算法1.如何判斷一個(gè)鏈表是否是回文結(jié)構(gòu)
????????這個(gè)問(wèn)題我一開(kāi)始就想到用棧解決,思路就是找到鏈表的中間節(jié)點(diǎn),然后將鏈表的尾部節(jié)點(diǎn)送入棧中。再一次出棧,每次出棧都與鏈表的頭部進(jìn)行比較,一旦有不相等的數(shù)據(jù)出現(xiàn),那么肯定不是回文,知道棧中元素全部放出,則返回是回文。
下邊給出三種思路:
????????需要額外O(n)空間復(fù)雜度,創(chuàng)建棧這個(gè)是我第一時(shí)間想到的,一般算法題我沒(méi)有思路的時(shí)候都會(huì)想想棧這個(gè)東西。?先遍歷鏈表,存儲(chǔ)到棧中,然后再pop出棧和鏈表頭部對(duì)比,只要碰到不相等的就證明不是回文。
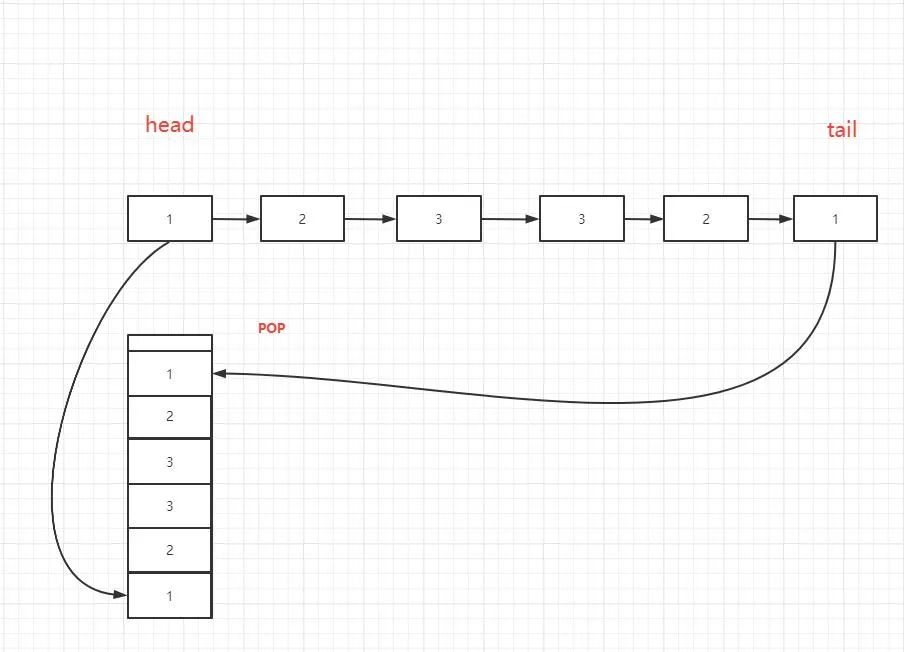
/**
* 需要額外O(n)空間復(fù)雜度
* 創(chuàng)建棧這個(gè)是我第一時(shí)間想到的,一般算法題我沒(méi)有思路的時(shí)候都會(huì)想想棧這個(gè)東西。
* 先遍歷鏈表,存儲(chǔ)到棧中,然后再pop出棧和鏈表頭部對(duì)比,只要碰到不相等的就證明不是回文
* @param head
* @return
*/
public static boolean isPalindrome1(Node head) {
Stackstack = new Stack ();
Node cur = head;
while(cur != null) {
stack.add(cur);
cur = cur.next;
}
cur = head;
while(!stack.isEmpty()) {
if(stack.pop().data != cur.data) {
return false;
}else {
cur = cur.next;
}
}
return true;
}
????????創(chuàng)建棧,空間復(fù)雜度占用O(n/2),設(shè)置快指針和慢指針,快指針走兩步,滿指針走一步,當(dāng)快指針不能走下去的時(shí)候,滿指針走到鏈表中間。將鏈表后邊的部分存儲(chǔ)到棧中,然后使用方法一進(jìn)行判斷。
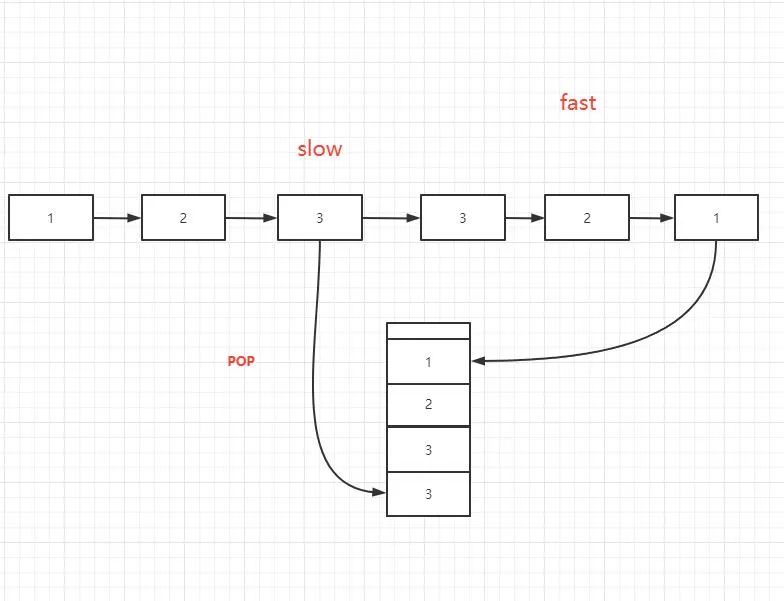
/**
* 創(chuàng)建棧,空間復(fù)雜度占用O(n/2)
* 設(shè)置快指針和慢指針,快指針走兩步,滿指針走一步,
* 當(dāng)快指針不能走下去的時(shí)候,滿指針走到鏈表中間。
* 將鏈表后邊的部分存儲(chǔ)到棧中,然后使用方法一進(jìn)行判斷。
* @param head
* @return
*/
public static boolean isPalindrome2(Node head) {
Node f = head;
Node s = head;
while( f.next!=null && f.next.next != null && s.next != null) {
f = f.next.next;
s = s.next;
}
Stackstack = new Stack ();
while(s != null) {
stack.add(s);
s = s.next;
}
f = head;
while(!stack.isEmpty()) {
if(stack.pop().data != f.data) {
return false;
}else {
f = f.next;
}
}
return true;
}
????????反轉(zhuǎn)鏈表,前邊兩種方法都額外引入了一個(gè)輔助空間棧,而這次我們直接在鏈表自身上進(jìn)行判斷,所以空間復(fù)雜度O(1),按照方法2的辦法找到list的中間節(jié)點(diǎn),將后半部分的list反轉(zhuǎn).反轉(zhuǎn)后一個(gè)指針從開(kāi)頭,另一個(gè)從中間逐個(gè)比較.?
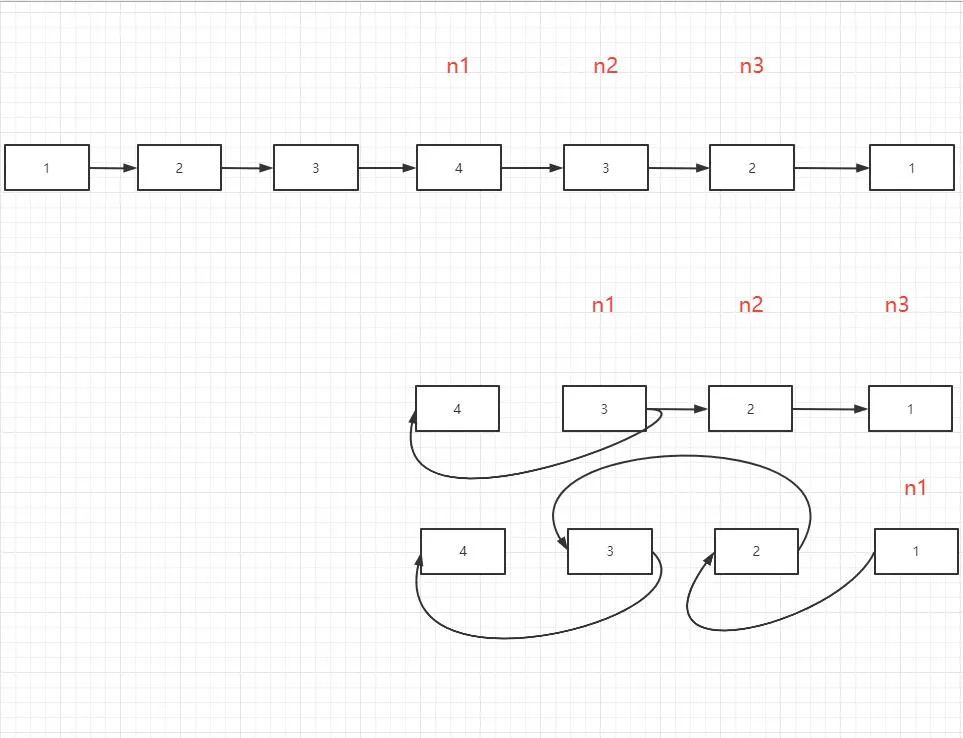
/**
* 反轉(zhuǎn)鏈表 空間復(fù)雜度O(1)
* 按照方法2的辦法找到list的中間節(jié)點(diǎn),將后半部分的list反轉(zhuǎn).反轉(zhuǎn)后
* 一個(gè)指針從開(kāi)頭,另一個(gè)從中間逐個(gè)比較.
* @param head
* @return
*/
public static boolean isPalindrome3(Node head) {
Node n1 = head;
Node n2 = head;
while(n2.next != null && n2.next.next != null) {
n1 = n1.next;
n2 = n2.next.next;
}//n1 在中間
n2 = n1.next;//n2代表后半
n1.next = null;
Node n3 = null;
//后半部分鏈表反轉(zhuǎn)
while(n2 != null) {
n3 = n2.next; //n3保存節(jié)點(diǎn)
n2.next = n1; //從中間節(jié)點(diǎn)開(kāi)始變?yōu)樾骆湵砦膊抗?jié)點(diǎn),知道n1為新節(jié)點(diǎn)首部。
n1 = n2;
n2 = n3;
}
n2 = head;
while(n1 != null && n2 != null) {
if(n1.data != n2.data) {
return false;
}else {
n1 = n1.next;
n2 = n2.next;
}
}
return true;
}
總代碼如下:
/**
* 鏈表是否是回文鏈表
*
* @author Ted
* @version 1.0
* @date 2021/10/8 17:38
*/
public class IsPalindrome {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Node n1 = new Node(1);
Node n2 = new Node(2);
n1.next =n2;
Node n3 = new Node(3);
n2.next = n3;
Node n4 = new Node(3);
n3.next = n4;
Node n5 = new Node(2);
n4.next = n5;
Node n6 = new Node(1);
n5.next = n6;
System.out.println(isPalindrome3(n1));
}
/**
* 需要額外O(n)空間復(fù)雜度
* 創(chuàng)建棧這個(gè)是我第一時(shí)間想到的,一般算法題我沒(méi)有思路的時(shí)候都會(huì)想想棧這個(gè)東西。
* 先遍歷鏈表,存儲(chǔ)到棧中,然后再pop出棧和鏈表頭部對(duì)比,只要碰到不相等的就證明不是回文
* @param head
* @return
*/
public static boolean isPalindrome1(Node head) {
Stackstack = new Stack ();
Node cur = head;
while(cur != null) {
stack.add(cur);
cur = cur.next;
}
cur = head;
while(!stack.isEmpty()) {
if(stack.pop().data != cur.data) {
return false;
}else {
cur = cur.next;
}
}
return true;
}
/**
* 創(chuàng)建棧,空間復(fù)雜度占用O(n/2)
* 設(shè)置快指針和慢指針,快指針走兩步,滿指針走一步,
* 當(dāng)快指針不能走下去的時(shí)候,滿指針走到鏈表中間。
* 將鏈表后邊的部分存儲(chǔ)到棧中,然后使用方法一進(jìn)行判斷。
* @param head
* @return
*/
public static boolean isPalindrome2(Node head) {
Node f = head.next;
Node s = head;
while( f.next!=null && f.next.next != null && s.next != null) {
f = f.next.next;
s = s.next;
}
Stackstack = new Stack ();
while(s != null) {
stack.add(s);
s = s.next;
}
f = head;
while(!stack.isEmpty()) {
if(stack.pop().data != f.data) {
return false;
}else {
f = f.next;
}
}
return true;
}
/**
* 反轉(zhuǎn)鏈表 空間復(fù)雜度O(1)
* 按照方法2的辦法找到list的中間節(jié)點(diǎn),將后半部分的list反轉(zhuǎn).反轉(zhuǎn)后
* 一個(gè)指針從開(kāi)頭,另一個(gè)從中間逐個(gè)比較.
* @param head
* @return
*/
public static boolean isPalindrome3(Node head) {
Node n1 = head;
Node n2 = head;
while(n2.next != null && n2.next.next != null) {
n1 = n1.next;
n2 = n2.next.next;
}//n1 在中間
n2 = n1.next;//n2代表后半
n1.next = null;
Node n3 = null;
//后半部分鏈表反轉(zhuǎn)
while(n2 != null) {
n3 = n2.next; //n3保存節(jié)點(diǎn)
n2.next = n1; //從中間節(jié)點(diǎn)開(kāi)始變?yōu)樾骆湵砦膊抗?jié)點(diǎn),知道n1為新節(jié)點(diǎn)首部。
n1 = n2;
n2 = n3;
}
n2 = head;
while(n1 != null && n2 != null) {
if(n1.data != n2.data) {
return false;
}else {
n1 = n1.next;
n2 = n2.next;
}
}
return true;
}
}
class Node {
Node next;
int data;
public Node (int data){
this.data = data;
}
}
????????遇到問(wèn)題不要慌不要亂,耐心的解決,當(dāng)前解決不了,著急是沒(méi)有什么用的,控制不了結(jié)局的事情除了耐心對(duì)待它還能有一線生機(jī),也不會(huì)有其他什么辦法了。
