10 種聚類算法的完整 Python 操作示例

來源:海豚數(shù)據(jù)科學(xué)實(shí)驗(yàn)室 本文約7000字,建議閱讀14分鐘
本文將介紹一篇關(guān)于聚類的文章,10種聚類介紹和Python代碼。
聚類是在輸入數(shù)據(jù)的特征空間中查找自然組的無(wú)監(jiān)督問題。 對(duì)于所有數(shù)據(jù)集,有許多不同的聚類算法和單一的最佳方法。 在 scikit-learn 機(jī)器學(xué)習(xí)庫(kù)的 Python 中如何實(shí)現(xiàn)、適配和使用頂級(jí)聚類算法。
聚類 聚類算法 聚類算法示例
庫(kù)安裝 聚類數(shù)據(jù)集 親和力傳播 聚合聚類 BIRCH DBSCAN K-均值 Mini-Batch K-均值 Mean Shift OPTICS 光譜聚類 高斯混合模型
一. 聚類
聚類分析,即聚類,是一項(xiàng)無(wú)監(jiān)督的機(jī)器學(xué)習(xí)任務(wù)。它包括自動(dòng)發(fā)現(xiàn)數(shù)據(jù)中的自然分組。與監(jiān)督學(xué)習(xí)(類似預(yù)測(cè)建模)不同,聚類算法只解釋輸入數(shù)據(jù),并在特征空間中找到自然組或群集。
聚類技術(shù)適用于沒有要預(yù)測(cè)的類,而是將實(shí)例劃分為自然組的情況。? —源自:《數(shù)據(jù)挖掘頁(yè):實(shí)用機(jī)器學(xué)習(xí)工具和技術(shù)》2016年。
這些群集可能反映出在從中繪制實(shí)例的域中工作的某種機(jī)制,這種機(jī)制使某些實(shí)例彼此具有比它們與其余實(shí)例更強(qiáng)的相似性。 —源自:《數(shù)據(jù)挖掘頁(yè):實(shí)用機(jī)器學(xué)習(xí)工具和技術(shù)》2016年。
該進(jìn)化樹可以被認(rèn)為是人工聚類分析的結(jié)果; 將正常數(shù)據(jù)與異常值或異常分開可能會(huì)被認(rèn)為是聚類問題; 根據(jù)自然行為將集群分開是一個(gè)集群?jiǎn)栴},稱為市場(chǎng)細(xì)分。
聚類是一種無(wú)監(jiān)督學(xué)習(xí)技術(shù),因此很難評(píng)估任何給定方法的輸出質(zhì)量。 —源自:《機(jī)器學(xué)習(xí)頁(yè):概率觀點(diǎn)》2012。
二. 聚類算法
有許多類型的聚類算法。許多算法在特征空間中的示例之間使用相似度或距離度量,以發(fā)現(xiàn)密集的觀測(cè)區(qū)域。因此,在使用聚類算法之前,擴(kuò)展數(shù)據(jù)通常是良好的實(shí)踐。
聚類分析的所有目標(biāo)的核心是被群集的各個(gè)對(duì)象之間的相似程度(或不同程度)的概念。聚類方法嘗試根據(jù)提供給對(duì)象的相似性定義對(duì)對(duì)象進(jìn)行分組。 —源自:《統(tǒng)計(jì)學(xué)習(xí)的要素:數(shù)據(jù)挖掘、推理和預(yù)測(cè)》,2016年
親和力傳播 聚合聚類 BIRCH DBSCAN K-均值 Mini-Batch K-均值 Mean Shift OPTICS 光譜聚類 高斯混合
三. 聚類算法示例
sudo pip install scikit-learn
# 檢查 scikit-learn 版本import sklearnprint(sklearn.__version__)
0.22.1
# 綜合分類數(shù)據(jù)集from numpy import wherefrom sklearn.datasets import make_classificationfrom matplotlib import pyplot# 定義數(shù)據(jù)集X, y = make_classification(n_samples=1000, n_features=2, n_informative=2, n_redundant=0, n_clusters_per_class=1, random_state=4)# 為每個(gè)類的樣本創(chuàng)建散點(diǎn)圖for class_value in range(2):# 獲取此類的示例的行索引row_ix = where(y == class_value)# 創(chuàng)建這些樣本的散布pyplot.scatter(X[row_ix, 0], X[row_ix, 1])# 繪制散點(diǎn)圖pyplot.show()
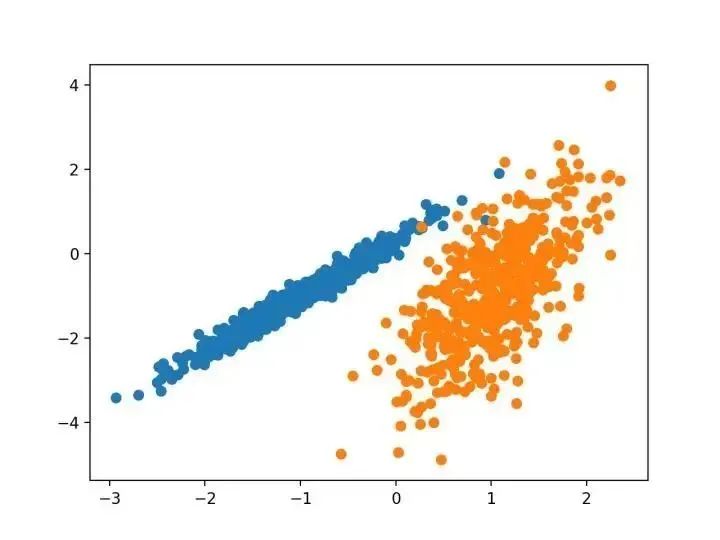
已知聚類著色點(diǎn)的合成聚類數(shù)據(jù)集的散點(diǎn)圖
接下來,我們可以開始查看應(yīng)用于此數(shù)據(jù)集的聚類算法的示例。我已經(jīng)做了一些最小的嘗試來調(diào)整每個(gè)方法到數(shù)據(jù)集。
3.親和力傳播
親和力傳播包括找到一組最能概括數(shù)據(jù)的范例。
我們?cè)O(shè)計(jì)了一種名為“親和傳播”的方法,它作為兩對(duì)數(shù)據(jù)點(diǎn)之間相似度的輸入度量。在數(shù)據(jù)點(diǎn)之間交換實(shí)值消息,直到一組高質(zhì)量的范例和相應(yīng)的群集逐漸出現(xiàn) —源自:《通過在數(shù)據(jù)點(diǎn)之間傳遞消息》2007。
# 親和力傳播聚類from numpy import uniquefrom numpy import wherefrom sklearn.datasets import make_classificationfrom sklearn.cluster import AffinityPropagationfrom matplotlib import pyplot# 定義數(shù)據(jù)集X, _ = make_classification(n_samples=1000, n_features=2, n_informative=2, n_redundant=0, n_clusters_per_class=1, random_state=4)# 定義模型model = AffinityPropagation(damping=0.9)# 匹配模型model.fit(X)# 為每個(gè)示例分配一個(gè)集群yhat = model.predict(X)# 檢索唯一群集clusters = unique(yhat)# 為每個(gè)群集的樣本創(chuàng)建散點(diǎn)圖for cluster in clusters:# 獲取此群集的示例的行索引row_ix = where(yhat == cluster)# 創(chuàng)建這些樣本的散布pyplot.scatter(X[row_ix, 0], X[row_ix, 1])# 繪制散點(diǎn)圖pyplot.show()
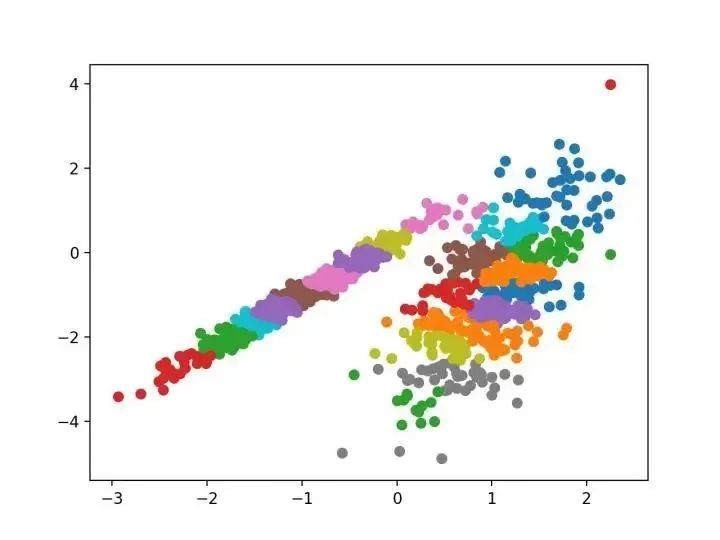
# 聚合聚類from numpy import uniquefrom numpy import wherefrom sklearn.datasets import make_classificationfrom sklearn.cluster import AgglomerativeClusteringfrom matplotlib import pyplot# 定義數(shù)據(jù)集X, _ = make_classification(n_samples=1000, n_features=2, n_informative=2, n_redundant=0, n_clusters_per_class=1, random_state=4)# 定義模型model = AgglomerativeClustering(n_clusters=2)# 模型擬合與聚類預(yù)測(cè)yhat = model.fit_predict(X)# 檢索唯一群集clusters = unique(yhat)# 為每個(gè)群集的樣本創(chuàng)建散點(diǎn)圖for cluster in clusters:# 獲取此群集的示例的行索引row_ix = where(yhat == cluster)# 創(chuàng)建這些樣本的散布pyplot.scatter(X[row_ix, 0], X[row_ix, 1])# 繪制散點(diǎn)圖pyplot.show()
BIRCH 遞增地和動(dòng)態(tài)地群集傳入的多維度量數(shù)據(jù)點(diǎn),以嘗試?yán)每捎觅Y源(即可用內(nèi)存和時(shí)間約束)產(chǎn)生最佳質(zhì)量的聚類。 —源自:《 BIRCH :1996年大型數(shù)據(jù)庫(kù)的高效數(shù)據(jù)聚類方法》
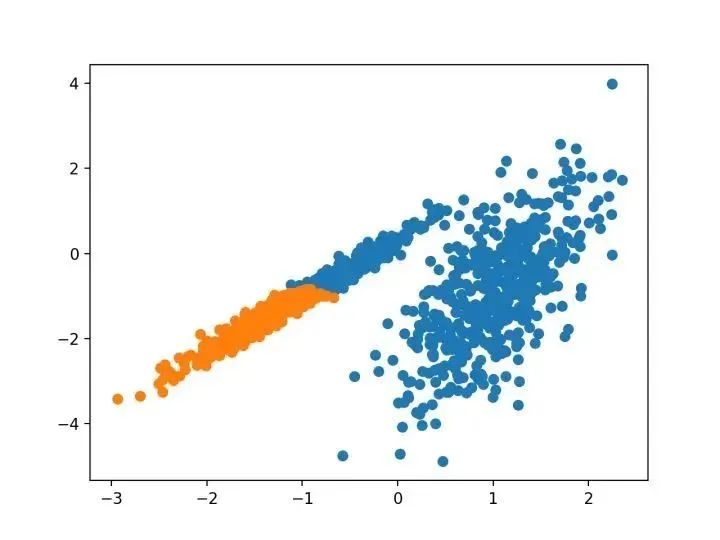
# birch聚類from numpy import uniquefrom numpy import wherefrom sklearn.datasets import make_classificationfrom sklearn.cluster import Birchfrom matplotlib import pyplot# 定義數(shù)據(jù)集X, _ = make_classification(n_samples=1000, n_features=2, n_informative=2, n_redundant=0, n_clusters_per_class=1, random_state=4)# 定義模型model = Birch(threshold=0.01, n_clusters=2)# 適配模型model.fit(X)# 為每個(gè)示例分配一個(gè)集群yhat = model.predict(X)# 檢索唯一群集clusters = unique(yhat)# 為每個(gè)群集的樣本創(chuàng)建散點(diǎn)圖for cluster in clusters:# 獲取此群集的示例的行索引row_ix = where(yhat == cluster)# 創(chuàng)建這些樣本的散布pyplot.scatter(X[row_ix, 0], X[row_ix, 1])# 繪制散點(diǎn)圖pyplot.show()
 使用BIRCH聚類確定具有聚類的數(shù)據(jù)集的散點(diǎn)圖
使用BIRCH聚類確定具有聚類的數(shù)據(jù)集的散點(diǎn)圖
…我們提出了新的聚類算法 DBSCAN 依賴于基于密度的概念的集群設(shè)計(jì),以發(fā)現(xiàn)任意形狀的集群。DBSCAN 只需要一個(gè)輸入?yún)?shù),并支持用戶為其確定適當(dāng)?shù)闹?/span> -源自:《基于密度的噪聲大空間數(shù)據(jù)庫(kù)聚類發(fā)現(xiàn)算法》,1996
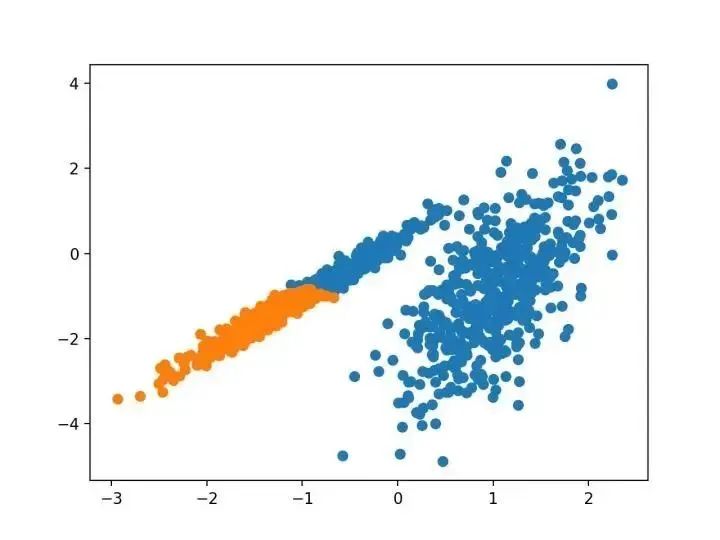
# dbscan 聚類from numpy import uniquefrom numpy import wherefrom sklearn.datasets import make_classificationfrom sklearn.cluster import DBSCANfrom matplotlib import pyplot# 定義數(shù)據(jù)集X, _ = make_classification(n_samples=1000, n_features=2, n_informative=2, n_redundant=0, n_clusters_per_class=1, random_state=4)# 定義模型model = DBSCAN(eps=0.30, min_samples=9)# 模型擬合與聚類預(yù)測(cè)yhat = model.fit_predict(X)# 檢索唯一群集clusters = unique(yhat)# 為每個(gè)群集的樣本創(chuàng)建散點(diǎn)圖for cluster in clusters:# 獲取此群集的示例的行索引row_ix = where(yhat == cluster)# 創(chuàng)建這些樣本的散布pyplot.scatter(X[row_ix, 0], X[row_ix, 1])# 繪制散點(diǎn)圖pyplot.show()
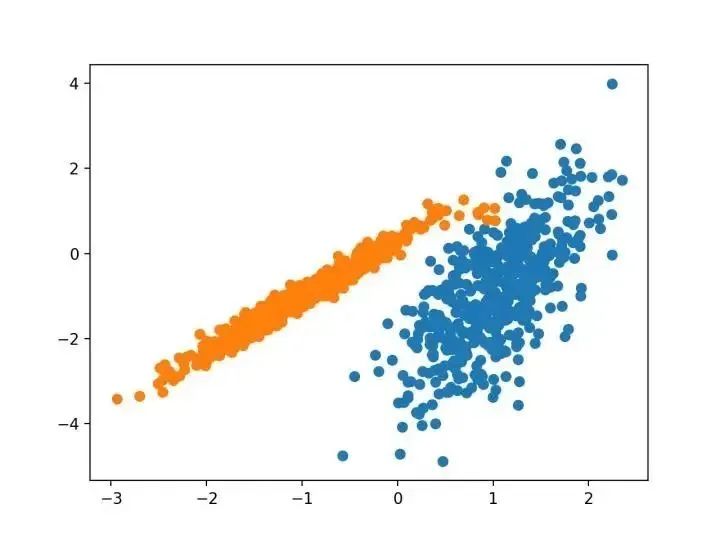
本文的主要目的是描述一種基于樣本將 N 維種群劃分為 k 個(gè)集合的過程。這個(gè)叫做“ K-均值”的過程似乎給出了在類內(nèi)方差意義上相當(dāng)有效的分區(qū)。 -源自:《關(guān)于多元觀測(cè)的分類和分析的一些方法》1967年
# k-means 聚類from numpy import uniquefrom numpy import wherefrom sklearn.datasets import make_classificationfrom sklearn.cluster import KMeansfrom matplotlib import pyplot# 定義數(shù)據(jù)集X, _ = make_classification(n_samples=1000, n_features=2, n_informative=2, n_redundant=0, n_clusters_per_class=1, random_state=4)# 定義模型model = KMeans(n_clusters=2)# 模型擬合model.fit(X)# 為每個(gè)示例分配一個(gè)集群yhat = model.predict(X)# 檢索唯一群集clusters = unique(yhat)# 為每個(gè)群集的樣本創(chuàng)建散點(diǎn)圖for cluster in clusters:# 獲取此群集的示例的行索引row_ix = where(yhat == cluster)# 創(chuàng)建這些樣本的散布pyplot.scatter(X[row_ix, 0], X[row_ix, 1])# 繪制散點(diǎn)圖pyplot.show()
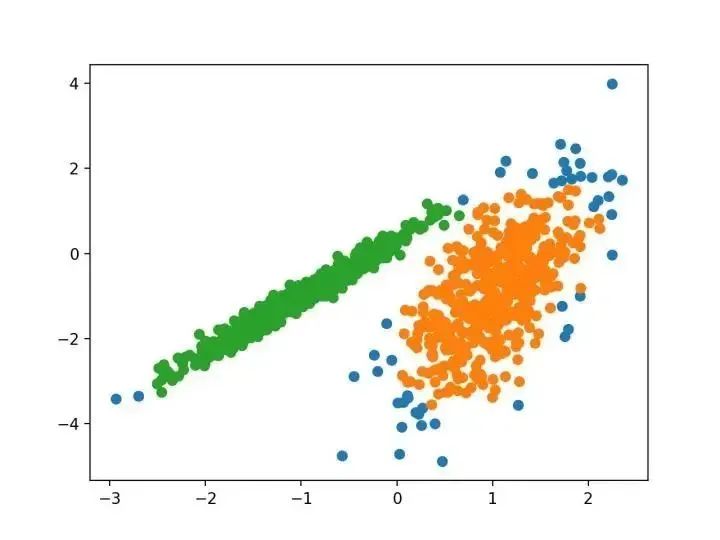
...我們建議使用 k-均值聚類的迷你批量?jī)?yōu)化。與經(jīng)典批處理算法相比,這降低了計(jì)算成本的數(shù)量級(jí),同時(shí)提供了比在線隨機(jī)梯度下降更好的解決方案。 —源自:《Web-Scale K-均值聚類》2010
# mini-batch k均值聚類from numpy import uniquefrom numpy import wherefrom sklearn.datasets import make_classificationfrom sklearn.cluster import MiniBatchKMeansfrom matplotlib import pyplot# 定義數(shù)據(jù)集X, _ = make_classification(n_samples=1000, n_features=2, n_informative=2, n_redundant=0, n_clusters_per_class=1, random_state=4)# 定義模型model = MiniBatchKMeans(n_clusters=2)# 模型擬合model.fit(X)# 為每個(gè)示例分配一個(gè)集群yhat = model.predict(X)# 檢索唯一群集clusters = unique(yhat)# 為每個(gè)群集的樣本創(chuàng)建散點(diǎn)圖for cluster in clusters:# 獲取此群集的示例的行索引row_ix = where(yhat == cluster)# 創(chuàng)建這些樣本的散布pyplot.scatter(X[row_ix, 0], X[row_ix, 1])# 繪制散點(diǎn)圖pyplot.show()
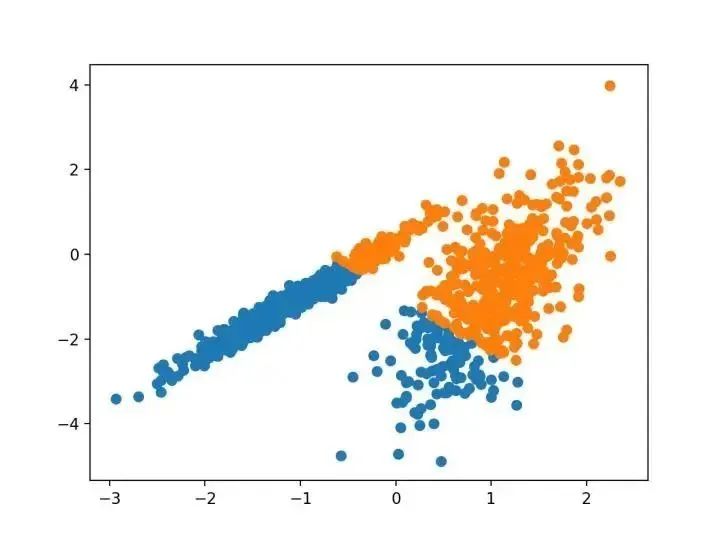
對(duì)離散數(shù)據(jù)證明了遞推平均移位程序收斂到最接近駐點(diǎn)的基礎(chǔ)密度函數(shù),從而證明了它在檢測(cè)密度模式中的應(yīng)用。 —源自:《Mean Shift :面向特征空間分析的穩(wěn)健方法》,2002
# 均值漂移聚類from numpy import uniquefrom numpy import wherefrom sklearn.datasets import make_classificationfrom sklearn.cluster import MeanShiftfrom matplotlib import pyplot# 定義數(shù)據(jù)集X, _ = make_classification(n_samples=1000, n_features=2, n_informative=2, n_redundant=0, n_clusters_per_class=1, random_state=4)# 定義模型model = MeanShift()# 模型擬合與聚類預(yù)測(cè)yhat = model.fit_predict(X)# 檢索唯一群集clusters = unique(yhat)# 為每個(gè)群集的樣本創(chuàng)建散點(diǎn)圖for cluster in clusters:# 獲取此群集的示例的行索引row_ix = where(yhat == cluster)# 創(chuàng)建這些樣本的散布pyplot.scatter(X[row_ix, 0], X[row_ix, 1])# 繪制散點(diǎn)圖pyplot.show()
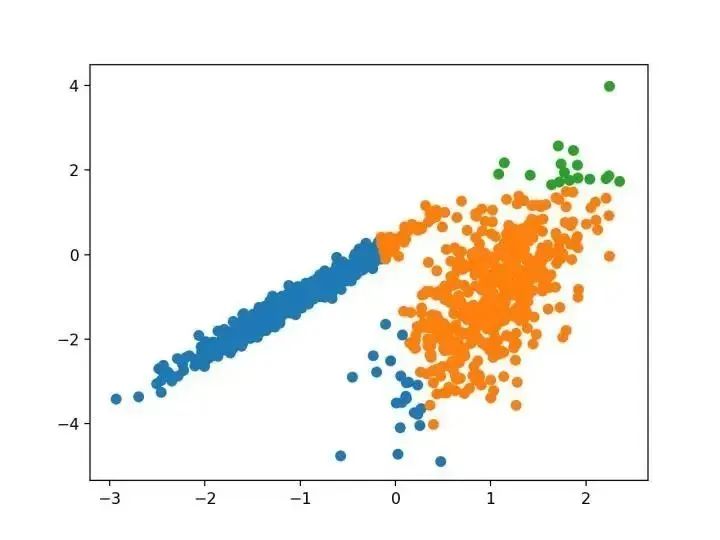
我們?yōu)榫垲惙治鲆肓艘环N新的算法,它不會(huì)顯式地生成一個(gè)數(shù)據(jù)集的聚類;而是創(chuàng)建表示其基于密度的聚類結(jié)構(gòu)的數(shù)據(jù)庫(kù)的增強(qiáng)排序。此群集排序包含相當(dāng)于密度聚類的信息,該信息對(duì)應(yīng)于范圍廣泛的參數(shù)設(shè)置。 —源自:《OPTICS :排序點(diǎn)以標(biāo)識(shí)聚類結(jié)構(gòu)》,1999
# optics聚類from numpy import uniquefrom numpy import wherefrom sklearn.datasets import make_classificationfrom sklearn.cluster import OPTICSfrom matplotlib import pyplot# 定義數(shù)據(jù)集X, _ = make_classification(n_samples=1000, n_features=2, n_informative=2, n_redundant=0, n_clusters_per_class=1, random_state=4)# 定義模型model = OPTICS(eps=0.8, min_samples=10)# 模型擬合與聚類預(yù)測(cè)yhat = model.fit_predict(X)# 檢索唯一群集clusters = unique(yhat)# 為每個(gè)群集的樣本創(chuàng)建散點(diǎn)圖for cluster in clusters:# 獲取此群集的示例的行索引row_ix = where(yhat == cluster)# 創(chuàng)建這些樣本的散布pyplot.scatter(X[row_ix, 0], X[row_ix, 1])# 繪制散點(diǎn)圖pyplot.show()
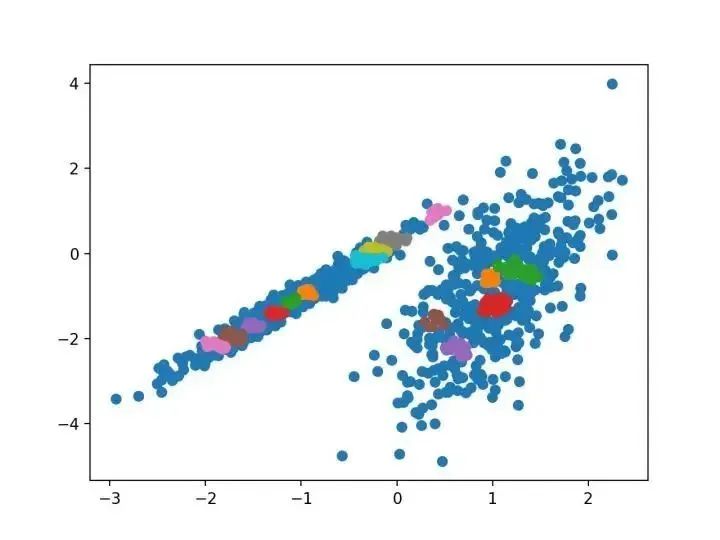
最近在許多領(lǐng)域出現(xiàn)的一個(gè)有希望的替代方案是使用聚類的光譜方法。這里,使用從點(diǎn)之間的距離導(dǎo)出的矩陣的頂部特征向量。 —源自:《關(guān)于光譜聚類:分析和算法》,2002年
# spectral clusteringfrom numpy import uniquefrom numpy import wherefrom sklearn.datasets import make_classificationfrom sklearn.cluster import SpectralClusteringfrom matplotlib import pyplot# 定義數(shù)據(jù)集X, _ = make_classification(n_samples=1000, n_features=2, n_informative=2, n_redundant=0, n_clusters_per_class=1, random_state=4)# 定義模型model = SpectralClustering(n_clusters=2)# 模型擬合與聚類預(yù)測(cè)yhat = model.fit_predict(X)# 檢索唯一群集clusters = unique(yhat)# 為每個(gè)群集的樣本創(chuàng)建散點(diǎn)圖for cluster in clusters:# 獲取此群集的示例的行索引row_ix = where(yhat == cluster)# 創(chuàng)建這些樣本的散布pyplot.scatter(X[row_ix, 0], X[row_ix, 1])# 繪制散點(diǎn)圖pyplot.show()
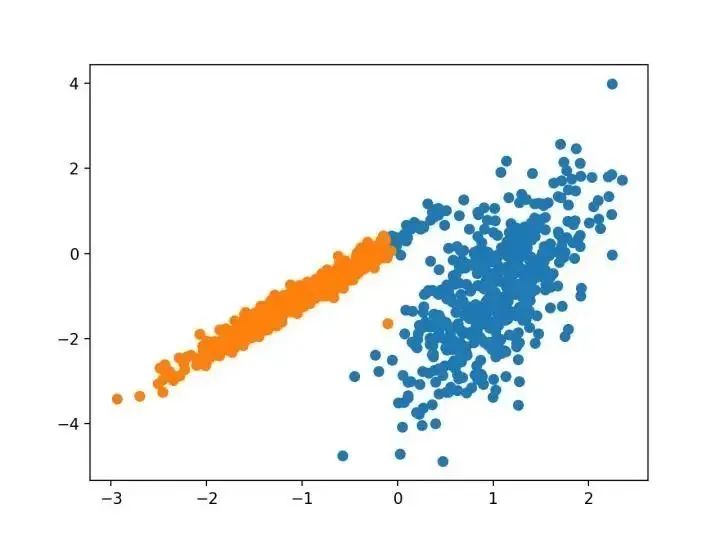
# 高斯混合模型from numpy import uniquefrom numpy import wherefrom sklearn.datasets import make_classificationfrom sklearn.mixture import GaussianMixturefrom matplotlib import pyplot# 定義數(shù)據(jù)集X, _ = make_classification(n_samples=1000, n_features=2, n_informative=2, n_redundant=0, n_clusters_per_class=1, random_state=4)# 定義模型model = GaussianMixture(n_components=2)# 模型擬合model.fit(X)# 為每個(gè)示例分配一個(gè)集群yhat = model.predict(X)# 檢索唯一群集clusters = unique(yhat)# 為每個(gè)群集的樣本創(chuàng)建散點(diǎn)圖for cluster in clusters:# 獲取此群集的示例的行索引row_ix = where(yhat == cluster)# 創(chuàng)建這些樣本的散布pyplot.scatter(X[row_ix, 0], X[row_ix, 1])# 繪制散點(diǎn)圖pyplot.show()
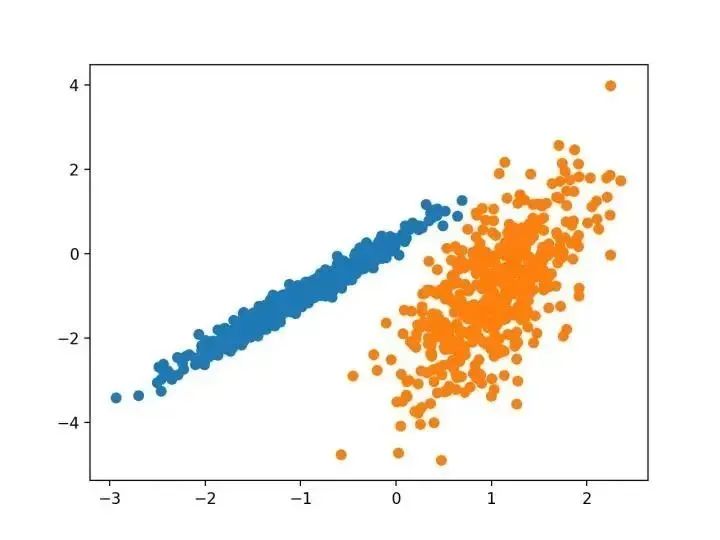
三. 總結(jié)
聚類是在特征空間輸入數(shù)據(jù)中發(fā)現(xiàn)自然組的無(wú)監(jiān)督問題。 有許多不同的聚類算法,對(duì)于所有數(shù)據(jù)集沒有單一的最佳方法。 在 scikit-learn 機(jī)器學(xué)習(xí)庫(kù)的 Python 中如何實(shí)現(xiàn)、適合和使用頂級(jí)聚類算法。
評(píng)論
圖片
表情
