單行人跟蹤
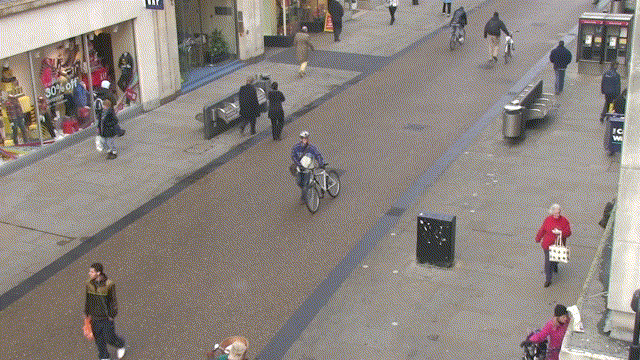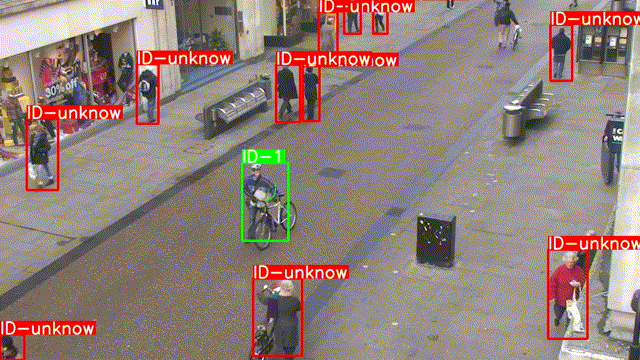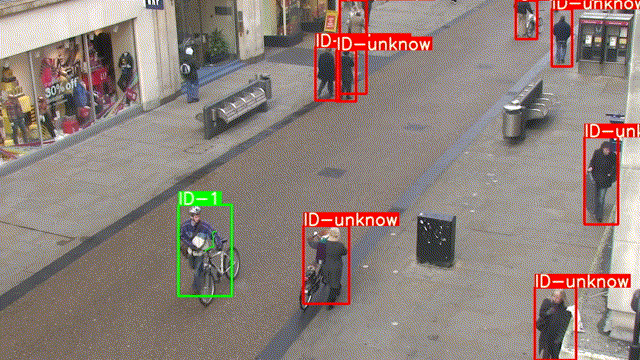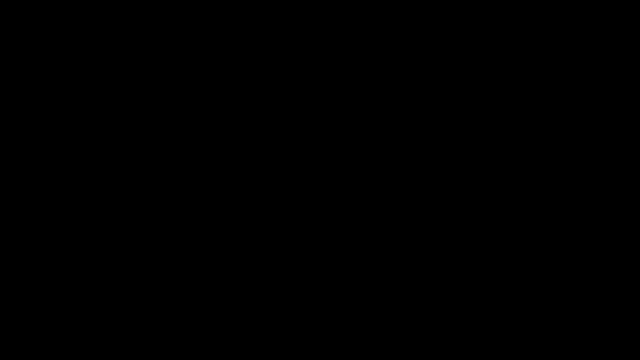
還記得前幾章推文中的這張GIF嗎,是的,今天我們就來實(shí)現(xiàn)一下這個單行人跟蹤.
前提文件
首先,在開始實(shí)現(xiàn)之前,我們需要以下的一些文件:
前幾章推文中訓(xùn)練好的行人重識別模型
目標(biāo)檢測算法,這里我使用的是Yolov5
使用到的源碼地址: https://github.com/ultralytics/yolov5
一段行人的視頻
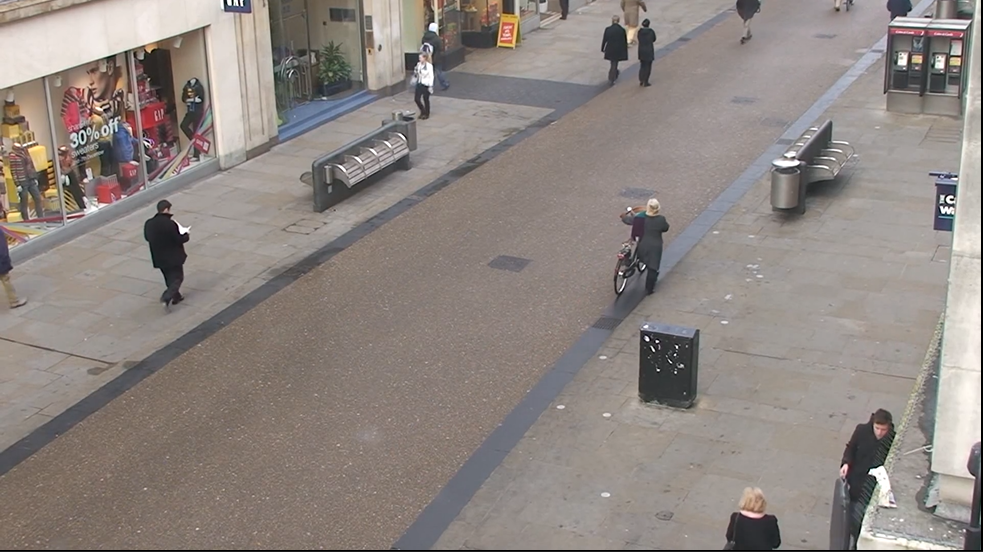

一張要跟蹤的行人的圖片

準(zhǔn)備工作
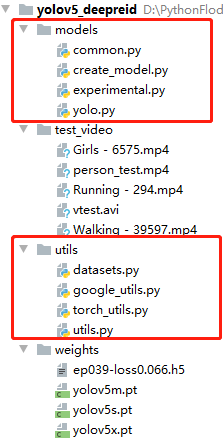
首先我們先clone一下yolov5的源碼,并下載好對應(yīng)的預(yù)訓(xùn)練模型,然后,新建一個項(xiàng)目,將Yolov5源碼中的models以及utils文件復(fù)制過來,并且,將我們行人重識別的模型和權(quán)重也分別復(fù)制到models與weights中.
接著,我們進(jìn)行編碼,首先導(dǎo)入依賴庫:
from utils.datasets import *from utils.utils import *import base64import osimport tensorflow as tfimport torchfrom models.create_model import Create_Modelimport heapqos.environ['CUDA_VISIBLE_DEVICES'] = "-1"print(torch.cuda.is_available())
接著,定義以下的三個函數(shù),用來進(jìn)行特征距離計算,以及物理距離計算:
# 獲得特征距離def person_distance(person_encodings, person_unknow):if len(person_encodings) == 0:return np.empty((0))l1 = np.sqrt(np.sum(np.square(person_encodings - person_unknow), axis=-1))return l1#判斷閾值def com_person(person_list, person, tolerance=1):dis = person_distance(person_list, person)return dis,list(dis <= tolerance)# 獲得最相似的行人def get_top1(centerxy_list, centerxy):centerxy_arr = np.array(centerxy_list)cenarr = np.array(centerxy)dis = list(np.sqrt(np.sum(np.square(centerxy_arr - cenarr), axis=-1)))min_num_index_list = map(dis.index, heapq.nsmallest(1, dis))return list(min_num_index_list)
關(guān)鍵代碼編寫
接著,是關(guān)鍵代碼的編寫,我們先定義一個run函數(shù),先加載模型與攝像頭,并進(jìn)行參數(shù)的定義:
def run():# 加載yolo檢測模型device = torch_utils.select_device('cpu')model = torch.load(model_path, map_location=device)['model']model.to(device).eval()input_size = (215, 90, 3)model_, pred_model = Create_Model(inpt=input_size, num_classes=1812)model_.load_weights('weights\ep039-loss0.066.h5')names = model.names if hasattr(model, 'names') else model.modules.names# 加載攝像頭video_capture = cv2.VideoCapture(Cam_num)video_FourCC = int(video_capture.get(cv2.CAP_PROP_FOURCC))video_fps = video_capture.get(cv2.CAP_PROP_FPS)video_size = (int(video_capture.get(cv2.CAP_PROP_FRAME_WIDTH)),int(video_capture.get(cv2.CAP_PROP_FRAME_HEIGHT)))out = cv2.VideoWriter('output.mp4', video_FourCC, video_fps, video_size)index = 0unknow_person_emb =[]center_xy = []know_center_xy_list=[]know_person_emb=None
然后,定義一個while循環(huán),用來讀取視頻流的數(shù)據(jù),進(jìn)行檢測與識別,這里代碼比較長,具體流程如下:
讀取每一幀的圖片進(jìn)行目標(biāo)檢測
過濾其他目標(biāo),只處理perosn目標(biāo)
獲取person目標(biāo)的ROI并提取特征
進(jìn)行特征距離以及物理距離的計算
判斷是否滿足識別閾值
識別成功進(jìn)行繪制
# 讀取視頻流數(shù)據(jù)while True:im0 = video_capture.read()iimage = im0.copy()# 數(shù)據(jù)標(biāo)準(zhǔn)化img = letterbox(im0, new_shape=image_size)[0]img = img[:, :, ::-1].transpose(2, 0, 1)img = np.ascontiguousarray(img)img = torch.from_numpy(img).to(device)img = img.half() if half else img.float() # uint8 to fp16/32img /= 255.0 # 0 - 255 to 0.0 - 1.0if img.ndimension() == 3:img = img.unsqueeze(0)# 目標(biāo)檢測計算pred = model(img, augment=False)[0]# uint8 to fp16/32if half:pred = pred.float()# 將目標(biāo)檢測的結(jié)果進(jìn)行NMS處理,去掉多余的框pred = non_max_suppression(pred, conf_thres, iou_thres,fast=True, classes=None, agnostic=False)# 循環(huán)處理獲取到的目標(biāo)數(shù)據(jù)for i, det in enumerate(pred):# 當(dāng)圖片中存在目標(biāo)時if det is not None and len(det):# 獲得目標(biāo)數(shù)據(jù):, :4] = scale_coords(img.shape[2:], det[:, :4], im0.shape).round()id = 0# 獲得目標(biāo)的 坐標(biāo),準(zhǔn)確度以及類別for *xyxy, conf, cls in det:# 這里我們只針對人這一類別進(jìn)行計算if names[int(cls)] == 'person':# 獲得左上角 以及右下角的坐標(biāo)c2 = (int(xyxy[0]), int(xyxy[1])), (int(xyxy[2]), int(xyxy[3]))# 獲得ROI 區(qū)域y_min = c1y_max = c2roi = iimage[y_min:y_max, x_min:x_max]roi = cv2.resize(roi,(90,215))# ROI數(shù)據(jù)標(biāo)準(zhǔn)化,進(jìn)入行人重識別別模型image_1 = np.asarray(roi).astype(np.float64) / 255photo1 = np.expand_dims(image_1 ,0)output1 = pred_model.predict(photo1)# 獲得中心點(diǎn)坐標(biāo)centerx = x_min+(x_max-x_min)/2centery = y_min+(y_max-y_min)/2=1# 如果當(dāng)前是第一幀,則提取已知圖片的特則,# 這一步可以放到前面進(jìn)行處理if index ==0:unknow_person_emb.append(output1)center_xy.append([centerx,centery])know_img = cv2.imread('person.jpg')know_img = cv2.resize(know_img,(90,215))know_img = np.asarray(know_img).astype(np.float64) / 255know_img = np.expand_dims(know_img, 0)know_person_emb = pred_model.predict(know_img)# 如果已經(jīng)不是第一幀了,就進(jìn)行識別else:# 獲得最為接近的行人特征以及坐標(biāo)# 這里使用上一幀以及當(dāng)前楨的坐標(biāo)進(jìn)行對比# 一般來說兩楨之間,行人的移動距離不會太大,我們用這個來輔助判斷min_index=get_top1(center_xy,[centerx,centery])# 獲得特征距離矩陣com_p = com_person(unknow_person_emb, know_person_emb, tolerance=0.8)# 如果最相似的行人的索引與特征距離矩陣中最小值的索引相同# 并且這個特征距離小于閾值,就說明找到了目標(biāo)if min_index[0] == dit.argmin() and com_p[dit.argmin()] == True:# 將識別結(jié)果繪制到圖片中label = 'ID-%s' % (1)im0, label=label, color=(0,255,0), line_thickness=5)# 更新坐標(biāo)以及特征=[centerx,centery]know_person_emb = output1# 只保存10個坐標(biāo)數(shù)據(jù) 用于繪制行走路徑if len(know_center_xy_list) < 10:centery])else:know_center_xy_list.remove(know_center_xy_list[0])centery])# 繪制目標(biāo)的行走路徑for i in range(1, len(know_center_xy_list)):y1 = know_center_xy_list[i - 1]y2 = know_center_xy_list[i](int(x1), int(y1)), (int(x2), int(y2)), (0, 255, 0), 2)# 未找到該人,進(jìn)行繪制else:unknow_person_emb.append(output1)centery])label = 'ID-%s' % ('unknow')im0, label=label, color=(0,0,255), line_thickness=5)# 將每一幀的圖片進(jìn)行保存out.write(im0)=1cv2.namedWindow('image',cv2.WINDOW_NORMAL)im0)if cv2.waitKey(1) == ord('q'):breakvideo_capture.release()out.release()cv2.destroyAllWindows()
程序運(yùn)行
最后,定義一些路徑以及參數(shù),即可右鍵運(yùn)行程序.
if __name__ == '__main__':# 基本設(shè)置model_path = 'weights\yolov5s.pt'hand_model_path = 'weights\hand_pose.h5'Cam_num = r'test_video\person_test.mp4'image_size = 416conf_thres = 0.4iou_thres = 0.4device = 'cpu'half = False# 運(yùn)行with torch.no_grad():run()
程序運(yùn)行結(jié)果如下:
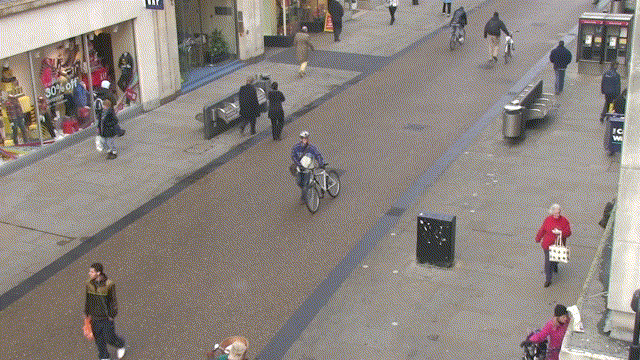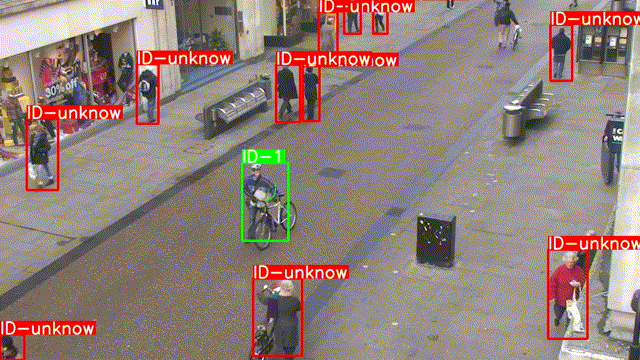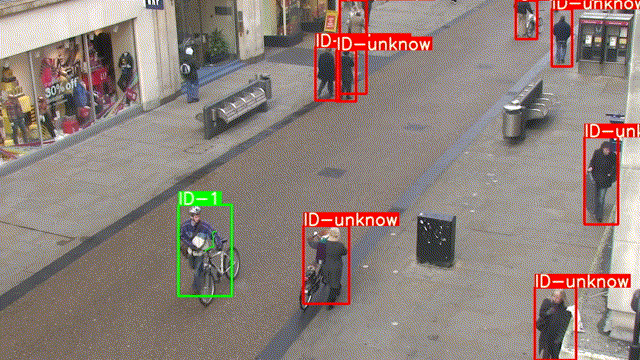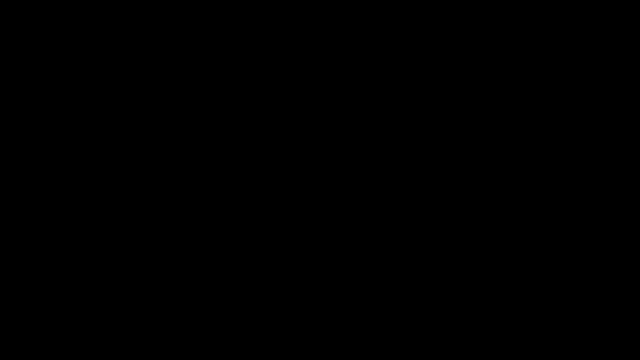
本章屬于單行人目標(biāo)跟蹤,在下一章中我們將實(shí)現(xiàn)多行人跟蹤,難度相對來說高了一點(diǎn),喜歡的同學(xué)記得關(guān)注噢!
