Python 自動化辦公-玩轉(zhuǎn) Word
只要是簡單重復的工作,就想辦法用 Python 來幫你解決吧,人生苦短,你需要 Python。
Word 是辦公軟件中使用頻率非常高的軟件之一了,假如你需要調(diào)整 100 個 Word 文檔的格式保持統(tǒng)一,或者要把 100 個 Word 全部轉(zhuǎn)換為 pdf,那么你就需要 Python 來幫忙了。
本文分享如何用 Python 來讀取 Word、寫入 Word、將 Word 轉(zhuǎn)換為 pdf。學會之后,如果遇到大量 Word 文件需要處理的時候,就不慌了。
python-docx 庫簡介
python-docx 是一個可以對 Word 進行讀寫操作的第三方庫,可以讀取 Word 內(nèi)容,可以為 Word 文檔添加段落、表格、圖片、標題,應用段落樣式、粗體和斜體、字符樣式。
執(zhí)行如下安裝命令即可完成安裝:
pip install python-docx
官方文檔: https://python-docx.readthedocs.io/
讀取 Word
這里我先創(chuàng)建了一個樣例,里面有標題、正文、表格:
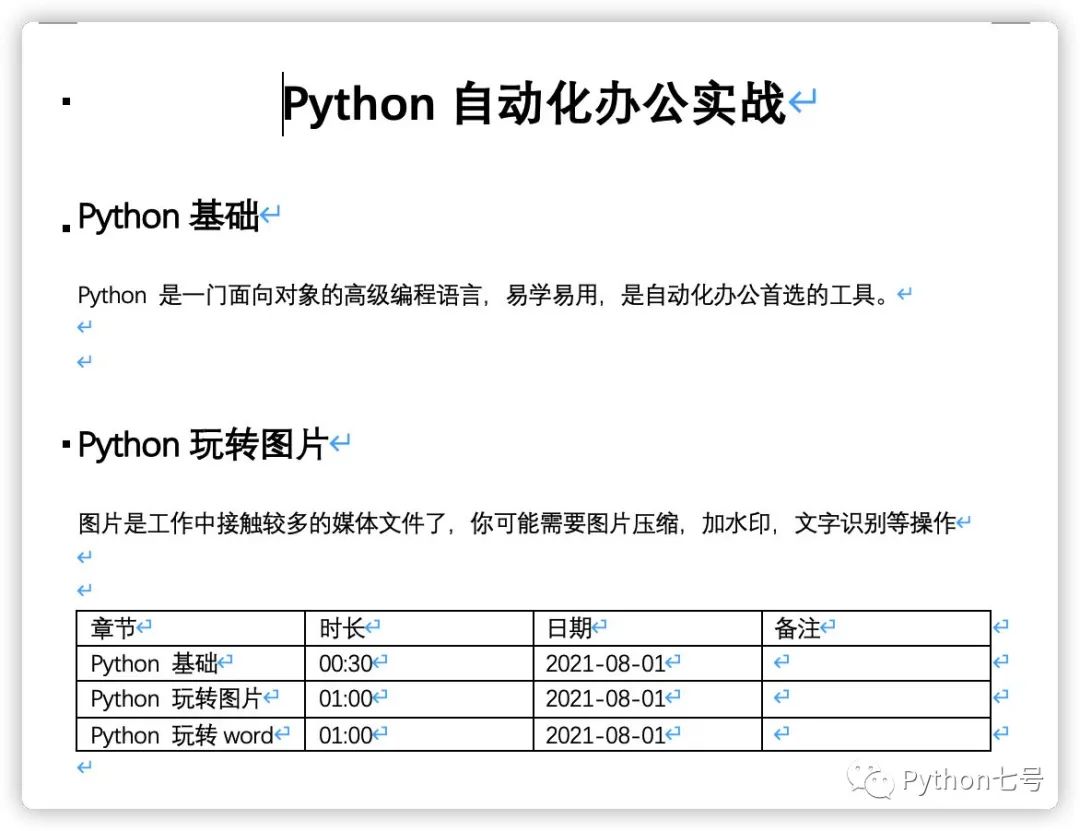
讀取 Word 內(nèi)容的代碼如下:
from docx import Document
def view_docs(docx_file):
# 打開文檔1
doc = Document(docx_file)
# 讀取每段內(nèi)容
pl = [ paragraph.text for paragraph in doc.paragraphs]
# 輸出讀取到的內(nèi)容
for i in pl:
print(i)
def view_docs_table(docx_file):
# 打開文檔1
doc = Document(docx_file)
# 讀取每段內(nèi)容
tables = [table for table in doc.tables]
for table in tables:
for row in table.rows:
for cell in row.cells:
print(cell.text, end=' ')
print()
print('\n')
if __name__ == '__main__':
view_docs("Python自動化辦公實戰(zhàn)課.docx")
view_docs_table("Python自動化辦公實戰(zhàn)課.docx")
運行結(jié)果如下:

寫入 Word
現(xiàn)在,用 Python 創(chuàng)建一個和剛才一樣的 Word 文檔:
from docx import Document
from docx.shared import Pt, RGBColor
from docx.oxml.ns import qn
from docx.enum.text import WD_PARAGRAPH_ALIGNMENT
from docx.table import _Cell
from docx.oxml import OxmlElement
def set_cell_border(cell: _Cell, **kwargs):
"""
Set cell`s border
Usage:
set_cell_border(
cell,
top={"sz": 12, "val": "single", "color": "#FF0000", "space": "0"},
bottom={"sz": 12, "color": "#00FF00", "val": "single"},
start={"sz": 24, "val": "dashed", "shadow": "true"},
end={"sz": 12, "val": "dashed"},
)
"""
tc = cell._tc
tcPr = tc.get_or_add_tcPr()
# check for tag existnace, if none found, then create one
tcBorders = tcPr.first_child_found_in("w:tcBorders")
if tcBorders is None:
tcBorders = OxmlElement('w:tcBorders')
tcPr.append(tcBorders)
# list over all available tags
for edge in ('start', 'top', 'end', 'bottom', 'insideH', 'insideV'):
edge_data = kwargs.get(edge)
if edge_data:
tag = 'w:{}'.format(edge)
# check for tag existnace, if none found, then create one
element = tcBorders.find(qn(tag))
if element is None:
element = OxmlElement(tag)
tcBorders.append(element)
# looks like order of attributes is important
for key in ["sz", "val", "color", "space", "shadow"]:
if key in edge_data:
element.set(qn('w:{}'.format(key)), str(edge_data[key]))
document = Document()
document.styles['Normal'].font.name = u'宋體'
document.styles['Normal']._element.rPr.rFonts.set(qn('w:eastAsia'), u'宋體')
##標題
def add_header(text, level, align='center'):
title_ = document.add_heading(level=level)
if align == 'center':
title_.alignment = WD_PARAGRAPH_ALIGNMENT.CENTER # 標題居中
elif align == 'right':
title_.alignment = WD_PARAGRAPH_ALIGNMENT.RIGHT # 標題居中
title_run = title_.add_run(text) # 添加標題內(nèi)容
# title_run.font.size = Pt(24) # 設(shè)置標題字體大小
title_run.font.name = 'Times New Roman' # 設(shè)置標題西文字體
title_run.font.color.rgb = RGBColor(0, 0, 0) # 字體顏色
title_run.element.rPr.rFonts.set(qn('w:eastAsia'), '微軟雅黑') # 設(shè)置標題中文字體
add_header(text='Python自動化辦公實戰(zhàn)', level=1)
add_header(text='Python基礎(chǔ)', level=2, align='left')
document.add_paragraph('Python 是一門面向?qū)ο蟮母呒壘幊陶Z言,易學易用,是自動化辦公首選的工具。')
add_header('Python玩轉(zhuǎn)圖片', level=2, align='left')
document.add_paragraph('圖片是工作中接觸較多的媒體文件了,你可能需要圖片壓縮,加水印,文字識別等操作')
records = (
('Python 基礎(chǔ)', '00:30', '2021-08-01', ''),
('Python 玩轉(zhuǎn)圖片', '01:00', '2021-08-01', ''),
('Python 玩轉(zhuǎn) Word', '01:00', '2021-08-01', ''),
)
table = document.add_table(rows=1, cols=4)
hdr_cells = table.rows[0].cells
hdr_cells[0].text = '章節(jié)'
hdr_cells[1].text = '時長'
hdr_cells[2].text = '日期'
hdr_cells[3].text = '備注'
for cell in hdr_cells:
set_cell_border(cell,
top={"sz": 12, "val": "single", "color": "#FF0000", "space": "0"},
bottom={"sz": 12, "val": "single", "color": "#FF0000", "space": "0"},
start={"sz": 12, "val": "single", "color": "#FF0000", "space": "0"},
end={"sz": 12, "val": "single", "color": "#FF0000", "space": "0"},
)
for chapter, time, date, note in records:
row_cells = table.add_row().cells
row_cells[0].text = chapter
row_cells[1].text = time
row_cells[2].text = date
row_cells[3].text = note
for cell in row_cells:
set_cell_border(cell,
top={"sz": 12, "val": "single", "color": "#FF0000", "space": "0"},
bottom={"sz": 12, "val": "single", "color": "#FF0000", "space": "0"},
start={"sz": 12, "val": "single", "color": "#FF0000", "space": "0"},
end={"sz": 12, "val": "single", "color": "#FF0000", "space": "0"},
)
document.save('Python自動化辦公實戰(zhàn).docx')
其中,為表格添加邊框的代碼由于比較復雜,單獨做為一個函數(shù)來調(diào)用。
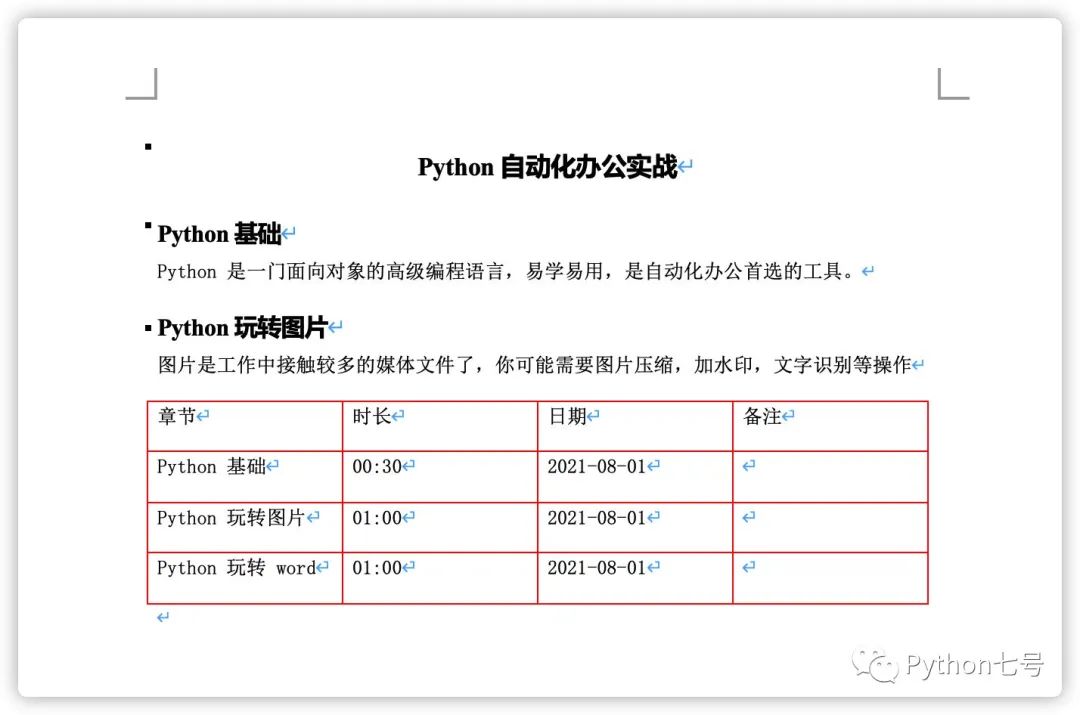
生成的 Word 文檔如下所示,其中表格邊框的顏色,標題的顏色,字體大小,樣式都是可以設(shè)置的:
其他操作
添加分頁符:
document.add_page_break()
添加圖片:
document.add_picture('monty-truth.png', width=Inches(1.25))
設(shè)置表格的列寬和行高
'''
設(shè)置列寬
可以設(shè)置每個單元格的寬,同列單元格寬度相同,如果定義了不同的寬度將以最大值準
'''
table.cell(0,0).width=Cm(10)
#設(shè)置行高
table.rows[0].height=Cm(2)
表格字體的設(shè)定:
from docx.enum.text import WD_PARAGRAPH_ALIGNMENT
#設(shè)置整個表格字體屬性
table.style.font.size=Pt(18)
table.style.font.color.rgb=RGBColor(255, 0, 0)
table.style.paragraph_format.alignment=WD_PARAGRAPH_ALIGNMENT.CENTER
合并單元格
cell_1=table.cell(1, 0)
cell_2=table.cell(2, 1)
cell_1.merge(cell_2)
修改文檔字體:
from docx import Document
from docx.shared import Pt #設(shè)置像素、縮進等
from docx.shared import RGBColor #設(shè)置字體顏色
from docx.oxml.ns import qn
doc = Document("xxx.docx")
for paragraph in doc.paragraphs:
for run in paragraph.runs:
run.font.bold = True
run.font.italic = True
run.font.underline = True
run.font.strike = True
run.font.shadow = True
run.font.size = Pt(18)
run.font.color.rgb = RGBColor(255,0,255)
run.font.name = "黑體"
# 設(shè)置像黑體這樣的中文字體,必須添加下面 2 行代碼
r = run._element.rPr.rFonts
r.set(qn("w:eastAsia"),"黑體")
doc.save("xxx.docx")
行間距調(diào)整:
paragraph.paragraph_format.line_spacing = 5.0
段前與段后間距調(diào)整:
#段前
paragraph.paragraph_format.space_before = Pt(12)
#段后
paragraph.paragraph_format.space_after = Pt(10)
Word 轉(zhuǎn) pdf
只需要兩行代碼就可以將 Word 轉(zhuǎn) pdf,這里使用的是三方庫 docx2pdf 使用前先 pip install docx2pdf。
具體代碼如下所示:
from docx2pdf import convert
convert("Python自動化辦公實戰(zhàn).docx", "Python自動化辦公實戰(zhàn).docx.pdf")
如果要對某個目錄下的 Word 批量轉(zhuǎn)換為 pdf,可以這樣:
from docx2pdf import convert
convert("目錄路徑/")
批量轉(zhuǎn)換為 pdf 時是否非常方便?
知道了這些小操作,就可以組裝大操作,比如后面可以用 Python 將 Word 轉(zhuǎn)換為 pdf 后作為附件發(fā)送郵件給其他人。
最后的話
本文分享了一種讀寫 Word 的方式,在日常工作中如果是重復性的 Word 操作,可考慮 Python 自動化,有問題請留言交流。閱讀原文可以查看 gitee 上的代碼。
