalize_corpus(train_corpus)
norm_test_corpus?=?normalize_corpus(test_corpus)
然后通過normalize_corpus函數(shù)對數(shù)據(jù)進行預(yù)處理。
def?textParse(text):
????listOfTokens=jieba.lcut(text)
????newList=[re.sub(r'\W*','',s)?for?s?in?listOfTokens]
????filtered_text=[tok?for?tok?in?newList?if?len(tok)>0]
????return?filtered_text
def?remove_stopwords(tokens):
????filtered_tokens?=?[token?for?token?in?tokens?if?token?not?in?stopword_list]
????filtered_text?=?'?'.join(filtered_tokens)
????return?filtered_text
def?normalize_corpus(corpus,?tokenize=False):
????normalized_corpus?=?[]
????for?text?in?corpus:
????????filtered_text?=?textParse(filtered_text)
????????filtered_text?=?remove_stopwords(filtered_text)
????????
????????normalized_corpus.append(filtered_text)
????return?normalized_corpus
里面包括textParse、remove_stopwords這兩個數(shù)據(jù)預(yù)處理操作。
textParse函數(shù)先通過jieba進行分詞,然后去除無用字符。
remove_stopwords函數(shù)先是加載stop_words.txt停用詞表,然后去除停用詞。
從而實現(xiàn)數(shù)據(jù)預(yù)處理。
2.3?構(gòu)建詞向量
#?詞袋模型特征
bow_vectorizer,?bow_train_features?=?bow_extractor(norm_train_corpus)
bow_test_features?=?bow_vectorizer.transform(norm_test_corpus)
#?tfidf?特征
tfidf_vectorizer,?tfidf_train_features?=?tfidf_extractor(norm_train_corpus)
tfidf_test_features?=?tfidf_vectorizer.transform(norm_test_corpus)
其中bow_extractor,tfidf_extractor兩個函數(shù)分別將訓(xùn)練集轉(zhuǎn)化為詞袋模型特征和tfidf特征。
from?sklearn.feature_extraction.text?import?CountVectorizer
def?bow_extractor(corpus,?ngram_range=(1,?1)):
????vectorizer?=?CountVectorizer(min_df=1,?ngram_range=ngram_range)
????features?=?vectorizer.fit_transform(corpus)
????return?vectorizer,?features
from?sklearn.feature_extraction.text?import?TfidfTransformer
def?tfidf_transformer(bow_matrix):
????transformer?=?TfidfTransformer(norm='l2',
???????????????????????????????????smooth_idf=True,
???????????????????????????????????use_idf=True)
????tfidf_matrix?=?transformer.fit_transform(bow_matrix)
????return?transformer,?tfidf_matrix
from?sklearn.feature_extraction.text?import?TfidfVectorizer
def?tfidf_extractor(corpus,?ngram_range=(1,?1)):
????vectorizer?=?TfidfVectorizer(min_df=1,
?????????????????????????????????norm='l2',
?????????????????????????????????smooth_idf=True,
?????????????????????????????????use_idf=True,
?????????????????????????????????ngram_range=ngram_range)
????features?=?vectorizer.fit_transform(corpus)
????return?vectorizer,?features
2.4 訓(xùn)練模型以及評估
對如上兩種不同的向量表示法,分別訓(xùn)練貝葉斯分類器、邏輯回歸分類器、支持向量機分類器,從而驗證效果。
from?sklearn.naive_bayes?import?MultinomialNB
from?sklearn.linear_model?import?SGDClassifier
from?sklearn.linear_model?import?LogisticRegression
mnb?=?MultinomialNB()
svm?=?SGDClassifier(loss='hinge',?n_iter_no_change=100)
lr?=?LogisticRegression()
#?基于詞袋模型的多項樸素貝葉斯
print("基于詞袋模型特征的貝葉斯分類器")
mnb_bow_predictions?=?train_predict_evaluate_model(classifier=mnb,
???????????????????????????????????????????????????train_features=bow_train_features,
???????????????????????????????????????????????????train_labels=train_labels,
???????????????????????????????????????????????????test_features=bow_test_features,
???????????????????????????????????????????????????test_labels=test_labels)
#?基于詞袋模型特征的邏輯回歸
print("基于詞袋模型特征的邏輯回歸")
lr_bow_predictions?=?train_predict_evaluate_model(classifier=lr,
??????????????????????????????????????????????????train_features=bow_train_features,
??????????????????????????????????????????????????train_labels=train_labels,
??????????????????????????????????????????????????test_features=bow_test_features,
??????????????????????????????????????????????????test_labels=test_labels)
#?基于詞袋模型的支持向量機方法
print("基于詞袋模型的支持向量機")
svm_bow_predictions?=?train_predict_evaluate_model(classifier=svm,
???????????????????????????????????????????????????train_features=bow_train_features,
???????????????????????????????????????????????????train_labels=train_labels,
???????????????????????????????????????????????????test_features=bow_test_features,
???????????????????????????????????????????????????test_labels=test_labels)
joblib.dump(svm,?'svm_bow.pkl')
#?基于tfidf的多項式樸素貝葉斯模型
print("基于tfidf的貝葉斯模型")
mnb_tfidf_predictions?=?train_predict_evaluate_model(classifier=mnb,
?????????????????????????????????????????????????????train_features=tfidf_train_features,
?????????????????????????????????????????????????????train_labels=train_labels,
?????????????????????????????????????????????????????test_features=tfidf_test_features,
?????????????????????????????????????????????????????test_labels=test_labels)
#?基于tfidf的邏輯回歸模型
print("基于tfidf的邏輯回歸模型")
lr_tfidf_predictions=train_predict_evaluate_model(classifier=lr,
?????????????????????????????????????????????????????train_features=tfidf_train_features,
?????????????????????????????????????????????????????train_labels=train_labels,
?????????????????????????????????????????????????????test_features=tfidf_test_features,
?????????????????????????????????????????????????????test_labels=test_labels)
#?基于tfidf的支持向量機模型
print("基于tfidf的支持向量機模型")
svm_tfidf_predictions?=?train_predict_evaluate_model(classifier=svm,
?????????????????????????????????????????????????????train_features=tfidf_train_features,
?????????????????????????????????????????????????????train_labels=train_labels,
?????????????????????????????????????????????????????test_features=tfidf_test_features,
?????????????????????????????????????????????????????test_labels=test_labels)
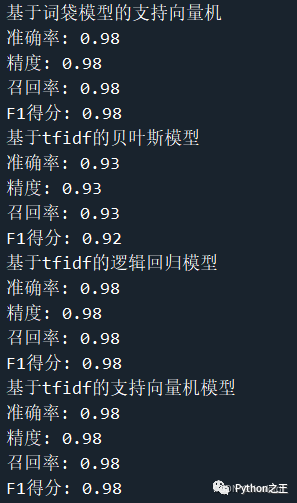
輸出結(jié)果如下所示
 總結(jié)
總結(jié)通過針對郵件內(nèi)容,并且轉(zhuǎn)化為兩種不同的詞向量進行不同模型的訓(xùn)練,從而得到基于tfidf的支持向量機模型效果最好,可以達到98%的準(zhǔn)確率。
原文:https://blog.csdn.net/kobepaul123/article/details/122868530
