【深度學(xué)習(xí)】高效輕量級語義分割綜述
原文:On Efficient Real-Time Semantic Segmentation: A Survey
鏈接:https://arxiv.org/abs/2206.08605
1摘要
語義分割是自動駕駛中視覺理解的重要組成部分。然而當前SOTA的模型都非常復(fù)雜和繁瑣,因此不適合部署在計算資源受限且耗時要求較低的車載芯片平臺上。本文深入研究了更緊湊、更高效的模型以解決上述問題,這些模型能夠部署在低內(nèi)存嵌入式系統(tǒng)上,同時滿足實時推理的需求。本文討論了該領(lǐng)域一些優(yōu)秀的工作,根據(jù)它們的主要貢獻進行歸類,最后本文評估了在相同軟硬件條件下模型的推理速度,這些條件代表了一個典型的高性能GPU和低內(nèi)存嵌入式GPU的實際部署場景。本文的實驗結(jié)果表明,許多工作能夠在資源受限的硬件上實現(xiàn)性能和耗時的平衡。
2數(shù)據(jù)集
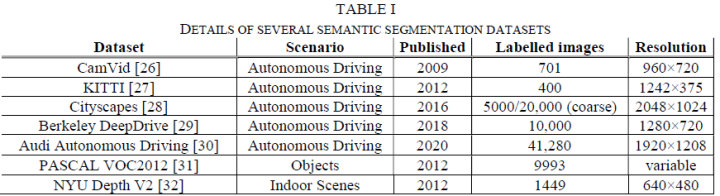
常見的分割數(shù)據(jù)集有CamVid[1], KITTI[2], Cityscapes[3], Berkeley DeepDrive[4], Audi Autonomous Driving[5], PASCAL VOC2012[6], NYU Depth V2[7]等。
3高效深度 CNN 的技術(shù)
降采樣和上采樣
降采樣:通過對輸入圖像進行降采樣以顯著減少計算量、增加推理速度,同時犧牲了輸出的精度。一般而言,大型復(fù)雜模型均需要使用降采樣來提升感受野,常用的下采樣操作是 max/average pooling。
上采樣:分割任務(wù)與其他視覺任務(wù)不同,通常希望保持輸入輸出的維度,因此必須使用上采樣恢復(fù)分辨率,常見的上采樣方法又雙線性插值、逆卷積等。
高效卷積
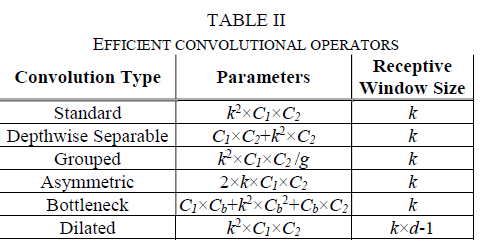
高效卷積的核心思想是通過堆疊卷積層在擴大模型感受野的同時,減少模型參數(shù)量和計算量。常見的高效卷積有Depthwise-Separable Convolution[8],Grouped Convolution[9],Asymmetric Convolution[10], Bottleneck[11], Dilated Convolution[12]。
殘差連接
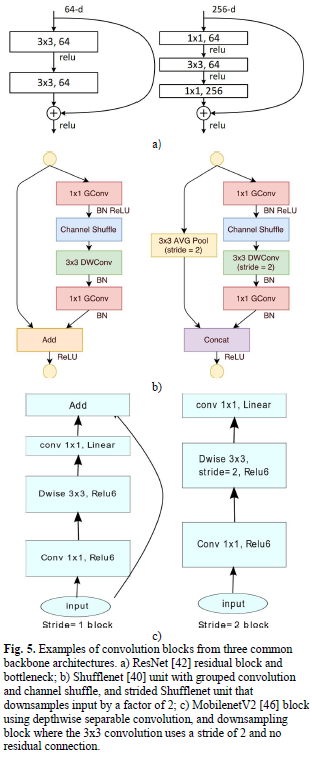
殘差連接通[11]常用于分割網(wǎng)絡(luò)中以改善反向傳播期間的梯度流和重用前一層特征。
主干網(wǎng)絡(luò)
許多語義分割模型采用若干廣泛使用的主干網(wǎng)絡(luò)作為特征提取器,常見的主干有ResNet[11],Squeezenet[13],Shufflenet[14],Mobilenet[15],MobileNetV2[16],EfficientNet[17]。
4杰出工作
編碼器-解碼器
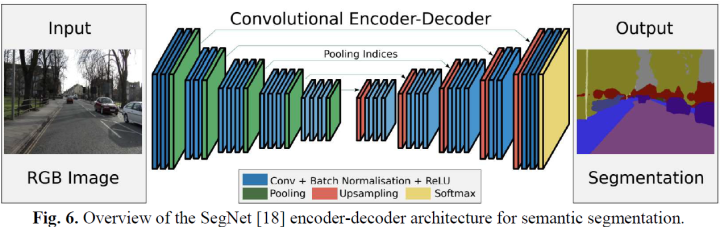
語義分割的核心結(jié)構(gòu)便是編碼器-解碼器。經(jīng)典的模型有SegNet、U-net、Efficient Neural Network (ENet)、SQNet等等。
多分支
基于編碼器-解碼器的方法的一個主要挑戰(zhàn)是保留在網(wǎng)絡(luò)早期提取的高分辨率細節(jié),因此一些多分支工作將原始輸入圖像以兩個或更多尺度送入網(wǎng)絡(luò)。經(jīng)典模型如Image Cascade Network (ICNet)、ContextNet、Guided Upsampling Network (GUN)等。
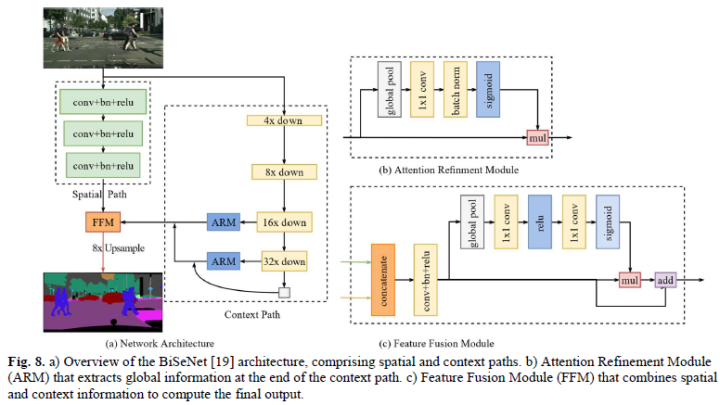
元學(xué)習(xí)
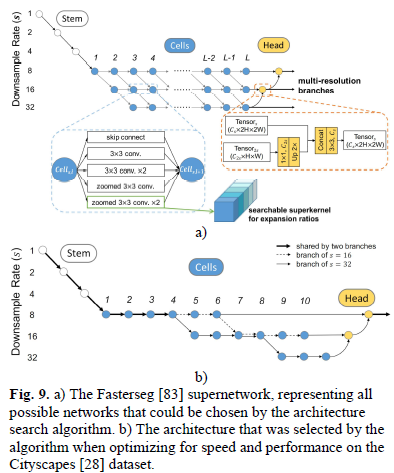
實時語義分割領(lǐng)域中大多數(shù)元學(xué)習(xí)模型都屬于NAS的范疇,是一種自動化設(shè)計神經(jīng)網(wǎng)絡(luò)結(jié)構(gòu)的過程的方法。NAS 通常只涉及可提供最佳結(jié)果的架構(gòu),但是在實時要求下,架構(gòu)大小、復(fù)雜性和推理時間構(gòu)成了優(yōu)化功能中應(yīng)考慮的其他因素。經(jīng)典的算法有SqueezeNAS、FasterSeg、Graph-Guided Architecture Search (GAS) 等。
注意力
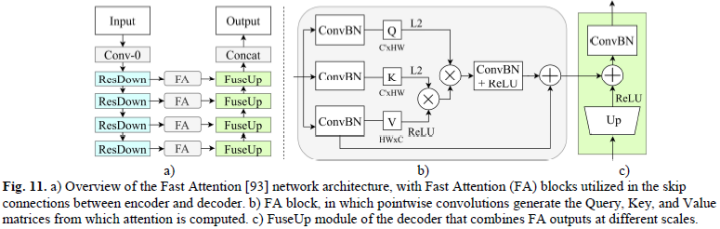
注意力機制已經(jīng)被證明是一種適用于視覺任務(wù)的關(guān)鍵技術(shù),但一般而言計算繁瑣且低效。盡管仍不適合實時推理,但一些工作如Deep Feature Aggregation (DFANet)、Lightweight Encoder-Decoder (LEDNet)等降低了注意力的復(fù)雜性。
訓(xùn)練優(yōu)化
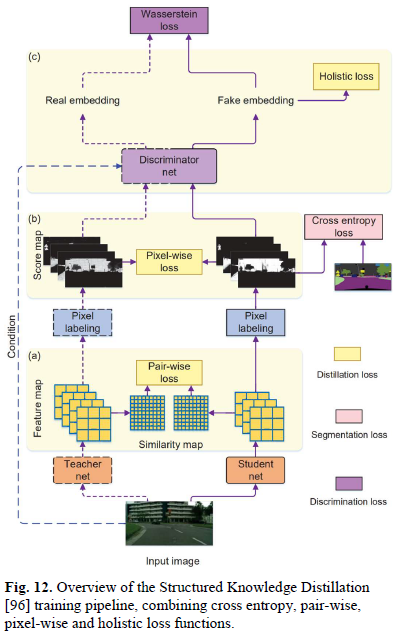
最后一類是采用現(xiàn)有網(wǎng)絡(luò)結(jié)構(gòu)并改變訓(xùn)練過程以提升模型性能的方法,常見的如知識蒸餾Structured Knowledge Distillation、Knowledge Adaptation等
5評估
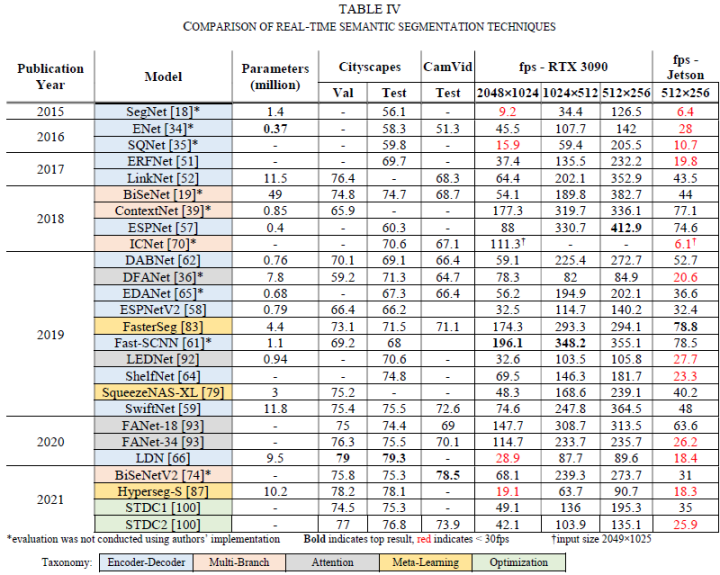
本文在Nvidia RTX 3090 GPU和嵌入式平臺Nvidia Jetson Xavier AGX Developer Kit兩種平臺下驗證了不同算法的耗時和性能。
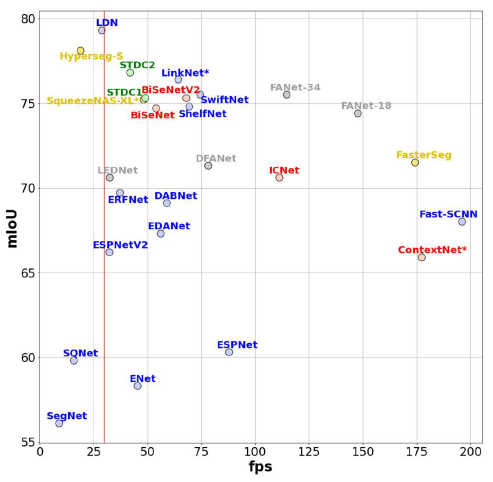
對比如下表所示:
6結(jié)論
本文討論了為解決資源受限硬件上的低耗時語義分割算法,并根據(jù)它們對該領(lǐng)域的主要貢獻進行討論和分類。最后本文進行了自己的實驗,在相同的軟硬件條件下分析算法的速度和性能,為模型選型提供參考,對未來工作的優(yōu)化提供思考方向。
7參考文獻
[1] G. J. Brostow, J. Fauqueur and R. Cipolla, "Semantic object classes in video: A high-definition ground truth database," Pattern Recognit. Lett., vol. 30, p. 88–97, 2009.
[2] A. Geiger, P. Lenz, C. Stiller and R. Urtasun, "Vision meets robotics: The KITTI dataset," Int. J. Robotics Res., vol. 32, p. 1231–1237, 2013.
[3] M. Cordts, M. Omran, S. Ramos, T. Rehfeld, M. Enzweiler, R. Benenson, U. Franke, S. Roth and B. Schiele, "The Cityscapes Dataset for Semantic Urban Scene Understanding," in 2016 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, CVPR 2016, Las Vegas, NV, USA, June 27-30, 2016, 2016.
[4] F. Yu, W. Xian, Y. Chen, F. Liu, M. Liao, V. Madhavan and T. Darrell, "BDD100K: A Diverse Driving Video Database with Scalable Annotation Tooling," CoRR, vol. abs/1805.04687, 2018.
[5] J. Geyer, Y. Kassahun, M. Mahmudi, X. Ricou, R. Durgesh, A. S. Chung, L. Hauswald, V. H. Pham, M. Mühlegg, S. Dorn, T. Fernandez, M. J?nicke, S. Mirashi, C. Savani, M. Sturm, O. Vorobiov, M. Oelker, S. Garreis and P. Schuberth, "A2D2: Audi Autonomous Driving Dataset," CoRR, vol. abs/2004.06320, 2020.
[6] M. Everingham, L. Van Gool, C. K. I. Williams, J. Winn and A. Zisserman, The PASCAL Visual Object Classes Challenge 2012 (VOC2012) Results.
[7] N. Silberman, P. Kohli and R. Fergus, "Indoor Segmentation and Support Inference from RGBD Images," in European Conference on Computer Vision, 2012.
[8] L. Sifre and S. Mallat, Rigid-Motion Scattering for Texture Classification, 2014.
[9] A. Krizhevsky, I. Sutskever and G. E. Hinton, "ImageNet Classification with Deep Convolutional Neural Networks," in Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems, 2012.
[10] M. Jaderberg, A. Vedaldi and A. Zisserman, Speeding up Convolutional Neural Networks with Low Rank Expansions, 2014.
[11] K. He, X. Zhang, S. Ren and J. Sun, "Deep Residual Learning for Image Recognition," in Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), 2016.
[12] G. Papandreou, I. Kokkinos and P.-A. Savalle, "Modeling Local and Global Deformations in Deep Learning: Epitomic Convolution, Multiple Instance Learning, and Sliding Window Detection," in Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), 2015.
[13] F. N. Iandola, S. Han, M. W. Moskewicz, K. Ashraf, W. J. Dally and K. Keutzer, SqueezeNet: AlexNet-level accuracy with 50x fewer parameters and <0.5MB model size, 2016.
[14] X. Zhang, X. Zhou, M. Lin and J. Sun, "ShuffleNet: An Extremely Efficient Convolutional Neural Network for Mobile Devices," in Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), 2018.
[15] A. G. Howard, M. Zhu, B. Chen, D. Kalenichenko, W. Wang, T. Weyand, M. Andreetto and H. Adam, MobileNets: Efficient Convolutional Neural Networks for Mobile Vision Applications, 2017.
[16] M. Sandler, A. Howard, M. Zhu, A. Zhmoginov and L.-C. Chen, "MobileNetV2: Inverted Residuals and Linear Bottlenecks," in Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), 2018.
往期精彩回顧
適合初學(xué)者入門人工智能的路線及資料下載 (圖文+視頻)機器學(xué)習(xí)入門系列下載 機器學(xué)習(xí)及深度學(xué)習(xí)筆記等資料打印 《統(tǒng)計學(xué)習(xí)方法》的代碼復(fù)現(xiàn)專輯 機器學(xué)習(xí)交流qq群955171419,加入微信群請掃碼
