10 種聚類算法的完整 Python 操作示例
今天給大家分享一篇關于聚類的文章,10種聚類介紹和Python代碼。
聚類是在輸入數據的特征空間中查找自然組的無監(jiān)督問題。
對于所有數據集,有許多不同的聚類算法和單一的最佳方法。
在 scikit-learn 機器學習庫的 Python 中如何實現(xiàn)、適配和使用頂級聚類算法。
聚類
聚類算法
聚類算法示例
庫安裝
聚類數據集
親和力傳播
聚合聚類
BIRCH
DBSCAN
K-均值
Mini-Batch K-均值
Mean Shift
OPTICS
光譜聚類
高斯混合模型
一.聚類
聚類技術適用于沒有要預測的類,而是將實例劃分為自然組的情況。?
—源自:《數據挖掘頁:實用機器學習工具和技術》2016年。
這些群集可能反映出在從中繪制實例的域中工作的某種機制,這種機制使某些實例彼此具有比它們與其余實例更強的相似性。
—源自:《數據挖掘頁:實用機器學習工具和技術》2016年。
該進化樹可以被認為是人工聚類分析的結果; 將正常數據與異常值或異常分開可能會被認為是聚類問題; 根據自然行為將集群分開是一個集群問題,稱為市場細分。
聚類是一種無監(jiān)督學習技術,因此很難評估任何給定方法的輸出質量。
—源自:《機器學習頁:概率觀點》2012。
二.聚類算法
聚類分析的所有目標的核心是被群集的各個對象之間的相似程度(或不同程度)的概念。聚類方法嘗試根據提供給對象的相似性定義對對象進行分組。
—源自:《統(tǒng)計學習的要素:數據挖掘、推理和預測》,2016年
一些聚類算法要求您指定或猜測數據中要發(fā)現(xiàn)的群集的數量,而另一些算法要求指定觀測之間的最小距離,其中示例可以被視為“關閉”或“連接”。因此,聚類分析是一個迭代過程,在該過程中,對所識別的群集的主觀評估被反饋回算法配置的改變中,直到達到期望的或適當的結果。scikit-learn 庫提供了一套不同的聚類算法供選擇。下面列出了10種比較流行的算法:
親和力傳播
聚合聚類
BIRCH
DBSCAN
K-均值
Mini-Batch K-均值
Mean Shift
OPTICS
光譜聚類
高斯混合
三.聚類算法示例
首先,讓我們安裝庫。不要跳過此步驟,因為你需要確保安裝了最新版本。你可以使用 pip Python 安裝程序安裝 scikit-learn 存儲庫,如下所示:
sudo?pip?install?scikit-learn
#?檢查?scikit-learn?版本
import?sklearn
print(sklearn.__version__)
0.22.1
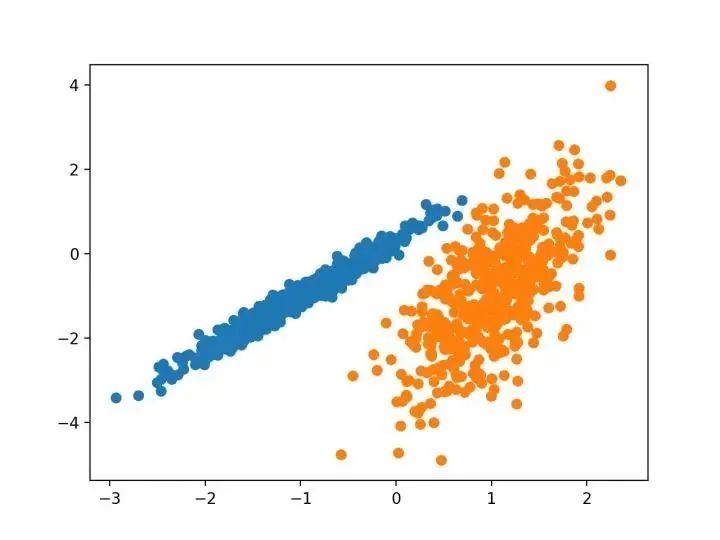
我們將使用 make _ classification ()函數創(chuàng)建一個測試二分類數據集。數據集將有1000個示例,每個類有兩個輸入要素和一個群集。這些群集在兩個維度上是可見的,因此我們可以用散點圖繪制數據,并通過指定的群集對圖中的點進行顏色繪制。
這將有助于了解,至少在測試問題上,群集的識別能力如何。該測試問題中的群集基于多變量高斯,并非所有聚類算法都能有效地識別這些類型的群集。因此,本教程中的結果不應用作比較一般方法的基礎。下面列出了創(chuàng)建和匯總合成聚類數據集的示例。
#?綜合分類數據集
from?numpy?import?where
from?sklearn.datasets?import?make_classification
from?matplotlib?import?pyplot
#?定義數據集
X,?y?=?make_classification(n_samples=1000,?n_features=2,?n_informative=2,?n_redundant=0,?n_clusters_per_class=1,?random_state=4)
#?為每個類的樣本創(chuàng)建散點圖
for?class_value?in?range(2):
#?獲取此類的示例的行索引
row_ix?=?where(y?==?class_value)
#?創(chuàng)建這些樣本的散布
pyplot.scatter(X[row_ix,?0],?X[row_ix,?1])
#?繪制散點圖
pyplot.show()
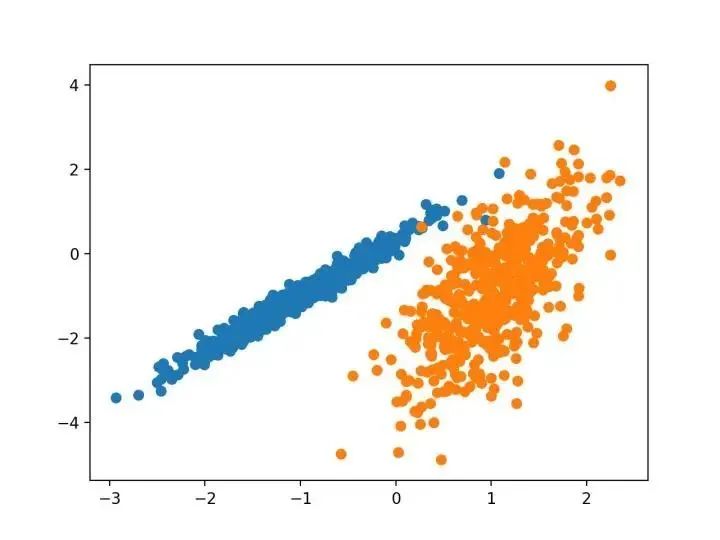
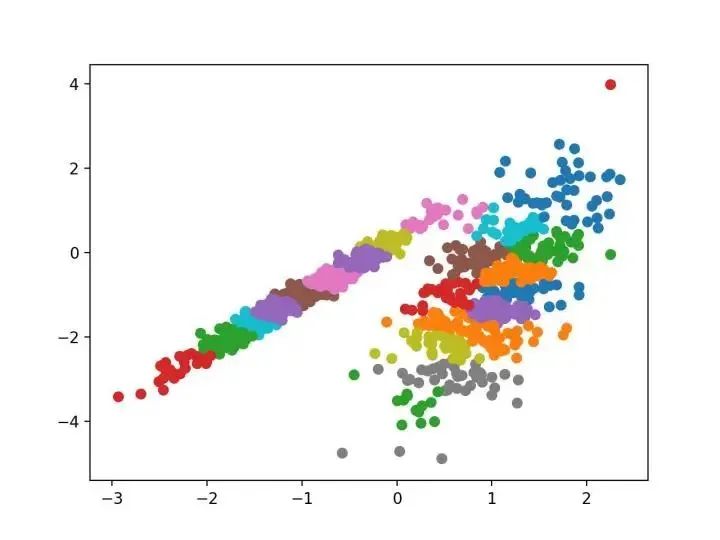
我們設計了一種名為“親和傳播”的方法,它作為兩對數據點之間相似度的輸入度量。在數據點之間交換實值消息,直到一組高質量的范例和相應的群集逐漸出現(xiàn)
—源自:《通過在數據點之間傳遞消息》2007。
它是通過 AffinityPropagation 類實現(xiàn)的,要調整的主要配置是將“ 阻尼 ”設置為0.5到1,甚至可能是“首選項”。
下面列出了完整的示例。
#?親和力傳播聚類
from?numpy?import?unique
from?numpy?import?where
from?sklearn.datasets?import?make_classification
from?sklearn.cluster?import?AffinityPropagation
from?matplotlib?import?pyplot
#?定義數據集
X,?_?=?make_classification(n_samples=1000,?n_features=2,?n_informative=2,?n_redundant=0,?n_clusters_per_class=1,?random_state=4)
#?定義模型
model?=?AffinityPropagation(damping=0.9)
#?匹配模型
model.fit(X)
#?為每個示例分配一個集群
yhat?=?model.predict(X)
#?檢索唯一群集
clusters?=?unique(yhat)
#?為每個群集的樣本創(chuàng)建散點圖
for?cluster?in?clusters:
#?獲取此群集的示例的行索引
row_ix?=?where(yhat?==?cluster)
#?創(chuàng)建這些樣本的散布
pyplot.scatter(X[row_ix,?0],?X[row_ix,?1])
#?繪制散點圖
pyplot.show()
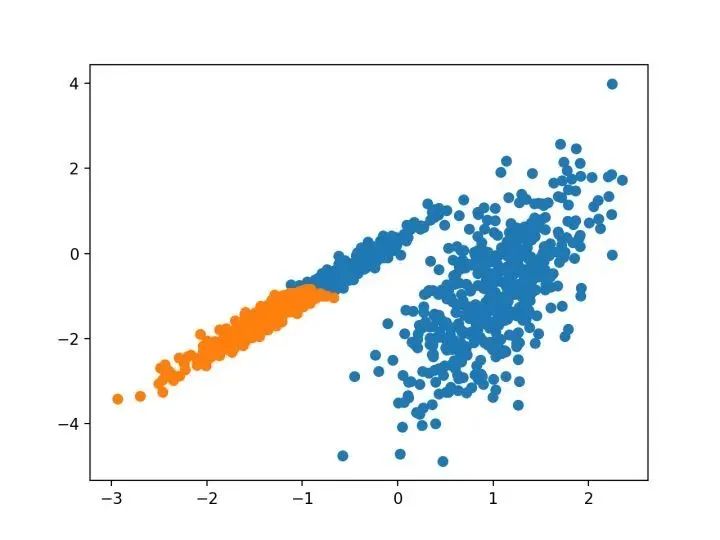
#?聚合聚類
from?numpy?import?unique
from?numpy?import?where
from?sklearn.datasets?import?make_classification
from?sklearn.cluster?import?AgglomerativeClustering
from?matplotlib?import?pyplot
#?定義數據集
X,?_?=?make_classification(n_samples=1000,?n_features=2,?n_informative=2,?n_redundant=0,?n_clusters_per_class=1,?random_state=4)
#?定義模型
model?=?AgglomerativeClustering(n_clusters=2)
#?模型擬合與聚類預測
yhat?=?model.fit_predict(X)
#?檢索唯一群集
clusters?=?unique(yhat)
#?為每個群集的樣本創(chuàng)建散點圖
for?cluster?in?clusters:
#?獲取此群集的示例的行索引
row_ix?=?where(yhat?==?cluster)
#?創(chuàng)建這些樣本的散布
pyplot.scatter(X[row_ix,?0],?X[row_ix,?1])
#?繪制散點圖
pyplot.show()
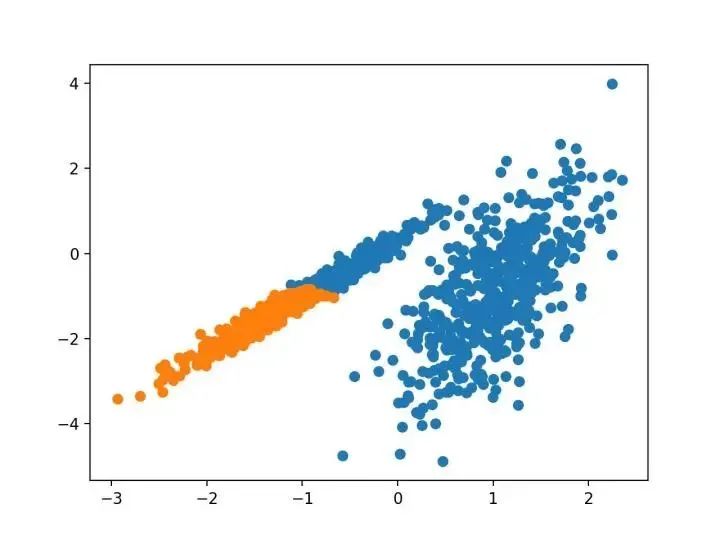
BIRCH 遞增地和動態(tài)地群集傳入的多維度量數據點,以嘗試利用可用資源(即可用內存和時間約束)產生最佳質量的聚類。
—源自:《 BIRCH :1996年大型數據庫的高效數據聚類方法》
#?birch聚類
from?numpy?import?unique
from?numpy?import?where
from?sklearn.datasets?import?make_classification
from?sklearn.cluster?import?Birch
from?matplotlib?import?pyplot
#?定義數據集
X,?_?=?make_classification(n_samples=1000,?n_features=2,?n_informative=2,?n_redundant=0,?n_clusters_per_class=1,?random_state=4)
#?定義模型
model?=?Birch(threshold=0.01,?n_clusters=2)
#?適配模型
model.fit(X)
#?為每個示例分配一個集群
yhat?=?model.predict(X)
#?檢索唯一群集
clusters?=?unique(yhat)
#?為每個群集的樣本創(chuàng)建散點圖
for?cluster?in?clusters:
#?獲取此群集的示例的行索引
row_ix?=?where(yhat?==?cluster)
#?創(chuàng)建這些樣本的散布
pyplot.scatter(X[row_ix,?0],?X[row_ix,?1])
#?繪制散點圖
pyplot.show()
…我們提出了新的聚類算法 DBSCAN 依賴于基于密度的概念的集群設計,以發(fā)現(xiàn)任意形狀的集群。DBSCAN 只需要一個輸入參數,并支持用戶為其確定適當的值
-源自:《基于密度的噪聲大空間數據庫聚類發(fā)現(xiàn)算法》,1996
它是通過 DBSCAN 類實現(xiàn)的,主要配置是“ eps ”和“ min _ samples ”超參數。
下面列出了完整的示例。
#?dbscan?聚類
from?numpy?import?unique
from?numpy?import?where
from?sklearn.datasets?import?make_classification
from?sklearn.cluster?import?DBSCAN
from?matplotlib?import?pyplot
#?定義數據集
X,?_?=?make_classification(n_samples=1000,?n_features=2,?n_informative=2,?n_redundant=0,?n_clusters_per_class=1,?random_state=4)
#?定義模型
model?=?DBSCAN(eps=0.30,?min_samples=9)
#?模型擬合與聚類預測
yhat?=?model.fit_predict(X)
#?檢索唯一群集
clusters?=?unique(yhat)
#?為每個群集的樣本創(chuàng)建散點圖
for?cluster?in?clusters:
#?獲取此群集的示例的行索引
row_ix?=?where(yhat?==?cluster)
#?創(chuàng)建這些樣本的散布
pyplot.scatter(X[row_ix,?0],?X[row_ix,?1])
#?繪制散點圖
pyplot.show()
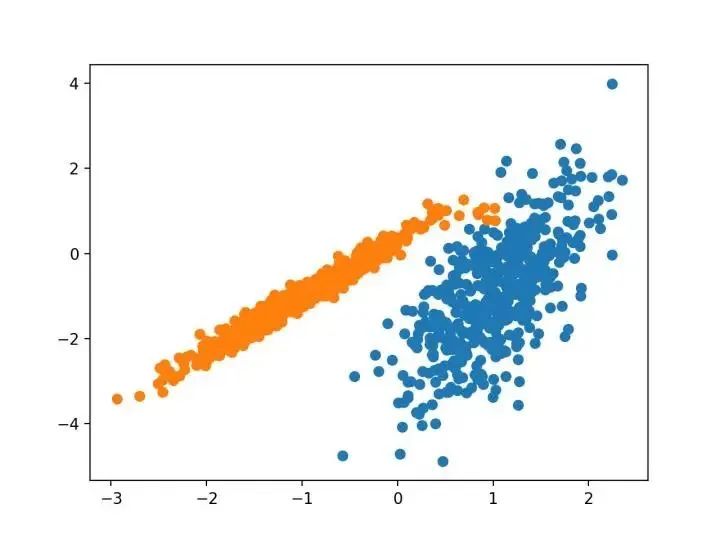
本文的主要目的是描述一種基于樣本將 N 維種群劃分為 k 個集合的過程。這個叫做“ K-均值”的過程似乎給出了在類內方差意義上相當有效的分區(qū)。
-源自:《關于多元觀測的分類和分析的一些方法》1967年
#?k-means?聚類
from?numpy?import?unique
from?numpy?import?where
from?sklearn.datasets?import?make_classification
from?sklearn.cluster?import?KMeans
from?matplotlib?import?pyplot
#?定義數據集
X,?_?=?make_classification(n_samples=1000,?n_features=2,?n_informative=2,?n_redundant=0,?n_clusters_per_class=1,?random_state=4)
#?定義模型
model?=?KMeans(n_clusters=2)
#?模型擬合
model.fit(X)
#?為每個示例分配一個集群
yhat?=?model.predict(X)
#?檢索唯一群集
clusters?=?unique(yhat)
#?為每個群集的樣本創(chuàng)建散點圖
for?cluster?in?clusters:
#?獲取此群集的示例的行索引
row_ix?=?where(yhat?==?cluster)
#?創(chuàng)建這些樣本的散布
pyplot.scatter(X[row_ix,?0],?X[row_ix,?1])
#?繪制散點圖
pyplot.show()
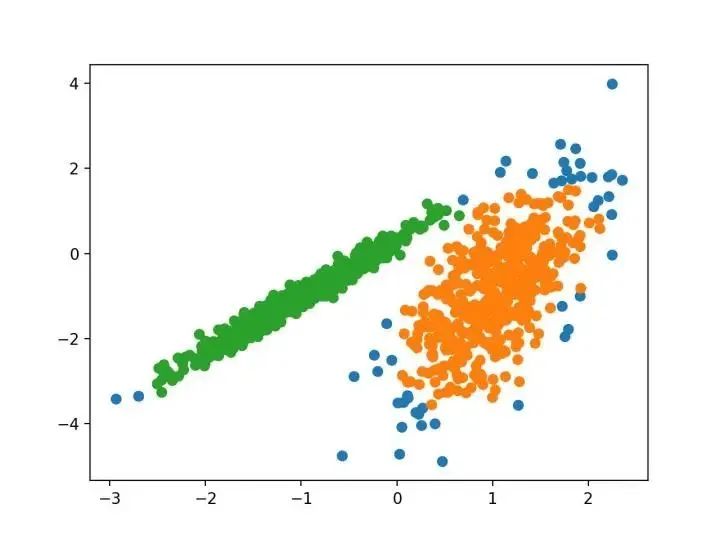
...我們建議使用 k-均值聚類的迷你批量優(yōu)化。與經典批處理算法相比,這降低了計算成本的數量級,同時提供了比在線隨機梯度下降更好的解決方案。
—源自:《Web-Scale K-均值聚類》2010
#?mini-batch?k均值聚類
from?numpy?import?unique
from?numpy?import?where
from?sklearn.datasets?import?make_classification
from?sklearn.cluster?import?MiniBatchKMeans
from?matplotlib?import?pyplot
#?定義數據集
X,?_?=?make_classification(n_samples=1000,?n_features=2,?n_informative=2,?n_redundant=0,?n_clusters_per_class=1,?random_state=4)
#?定義模型
model?=?MiniBatchKMeans(n_clusters=2)
#?模型擬合
model.fit(X)
#?為每個示例分配一個集群
yhat?=?model.predict(X)
#?檢索唯一群集
clusters?=?unique(yhat)
#?為每個群集的樣本創(chuàng)建散點圖
for?cluster?in?clusters:
#?獲取此群集的示例的行索引
row_ix?=?where(yhat?==?cluster)
#?創(chuàng)建這些樣本的散布
pyplot.scatter(X[row_ix,?0],?X[row_ix,?1])
#?繪制散點圖
pyplot.show()
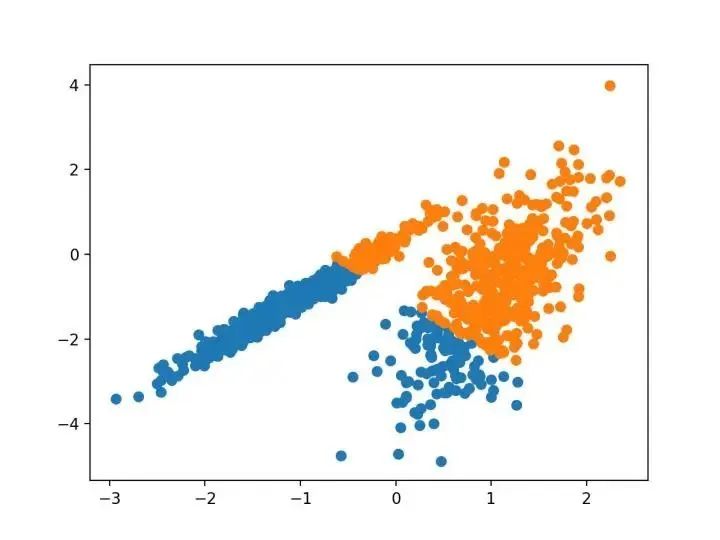
對離散數據證明了遞推平均移位程序收斂到最接近駐點的基礎密度函數,從而證明了它在檢測密度模式中的應用。
—源自:《Mean Shift :面向特征空間分析的穩(wěn)健方法》,2002
#?均值漂移聚類
from?numpy?import?unique
from?numpy?import?where
from?sklearn.datasets?import?make_classification
from?sklearn.cluster?import?MeanShift
from?matplotlib?import?pyplot
#?定義數據集
X,?_?=?make_classification(n_samples=1000,?n_features=2,?n_informative=2,?n_redundant=0,?n_clusters_per_class=1,?random_state=4)
#?定義模型
model?=?MeanShift()
#?模型擬合與聚類預測
yhat?=?model.fit_predict(X)
#?檢索唯一群集
clusters?=?unique(yhat)
#?為每個群集的樣本創(chuàng)建散點圖
for?cluster?in?clusters:
#?獲取此群集的示例的行索引
row_ix?=?where(yhat?==?cluster)
#?創(chuàng)建這些樣本的散布
pyplot.scatter(X[row_ix,?0],?X[row_ix,?1])
#?繪制散點圖
pyplot.show()
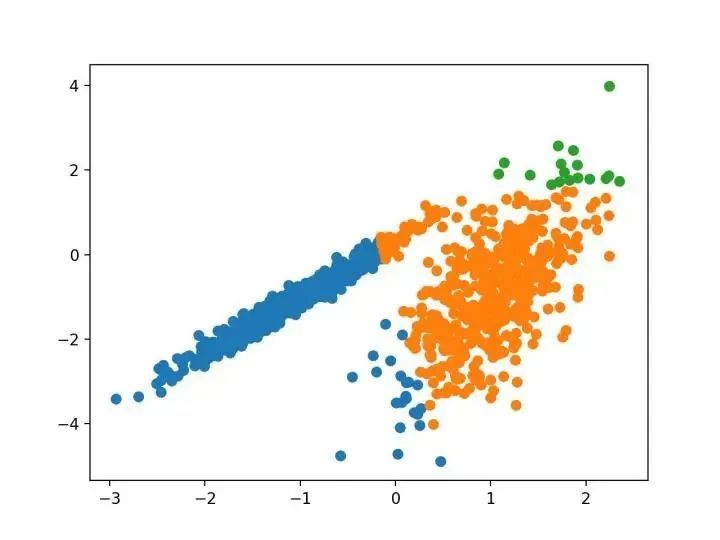
我們?yōu)榫垲惙治鲆肓艘环N新的算法,它不會顯式地生成一個數據集的聚類;而是創(chuàng)建表示其基于密度的聚類結構的數據庫的增強排序。此群集排序包含相當于密度聚類的信息,該信息對應于范圍廣泛的參數設置。
—源自:《OPTICS :排序點以標識聚類結構》,1999
#?optics聚類
from?numpy?import?unique
from?numpy?import?where
from?sklearn.datasets?import?make_classification
from?sklearn.cluster?import?OPTICS
from?matplotlib?import?pyplot
#?定義數據集
X,?_?=?make_classification(n_samples=1000,?n_features=2,?n_informative=2,?n_redundant=0,?n_clusters_per_class=1,?random_state=4)
#?定義模型
model?=?OPTICS(eps=0.8,?min_samples=10)
#?模型擬合與聚類預測
yhat?=?model.fit_predict(X)
#?檢索唯一群集
clusters?=?unique(yhat)
#?為每個群集的樣本創(chuàng)建散點圖
for?cluster?in?clusters:
#?獲取此群集的示例的行索引
row_ix?=?where(yhat?==?cluster)
#?創(chuàng)建這些樣本的散布
pyplot.scatter(X[row_ix,?0],?X[row_ix,?1])
#?繪制散點圖
pyplot.show()
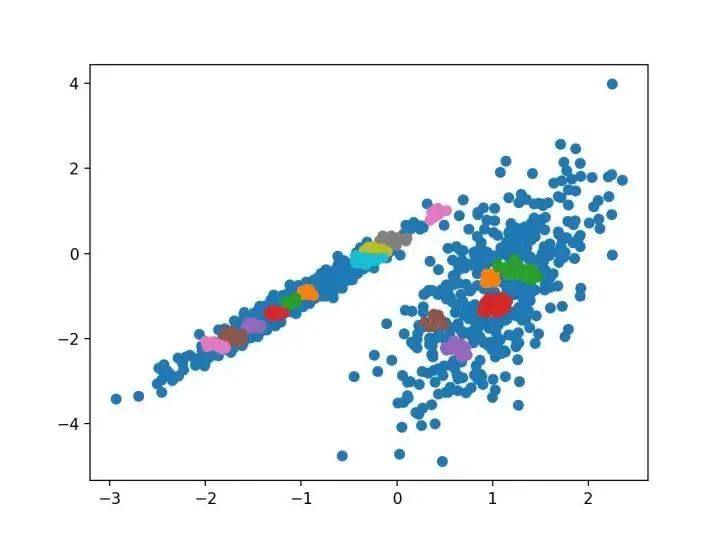
最近在許多領域出現(xiàn)的一個有希望的替代方案是使用聚類的光譜方法。這里,使用從點之間的距離導出的矩陣的頂部特征向量。
—源自:《關于光譜聚類:分析和算法》,2002年
#?spectral?clustering
from?numpy?import?unique
from?numpy?import?where
from?sklearn.datasets?import?make_classification
from?sklearn.cluster?import?SpectralClustering
from?matplotlib?import?pyplot
#?定義數據集
X,?_?=?make_classification(n_samples=1000,?n_features=2,?n_informative=2,?n_redundant=0,?n_clusters_per_class=1,?random_state=4)
#?定義模型
model?=?SpectralClustering(n_clusters=2)
#?模型擬合與聚類預測
yhat?=?model.fit_predict(X)
#?檢索唯一群集
clusters?=?unique(yhat)
#?為每個群集的樣本創(chuàng)建散點圖
for?cluster?in?clusters:
#?獲取此群集的示例的行索引
row_ix?=?where(yhat?==?cluster)
#?創(chuàng)建這些樣本的散布
pyplot.scatter(X[row_ix,?0],?X[row_ix,?1])
#?繪制散點圖
pyplot.show()
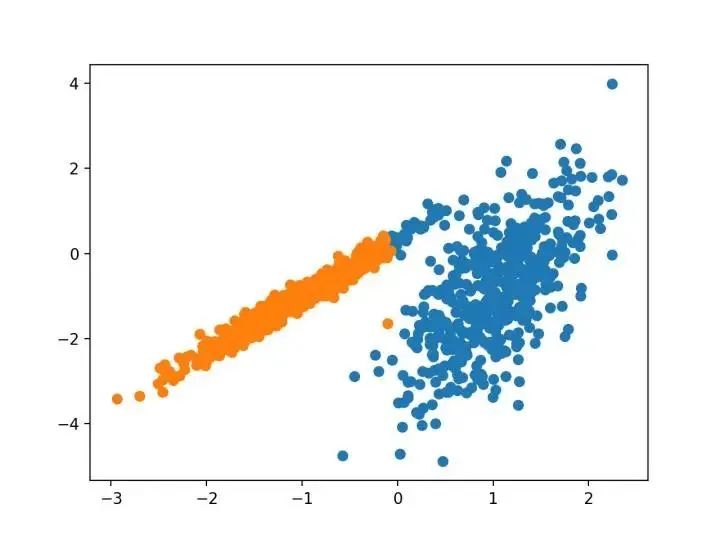
#?高斯混合模型
from?numpy?import?unique
from?numpy?import?where
from?sklearn.datasets?import?make_classification
from?sklearn.mixture?import?GaussianMixture
from?matplotlib?import?pyplot
#?定義數據集
X,?_?=?make_classification(n_samples=1000,?n_features=2,?n_informative=2,?n_redundant=0,?n_clusters_per_class=1,?random_state=4)
#?定義模型
model?=?GaussianMixture(n_components=2)
#?模型擬合
model.fit(X)
#?為每個示例分配一個集群
yhat?=?model.predict(X)
#?檢索唯一群集
clusters?=?unique(yhat)
#?為每個群集的樣本創(chuàng)建散點圖
for?cluster?in?clusters:
#?獲取此群集的示例的行索引
row_ix?=?where(yhat?==?cluster)
#?創(chuàng)建這些樣本的散布
pyplot.scatter(X[row_ix,?0],?X[row_ix,?1])
#?繪制散點圖
pyplot.show()
三.總結
聚類是在特征空間輸入數據中發(fā)現(xiàn)自然組的無監(jiān)督問題。
有許多不同的聚類算法,對于所有數據集沒有單一的最佳方法。
在 scikit-learn 機器學習庫的 Python 中如何實現(xiàn)、適合和使用頂級聚類算法。
