前端進(jìn)階:從零實(shí)現(xiàn)單向 & 雙向鏈表

前言
前端工程師對(duì)于算法和數(shù)據(jù)結(jié)構(gòu)這塊的知識(shí)的掌握程度,是進(jìn)階高級(jí)工程師的非常重要的標(biāo)志之一,為了總結(jié)一下數(shù)據(jù)結(jié)構(gòu)和算法方面的知識(shí),筆者今天繼續(xù)把鏈表這一塊的知識(shí)補(bǔ)上,也作為自己知識(shí)體系的一個(gè)梳理,筆者早在去年就寫過一篇關(guān)于使用javascript實(shí)現(xiàn)二叉樹和二叉搜索樹的文章,如果感興趣或者想進(jìn)階高級(jí)的朋友們可以參考學(xué)習(xí)一下: JavaScript 中的二叉樹以及二叉搜索樹的實(shí)現(xiàn)及應(yīng)用.
你將收獲
鏈表的概念和應(yīng)用 原生javascript實(shí)現(xiàn)一條單向鏈表 原生javascript實(shí)現(xiàn)一條個(gè)雙單向鏈表 鏈表和數(shù)組的對(duì)比及優(yōu)缺點(diǎn)
正文
1. 鏈表的概念和應(yīng)用
鏈表是一種線性表數(shù)據(jù)結(jié)構(gòu),由一系列結(jié)點(diǎn)(鏈表中每一個(gè)元素稱為結(jié)點(diǎn))組成,結(jié)點(diǎn)可以在運(yùn)行時(shí)動(dòng)態(tài)生成。每個(gè)結(jié)點(diǎn)包括兩個(gè)部分:一個(gè)是存儲(chǔ)數(shù)據(jù)元素的數(shù)據(jù)域,另一個(gè)是存儲(chǔ)下一個(gè)結(jié)點(diǎn)地址的指針域。
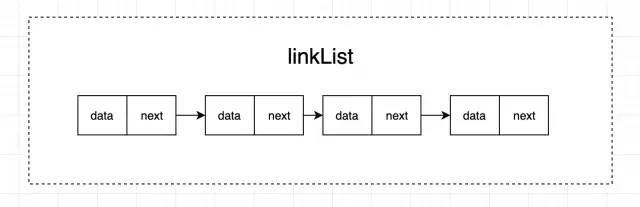
鏈表是非連續(xù)的,所以說從底層存儲(chǔ)結(jié)構(gòu)上看,它不需要一整塊連續(xù)的存儲(chǔ)空間,而是通過“指針”將一組零散的數(shù)據(jù)單元串聯(lián)起來成為一個(gè)整體。鏈表也有幾種不同的類型:單向鏈表,雙向鏈表,循環(huán)鏈表。上圖就是一種單向鏈表。由其定義不難發(fā)現(xiàn)雙向鏈表無非就是每個(gè)節(jié)點(diǎn)加上了前后節(jié)點(diǎn)的指針引用,如下圖所示:
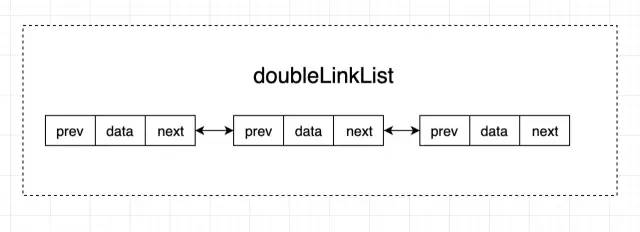
那什么是循環(huán)鏈表呢?循環(huán)鏈表本質(zhì)上是一種特殊的單向鏈表,唯一的區(qū)別就在于它的尾結(jié)點(diǎn)指向了鏈表的頭結(jié)點(diǎn),這樣首尾相連,形成了一個(gè)環(huán),所以叫做循環(huán)鏈表。如下圖所示:
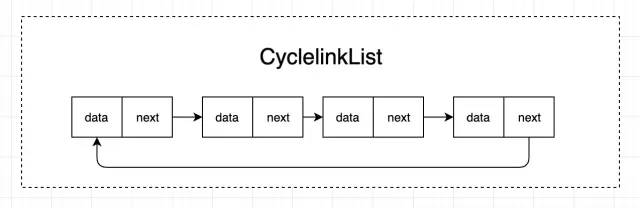
當(dāng)然我們還可以擴(kuò)展出雙向循環(huán)鏈表,這里就不一一舉例了。總之鏈表結(jié)構(gòu)在計(jì)算機(jī)底層語言中應(yīng)用的比較多,當(dāng)我們?cè)谟酶呒?jí)語言做編程時(shí)可能不會(huì)察覺,比如我們用javascript敲js的時(shí)候,其實(shí)我們?cè)谏钊肓私怄湵碇笪覀兙蜁?huì)發(fā)現(xiàn)鏈表有很多應(yīng)用場(chǎng)景,比如LRU 緩存淘汰,最近消息推送等。
舉個(gè)更接地氣的,當(dāng)我們?cè)谟肞S畫圖時(shí)軟件提供了一個(gè)動(dòng)作面板,可以記錄用戶之前的操作記錄,并批量執(zhí)行動(dòng)作,或者當(dāng)我們?cè)谑褂镁庉嬈鲿r(shí)的回退撤銷功能等,用鏈表結(jié)構(gòu)來存儲(chǔ)狀態(tài)信息還是比較方便的。
最近比較火的react hooks API,其結(jié)構(gòu)也是一個(gè)鏈表型的數(shù)據(jù)結(jié)構(gòu),所以學(xué)習(xí)鏈表還是非常有幫助的。讀到這里可能還是有點(diǎn)懵,接下來我們先用js實(shí)現(xiàn)一個(gè)鏈表,這樣有助于理解鏈表的本質(zhì),后面筆者會(huì)總結(jié)一下鏈表和數(shù)組的對(duì)比以及優(yōu)劣勢(shì),方便大家對(duì)鏈表有一個(gè)更加直觀的認(rèn)識(shí)。
2.原生javascript實(shí)現(xiàn)一條單向鏈表
在上面一節(jié)介紹的鏈表結(jié)構(gòu)中大家可能對(duì)鏈表有了初步的認(rèn)識(shí),因?yàn)閖avascript中沒有鏈表的數(shù)據(jù)結(jié)構(gòu),為了模擬鏈表結(jié)構(gòu),我們可以通過js面向?qū)ο蟮姆绞綄?shí)現(xiàn)一個(gè)鏈表結(jié)構(gòu)及其API,具體設(shè)計(jì)如下:
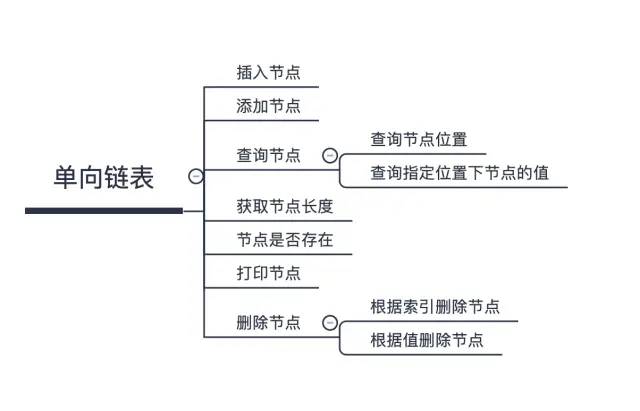
有了以上需求點(diǎn)之后,這個(gè)鏈表才是基本可用的鏈表,那么我們一步步來實(shí)現(xiàn)它吧。
2.1 定義鏈表結(jié)構(gòu)
為了實(shí)現(xiàn)鏈表以及鏈表的操作,首先我們需要先定義鏈表的基本結(jié)構(gòu),第一步就是定義節(jié)點(diǎn)的數(shù)據(jù)結(jié)構(gòu)。我們知道一個(gè)節(jié)點(diǎn)會(huì)有自己的值以及指向下一個(gè)節(jié)點(diǎn)的引用,所以可以這樣定義節(jié)點(diǎn):
let Node = function(el) {
this.el = el;
this.next = null;
}復(fù)制代碼
// 單向鏈表, 每一個(gè)元素都有一個(gè)存儲(chǔ)元素自身的節(jié)點(diǎn)和一個(gè)指向下一個(gè)元素引用的節(jié)點(diǎn)組成
function linkedList() {
let Node = function(el) {
this.el = el;
this.next = null;
}
let length = 0
let head = null // 用來存儲(chǔ)第一個(gè)元素的引用
// 尾部添加元素
this.append = (el) => {};
//插入元素
this.insert = (pos, el) => {};
// 移除指定位置的元素
this.removeAt = (pos) => {};
// 移除指定節(jié)點(diǎn)
this.remove = (el) => {};
// 查詢節(jié)點(diǎn)所在位置
this.indexOf = (el) => {};
// 判斷鏈表是否為空
this.isEmpty = () => {};
// 返回鏈表長度
this.size = () => {};
// 將鏈表轉(zhuǎn)化為數(shù)組返回
this.toArray = () => {};
}復(fù)制代碼
由以上代碼我們可以知道鏈表的初始長度為0,頭部元素為null,接下來我們實(shí)現(xiàn)添加節(jié)點(diǎn)的功能。
2.2 實(shí)現(xiàn)添加節(jié)點(diǎn)
追加節(jié)點(diǎn)的時(shí)候首先需要知道頭部節(jié)點(diǎn)是否存在,如果不存在直接賦值,存在的話則從頭部開始遍歷,直到找到下一個(gè)節(jié)點(diǎn)為空的節(jié)點(diǎn),再賦值,并將鏈表長度+1,代碼如下:
// 尾部添加元素
this.append = (el) => {
let node = new Node(el),
current;
if(!head) {
head = node
}else {
current = head;
while(current.next) {
current = current.next;
}
current.next = node;
}
length++
};復(fù)制代碼
2.3 實(shí)現(xiàn)插入節(jié)點(diǎn)
實(shí)現(xiàn)插入節(jié)點(diǎn)邏輯首先我們要考慮邊界條件,如果插入的位置在頭部或者比尾部位置還大,我們就沒必要從頭遍歷一遍處理了,這樣可以提高性能,所以我們可以這樣處理:
//插入元素
this.insert = (pos, el) => {
if(pos >=0 && pos <= length) {
let node = new Node(el),
previousNode = null,
current = head,
curIdx = 0;
if(pos === 0) {
node.next = current;
head = node;
}else {
while(curIdx++ < pos) {
previousNode = current;
current = current.next;
}
node.next = current;
previousNode.next = node;
length++;
return true
}
}else {
return false
}
};復(fù)制代碼
2.4 根據(jù)節(jié)點(diǎn)的值查詢節(jié)點(diǎn)位置
根據(jù)節(jié)點(diǎn)的值查詢節(jié)點(diǎn)位置實(shí)現(xiàn)起來比較簡(jiǎn)單,我們只要從頭開始遍歷,然后找到對(duì)應(yīng)的值之后記錄一下索引即可:
// 查詢節(jié)點(diǎn)所在位置
this.indexOf = (el) => {
let idx = -1,
curIdx = -1,
current = head;
while(current) {
idx++
if(current.el === el) {
curIdx = idx
break;
}
current = current.next;
}
return curIdx
};復(fù)制代碼
這里我們之所以要用idx和curIdx兩個(gè)變量來處理,是因?yàn)槿绻脩魝魅氲闹挡辉阪湵砝铮敲磇dx的值就會(huì)有問題,所以用curIdx來保證準(zhǔn)確性。
2.5 移除指定位置的節(jié)點(diǎn)
移除指定位置的節(jié)點(diǎn)也需要判斷一下邊界條件,可插入節(jié)點(diǎn)類似,但要注意移除之后一定要將鏈表長度-1,代碼如下:
// 移除指定位置的元素
this.removeAt = (pos) => {
// 檢測(cè)邊界條件
if(pos >=0 && pos < length) {
let previousNode = null,
current = head,
curIdx = 0;
if(pos === 0) {
// 如果pos為第一個(gè)元素
head = current.next
}else {
while(curIdx++ < pos) {
previousNode = current;
current = current.next;
}
previousNode.next = current.next;
}
length --;
return current.el
}else {
return null
}
};復(fù)制代碼
2.6 移除指定節(jié)點(diǎn)
移除指定節(jié)點(diǎn)實(shí)現(xiàn)非常簡(jiǎn)單,我們只需要利用之前實(shí)現(xiàn)好的查找節(jié)點(diǎn)先找到節(jié)點(diǎn)的位置,然后再用實(shí)現(xiàn)過的removeAt即可,代碼如下:
// 移除指定節(jié)點(diǎn)
this.remove = (el) => {
let idx = this.indexOf(el);
this.removeAt(idx);
};復(fù)制代碼
2.7 獲取節(jié)點(diǎn)長度
// 返回鏈表長度
this.size = () => {
return length
};復(fù)制代碼
2.8 判斷鏈表是否為空
// 返回鏈表長度
this.size = () => {
return length
};復(fù)制代碼
2.9 打印節(jié)點(diǎn)
打印節(jié)點(diǎn)實(shí)現(xiàn)方式有很多,大家可以按照自己喜歡的格式打印,這里筆者直接將其打印為數(shù)組格式輸出,代碼如下:
// 將鏈表轉(zhuǎn)化為數(shù)組返回
this.toArray = () => {
let current = head,
results = [];
while(current) {
results.push(current.el);
current = current.next;
}
return results
};復(fù)制代碼
let link = new linkedList()
// 添加節(jié)點(diǎn)
link.append(1)
link.append(2)
// 查找節(jié)點(diǎn)
link.indexOf(2)
// ...復(fù)制代碼
3.原生javascript實(shí)現(xiàn)一條個(gè)雙單向鏈表
有了單向鏈表的實(shí)現(xiàn)基礎(chǔ),實(shí)現(xiàn)雙向鏈表也很簡(jiǎn)單了,我們無非要關(guān)注的是雙向鏈表的節(jié)點(diǎn)創(chuàng)建,這里筆者實(shí)現(xiàn)一個(gè)例子供大家參考:
let Node = function(el) {
this.el = el;
this.previous = null;
this.next = null;
}
let length = 0
let head = null // 用來存儲(chǔ)頭部元素的引用
let tail = null // 用來存儲(chǔ)尾部元素的引用復(fù)制代碼
由代碼可知我們?cè)诠?jié)點(diǎn)中會(huì)有上一個(gè)節(jié)點(diǎn)的引用以及下一個(gè)節(jié)點(diǎn)的引用,同時(shí)這里筆者添加了頭部節(jié)點(diǎn)和尾部節(jié)點(diǎn)方便大家操作。大家可以根據(jù)自己的需求實(shí)現(xiàn)雙向鏈表的功能,這里筆者提供一份自己實(shí)現(xiàn)的代碼,可以參考交流一下:
// 雙向鏈表, 每一個(gè)元素都有一個(gè)存儲(chǔ)元素自身的節(jié)點(diǎn)和指向上一個(gè)元素引用以及下一個(gè)元素引用的節(jié)點(diǎn)組成
function doubleLinkedList() {
let Node = function(el) {
this.el = el;
this.previous = null;
this.next = null;
}
let length = 0
let head = null // 用來存儲(chǔ)頭部元素的引用
let tail = null // 用來存儲(chǔ)尾部元素的引用
// 尾部添加元素
this.append = (el) => {
let node = new Node(el)
if(!head) {
head = node
}else {
tail.next = node;
node.previous = tail;
}
tail = node;
length++
};
// 插入元素
this.insert = (pos, el) => {
if(pos >=0 && pos < length) {
let node = new Node(el);
if(pos === length - 1) {
// 在尾部插入
node.previous = tail.previous;
node.next = tail;
tail.previous = node;
length++;
return true
}
let current = head,
i = 0;
while(i < pos) {
current = current.next;
i++
}
node.next = current;
node.previous = current.previous;
current.previous.next = node;
current.previous = node;
length ++;
return true
}else {
throw new RangeError(`插入范圍有誤`)
}
};
// 移除指定位置的元素
this.removeAt = (pos) => {
// 檢測(cè)邊界條件
if(pos < 0 || pos >= length) {
throw new RangeError(`刪除范圍有誤`)
}else {
if(length) {
if(pos === length - 1) {
// 如果刪除節(jié)點(diǎn)位置為尾節(jié)點(diǎn),直接刪除,節(jié)省查找時(shí)間
let previous = tail.previous;
previous.next = null;
length --;
return tail.el
}else {
let current = head,
previous = null,
next = null,
i = 0;
while(i < pos) {
current = current.next
i++
}
previous = current.previous;
next = current.next;
previous.next = next;
length --;
return current.el
}
}else {
return null
}
}
};
// 移除指定節(jié)點(diǎn)
this.remove = (el) => {
let idx = this.indexOf(el);
this.removeAt(idx);
};
// 查詢指定位置的鏈表元素
this.get = (index) => {
if(index < 0 || index >= length) {
return undefined
}else {
if(length) {
if(index === length - 1) {
return tail.el
}
let current = head,
i = 0;
while(i < index) {
current = current.next
i++
}
return current.el
}else {
return undefined
}
}
}
// 查詢節(jié)點(diǎn)所在位置
this.indexOf = (el) => {
let idx = -1,
current = head,
curIdx = -1;
while(current) {
idx++
if(current.el === el) {
curIdx = idx;
break;
}
current = current.next;
}
return curIdx
};
// 判斷鏈表是否為空
this.isEmpty = () => {
return length === 0
};
// 返回鏈表長度
this.size = () => {
return length
};
// 將鏈表轉(zhuǎn)化為數(shù)組返回
this.toArray = () => {
let current = head,
results = [];
while(current) {
results.push(current.el);
current = current.next;
}
return results
};
}復(fù)制代碼
4.鏈表和數(shù)組的對(duì)比及優(yōu)缺點(diǎn)
實(shí)現(xiàn)完鏈表之后我們會(huì)對(duì)鏈表有更深入的認(rèn)知,接下來我們進(jìn)一步分析鏈表的優(yōu)缺點(diǎn)。筆者將從3個(gè)維度來帶大家分析鏈表的性能情況:
插入刪除性能
查詢性能
內(nèi)存占用
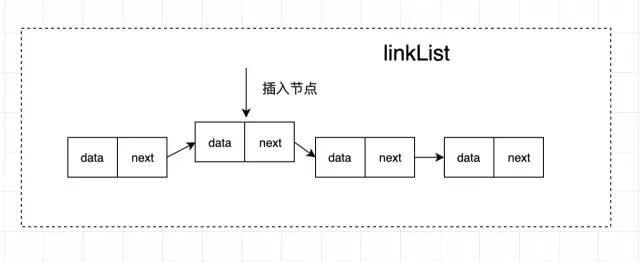
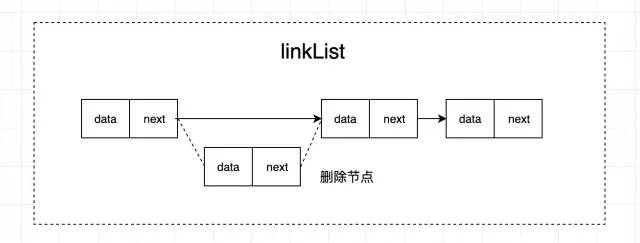
由上圖可以發(fā)現(xiàn),鏈表的插入、刪除數(shù)據(jù)效率非常高,只需要考慮相鄰結(jié)點(diǎn)的指針變化,因?yàn)椴恍枰苿?dòng)其他節(jié)點(diǎn),時(shí)間復(fù)雜度是 O(1)。
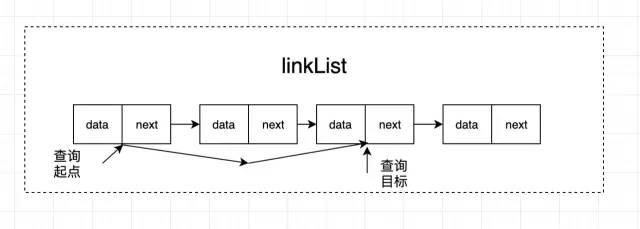
我們對(duì)鏈表進(jìn)行每一次查詢時(shí),都需要從鏈表的頭部開始找起,一步步遍歷到目標(biāo)節(jié)點(diǎn),這個(gè)過程效率是非常低的,時(shí)間復(fù)雜度是 O(n)。這方面我們使用數(shù)組的話效率會(huì)更高一點(diǎn)。
我們?cè)倏纯磧?nèi)存占用。鏈表的內(nèi)存消耗比較大,因?yàn)槊總€(gè)結(jié)點(diǎn)除了要存儲(chǔ)數(shù)據(jù)本身,還要儲(chǔ)存前后結(jié)點(diǎn)的地址。但是好處是可以動(dòng)態(tài)分配內(nèi)存。
另一方面,對(duì)于數(shù)組來說,也存在一些缺點(diǎn),比如數(shù)組必須占用整塊、連續(xù)的內(nèi)存空間,如果聲明的數(shù)組數(shù)據(jù)量過大,可能會(huì)導(dǎo)致“內(nèi)存不足”。其次就是數(shù)組一旦需要擴(kuò)容,會(huì)重新申請(qǐng)連續(xù)的內(nèi)存空間,并且需要把上一次的數(shù)組數(shù)據(jù)全部copy到新的內(nèi)存空間中。
綜上所述,當(dāng)我們的數(shù)據(jù)存在頻繁的插入刪除操作時(shí),我們可以采用鏈表結(jié)構(gòu)來存儲(chǔ)我們的數(shù)據(jù),如果涉及到頻繁查找的操作,我們可以采用數(shù)組來處理。實(shí)際工作中很多底層框架的封裝都是采用組合模式進(jìn)行設(shè)計(jì),一般純粹采用某種數(shù)據(jù)結(jié)構(gòu)的比較少,所以具體還是要根據(jù)所處環(huán)境進(jìn)行適當(dāng)?shù)姆桨冈O(shè)計(jì)。
??愛心三連擊
1.看到這里了就點(diǎn)個(gè)在看支持下吧,你的「點(diǎn)贊,在看」是我創(chuàng)作的動(dòng)力。
2.關(guān)注公眾號(hào)趣談前端,進(jìn)程序員優(yōu)質(zhì)學(xué)習(xí)交流群, 字節(jié), 阿里大佬和你一起學(xué)習(xí)成長!
