機(jī)器學(xué)習(xí)最困難的部分:超參數(shù)調(diào)試
點(diǎn)擊下方卡片,關(guān)注“新機(jī)器視覺”公眾號(hào)
視覺/圖像重磅干貨,第一時(shí)間送達(dá)
作者:Sivasai,轉(zhuǎn)載自:AI公園
ML工作流中最困難的部分之一是為模型找到最好的超參數(shù)。ML模型的性能與超參數(shù)直接相關(guān)。
維基百科上說,“Hyperparameter optimization或tuning是為學(xué)習(xí)算法選擇一組最優(yōu)的hyperparameters的問題”。
ML工作流中最困難的部分之一是為模型找到最好的超參數(shù)。ML模型的性能與超參數(shù)直接相關(guān)。超參數(shù)調(diào)優(yōu)的越好,得到的模型就越好。調(diào)優(yōu)超參數(shù)可能是非常乏味和困難的,更像是一門藝術(shù)而不是科學(xué)。
超參數(shù)是在建立模型時(shí)用于控制算法行為的參數(shù)。這些參數(shù)不能從常規(guī)訓(xùn)練過程中獲得。在對(duì)模型進(jìn)行訓(xùn)練之前,需要對(duì)它們進(jìn)行賦值。
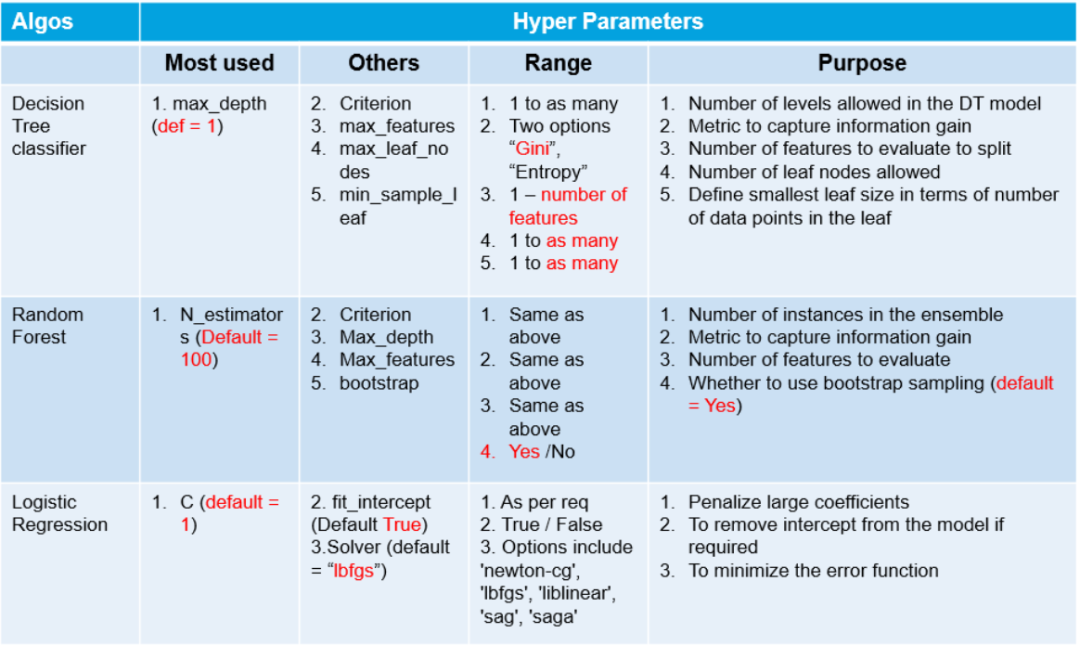
傳統(tǒng)的手工調(diào)參 網(wǎng)格搜索 隨機(jī)搜索 貝葉斯搜索
1. 傳統(tǒng)手工搜索
在傳統(tǒng)的調(diào)參過程中,我們通過訓(xùn)練算法手動(dòng)檢查隨機(jī)超參數(shù)集,并選擇符合我們目標(biāo)的最佳參數(shù)集。
我們看看代碼:
#importing required libraries
from sklearn.neighbors import KNeighborsClassifier
from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split
from sklearn.model_selection import KFold , cross_val_score
from sklearn.datasets import load_wine
wine = load_wine()
X = wine.data
y = wine.target
#splitting the data into train and test set
X_train,X_test,y_train,y_test = train_test_split(X,y,test_size = 0.3,random_state = 14)
#declaring parameters grid
k_value = list(range(2,11))
algorithm = ['auto','ball_tree','kd_tree','brute']
scores = []
best_comb = []
kfold = KFold(n_splits=5)
#hyperparameter tunning
for algo in algorithm:
for k in k_value:
knn = KNeighborsClassifier(n_neighbors=k,algorithm=algo)
results = cross_val_score(knn,X_train,y_train,cv = kfold)
print(f'Score:{round(results.mean(),4)} with algo = {algo} , K = {k}')
scores.append(results.mean())
best_comb.append((k,algo))
best_param = best_comb[scores.index(max(scores))]
print(f'\nThe Best Score : {max(scores)}')
print(f"['algorithm': {best_param[1]} ,'n_neighbors': {best_param[0]}]")
缺點(diǎn):
沒辦法確保得到最佳的參數(shù)組合。 這是一個(gè)不斷試錯(cuò)的過程,所以,非常的耗時(shí)。
2. 網(wǎng)格搜索
網(wǎng)格搜索是一種基本的超參數(shù)調(diào)優(yōu)技術(shù)。它類似于手動(dòng)調(diào)優(yōu),為網(wǎng)格中指定的所有給定超參數(shù)值的每個(gè)排列構(gòu)建模型,評(píng)估并選擇最佳模型。考慮上面的例子,其中兩個(gè)超參數(shù)k_value =[2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9,10] & algorithm =[' auto ', ' ball_tree ', ' kd_tree ', ' brute '],在這個(gè)例子中,它總共構(gòu)建了9*4 = 36不同的模型。
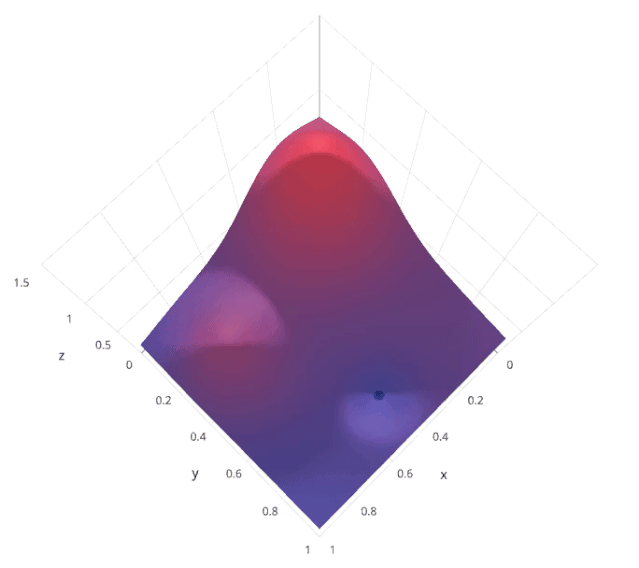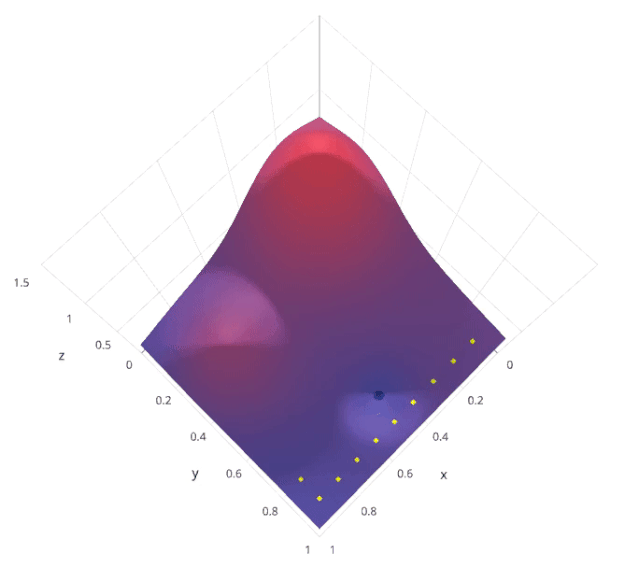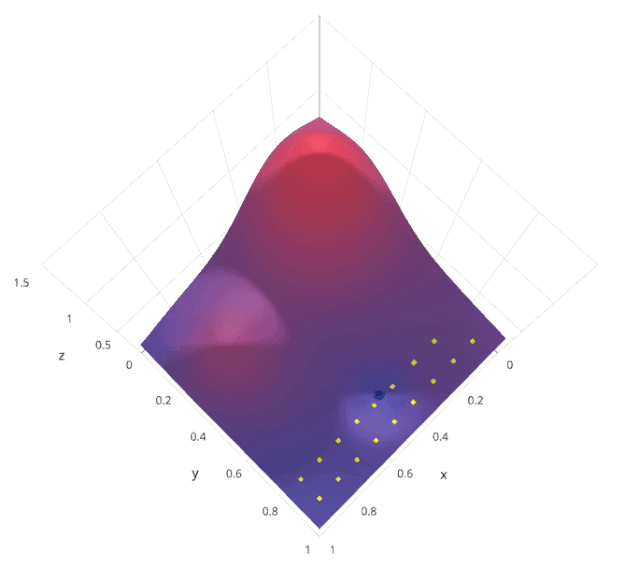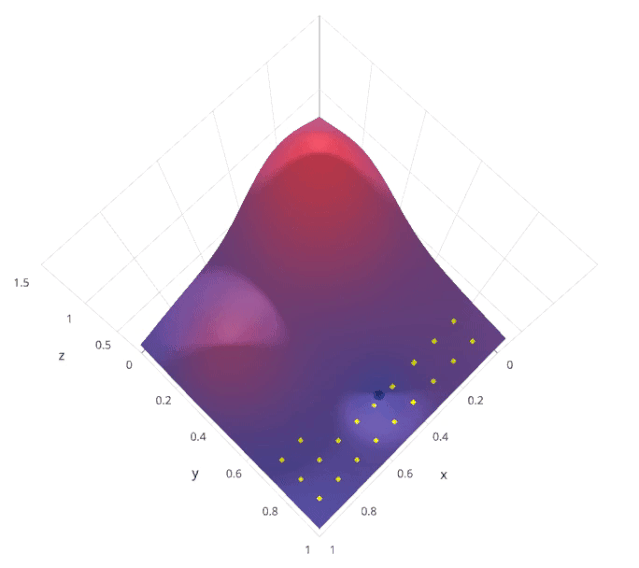
讓我們來了解一下sklearn的GridSearchCV是如何工作的:
from sklearn.model_selection import GridSearchCV
knn = KNeighborsClassifier()
grid_param = { 'n_neighbors' : list(range(2,11)) ,
'algorithm' : ['auto','ball_tree','kd_tree','brute'] }
grid = GridSearchCV(knn,grid_param,cv = 5)
grid.fit(X_train,y_train)
#best parameter combination
grid.best_params_
#Score achieved with best parameter combination
grid.best_score_
#all combinations of hyperparameters
grid.cv_results_['params']
#average scores of cross-validation
grid.cv_results_['mean_test_score']
缺點(diǎn):
由于它嘗試了超參數(shù)的每一個(gè)組合,并根據(jù)交叉驗(yàn)證得分選擇了最佳組合,這使得GridsearchCV非常慢。
3. 隨機(jī)搜索
使用隨機(jī)搜索代替網(wǎng)格搜索的動(dòng)機(jī)是,在許多情況下,所有的超參數(shù)可能不是同等重要的。隨機(jī)搜索從超參數(shù)空間中隨機(jī)選擇參數(shù)組合,參數(shù)由n_iter給定的固定迭代次數(shù)的情況下選擇。實(shí)驗(yàn)證明,隨機(jī)搜索的結(jié)果優(yōu)于網(wǎng)格搜索。
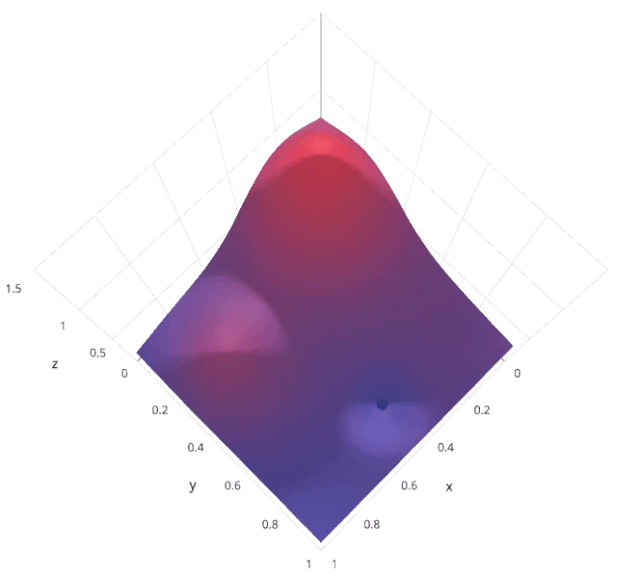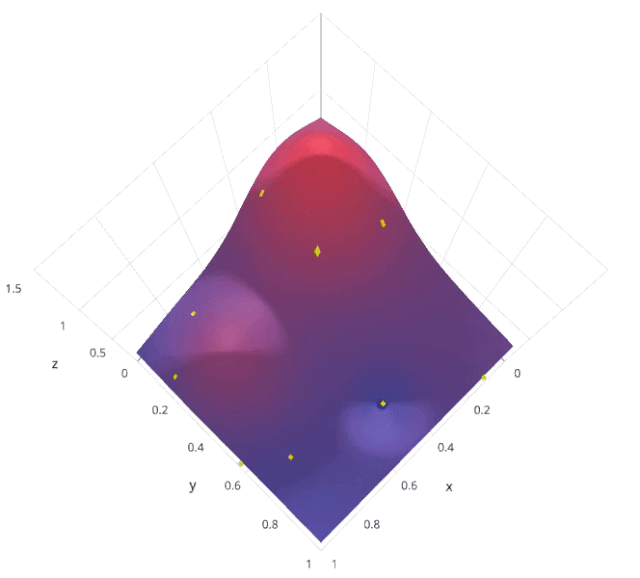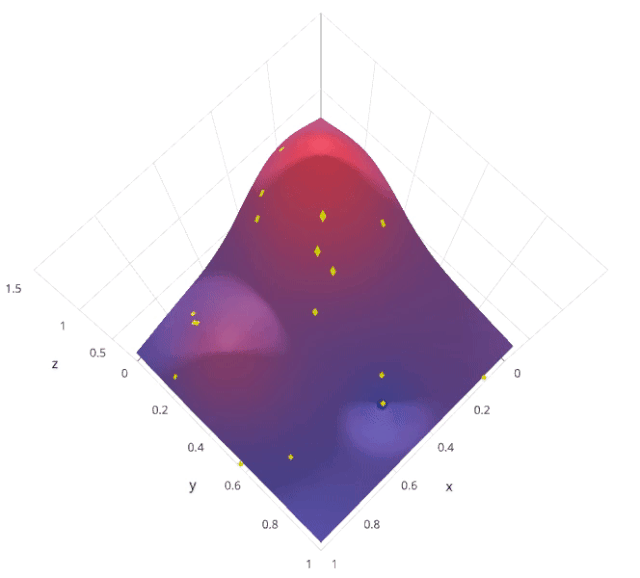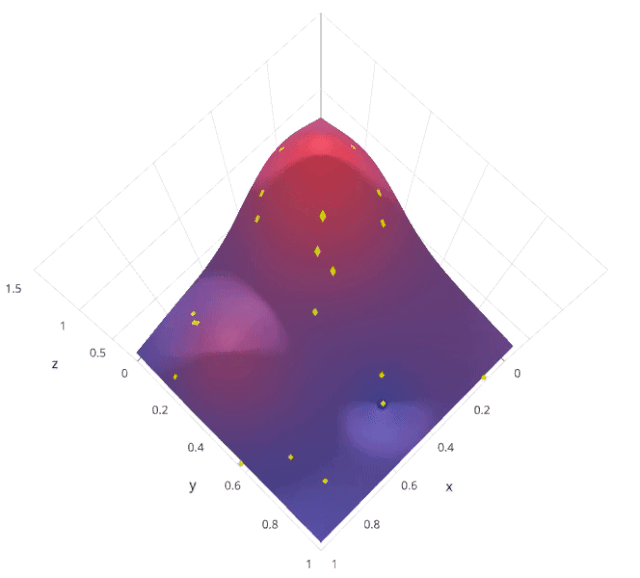
讓我們來了解sklearn的RandomizedSearchCV是如何工作的,
from sklearn.model_selection import RandomizedSearchCV
knn = KNeighborsClassifier()
grid_param = { 'n_neighbors' : list(range(2,11)) ,
'algorithm' : ['auto','ball_tree','kd_tree','brute'] }
rand_ser = RandomizedSearchCV(knn,grid_param,n_iter=10)
rand_ser.fit(X_train,y_train)
#best parameter combination
rand_ser.best_params_
#score achieved with best parameter combination
rand_ser.best_score_
#all combinations of hyperparameters
rand_ser.cv_results_['params']
#average scores of cross-validation
rand_ser.cv_results_['mean_test_score']
缺點(diǎn):
隨機(jī)搜索的問題是它不能保證給出最好的參數(shù)組合。
4. 貝葉斯搜索
貝葉斯優(yōu)化屬于一類優(yōu)化算法,稱為基于序列模型的優(yōu)化(SMBO)算法。這些算法使用先前對(duì)損失f的觀察結(jié)果,以確定下一個(gè)(最優(yōu))點(diǎn)來抽樣f。該算法大致可以概括如下。
使用先前評(píng)估的點(diǎn)X1*:n*,計(jì)算損失f的后驗(yàn)期望。 在新的點(diǎn)X的抽樣損失f,從而最大化f的期望的某些方法。該方法指定f域的哪些區(qū)域最適于抽樣。
重復(fù)這些步驟,直到滿足某些收斂準(zhǔn)則。
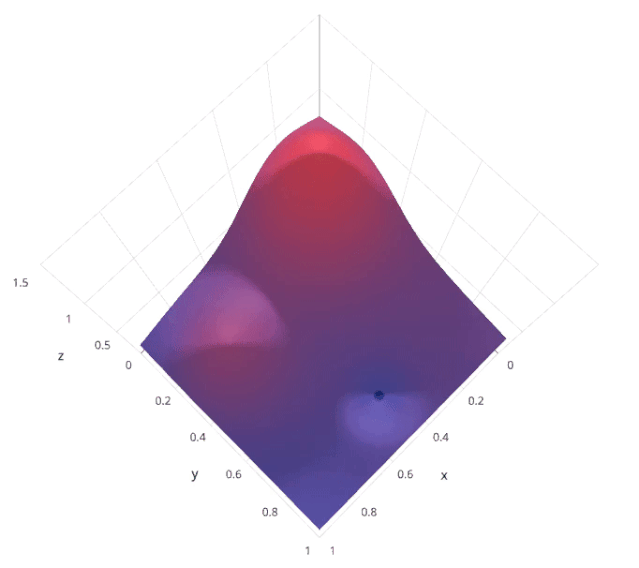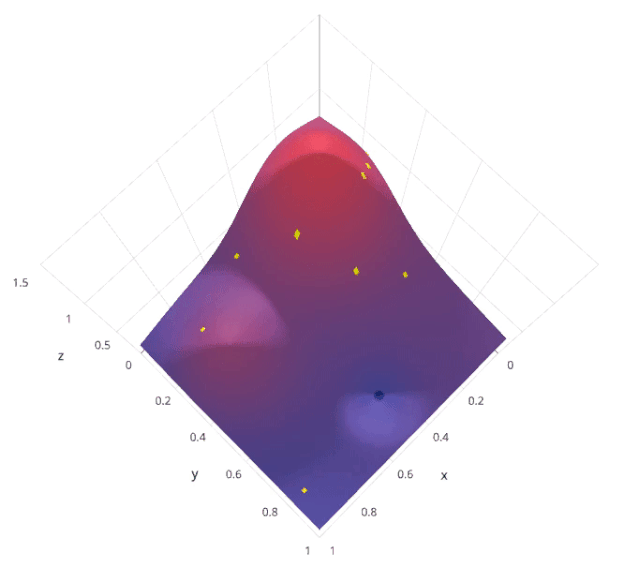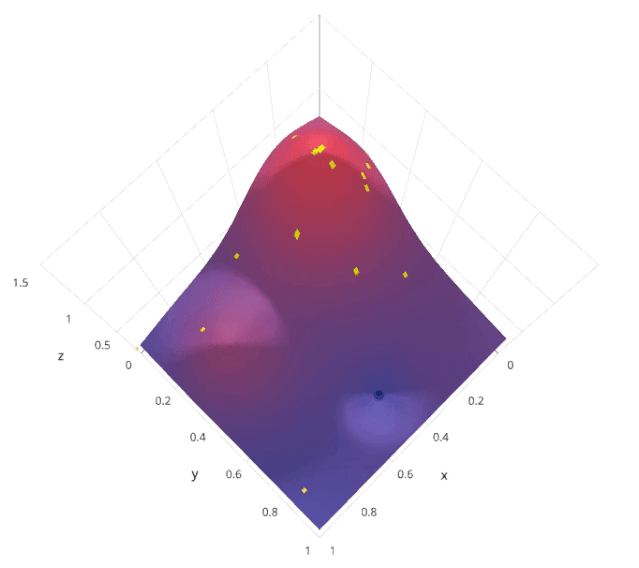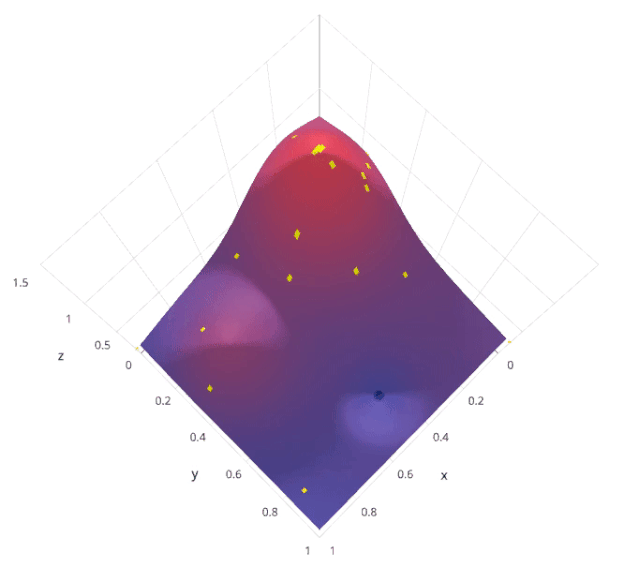
讓我們用scikit- optimization的BayesSearchCV來理解這
Installation: pip install scikit-optimize
from skopt import BayesSearchCV
import warnings
warnings.filterwarnings("ignore")
# parameter ranges are specified by one of below
from skopt.space import Real, Categorical, Integer
knn = KNeighborsClassifier()
#defining hyper-parameter grid
grid_param = { 'n_neighbors' : list(range(2,11)) ,
'algorithm' : ['auto','ball_tree','kd_tree','brute'] }
#initializing Bayesian Search
Bayes = BayesSearchCV(knn , grid_param , n_iter=30 , random_state=14)
Bayes.fit(X_train,y_train)
#best parameter combination
Bayes.best_params_
#score achieved with best parameter combination
Bayes.best_score_
#all combinations of hyperparameters
Bayes.cv_results_['params']
#average scores of cross-validation
Bayes.cv_results_['mean_test_score']
另一個(gè)實(shí)現(xiàn)貝葉斯搜索的類似庫(kù)是bayesian-optimization。
Installation: pip install bayesian-optimization
缺點(diǎn):
要在2維或3維的搜索空間中得到一個(gè)好的代理曲面需要十幾個(gè)樣本,增加搜索空間的維數(shù)需要更多的樣本。
在確定參數(shù)的最佳組合的保證和計(jì)算時(shí)間之間總是存在權(quán)衡。如果超參數(shù)空間(超參數(shù)個(gè)數(shù))非常大,則使用隨機(jī)搜索找到超參數(shù)的潛在組合,然后在該局部使用網(wǎng)格搜索(超參數(shù)的潛在組合)選擇最優(yōu)特征。
—版權(quán)聲明—
僅用于學(xué)術(shù)分享,版權(quán)屬于原作者。
若有侵權(quán),請(qǐng)聯(lián)系微信號(hào):yiyang-sy 刪除或修改!
