Pandas+Numpy+Sklearn隨機(jī)取數(shù)
本文轉(zhuǎn)自公眾號(hào):尤而小屋
本文記錄的是如何使用Python、pandas、numpy、scikit-learn來(lái)實(shí)現(xiàn)隨機(jī)打亂、抽取和切割數(shù)據(jù)。主要的方法包含:
sample shuffle np.random.permutation train_test_split

導(dǎo)入數(shù)據(jù)
In [1]:
import pandas as pd
import numpy as np
import random # 隨機(jī)模塊
import plotly_express as px # 可視化庫(kù)
import plotly.graph_objects as go
內(nèi)置數(shù)據(jù)
采用的是plotly庫(kù)中內(nèi)置的一份消費(fèi)數(shù)據(jù)集:
In [2]:
df = px.data.tips()
df.head()
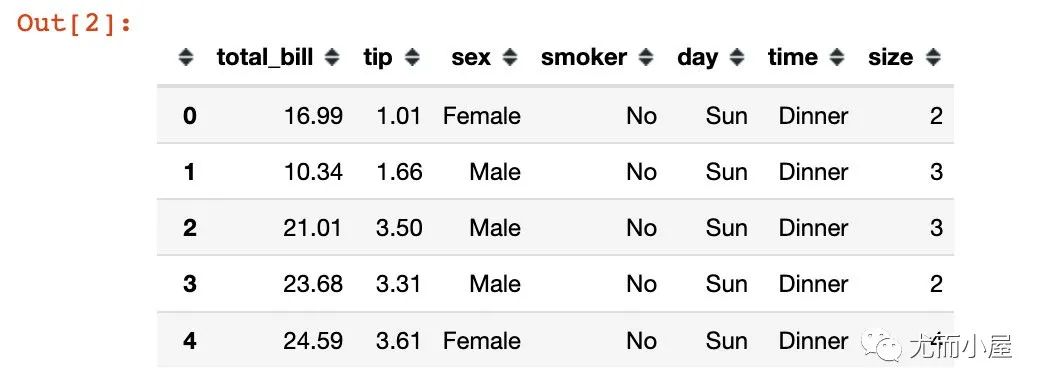
基本信息
In [3]:
df.shape
Out[3]:
(244, 7)
In [4]:
columns = df.columns
columns
Out[4]:
Index(['total_bill', 'tip', 'sex', 'smoker', 'day', 'time', 'size'], dtype='object')
sample實(shí)現(xiàn)
行方向
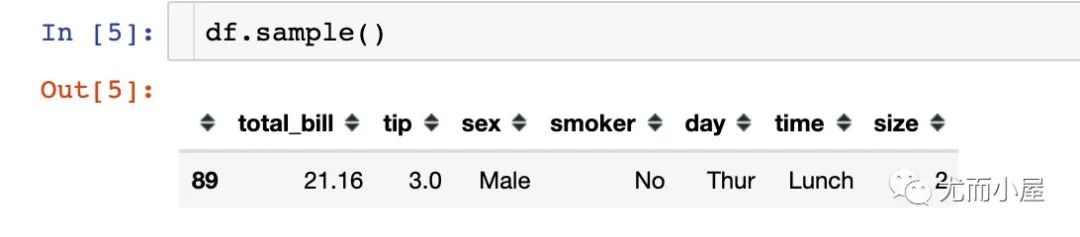
In [5]:
隨機(jī)抽取一行記錄:
df.sample() # 隨機(jī)抽取一行記錄
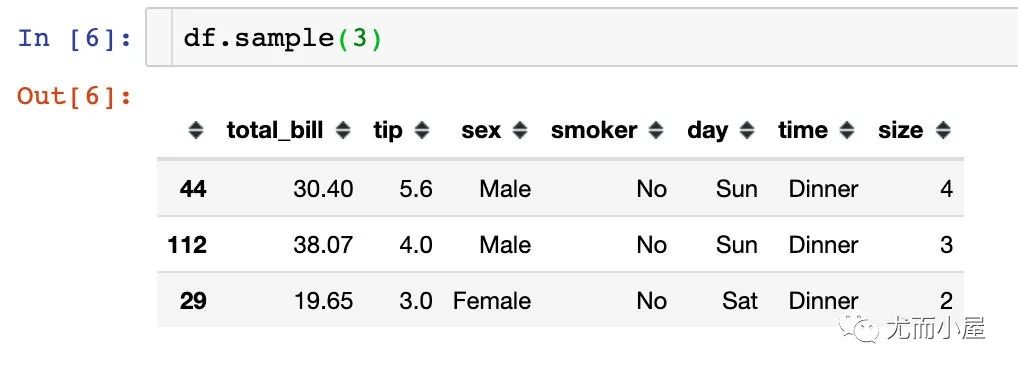
隨機(jī)抽取多行數(shù)據(jù):
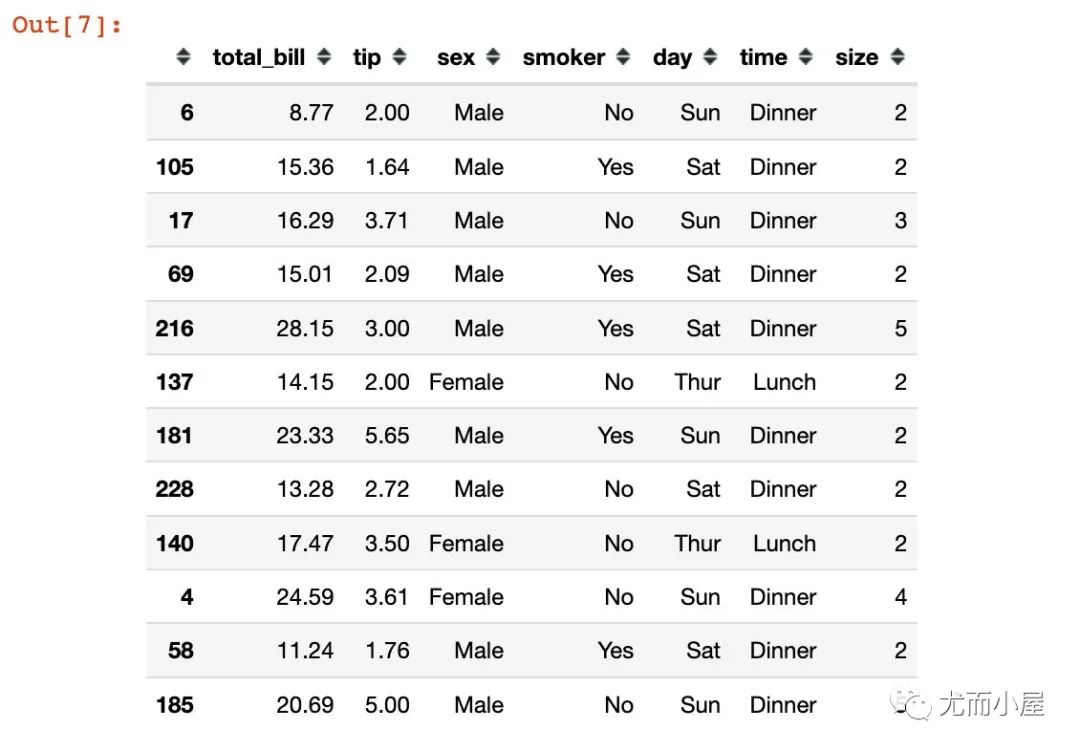
通過(guò)參數(shù)frac實(shí)現(xiàn)按照比例隨機(jī)抽樣:
df.sample(frac=0.05)
列方向
主要是選擇不同數(shù)量或者比例的屬性;整體的行數(shù)量是不變的
In [8]:
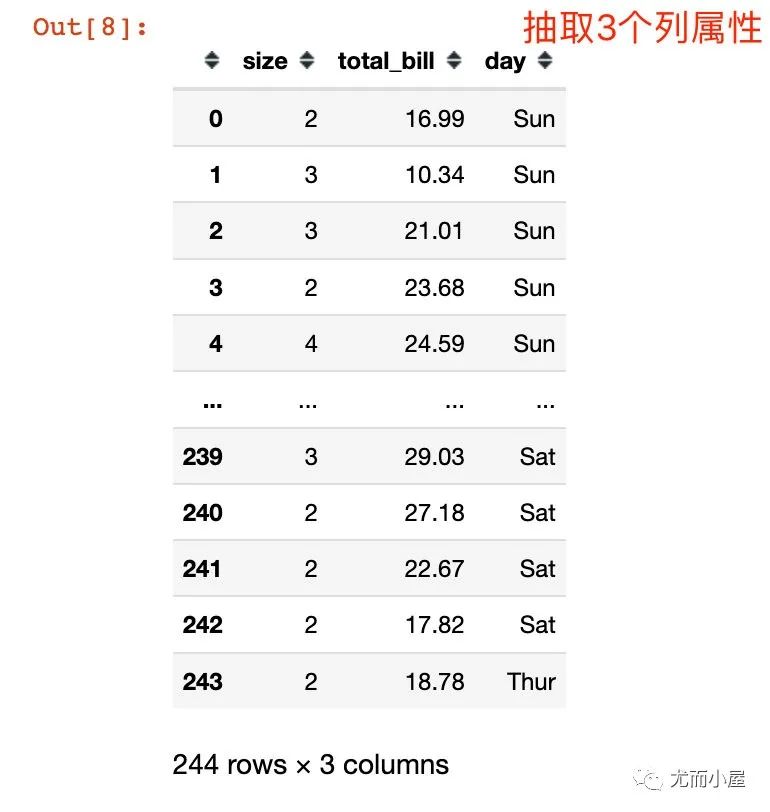
df.sample(3, axis=1) # 在列屬性上抽取
shuffle實(shí)現(xiàn)
scikit-Learn的shuffle
In [9]:
from sklearn.utils import shuffle
In [10]:
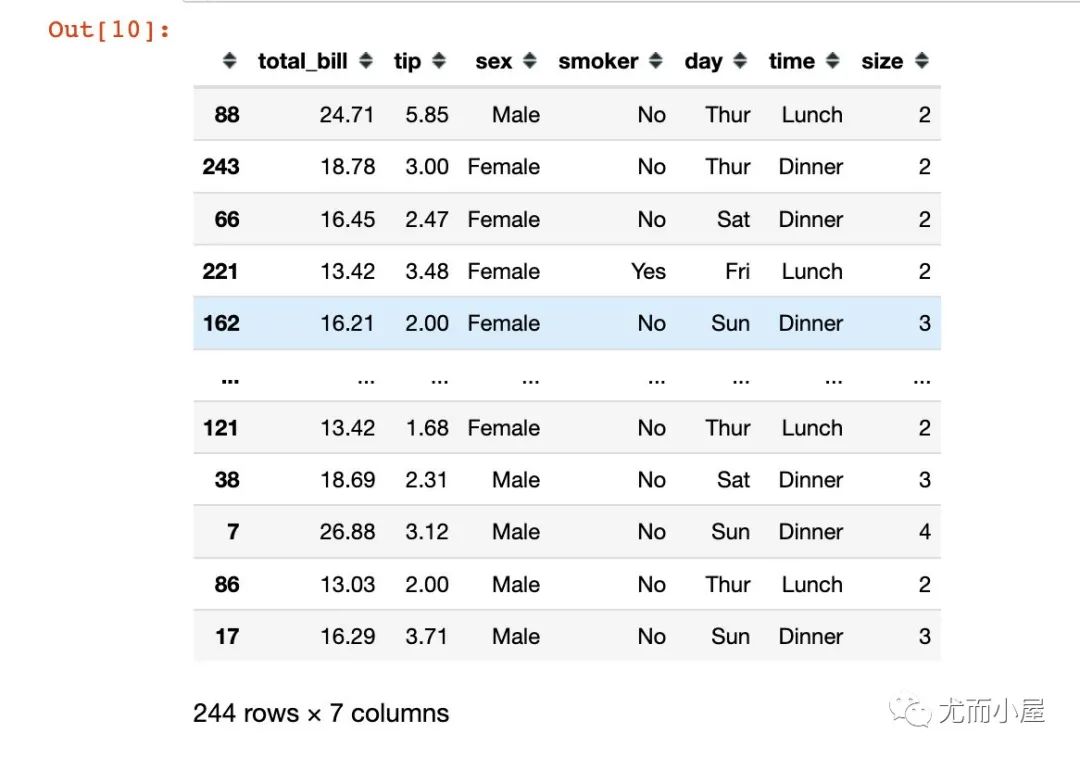
shuffle(df) # 打亂數(shù)據(jù)
random模塊的shuffle
In [11]:
length = list(range(len(df))) # 原始的長(zhǎng)度作為索引
length[:5]
Out[11]:
[0, 1, 2, 3, 4]
In [12]:
random.shuffle(length) # 打亂索引
In [13]:
length[:5]
Out[13]:
[136, 35, 207, 127, 29] # 打亂后的結(jié)果
In [14]:
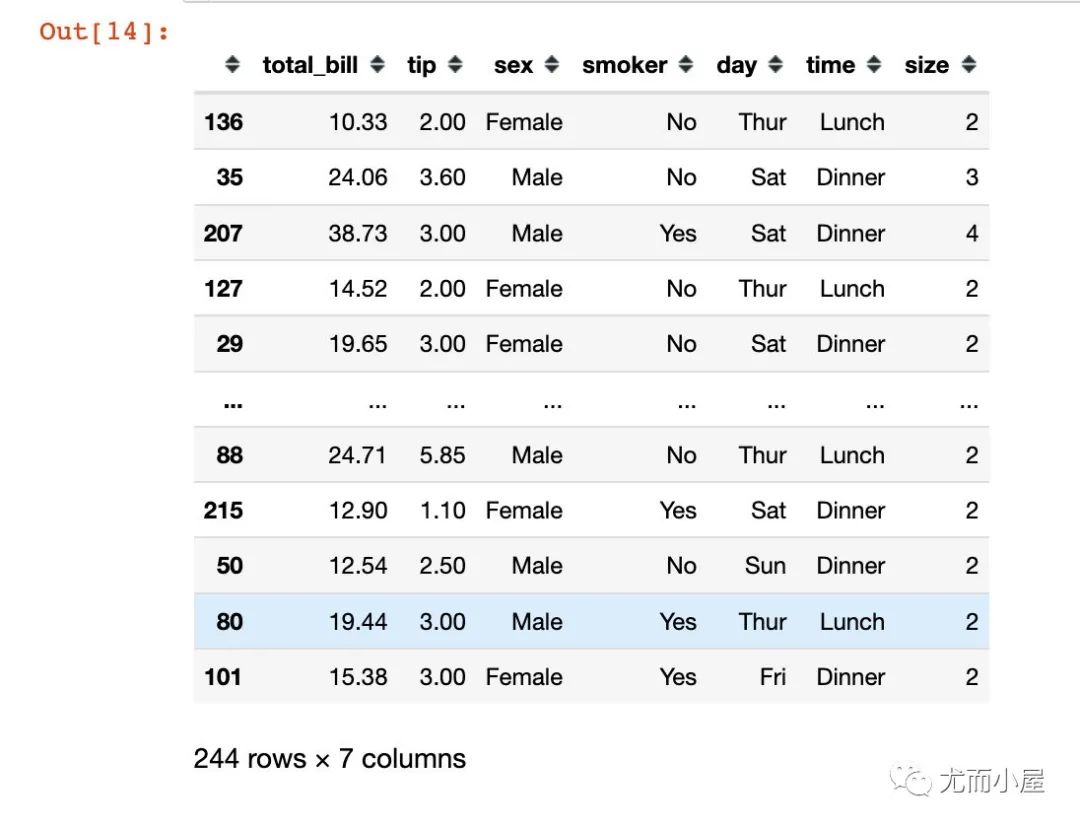
df.iloc[length] # 通過(guò)打亂后的索引獲取數(shù)據(jù)
numpy實(shí)現(xiàn)
In [15]:
# 先打亂每個(gè)索引
np.random.permutation(len(df))
Out[15]:
array([223, 98, 238, 17, 101, 26, 122, 212, 27, 79, 210, 147, 176,
82, 164, 142, 141, 219, 6, 63, 185, 112, 158, 188, 242, 207,
45, 55, 178, 150, 217, 32, 16, 160, 157, 234, 95, 174, 93,
52, 57, 220, 216, 230, 35, 86, 125, 114, 100, 73, 83, 88,
34, 7, 40, 115, 97, 165, 84, 18, 197, 151, 135, 121, 72,
173, 228, 143, 227, 9, 183, 56, 23, 237, 136, 106, 133, 189,
139, 0, 208, 74, 166, 4, 68, 12, 71, 85, 172, 138, 149,
144, 232, 186, 99, 130, 41, 201, 204, 10, 167, 195, 66, 159,
213, 87, 103, 117, 31, 211, 190, 24, 243, 127, 48, 218, 233,
113, 81, 235, 229, 206, 96, 46, 222, 50, 156, 180, 214, 124,
240, 140, 89, 225, 2, 120, 58, 169, 193, 39, 102, 104, 148,
184, 170, 152, 153, 146, 179, 137, 129, 64, 3, 65, 128, 90,
110, 14, 226, 181, 131, 203, 221, 80, 51, 94, 231, 44, 108,
43, 145, 47, 75, 162, 163, 69, 126, 200, 1, 123, 37, 205,
111, 25, 91, 11, 42, 67, 118, 196, 161, 28, 116, 105, 33,
38, 78, 76, 224, 20, 202, 171, 177, 107, 8, 209, 239, 77,
241, 154, 5, 198, 92, 61, 182, 36, 70, 22, 54, 187, 175,
119, 215, 49, 134, 21, 60, 62, 168, 59, 155, 194, 109, 132,
19, 199, 29, 191, 13, 30, 192, 236, 15, 53])
In [16]:
# 通過(guò)打亂后的索引來(lái)選擇數(shù)據(jù)
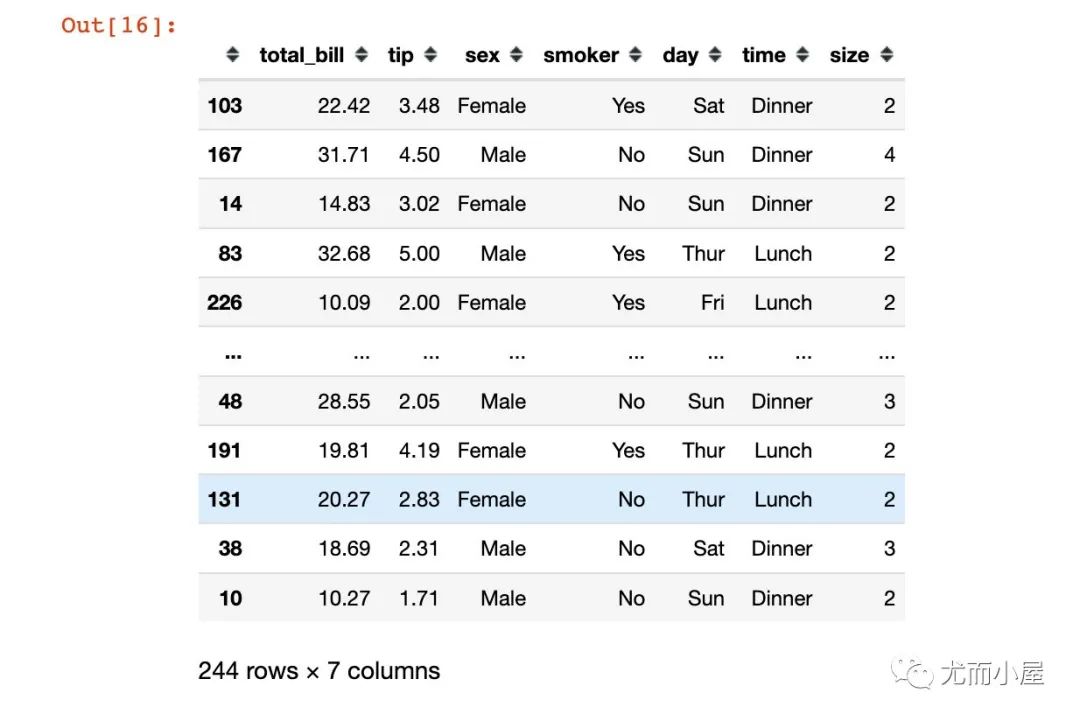
df.iloc[np.random.permutation(len(df))]
train_test_split實(shí)現(xiàn)
from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split
data = []
for i in train_test_split(df, test_size=0.2):
data.append(i)
In [18]:
第一份數(shù)據(jù)是80%的:
data[0] # 80%的數(shù)據(jù)
剩余的20%的數(shù)據(jù):
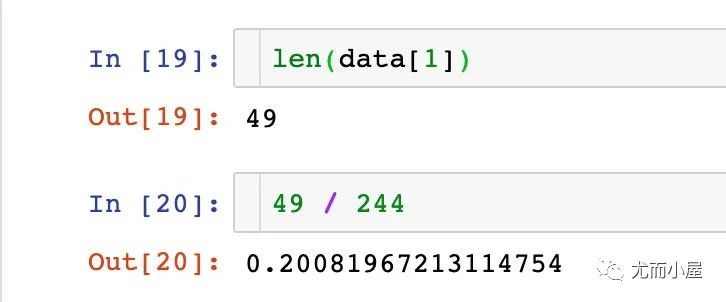
相關(guān)閱讀:
評(píng)論
圖片
表情
