深度學(xué)習(xí)模型參數(shù)量/計算量和推理速度計算

極市導(dǎo)讀
?本文總結(jié)了一些關(guān)于模型參數(shù)量計算以及推理速度計算的方法,附有相關(guān)代碼。?>>加入極市CV技術(shù)交流群,走在計算機視覺的最前沿
1.FLOPs和Params計算
1.1概念理解
FLOPS: 注意全大寫,是floating point operations per second的縮寫,意指每秒浮點運算次數(shù),理解為計算速度。是一個衡量硬件性能的指標(biāo)。
計算公式:
對卷積層:(K_h * K_w * C_in * C_out)?*?(H_out * W_out)
對全連接層:C_in * C_out
FLOPs: 注意s小寫,是floating point operations的縮寫(s表復(fù)數(shù)),意指浮點運算數(shù),理解為計算量。可以用來衡量算法/模型的復(fù)雜度

Params: 是指模型訓(xùn)練中需要訓(xùn)練的參數(shù)總數(shù)
模型參數(shù)量計算公式為:
對卷積層:(K_h * K_w * C_in)* C_out
對全連接層:C_in * C_out

注意:
1.params只與你定義的網(wǎng)絡(luò)結(jié)構(gòu)有關(guān),和forward的任何操作無關(guān)。即定義好了網(wǎng)絡(luò)結(jié)構(gòu),參數(shù)就已經(jīng)決定了。FLOPs和不同的層運算結(jié)構(gòu)有關(guān)。如果forward時在同一層(同一名字命名的層)多次運算,F(xiàn)LOPs不會增加
2.Model_size?=?4*params??模型大小約為參數(shù)量的4倍
補充:
MAC:內(nèi)存訪問成本
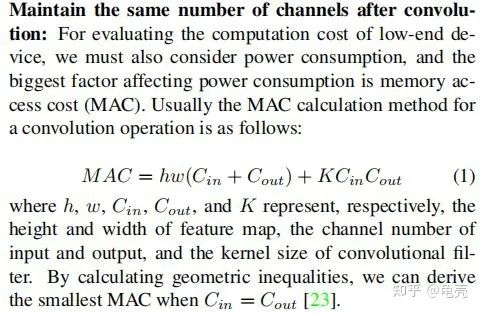
1.2計算方法
方法1-使用thop庫
'''
code?by?zzg-2020-05-19
pip?install?thop
'''
import?torch
from?thop?import?profile
from?models.yolo_nano?import?YOLONano
device?=?torch.device("cpu")
#input_shape?of?model,batch_size=1
net?=?YOLONano(num_classes=20,?image_size=416)?##定義好的網(wǎng)絡(luò)模型
input?=?torch.randn(1,?3,?416,?416)
flops,?params?=?profile(net,?inputs=(input,?))
print("FLOPs=",?str(flops/1e9)?+'{}'.format("G"))
print("params=",?str(params/1e6)+'{}'.format("M")
方法2-使用torchstat庫
'''
在PyTorch中,可以使用torchstat這個庫來查看網(wǎng)絡(luò)模型的一些信息,包括總的參數(shù)量params、MAdd、顯卡內(nèi)存占用量和FLOPs等
pip?install?torchstat
'''
from?torchstat?import?stat
from?torchvision.models?import?resnet50
model?=?resnet50()
stat(model,?(3,?224,?224))
方法3-使用 ptflops:https://github.com/sovrasov/flops-counter.pytorch
#pip?install?ptflops
from?ptflops?import?get_model_complexity_info
from?torchvision.models?import?resnet50
model?=?resnet50()
flops,?params?=?get_model_complexity_info(model,?(3,?224,?224),?as_strings=True,?print_per_layer_stat=True)
print('Flops:??'?+?flops)
print('Params:?'?+?params)
參考:
https://www.cnblogs.com/king-lps/p/10904552.html
https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/337810633
2.模型推理速度計算
2.1 模型推理速度正確計算
需要克服GPU異步執(zhí)行和GPU預(yù)熱兩個問題,下面例子使用 Efficient-net-b0,在進行任何時間測量之前,我們通過網(wǎng)絡(luò)運行一些虛擬示例來進行“GPU 預(yù)熱”。這將自動初始化 GPU 并防止它在我們測量時間時進入省電模式。接下來,我們使用 tr.cuda.event 來測量 GPU 上的時間。在這里使用 torch.cuda.synchronize() 至關(guān)重要。這行代碼執(zhí)行主機和設(shè)備(即GPU和CPU)之間的同步,因此只有在GPU上運行的進程完成后才會進行時間記錄。這克服了不同步執(zhí)行的問題。
model?=?EfficientNet.from_pretrained(‘efficientnet-b0’)
device?=?torch.device(“cuda”)
model.to(device)
dummy_input?=?torch.randn(1,?3,?224,?224,dtype=torch.float).to(device)
starter,?ender?=?torch.cuda.Event(enable_timing=True),?torch.cuda.Event(enable_timing=True)
repetitions?=?300
timings=np.zeros((repetitions,1))
#GPU-WARM-UP
for?_?in?range(10):
???_?=?model(dummy_input)
#?MEASURE?PERFORMANCE
with?torch.no_grad():
??for?rep?in?range(repetitions):
?????starter.record()
?????_?=?model(dummy_input)
?????ender.record()
?????#?WAIT?FOR?GPU?SYNC
?????torch.cuda.synchronize()
?????curr_time?=?starter.elapsed_time(ender)
?????timings[rep]?=?curr_time
mean_syn?=?np.sum(timings)?/?repetitions
std_syn?=?np.std(timings)
mean_fps?=?1000.?/?mean_syn
print('?*?Mean@1?{mean_syn:.3f}ms?Std@5?{std_syn:.3f}ms?FPS@1?{mean_fps:.2f}'.format(mean_syn=mean_syn,?std_syn=std_syn,?mean_fps=mean_fps))
print(mean_syn)
2.2 模型吞吐量計算
神經(jīng)網(wǎng)絡(luò)的吞吐量定義為網(wǎng)絡(luò)在單位時間內(nèi)(例如,一秒)可以處理的最大輸入實例數(shù)。與涉及單個實例處理的延遲不同,為了實現(xiàn)最大吞吐量,我們希望并行處理盡可能多的實例。有效的并行性顯然依賴于數(shù)據(jù)、模型和設(shè)備。因此,為了正確測量吞吐量,我們執(zhí)行以下兩個步驟:(1)我們估計允許最大并行度的最佳批量大小;(2)給定這個最佳批量大小,我們測量網(wǎng)絡(luò)在一秒鐘內(nèi)可以處理的實例數(shù)
要找到最佳批量大小,一個好的經(jīng)驗法則是達(dá)到 GPU 對給定數(shù)據(jù)類型的內(nèi)存限制。這個大小當(dāng)然取決于硬件類型和網(wǎng)絡(luò)的大小。找到這個最大批量大小的最快方法是執(zhí)行二進制搜索。當(dāng)時間不重要時,簡單的順序搜索就足夠了。為此,我們使用 for 循環(huán)將批量大小增加 1,直到達(dá)到運行時錯誤為止,這確定了 GPU 可以處理的最大批量大小,用于我們的神經(jīng)網(wǎng)絡(luò)模型及其處理的輸入數(shù)據(jù)。
在找到最佳批量大小后,我們計算實際吞吐量。為此,我們希望處理多個批次(100 個批次就足夠了),然后使用以下公式:
(批次數(shù)?X?批次大小)/(以秒為單位的總時間)
這個公式給出了我們的網(wǎng)絡(luò)可以在一秒鐘內(nèi)處理的示例數(shù)量。下面的代碼提供了一種執(zhí)行上述計算的簡單方法(給定最佳批量大小)
model?=?EfficientNet.from_pretrained(‘efficientnet-b0’)
device?=?torch.device(“cuda”)
model.to(device)
dummy_input?=?torch.randn(optimal_batch_size,?3,224,224,?dtype=torch.float).to(device)
repetitions=100
total_time?=?0
with?torch.no_grad():
??for?rep?in?range(repetitions):
?????starter,?ender?=?torch.cuda.Event(enable_timing=True),torch.cuda.Event(enable_timing=True)
?????starter.record()
?????_?=?model(dummy_input)
?????ender.record()
?????torch.cuda.synchronize()
?????curr_time?=?starter.elapsed_time(ender)/1000
?????total_time?+=?curr_time
Throughput?=?(repetitions*optimal_batch_size)/total_time
print(‘Final?Throughput:’,Throughput)
參考:
https://www.cnblogs.com/king-lps/p/10904552.html
https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/337810633
如果覺得有用,就請分享到朋友圈吧!
公眾號后臺回復(fù)“CVPR21檢測”獲取CVPR2021目標(biāo)檢測論文下載~

#?CV技術(shù)社群邀請函?#

備注:姓名-學(xué)校/公司-研究方向-城市(如:小極-北大-目標(biāo)檢測-深圳)
即可申請加入極市目標(biāo)檢測/圖像分割/工業(yè)檢測/人臉/醫(yī)學(xué)影像/3D/SLAM/自動駕駛/超分辨率/姿態(tài)估計/ReID/GAN/圖像增強/OCR/視頻理解等技術(shù)交流群
每月大咖直播分享、真實項目需求對接、求職內(nèi)推、算法競賽、干貨資訊匯總、與?10000+來自港科大、北大、清華、中科院、CMU、騰訊、百度等名校名企視覺開發(fā)者互動交流~